Music Genre Classification and Variance Comparison on Number of Genres
|
|
|
- Christine Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Music Genre Classification and Variance Comparison on Number of Genres Miguel Francisco, Dong Myung Kim, 1 Abstract In this project we apply machine learning techniques to build a music genre classifier. Focusing on the sonic properties of music, as opposed to metadata, we examine the classification accuracy of two types of features coefficients, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients and Chroma Features, using multi-class support vector machines. We hope to achieve significant improvements over random guessing and identify which coefficient yields higher accuracy. Additionally, we will classify songs into different numbers of genres, to analyze how the number of classes affects accuracy for each model. 2 Introduction As music recommendation and auto-generated playlists become wildly popular, techniques to automatically classify the genre of any given song are anticipated to have important applications in such industries. Specifically, with the increasing volume of new music, it is much more efficient to rely on an accurate genre classification system rather than hiring musical experts or crowdsourcing to determine genre. 3 Data The MARSYAS (Music Audio Retrieval and Synthesis for Audio Signals) open source software framework hosts the GTZAN Genre Collection [1], a collection of 30-second snippets of 1,000 songs in the.au file format covering ten different genres: blues, classical, country, disco, hip-hop, jazz, metal, pop, reggae, and rock. Although there are much larger music datasets such as the Million Song Dataset, the retrieval of actual audio is made much easier with the GTZAN dataset, as opposed to the Million Song Dataset, which is actually a collection of metadata. Furthermore, genre tagging in the Million Song Dataset is by artist, rather than by song, so it does not account for cases where the artists may span different musical styles. 3.1 MFCCs There are many ways to numerically represent audio files. Mel-Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients (MFCCs) are one of the widely used feature extraction methods for machine learning in music-related fields (visualized below). These are based on cepstral representation (a nonlinear spectrum of a
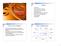
2 Figure 1: The sonic waveform and corresponding MFCC representation of classical au from the GTZAN dataset Figure 2: The pitch representation (left) and corresponding chroma (right) of classical au from the GTZAN dataset spectrum ), but unlike the cepstrum, the Mel-Frequency Cepstrum uses frequency bands that are equally spaced over the mel-scale, and therefore are expected to produce a better representation of sound, closer to actual human perception. Generating these coefficients requires a complex procedure including the Fourier transform, so we relied on open-source MFCC extraction software developed by Kamil Wojcicki[2]. As far as parameters are concerned, we settled on 12 cepstral coefficients and 18/15,000 (Hz) lower/upper frequency limits, a reasonable choice for investigating the audible sound spectrum. MFCCs are based more on the timbre of the sound signals, and form an interesting contrast with chroma features (discussed more in depth later) which are based on pitch classes. We thought that contrasting the efficiency of two different coefficients in genre classification would be interesting, and also explored how increasing the number of features by combining both MFCCs and Chroma Features would impact the classification accuracy. 3.2 Chroma Features which are generated using the short-time energy distributions over the chroma bands. The twelve chroma bands correspond to the twelve traditional pitch classes (C, C#, D, ) and as a result the chroma features have strong correlations with the harmonic progressions of the audio signals. We relied on the open-source Chroma Toolbox by Mϋller in order to generate chroma feature for our dataset. 3.3 MFCCs and Chroma Features Combined Both MFCCs and Chroma Features generate a matrix for each 30 second snippet of audio. However the amount of features generated (number of entries in the generated feature matrix per snippet) is vastly different (~3000 for MFCCs and ~300 for Chroma Features). We have appended the Chroma Features to the MFCCs (after converting them to feature vectors) for simplicity, but the sheer volume of data that the MFCC holds naturally gives it more weight. 4 Methodology Genre classification is a supervised learning problem, hence we have limited our attention to the supervised learning algorithms such as
3 Another widely used feature representation of audio signals is the set of chroma features, As mentioned above, both MFCCs and Chroma Features are in matrix form, but the classification method that we used (multi-class support vector machines) does not support multidimensional matrices (one feature matrix per training example). We instead turned each feature matrix into a feature vector by appending each row vector after another. To assess the accuracy of the classifications, we used 10-fold cross validation to estimate the generalization error. 4.1 Multi-class SVMs Since there are 10 total possible genres, we support vector machines. used multi-class support vector machines, a simple application of the traditional two-class support vector machines. A multi-class SVM uses a one vs. all approach; one support vector machine is trained for one class of training observations (the example is a member of this class, or is a member of any of the other classes). The testing example is tested against all classifiers, and we choose the class with the highest probability/confidence score. We used multi-svv code provided by Cody[3] which builds upon the svmtrain function provided by MATLAB. Figure 3: Comparison of accuracy of the multi-class SVM on different genre subsets and feature representations
4 5 Evaluation We ran three multi-class SVM tests: one using only chroma as features, one using only one MFCCs, and the third using both, as detailed in section 3.3. While we worked with a relatively small data set of only 100 snippets per genre where each snippet was the first 30 seconds of a song in the particular genre, the difference in accuracy shown above (Figure 3) seems to be statistically significant and therefore applicable to a larger dataset. As the graph above shows, both MFCCs and Chroma Features showed statistically significant improvements over random guessing, which we used as the control to compare the classification accuracy, from binary classification to classifying snippets into all ten genres. Chroma Features did not lead to a higher accuracy than that of MFCCs, and at times, even showed a lower classification accuracy. As discussed in section 3.3, this can possibly be a result of not equally weighting the two coefficients, and the lower classification accuracy than MFCCs only on four and eight genres is possibly due to having too many predictors and therefore overfitting. 6 Conclusion and Future Work Our results suggest that a multi-class SVM is a very effective way to distinguish between a smaller amount of genres, but it loses accuracy when more genres are added, specifically when the added genres have similar musical qualities. Although chroma features have significant roles in other situations such as music transcription or song identification, the higher classification
5 The classification accuracy declined exponentially as the number of genres increased, but the classification accuracy for MFCCs and MFCCs with Chroma remained ~2.5 times higher than that of the control regardless of the number of genres. Chroma Features showed higher classification accuracy than the control, but significantly lower accuracy than that of MFCCs. This could be due to the fact that the MFCCs have almost ten times the amount of predictors compared to Chroma Features, but large number of predictors compared to observations might also lead to overfitting, which tends to produce worse prediction results for a test set. The large difference in accuracy is probably due to the musical property that these coefficients are based on; MFCCs are based on timbre, and Chroma Features are based on pitch class. The combination of MFCCs and accuracy of MFCCs, even sometimes when combined with chroma features, signifies that the timbre of the sound, as opposed to the note values, holds greater weights in differentiating between genres. Furthermore, this proves that even if similar melodies and chord structures are shared between songs, the combination of instrumentation and vocal tone determine genre. In further work, we hope to use principal components analysis to determine the 300 most representative components of each song s MFCC in order to better test the effectiveness of chroma features when combined with MFCCs. Additionally, we would like to explore additional algorithms that might possibly have higher classification accuracy even on a larger amount of genres. Although the multi-class SVM is significantly better than random, it is not entirely effective. Works Cited [1] G. Tzanetakis and P. Cook (2002). GTZAN Genre Colection. Retrieved from Dec [2] Wojcicki, Kamil. "HTK MFCC MATLAB." MATLAB Central File Exchange. N.p., 11 Sept Web. 23 Nov [3] Cody. "Multi Class SVM." MATLAB Central File Exchange. N.p., 7 Dec Web. 27 Nov
Supervised Learning in Genre Classification
 Supervised Learning in Genre Classification Introduction & Motivation Mohit Rajani and Luke Ekkizogloy {i.mohit,luke.ekkizogloy}@gmail.com Stanford University, CS229: Machine Learning, 2009 Now that music
Supervised Learning in Genre Classification Introduction & Motivation Mohit Rajani and Luke Ekkizogloy {i.mohit,luke.ekkizogloy}@gmail.com Stanford University, CS229: Machine Learning, 2009 Now that music
WHAT MAKES FOR A HIT POP SONG? WHAT MAKES FOR A POP SONG?
 WHAT MAKES FOR A HIT POP SONG? WHAT MAKES FOR A POP SONG? NICHOLAS BORG AND GEORGE HOKKANEN Abstract. The possibility of a hit song prediction algorithm is both academically interesting and industry motivated.
WHAT MAKES FOR A HIT POP SONG? WHAT MAKES FOR A POP SONG? NICHOLAS BORG AND GEORGE HOKKANEN Abstract. The possibility of a hit song prediction algorithm is both academically interesting and industry motivated.
MUSI-6201 Computational Music Analysis
 MUSI-6201 Computational Music Analysis Part 9.1: Genre Classification alexander lerch November 4, 2015 temporal analysis overview text book Chapter 8: Musical Genre, Similarity, and Mood (pp. 151 155)
MUSI-6201 Computational Music Analysis Part 9.1: Genre Classification alexander lerch November 4, 2015 temporal analysis overview text book Chapter 8: Musical Genre, Similarity, and Mood (pp. 151 155)
Chord Classification of an Audio Signal using Artificial Neural Network
 Chord Classification of an Audio Signal using Artificial Neural Network Ronesh Shrestha Student, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Chord Classification of an Audio Signal using Artificial Neural Network Ronesh Shrestha Student, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Detecting Musical Key with Supervised Learning
 Detecting Musical Key with Supervised Learning Robert Mahieu Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University rmahieu@stanford.edu Abstract This paper proposes and tests performance of two different
Detecting Musical Key with Supervised Learning Robert Mahieu Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University rmahieu@stanford.edu Abstract This paper proposes and tests performance of two different
Can Song Lyrics Predict Genre? Danny Diekroeger Stanford University
 Can Song Lyrics Predict Genre? Danny Diekroeger Stanford University danny1@stanford.edu 1. Motivation and Goal Music has long been a way for people to express their emotions. And because we all have a
Can Song Lyrics Predict Genre? Danny Diekroeger Stanford University danny1@stanford.edu 1. Motivation and Goal Music has long been a way for people to express their emotions. And because we all have a
Music Genre Classification
 Music Genre Classification chunya25 Fall 2017 1 Introduction A genre is defined as a category of artistic composition, characterized by similarities in form, style, or subject matter. [1] Some researchers
Music Genre Classification chunya25 Fall 2017 1 Introduction A genre is defined as a category of artistic composition, characterized by similarities in form, style, or subject matter. [1] Some researchers
Automatic Rhythmic Notation from Single Voice Audio Sources
 Automatic Rhythmic Notation from Single Voice Audio Sources Jack O Reilly, Shashwat Udit Introduction In this project we used machine learning technique to make estimations of rhythmic notation of a sung
Automatic Rhythmic Notation from Single Voice Audio Sources Jack O Reilly, Shashwat Udit Introduction In this project we used machine learning technique to make estimations of rhythmic notation of a sung
Release Year Prediction for Songs
 Release Year Prediction for Songs [CSE 258 Assignment 2] Ruyu Tan University of California San Diego PID: A53099216 rut003@ucsd.edu Jiaying Liu University of California San Diego PID: A53107720 jil672@ucsd.edu
Release Year Prediction for Songs [CSE 258 Assignment 2] Ruyu Tan University of California San Diego PID: A53099216 rut003@ucsd.edu Jiaying Liu University of California San Diego PID: A53107720 jil672@ucsd.edu
AUTOREGRESSIVE MFCC MODELS FOR GENRE CLASSIFICATION IMPROVED BY HARMONIC-PERCUSSION SEPARATION
 AUTOREGRESSIVE MFCC MODELS FOR GENRE CLASSIFICATION IMPROVED BY HARMONIC-PERCUSSION SEPARATION Halfdan Rump, Shigeki Miyabe, Emiru Tsunoo, Nobukata Ono, Shigeki Sagama The University of Tokyo, Graduate
AUTOREGRESSIVE MFCC MODELS FOR GENRE CLASSIFICATION IMPROVED BY HARMONIC-PERCUSSION SEPARATION Halfdan Rump, Shigeki Miyabe, Emiru Tsunoo, Nobukata Ono, Shigeki Sagama The University of Tokyo, Graduate
Composer Identification of Digital Audio Modeling Content Specific Features Through Markov Models
 Composer Identification of Digital Audio Modeling Content Specific Features Through Markov Models Aric Bartle (abartle@stanford.edu) December 14, 2012 1 Background The field of composer recognition has
Composer Identification of Digital Audio Modeling Content Specific Features Through Markov Models Aric Bartle (abartle@stanford.edu) December 14, 2012 1 Background The field of composer recognition has
Singer Traits Identification using Deep Neural Network
 Singer Traits Identification using Deep Neural Network Zhengshan Shi Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics Stanford University kittyshi@stanford.edu Abstract The author investigates automatic
Singer Traits Identification using Deep Neural Network Zhengshan Shi Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics Stanford University kittyshi@stanford.edu Abstract The author investigates automatic
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development MUSICAL INSTRUMENT IDENTIFICATION AND STATUS FINDING WITH MFCC
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 5.71 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 5, Issue 04, April -2018 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 MUSICAL
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 5.71 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 5, Issue 04, April -2018 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 MUSICAL
Automatic Music Genre Classification
 Automatic Music Genre Classification Nathan YongHoon Kwon, SUNY Binghamton Ingrid Tchakoua, Jackson State University Matthew Pietrosanu, University of Alberta Freya Fu, Colorado State University Yue Wang,
Automatic Music Genre Classification Nathan YongHoon Kwon, SUNY Binghamton Ingrid Tchakoua, Jackson State University Matthew Pietrosanu, University of Alberta Freya Fu, Colorado State University Yue Wang,
INTER GENRE SIMILARITY MODELLING FOR AUTOMATIC MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION
 INTER GENRE SIMILARITY MODELLING FOR AUTOMATIC MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION ULAŞ BAĞCI AND ENGIN ERZIN arxiv:0907.3220v1 [cs.sd] 18 Jul 2009 ABSTRACT. Music genre classification is an essential tool for
INTER GENRE SIMILARITY MODELLING FOR AUTOMATIC MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION ULAŞ BAĞCI AND ENGIN ERZIN arxiv:0907.3220v1 [cs.sd] 18 Jul 2009 ABSTRACT. Music genre classification is an essential tool for
Subjective Similarity of Music: Data Collection for Individuality Analysis
 Subjective Similarity of Music: Data Collection for Individuality Analysis Shota Kawabuchi and Chiyomi Miyajima and Norihide Kitaoka and Kazuya Takeda Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan E-mail: shota.kawabuchi@g.sp.m.is.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Subjective Similarity of Music: Data Collection for Individuality Analysis Shota Kawabuchi and Chiyomi Miyajima and Norihide Kitaoka and Kazuya Takeda Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan E-mail: shota.kawabuchi@g.sp.m.is.nagoya-u.ac.jp
hit), and assume that longer incidental sounds (forest noise, water, wind noise) resemble a Gaussian noise distribution.
 CS 229 FINAL PROJECT A SOUNDHOUND FOR THE SOUNDS OF HOUNDS WEAKLY SUPERVISED MODELING OF ANIMAL SOUNDS ROBERT COLCORD, ETHAN GELLER, MATTHEW HORTON Abstract: We propose a hybrid approach to generating
CS 229 FINAL PROJECT A SOUNDHOUND FOR THE SOUNDS OF HOUNDS WEAKLY SUPERVISED MODELING OF ANIMAL SOUNDS ROBERT COLCORD, ETHAN GELLER, MATTHEW HORTON Abstract: We propose a hybrid approach to generating
Singer Recognition and Modeling Singer Error
 Singer Recognition and Modeling Singer Error Johan Ismael Stanford University jismael@stanford.edu Nicholas McGee Stanford University ndmcgee@stanford.edu 1. Abstract We propose a system for recognizing
Singer Recognition and Modeling Singer Error Johan Ismael Stanford University jismael@stanford.edu Nicholas McGee Stanford University ndmcgee@stanford.edu 1. Abstract We propose a system for recognizing
Features for Audio and Music Classification
 Features for Audio and Music Classification Martin F. McKinney and Jeroen Breebaart Auditory and Multisensory Perception, Digital Signal Processing Group Philips Research Laboratories Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Features for Audio and Music Classification Martin F. McKinney and Jeroen Breebaart Auditory and Multisensory Perception, Digital Signal Processing Group Philips Research Laboratories Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Homework 2 Key-finding algorithm
 Homework 2 Key-finding algorithm Li Su Research Center for IT Innovation, Academia, Taiwan lisu@citi.sinica.edu.tw (You don t need any solid understanding about the musical key before doing this homework,
Homework 2 Key-finding algorithm Li Su Research Center for IT Innovation, Academia, Taiwan lisu@citi.sinica.edu.tw (You don t need any solid understanding about the musical key before doing this homework,
Music Information Retrieval
 Music Information Retrieval Automatic genre classification from acoustic features DANIEL RÖNNOW and THEODOR TWETMAN Bachelor of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2012 Music Information Retrieval Automatic
Music Information Retrieval Automatic genre classification from acoustic features DANIEL RÖNNOW and THEODOR TWETMAN Bachelor of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2012 Music Information Retrieval Automatic
Automatic Music Similarity Assessment and Recommendation. A Thesis. Submitted to the Faculty. Drexel University. Donald Shaul Williamson
 Automatic Music Similarity Assessment and Recommendation A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Drexel University by Donald Shaul Williamson in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
Automatic Music Similarity Assessment and Recommendation A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Drexel University by Donald Shaul Williamson in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
Outline. Why do we classify? Audio Classification
 Outline Introduction Music Information Retrieval Classification Process Steps Pitch Histograms Multiple Pitch Detection Algorithm Musical Genre Classification Implementation Future Work Why do we classify
Outline Introduction Music Information Retrieval Classification Process Steps Pitch Histograms Multiple Pitch Detection Algorithm Musical Genre Classification Implementation Future Work Why do we classify
A Survey of Audio-Based Music Classification and Annotation
 A Survey of Audio-Based Music Classification and Annotation Zhouyu Fu, Guojun Lu, Kai Ming Ting, and Dengsheng Zhang IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, vol. 13, no. 2, April 2011 presenter: Yin-Tzu Lin ( 阿孜孜 ^.^)
A Survey of Audio-Based Music Classification and Annotation Zhouyu Fu, Guojun Lu, Kai Ming Ting, and Dengsheng Zhang IEEE Trans. on Multimedia, vol. 13, no. 2, April 2011 presenter: Yin-Tzu Lin ( 阿孜孜 ^.^)
DAY 1. Intelligent Audio Systems: A review of the foundations and applications of semantic audio analysis and music information retrieval
 DAY 1 Intelligent Audio Systems: A review of the foundations and applications of semantic audio analysis and music information retrieval Jay LeBoeuf Imagine Research jay{at}imagine-research.com Rebecca
DAY 1 Intelligent Audio Systems: A review of the foundations and applications of semantic audio analysis and music information retrieval Jay LeBoeuf Imagine Research jay{at}imagine-research.com Rebecca
Effects of acoustic degradations on cover song recognition
 Signal Processing in Acoustics: Paper 68 Effects of acoustic degradations on cover song recognition Julien Osmalskyj (a), Jean-Jacques Embrechts (b) (a) University of Liège, Belgium, josmalsky@ulg.ac.be
Signal Processing in Acoustics: Paper 68 Effects of acoustic degradations on cover song recognition Julien Osmalskyj (a), Jean-Jacques Embrechts (b) (a) University of Liège, Belgium, josmalsky@ulg.ac.be
Music Information Retrieval
 CTP 431 Music and Audio Computing Music Information Retrieval Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) Juhan Nam 1 Introduction ü Instrument: Piano ü Composer: Chopin ü Key: E-minor ü Melody - ELO
CTP 431 Music and Audio Computing Music Information Retrieval Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) Juhan Nam 1 Introduction ü Instrument: Piano ü Composer: Chopin ü Key: E-minor ü Melody - ELO
Recommending Music for Language Learning: The Problem of Singing Voice Intelligibility
 Recommending Music for Language Learning: The Problem of Singing Voice Intelligibility Karim M. Ibrahim (M.Sc.,Nile University, Cairo, 2016) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Recommending Music for Language Learning: The Problem of Singing Voice Intelligibility Karim M. Ibrahim (M.Sc.,Nile University, Cairo, 2016) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
Music genre classification using a hierarchical long short term memory (LSTM) model
 Chun Pui Tang, Ka Long Chui, Ying Kin Yu, Zhiliang Zeng, Kin Hong Wong, "Music Genre classification using a hierarchical Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) model", International Workshop on Pattern Recognition
Chun Pui Tang, Ka Long Chui, Ying Kin Yu, Zhiliang Zeng, Kin Hong Wong, "Music Genre classification using a hierarchical Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) model", International Workshop on Pattern Recognition
TOWARD UNDERSTANDING EXPRESSIVE PERCUSSION THROUGH CONTENT BASED ANALYSIS
 TOWARD UNDERSTANDING EXPRESSIVE PERCUSSION THROUGH CONTENT BASED ANALYSIS Matthew Prockup, Erik M. Schmidt, Jeffrey Scott, and Youngmoo E. Kim Music and Entertainment Technology Laboratory (MET-lab) Electrical
TOWARD UNDERSTANDING EXPRESSIVE PERCUSSION THROUGH CONTENT BASED ANALYSIS Matthew Prockup, Erik M. Schmidt, Jeffrey Scott, and Youngmoo E. Kim Music and Entertainment Technology Laboratory (MET-lab) Electrical
Instrument Recognition in Polyphonic Mixtures Using Spectral Envelopes
 Instrument Recognition in Polyphonic Mixtures Using Spectral Envelopes hello Jay Biernat Third author University of Rochester University of Rochester Affiliation3 words jbiernat@ur.rochester.edu author3@ismir.edu
Instrument Recognition in Polyphonic Mixtures Using Spectral Envelopes hello Jay Biernat Third author University of Rochester University of Rochester Affiliation3 words jbiernat@ur.rochester.edu author3@ismir.edu
Music Emotion Recognition. Jaesung Lee. Chung-Ang University
 Music Emotion Recognition Jaesung Lee Chung-Ang University Introduction Searching Music in Music Information Retrieval Some information about target music is available Query by Text: Title, Artist, or
Music Emotion Recognition Jaesung Lee Chung-Ang University Introduction Searching Music in Music Information Retrieval Some information about target music is available Query by Text: Title, Artist, or
Automatic Laughter Detection
 Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox 1803707 knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 1, 006 Abstract We built a system to automatically detect laughter from acoustic features of audio. To implement the system,
Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox 1803707 knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 1, 006 Abstract We built a system to automatically detect laughter from acoustic features of audio. To implement the system,
Recognising Cello Performers using Timbre Models
 Recognising Cello Performers using Timbre Models Chudy, Magdalena; Dixon, Simon For additional information about this publication click this link. http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/jspui/handle/123456789/5013 Information
Recognising Cello Performers using Timbre Models Chudy, Magdalena; Dixon, Simon For additional information about this publication click this link. http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/jspui/handle/123456789/5013 Information
Music Similarity and Cover Song Identification: The Case of Jazz
 Music Similarity and Cover Song Identification: The Case of Jazz Simon Dixon and Peter Foster s.e.dixon@qmul.ac.uk Centre for Digital Music School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Queen Mary
Music Similarity and Cover Song Identification: The Case of Jazz Simon Dixon and Peter Foster s.e.dixon@qmul.ac.uk Centre for Digital Music School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Queen Mary
CS229 Project Report Polyphonic Piano Transcription
 CS229 Project Report Polyphonic Piano Transcription Mohammad Sadegh Ebrahimi Stanford University Jean-Baptiste Boin Stanford University sadegh@stanford.edu jbboin@stanford.edu 1. Introduction In this project
CS229 Project Report Polyphonic Piano Transcription Mohammad Sadegh Ebrahimi Stanford University Jean-Baptiste Boin Stanford University sadegh@stanford.edu jbboin@stanford.edu 1. Introduction In this project
Automatic Laughter Detection
 Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox Final Project (EECS 94) knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 1, 006 1 Introduction Laughter is a powerful cue in communication. It communicates to listeners the emotional
Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox Final Project (EECS 94) knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 1, 006 1 Introduction Laughter is a powerful cue in communication. It communicates to listeners the emotional
Composer Style Attribution
 Composer Style Attribution Jacqueline Speiser, Vishesh Gupta Introduction Josquin des Prez (1450 1521) is one of the most famous composers of the Renaissance. Despite his fame, there exists a significant
Composer Style Attribution Jacqueline Speiser, Vishesh Gupta Introduction Josquin des Prez (1450 1521) is one of the most famous composers of the Renaissance. Despite his fame, there exists a significant
A QUERY BY EXAMPLE MUSIC RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM
 A QUER B EAMPLE MUSIC RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM H. HARB AND L. CHEN Maths-Info department, Ecole Centrale de Lyon. 36, av. Guy de Collongue, 69134, Ecully, France, EUROPE E-mail: {hadi.harb, liming.chen}@ec-lyon.fr
A QUER B EAMPLE MUSIC RETRIEVAL ALGORITHM H. HARB AND L. CHEN Maths-Info department, Ecole Centrale de Lyon. 36, av. Guy de Collongue, 69134, Ecully, France, EUROPE E-mail: {hadi.harb, liming.chen}@ec-lyon.fr
A CLASSIFICATION APPROACH TO MELODY TRANSCRIPTION
 A CLASSIFICATION APPROACH TO MELODY TRANSCRIPTION Graham E. Poliner and Daniel P.W. Ellis LabROSA, Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, New York NY 127 USA {graham,dpwe}@ee.columbia.edu
A CLASSIFICATION APPROACH TO MELODY TRANSCRIPTION Graham E. Poliner and Daniel P.W. Ellis LabROSA, Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, New York NY 127 USA {graham,dpwe}@ee.columbia.edu
Computational Models of Music Similarity. Elias Pampalk National Institute for Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
 Computational Models of Music Similarity 1 Elias Pampalk National Institute for Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Abstract The perceived similarity of two pieces of music is multi-dimensional,
Computational Models of Music Similarity 1 Elias Pampalk National Institute for Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Abstract The perceived similarity of two pieces of music is multi-dimensional,
Music Mood Classification - an SVM based approach. Sebastian Napiorkowski
 Music Mood Classification - an SVM based approach Sebastian Napiorkowski Topics on Computer Music (Seminar Report) HPAC - RWTH - SS2015 Contents 1. Motivation 2. Quantification and Definition of Mood 3.
Music Mood Classification - an SVM based approach Sebastian Napiorkowski Topics on Computer Music (Seminar Report) HPAC - RWTH - SS2015 Contents 1. Motivation 2. Quantification and Definition of Mood 3.
Creating a Feature Vector to Identify Similarity between MIDI Files
 Creating a Feature Vector to Identify Similarity between MIDI Files Joseph Stroud 2017 Honors Thesis Advised by Sergio Alvarez Computer Science Department, Boston College 1 Abstract Today there are many
Creating a Feature Vector to Identify Similarity between MIDI Files Joseph Stroud 2017 Honors Thesis Advised by Sergio Alvarez Computer Science Department, Boston College 1 Abstract Today there are many
Week 14 Music Understanding and Classification
 Week 14 Music Understanding and Classification Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Music & Art Overview n Music Style Classification n What s a classifier? n Naïve Bayesian Classifiers n
Week 14 Music Understanding and Classification Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Music & Art Overview n Music Style Classification n What s a classifier? n Naïve Bayesian Classifiers n
Recognising Cello Performers Using Timbre Models
 Recognising Cello Performers Using Timbre Models Magdalena Chudy and Simon Dixon Abstract In this paper, we compare timbre features of various cello performers playing the same instrument in solo cello
Recognising Cello Performers Using Timbre Models Magdalena Chudy and Simon Dixon Abstract In this paper, we compare timbre features of various cello performers playing the same instrument in solo cello
Mood Tracking of Radio Station Broadcasts
 Mood Tracking of Radio Station Broadcasts Jacek Grekow Faculty of Computer Science, Bialystok University of Technology, Wiejska 45A, Bialystok 15-351, Poland j.grekow@pb.edu.pl Abstract. This paper presents
Mood Tracking of Radio Station Broadcasts Jacek Grekow Faculty of Computer Science, Bialystok University of Technology, Wiejska 45A, Bialystok 15-351, Poland j.grekow@pb.edu.pl Abstract. This paper presents
HIT SONG SCIENCE IS NOT YET A SCIENCE
 HIT SONG SCIENCE IS NOT YET A SCIENCE François Pachet Sony CSL pachet@csl.sony.fr Pierre Roy Sony CSL roy@csl.sony.fr ABSTRACT We describe a large-scale experiment aiming at validating the hypothesis that
HIT SONG SCIENCE IS NOT YET A SCIENCE François Pachet Sony CSL pachet@csl.sony.fr Pierre Roy Sony CSL roy@csl.sony.fr ABSTRACT We describe a large-scale experiment aiming at validating the hypothesis that
Acoustic Scene Classification
 Acoustic Scene Classification Marc-Christoph Gerasch Seminar Topics in Computer Music - Acoustic Scene Classification 6/24/2015 1 Outline Acoustic Scene Classification - definition History and state of
Acoustic Scene Classification Marc-Christoph Gerasch Seminar Topics in Computer Music - Acoustic Scene Classification 6/24/2015 1 Outline Acoustic Scene Classification - definition History and state of
Predicting Time-Varying Musical Emotion Distributions from Multi-Track Audio
 Predicting Time-Varying Musical Emotion Distributions from Multi-Track Audio Jeffrey Scott, Erik M. Schmidt, Matthew Prockup, Brandon Morton, and Youngmoo E. Kim Music and Entertainment Technology Laboratory
Predicting Time-Varying Musical Emotion Distributions from Multi-Track Audio Jeffrey Scott, Erik M. Schmidt, Matthew Prockup, Brandon Morton, and Youngmoo E. Kim Music and Entertainment Technology Laboratory
Lyrics Classification using Naive Bayes
 Lyrics Classification using Naive Bayes Dalibor Bužić *, Jasminka Dobša ** * College for Information Technologies, Klaićeva 7, Zagreb, Croatia ** Faculty of Organization and Informatics, Pavlinska 2, Varaždin,
Lyrics Classification using Naive Bayes Dalibor Bužić *, Jasminka Dobša ** * College for Information Technologies, Klaićeva 7, Zagreb, Croatia ** Faculty of Organization and Informatics, Pavlinska 2, Varaždin,
Classification of Timbre Similarity
 Classification of Timbre Similarity Corey Kereliuk McGill University March 15, 2007 1 / 16 1 Definition of Timbre What Timbre is Not What Timbre is A 2-dimensional Timbre Space 2 3 Considerations Common
Classification of Timbre Similarity Corey Kereliuk McGill University March 15, 2007 1 / 16 1 Definition of Timbre What Timbre is Not What Timbre is A 2-dimensional Timbre Space 2 3 Considerations Common
The Million Song Dataset
 The Million Song Dataset AUDIO FEATURES The Million Song Dataset There is no data like more data Bob Mercer of IBM (1985). T. Bertin-Mahieux, D.P.W. Ellis, B. Whitman, P. Lamere, The Million Song Dataset,
The Million Song Dataset AUDIO FEATURES The Million Song Dataset There is no data like more data Bob Mercer of IBM (1985). T. Bertin-Mahieux, D.P.W. Ellis, B. Whitman, P. Lamere, The Million Song Dataset,
Singer Identification
 Singer Identification Bertrand SCHERRER McGill University March 15, 2007 Bertrand SCHERRER (McGill University) Singer Identification March 15, 2007 1 / 27 Outline 1 Introduction Applications Challenges
Singer Identification Bertrand SCHERRER McGill University March 15, 2007 Bertrand SCHERRER (McGill University) Singer Identification March 15, 2007 1 / 27 Outline 1 Introduction Applications Challenges
Computational Modelling of Harmony
 Computational Modelling of Harmony Simon Dixon Centre for Digital Music, Queen Mary University of London, Mile End Rd, London E1 4NS, UK simon.dixon@elec.qmul.ac.uk http://www.elec.qmul.ac.uk/people/simond
Computational Modelling of Harmony Simon Dixon Centre for Digital Music, Queen Mary University of London, Mile End Rd, London E1 4NS, UK simon.dixon@elec.qmul.ac.uk http://www.elec.qmul.ac.uk/people/simond
GCT535- Sound Technology for Multimedia Timbre Analysis. Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam
 GCT535- Sound Technology for Multimedia Timbre Analysis Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam 1 Outlines Timbre Analysis Definition of Timbre Timbre Features Zero-crossing rate Spectral
GCT535- Sound Technology for Multimedia Timbre Analysis Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam 1 Outlines Timbre Analysis Definition of Timbre Timbre Features Zero-crossing rate Spectral
Speech and Speaker Recognition for the Command of an Industrial Robot
 Speech and Speaker Recognition for the Command of an Industrial Robot CLAUDIA MOISA*, HELGA SILAGHI*, ANDREI SILAGHI** *Dept. of Electric Drives and Automation University of Oradea University Street, nr.
Speech and Speaker Recognition for the Command of an Industrial Robot CLAUDIA MOISA*, HELGA SILAGHI*, ANDREI SILAGHI** *Dept. of Electric Drives and Automation University of Oradea University Street, nr.
The song remains the same: identifying versions of the same piece using tonal descriptors
 The song remains the same: identifying versions of the same piece using tonal descriptors Emilia Gómez Music Technology Group, Universitat Pompeu Fabra Ocata, 83, Barcelona emilia.gomez@iua.upf.edu Abstract
The song remains the same: identifying versions of the same piece using tonal descriptors Emilia Gómez Music Technology Group, Universitat Pompeu Fabra Ocata, 83, Barcelona emilia.gomez@iua.upf.edu Abstract
Automatic Piano Music Transcription
 Automatic Piano Music Transcription Jianyu Fan Qiuhan Wang Xin Li Jianyu.Fan.Gr@dartmouth.edu Qiuhan.Wang.Gr@dartmouth.edu Xi.Li.Gr@dartmouth.edu 1. Introduction Writing down the score while listening
Automatic Piano Music Transcription Jianyu Fan Qiuhan Wang Xin Li Jianyu.Fan.Gr@dartmouth.edu Qiuhan.Wang.Gr@dartmouth.edu Xi.Li.Gr@dartmouth.edu 1. Introduction Writing down the score while listening
Content-based music retrieval
 Music retrieval 1 Music retrieval 2 Content-based music retrieval Music information retrieval (MIR) is currently an active research area See proceedings of ISMIR conference and annual MIREX evaluations
Music retrieval 1 Music retrieval 2 Content-based music retrieval Music information retrieval (MIR) is currently an active research area See proceedings of ISMIR conference and annual MIREX evaluations
Melody Extraction from Generic Audio Clips Thaminda Edirisooriya, Hansohl Kim, Connie Zeng
 Melody Extraction from Generic Audio Clips Thaminda Edirisooriya, Hansohl Kim, Connie Zeng Introduction In this project we were interested in extracting the melody from generic audio files. Due to the
Melody Extraction from Generic Audio Clips Thaminda Edirisooriya, Hansohl Kim, Connie Zeng Introduction In this project we were interested in extracting the melody from generic audio files. Due to the
Data Driven Music Understanding
 Data Driven Music Understanding Dan Ellis Laboratory for Recognition and Organization of Speech and Audio Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University, NY USA http://labrosa.ee.columbia.edu/ 1. Motivation:
Data Driven Music Understanding Dan Ellis Laboratory for Recognition and Organization of Speech and Audio Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University, NY USA http://labrosa.ee.columbia.edu/ 1. Motivation:
Application Of Missing Feature Theory To The Recognition Of Musical Instruments In Polyphonic Audio
 Application Of Missing Feature Theory To The Recognition Of Musical Instruments In Polyphonic Audio Jana Eggink and Guy J. Brown Department of Computer Science, University of Sheffield Regent Court, 11
Application Of Missing Feature Theory To The Recognition Of Musical Instruments In Polyphonic Audio Jana Eggink and Guy J. Brown Department of Computer Science, University of Sheffield Regent Court, 11
LEARNING SPECTRAL FILTERS FOR SINGLE- AND MULTI-LABEL CLASSIFICATION OF MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS. Patrick Joseph Donnelly
 LEARNING SPECTRAL FILTERS FOR SINGLE- AND MULTI-LABEL CLASSIFICATION OF MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS by Patrick Joseph Donnelly A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
LEARNING SPECTRAL FILTERS FOR SINGLE- AND MULTI-LABEL CLASSIFICATION OF MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS by Patrick Joseph Donnelly A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Topic 10. Multi-pitch Analysis
 Topic 10 Multi-pitch Analysis What is pitch? Common elements of music are pitch, rhythm, dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture. An auditory perceptual attribute in terms of which sounds
Topic 10 Multi-pitch Analysis What is pitch? Common elements of music are pitch, rhythm, dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture. An auditory perceptual attribute in terms of which sounds
Automatic Musical Pattern Feature Extraction Using Convolutional Neural Network
 Automatic Musical Pattern Feature Extraction Using Convolutional Neural Network Tom LH. Li, Antoni B. Chan and Andy HW. Chun Abstract Music genre classification has been a challenging yet promising task
Automatic Musical Pattern Feature Extraction Using Convolutional Neural Network Tom LH. Li, Antoni B. Chan and Andy HW. Chun Abstract Music genre classification has been a challenging yet promising task
SONG-LEVEL FEATURES AND SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES FOR MUSIC CLASSIFICATION
 SONG-LEVEL FEATURES AN SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES FOR MUSIC CLASSIFICATION Michael I. Mandel and aniel P.W. Ellis LabROSA, ept. of Elec. Eng., Columbia University, NY NY USA {mim,dpwe}@ee.columbia.edu ABSTRACT
SONG-LEVEL FEATURES AN SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES FOR MUSIC CLASSIFICATION Michael I. Mandel and aniel P.W. Ellis LabROSA, ept. of Elec. Eng., Columbia University, NY NY USA {mim,dpwe}@ee.columbia.edu ABSTRACT
Analytic Comparison of Audio Feature Sets using Self-Organising Maps
 Analytic Comparison of Audio Feature Sets using Self-Organising Maps Rudolf Mayer, Jakob Frank, Andreas Rauber Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems Vienna University of Technology,
Analytic Comparison of Audio Feature Sets using Self-Organising Maps Rudolf Mayer, Jakob Frank, Andreas Rauber Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems Vienna University of Technology,
Research & Development. White Paper WHP 232. A Large Scale Experiment for Mood-based Classification of TV Programmes BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION
 Research & Development White Paper WHP 232 September 2012 A Large Scale Experiment for Mood-based Classification of TV Programmes Jana Eggink, Denise Bland BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION White Paper
Research & Development White Paper WHP 232 September 2012 A Large Scale Experiment for Mood-based Classification of TV Programmes Jana Eggink, Denise Bland BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION White Paper
Music Composition with RNN
 Music Composition with RNN Jason Wang Department of Statistics Stanford University zwang01@stanford.edu Abstract Music composition is an interesting problem that tests the creativity capacities of artificial
Music Composition with RNN Jason Wang Department of Statistics Stanford University zwang01@stanford.edu Abstract Music composition is an interesting problem that tests the creativity capacities of artificial
LEARNING A FEATURE SPACE FOR SIMILARITY IN WORLD MUSIC
 LEARNING A FEATURE SPACE FOR SIMILARITY IN WORLD MUSIC Maria Panteli, Emmanouil Benetos, Simon Dixon Centre for Digital Music, Queen Mary University of London, United Kingdom {m.panteli, emmanouil.benetos,
LEARNING A FEATURE SPACE FOR SIMILARITY IN WORLD MUSIC Maria Panteli, Emmanouil Benetos, Simon Dixon Centre for Digital Music, Queen Mary University of London, United Kingdom {m.panteli, emmanouil.benetos,
Enabling editors through machine learning
 Meta Follow Meta is an AI company that provides academics & innovation-driven companies with powerful views of t Dec 9, 2016 9 min read Enabling editors through machine learning Examining the data science
Meta Follow Meta is an AI company that provides academics & innovation-driven companies with powerful views of t Dec 9, 2016 9 min read Enabling editors through machine learning Examining the data science
Music Information Retrieval Community
 Music Information Retrieval Community What: Developing systems that retrieve music When: Late 1990 s to Present Where: ISMIR - conference started in 2000 Why: lots of digital music, lots of music lovers,
Music Information Retrieval Community What: Developing systems that retrieve music When: Late 1990 s to Present Where: ISMIR - conference started in 2000 Why: lots of digital music, lots of music lovers,
Musical Instrument Identification Using Principal Component Analysis and Multi-Layered Perceptrons
 Musical Instrument Identification Using Principal Component Analysis and Multi-Layered Perceptrons Róisín Loughran roisin.loughran@ul.ie Jacqueline Walker jacqueline.walker@ul.ie Michael O Neill University
Musical Instrument Identification Using Principal Component Analysis and Multi-Layered Perceptrons Róisín Loughran roisin.loughran@ul.ie Jacqueline Walker jacqueline.walker@ul.ie Michael O Neill University
MUSIC TONALITY FEATURES FOR SPEECH/MUSIC DISCRIMINATION. Gregory Sell and Pascal Clark
 214 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) MUSIC TONALITY FEATURES FOR SPEECH/MUSIC DISCRIMINATION Gregory Sell and Pascal Clark Human Language Technology Center
214 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) MUSIC TONALITY FEATURES FOR SPEECH/MUSIC DISCRIMINATION Gregory Sell and Pascal Clark Human Language Technology Center
Combination of Audio & Lyrics Features for Genre Classication in Digital Audio Collections
 1/23 Combination of Audio & Lyrics Features for Genre Classication in Digital Audio Collections Rudolf Mayer, Andreas Rauber Vienna University of Technology {mayer,rauber}@ifs.tuwien.ac.at Robert Neumayer
1/23 Combination of Audio & Lyrics Features for Genre Classication in Digital Audio Collections Rudolf Mayer, Andreas Rauber Vienna University of Technology {mayer,rauber}@ifs.tuwien.ac.at Robert Neumayer
Music Recommendation from Song Sets
 Music Recommendation from Song Sets Beth Logan Cambridge Research Laboratory HP Laboratories Cambridge HPL-2004-148 August 30, 2004* E-mail: Beth.Logan@hp.com music analysis, information retrieval, multimedia
Music Recommendation from Song Sets Beth Logan Cambridge Research Laboratory HP Laboratories Cambridge HPL-2004-148 August 30, 2004* E-mail: Beth.Logan@hp.com music analysis, information retrieval, multimedia
Feature-Based Analysis of Haydn String Quartets
 Feature-Based Analysis of Haydn String Quartets Lawson Wong 5/5/2 Introduction When listening to multi-movement works, amateur listeners have almost certainly asked the following situation : Am I still
Feature-Based Analysis of Haydn String Quartets Lawson Wong 5/5/2 Introduction When listening to multi-movement works, amateur listeners have almost certainly asked the following situation : Am I still
Topics in Computer Music Instrument Identification. Ioanna Karydi
 Topics in Computer Music Instrument Identification Ioanna Karydi Presentation overview What is instrument identification? Sound attributes & Timbre Human performance The ideal algorithm Selected approaches
Topics in Computer Music Instrument Identification Ioanna Karydi Presentation overview What is instrument identification? Sound attributes & Timbre Human performance The ideal algorithm Selected approaches
A System for Automatic Chord Transcription from Audio Using Genre-Specific Hidden Markov Models
 A System for Automatic Chord Transcription from Audio Using Genre-Specific Hidden Markov Models Kyogu Lee Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305, USA
A System for Automatic Chord Transcription from Audio Using Genre-Specific Hidden Markov Models Kyogu Lee Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305, USA
Video-based Vibrato Detection and Analysis for Polyphonic String Music
 Video-based Vibrato Detection and Analysis for Polyphonic String Music Bochen Li, Karthik Dinesh, Gaurav Sharma, Zhiyao Duan Audio Information Research Lab University of Rochester The 18 th International
Video-based Vibrato Detection and Analysis for Polyphonic String Music Bochen Li, Karthik Dinesh, Gaurav Sharma, Zhiyao Duan Audio Information Research Lab University of Rochester The 18 th International
EE391 Special Report (Spring 2005) Automatic Chord Recognition Using A Summary Autocorrelation Function
 EE391 Special Report (Spring 25) Automatic Chord Recognition Using A Summary Autocorrelation Function Advisor: Professor Julius Smith Kyogu Lee Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA)
EE391 Special Report (Spring 25) Automatic Chord Recognition Using A Summary Autocorrelation Function Advisor: Professor Julius Smith Kyogu Lee Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics (CCRMA)
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Improving Music Genre Classification Using Automatically Induced Harmony Rules
 Journal of New Music Research Vol. 00, No. 00, Month 200x, 1 18 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improving Music Genre Classification Using Automatically Induced Harmony Rules Amélie Anglade 1, Emmanouil Benetos 1, Matthias
Journal of New Music Research Vol. 00, No. 00, Month 200x, 1 18 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improving Music Genre Classification Using Automatically Induced Harmony Rules Amélie Anglade 1, Emmanouil Benetos 1, Matthias
Using Genre Classification to Make Content-based Music Recommendations
 Using Genre Classification to Make Content-based Music Recommendations Robbie Jones (rmjones@stanford.edu) and Karen Lu (karenlu@stanford.edu) CS 221, Autumn 2016 Stanford University I. Introduction Our
Using Genre Classification to Make Content-based Music Recommendations Robbie Jones (rmjones@stanford.edu) and Karen Lu (karenlu@stanford.edu) CS 221, Autumn 2016 Stanford University I. Introduction Our
HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS FOR SPECTRAL SIMILARITY OF SONGS. Arthur Flexer, Elias Pampalk, Gerhard Widmer
 Proc. of the 8 th Int. Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx 5), Madrid, Spain, September 2-22, 25 HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS FOR SPECTRAL SIMILARITY OF SONGS Arthur Flexer, Elias Pampalk, Gerhard Widmer
Proc. of the 8 th Int. Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx 5), Madrid, Spain, September 2-22, 25 HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS FOR SPECTRAL SIMILARITY OF SONGS Arthur Flexer, Elias Pampalk, Gerhard Widmer
LSTM Neural Style Transfer in Music Using Computational Musicology
 LSTM Neural Style Transfer in Music Using Computational Musicology Jett Oristaglio Dartmouth College, June 4 2017 1. Introduction In the 2016 paper A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style, Gatys et al. discovered
LSTM Neural Style Transfer in Music Using Computational Musicology Jett Oristaglio Dartmouth College, June 4 2017 1. Introduction In the 2016 paper A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style, Gatys et al. discovered
POST-PROCESSING FIDDLE : A REAL-TIME MULTI-PITCH TRACKING TECHNIQUE USING HARMONIC PARTIAL SUBTRACTION FOR USE WITHIN LIVE PERFORMANCE SYSTEMS
 POST-PROCESSING FIDDLE : A REAL-TIME MULTI-PITCH TRACKING TECHNIQUE USING HARMONIC PARTIAL SUBTRACTION FOR USE WITHIN LIVE PERFORMANCE SYSTEMS Andrew N. Robertson, Mark D. Plumbley Centre for Digital Music
POST-PROCESSING FIDDLE : A REAL-TIME MULTI-PITCH TRACKING TECHNIQUE USING HARMONIC PARTIAL SUBTRACTION FOR USE WITHIN LIVE PERFORMANCE SYSTEMS Andrew N. Robertson, Mark D. Plumbley Centre for Digital Music
A Categorical Approach for Recognizing Emotional Effects of Music
 A Categorical Approach for Recognizing Emotional Effects of Music Mohsen Sahraei Ardakani 1 and Ehsan Arbabi School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran,
A Categorical Approach for Recognizing Emotional Effects of Music Mohsen Sahraei Ardakani 1 and Ehsan Arbabi School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran,
Music Information Retrieval with Temporal Features and Timbre
 Music Information Retrieval with Temporal Features and Timbre Angelina A. Tzacheva and Keith J. Bell University of South Carolina Upstate, Department of Informatics 800 University Way, Spartanburg, SC
Music Information Retrieval with Temporal Features and Timbre Angelina A. Tzacheva and Keith J. Bell University of South Carolina Upstate, Department of Informatics 800 University Way, Spartanburg, SC
ISMIR 2008 Session 2a Music Recommendation and Organization
 A COMPARISON OF SIGNAL-BASED MUSIC RECOMMENDATION TO GENRE LABELS, COLLABORATIVE FILTERING, MUSICOLOGICAL ANALYSIS, HUMAN RECOMMENDATION, AND RANDOM BASELINE Terence Magno Cooper Union magno.nyc@gmail.com
A COMPARISON OF SIGNAL-BASED MUSIC RECOMMENDATION TO GENRE LABELS, COLLABORATIVE FILTERING, MUSICOLOGICAL ANALYSIS, HUMAN RECOMMENDATION, AND RANDOM BASELINE Terence Magno Cooper Union magno.nyc@gmail.com
Detecting Changes in Music Using Compression
 Detecting Changes in Music Using Compression BA Thesis (Afstudeerscriptie) written by Arseni Storojev (born April 27th, 1987 in Kazan, Russia) under the supervision of Maarten van Someren and Sennay Ghebreab,
Detecting Changes in Music Using Compression BA Thesis (Afstudeerscriptie) written by Arseni Storojev (born April 27th, 1987 in Kazan, Russia) under the supervision of Maarten van Someren and Sennay Ghebreab,
Improving Frame Based Automatic Laughter Detection
 Improving Frame Based Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox EE225D Class Project knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 13, 2007 Abstract Laughter recognition is an underexplored area of research. My goal for
Improving Frame Based Automatic Laughter Detection Mary Knox EE225D Class Project knoxm@eecs.berkeley.edu December 13, 2007 Abstract Laughter recognition is an underexplored area of research. My goal for
SYNTHESIS FROM MUSICAL INSTRUMENT CHARACTER MAPS
 Published by Institute of Electrical Engineers (IEE). 1998 IEE, Paul Masri, Nishan Canagarajah Colloquium on "Audio and Music Technology"; November 1998, London. Digest No. 98/470 SYNTHESIS FROM MUSICAL
Published by Institute of Electrical Engineers (IEE). 1998 IEE, Paul Masri, Nishan Canagarajah Colloquium on "Audio and Music Technology"; November 1998, London. Digest No. 98/470 SYNTHESIS FROM MUSICAL
Classification of Musical Instruments sounds by Using MFCC and Timbral Audio Descriptors
 Classification of Musical Instruments sounds by Using MFCC and Timbral Audio Descriptors Priyanka S. Jadhav M.E. (Computer Engineering) G. H. Raisoni College of Engg. & Mgmt. Wagholi, Pune, India E-mail:
Classification of Musical Instruments sounds by Using MFCC and Timbral Audio Descriptors Priyanka S. Jadhav M.E. (Computer Engineering) G. H. Raisoni College of Engg. & Mgmt. Wagholi, Pune, India E-mail:
A NOVEL CEPSTRAL REPRESENTATION FOR TIMBRE MODELING OF SOUND SOURCES IN POLYPHONIC MIXTURES
 A NOVEL CEPSTRAL REPRESENTATION FOR TIMBRE MODELING OF SOUND SOURCES IN POLYPHONIC MIXTURES Zhiyao Duan 1, Bryan Pardo 2, Laurent Daudet 3 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
A NOVEL CEPSTRAL REPRESENTATION FOR TIMBRE MODELING OF SOUND SOURCES IN POLYPHONIC MIXTURES Zhiyao Duan 1, Bryan Pardo 2, Laurent Daudet 3 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
MELODY ANALYSIS FOR PREDICTION OF THE EMOTIONS CONVEYED BY SINHALA SONGS
 MELODY ANALYSIS FOR PREDICTION OF THE EMOTIONS CONVEYED BY SINHALA SONGS M.G.W. Lakshitha, K.L. Jayaratne University of Colombo School of Computing, Sri Lanka. ABSTRACT: This paper describes our attempt
MELODY ANALYSIS FOR PREDICTION OF THE EMOTIONS CONVEYED BY SINHALA SONGS M.G.W. Lakshitha, K.L. Jayaratne University of Colombo School of Computing, Sri Lanka. ABSTRACT: This paper describes our attempt
Lecture 9 Source Separation
 10420CS 573100 音樂資訊檢索 Music Information Retrieval Lecture 9 Source Separation Yi-Hsuan Yang Ph.D. http://www.citi.sinica.edu.tw/pages/yang/ yang@citi.sinica.edu.tw Music & Audio Computing Lab, Research
10420CS 573100 音樂資訊檢索 Music Information Retrieval Lecture 9 Source Separation Yi-Hsuan Yang Ph.D. http://www.citi.sinica.edu.tw/pages/yang/ yang@citi.sinica.edu.tw Music & Audio Computing Lab, Research
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007
 19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 AN HMM BASED INVESTIGATION OF DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS OF THE SAME TYPE PACS: 43.75.-z Eichner, Matthias; Wolff, Matthias;
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 AN HMM BASED INVESTIGATION OF DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS OF THE SAME TYPE PACS: 43.75.-z Eichner, Matthias; Wolff, Matthias;
A PERPLEXITY BASED COVER SONG MATCHING SYSTEM FOR SHORT LENGTH QUERIES
 12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR 2011) A PERPLEXITY BASED COVER SONG MATCHING SYSTEM FOR SHORT LENGTH QUERIES Erdem Unal 1 Elaine Chew 2 Panayiotis Georgiou
12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR 2011) A PERPLEXITY BASED COVER SONG MATCHING SYSTEM FOR SHORT LENGTH QUERIES Erdem Unal 1 Elaine Chew 2 Panayiotis Georgiou
CTP431- Music and Audio Computing Music Information Retrieval. Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam
 CTP431- Music and Audio Computing Music Information Retrieval Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam 1 Introduction ü Instrument: Piano ü Genre: Classical ü Composer: Chopin ü Key: E-minor
CTP431- Music and Audio Computing Music Information Retrieval Graduate School of Culture Technology KAIST Juhan Nam 1 Introduction ü Instrument: Piano ü Genre: Classical ü Composer: Chopin ü Key: E-minor
FACTORS AFFECTING AUTOMATIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION: AN INVESTIGATION INCORPORATING NON-WESTERN MUSICAL FORMS
 FACTORS AFFECTING AUTOMATIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION: AN INVESTIGATION INCORPORATING NON-WESTERN MUSICAL FORMS Noris Mohd Norowi, Shyamala Doraisamy, Rahmita Wirza Faculty of Computer Science and Information
FACTORS AFFECTING AUTOMATIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION: AN INVESTIGATION INCORPORATING NON-WESTERN MUSICAL FORMS Noris Mohd Norowi, Shyamala Doraisamy, Rahmita Wirza Faculty of Computer Science and Information
