(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
|
|
|
- Bennett Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl /691; 34.5/690 THEREOF (57) ABSTRACT (76) Inventors: Jae-Woo RYU, Yongin-City (KR): A display device includes: a display unit including plurality Do-Ik KIM, Yongin-city (KR) of pixels connected to a plurality of scan lines and a plurality s of data lines and emitting light according to corresponding image data; a dummy pixel connected to a dummy Scan line (21) Appl. No.: 13/067,480 and a dummy data line; and a compensation image data gen erator calculating a compensation amount according to an (22) Filed: Jun. 3, 2011 accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element to detect the compensation amount corre O O sponding to each accumulation light emitting time of a plu (30) Foreign Application Priority Data rality of second organic light emitting elements of the plural Sep. 2, 2010 (KR) ity of pixels by using a decreasing amount of luminance s corresponding a resistance of a first organic light emitting O O element according to an accumulation light emitting time of Publication Classification the first organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel, (51) Int. Cl. and compensating the corresponding image data according to G09G 5/10 ( ) the detected compensation amount. Signal controller DRDGDB Compensation image data generator CDRCDGCDB 300
2
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 3 US 2012/ A1 FIG. 2 PXD Dd ELVDD Sd M2 VoLED E VSS
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2012/ A1 800'000' //089 O?esuaduu00 80'00'80 GHTOA
5 DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF BACKGROUND Field 0002 Embodiments relate to a display device and a driv ing method thereof. More particularly, embodiments relate to an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display and a driving method thereof Description of the Related Art A display device has a display area in which a plu rality of pixels are disposed on a Substrate in a matrix form. The display device performs a display operation by selec tively applying a data signal to a pixel connected to a scan line and a data line. The display device is classified into a passive matrix light emitting display device and an active matrix light emitting display device according to a driving scheme of the pixels. The active matrix light emitting display device, in which unit pixels are selectively lit, is primarily used because of its enhanced resolution, contrast, and operation speed The display device is used for portable information terminals, such as personal computers, mobile phones, PDAs, as well as monitors for various information equipment. Cur rently, an LCD using a liquid crystal panel, an organic light emitting diode display using an organic light emitting diode, a PDP using a plasma panel, etc., are known in the field. In recent years, various light emitting display devices having less weight and Volume than a cathode ray tube have been developed. In particular, an organic light emitting diode dis play having excellent emission efficiency, luminance, view ing angles, and rapid response speed has attracted public attention However, as the usage time of the organic light emitting element is increased, the luminance is deteriorated. This deterioration results in image degradation, e.g. image Sticking. Conventionally, a photosensor sensing the lumi nance of the organic light emitting element is provided. When the luminance is decreased, the decreased luminance is com pensated. However, problems such as an increase of material cost, difficulty of coupling and decoupling thereof, and mea Suring error according to the usage of the photosensor are generated The above disclosed information is only for under standing the background of the invention. Therefore, it may contain information that does not form the prior art that is already known in this country to a person of ordinary skill in the art. SUMMARY 0008 Embodiments are therefore directed to a display device, which substantially overcome one or more of the problems due to the limitations and disadvantages of the related art It is therefore a feature of an embodiment to provide a display device capable of preventing image Sticking due to luminance deterioration without an additional photosensor It is therefore another feature of an embodiment to provide a method for driving a display device capable of preventing image Sticking due to luminance deterioration without an additional photosensor At least one of the above and other features and advantages may be realized by providing a display device including a display unit including a plurality of pixels con nected to a plurality of scan lines and a plurality of data lines, the plurality of pixels emitting light according to correspond ing image data; a dummy pixel connected to a dummy Scan line and a dummy data line, the dummy line including a first organic light emitting element and each pixel including a second organic light emitting element; and a compensation image data generator configured to: calculate a compensation amount according to an accumulation light emitting time of a first organic light emitting element; detect the compensation amount corresponding to each accumulation light emitting time of the plurality of second organic light emitting elements using a decreasing amount of luminance corresponding to a resistance of the first organic light emitting element according to an accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel; and compensate the corresponding image data according to the detected compen sation amount. The compensation image data generator may be configured to sense resistance of the first organic light emitting element according to a sensing Voltage generated to both terminals of the first organic light emitting element when a predetermined current flows in the first organic light emit ting element The compensation image data generator may include: a memory storing the decreasing amount of lumi nance of the first organic light emitting element correspond ing to the sensing Voltage; a timer measuring the accumula tion light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; a data sum unit accumulating and Summing the image data respectively corresponding to the plurality of pix els per each pixel; a compensation amount calculator calcu lating the compensation amount of the corresponding image data according to the accumulation light emitting time by using the resistance of the first organic light emitting element and the accumulation light emitting time; and an image data compensator sensing each accumulation light emitting time of the plurality of second organic light emitting elements and modulating the corresponding image data into the compen sation amount corresponding to the accumulation light emit ting time The compensation amount calculator may detect the decreasing amount of luminance corresponding to the sens ing Voltage and may calculate the increasing amount of the accumulation light emitting time corresponding to the detected decreasing amount of luminance as the compensa tion amount. The display device may further include a lookup table storing the compensation amount time calculated from the compensation amount calculator according to the accu mulation light emitting time. The image data compensator may modulate the corresponding image data for the predeter mined compensation unit time. The dummy pixel may receive a dummy data Voltage corresponding to a full white grayscale through the dummy data line At least one of the above and other features and advantages may also be realized by providing a method for driving a display device including a dummy pixel including a first organic light emitting element and a plurality of pixels respectively including a second organic light emitting ele ment. The method includes: calculating a compensation amount according to an accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element by using a decreasing amount of luminance corresponding to resistance of a first organic light emitting element according to the accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; determining a compensation amount corresponding to the
6 accumulation light emitting time of each second organic light emitting element; and compensating the image data respec tively corresponding to the plurality of pixels according to the calculated compensation amount Calculating the compensation amount may include: detecting the sensing Voltage between both terminals of the first organic light emitting element when a predetermined current flows to the first organic light emitting element; mea Suring the accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; and calculating the increasing amount of the light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element corresponding to the decreasing amount of the lumi nance by using the decreasing amount of luminance of the first organic light emitting element corresponding to the sens ing Voltage. Compensating the image data may be executed every predetermined compensation unit time. The method may further include applying a dummy data Voltage corre sponding to a full white grayscale to the dummy pixel. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other features and advantages will become more apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art by describing in detail exemplary embodiments with reference to the attached drawings, in which: 0017 FIG. 1 illustrates a block diagram of a display device according to an exemplary embodiment FIG. 2 illustrates an equivalent circuit diagram of a dummy pixel PX D shown in FIG FIG.3 illustrates a detailed block diagram of a com pensation image data generator 500 shown in FIG. 1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION 0020 Korean Patent Application No , filed on Sep. 2, 2010, in the Korean Intellectual Property Office, and entitled: Display Device and Driving Method Thereof is incorporated by reference herein in its entirety Example embodiments will now be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying draw ings; however, they may be embodied in different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art Throughout this specification and the claims that follow, when it is described that an element is coupled to another element, the element may be directly coupled to the other element or electrically coupled to the other element through a third element. In addition, unless explicitly described to the contrary, the word comprise' and variations such as comprises or comprising will be understood to imply the inclusion of stated elements but not the exclusion of any other elements FIG. 1 illustrates a block diagram of a display device according to an exemplary embodiment. FIG. 2 is an equiva lent circuit diagram of a dummy pixel PX D shown in FIG Referring to FIG. 1, a display device according to the present embodiment includes a display unit 100, a dummy pixel PX D, a scan driver 200, a data driver 300, a signal controller 400, and a compensation image data generator 500. The display unit 100 may include a plurality of signal lines S1-Sn and D1-Dm, a plurality of pixels PX connected thereto, and arranged in a matrix format The signal lines S1-Sn and D1-Dm includes a plu rality of Scan lines S1-Sn transmitting scan signals and a plurality of data lines D1-Dm transmitting data signals. The scan lines S1-Sn may be arranged in parallel along a row direction. The data lines D1-Dm may be arranged in parallel along a column direction intersecting the scan lines S1-Sn Also, a dummy pixel PX D may be connected to a dummy scan line SD and a dummy data line Dd. The dummy pixel PX D may be separately formed outside the display unit 100 when forming the plurality of pixels PX of the display unit 100. The dummy pixel PX D may have the same char acteristics as the plurality of pixels PX of the display unit 100. (0027. Referring to FIG. 2, the dummy pixel PX D includes an organic light emitting element, a driving transis tor M1, a capacitor Cst, and a Switching transistor M The driving transistor M1 has a source terminal receiving the first driving voltage ELVDd and a drainterminal connected to an anode terminal of the organic light emitting element. A gate terminal of the driving transistor M1 is con nected to the drain terminal of the switching transistor M2. The driving transistor M1 allows a driving current I, of which magnitude varies depending on a Voltage applied between the gate terminal and the source terminal, to flow to the organic light emitting diode (OLED) The switching transistor M2 has a gate terminal connected to the dummy Scan line SD and a source terminal connected to the dummy data line Dd. The Switching transis tor M2 performs the Switching operation in response to the scan signal applied to the dummy scan line SD. When the Switching transistor M2 is turned on, the data signal applied to the dummy data line Dd, i.e., the data Voltage, is transmitted to the gate terminal of the driving transistor M The capacitor Cst is connected between the source terminal and the gate terminal of the driving transistor M1. The capacitor Cst is charged by the data Voltage applied to the gate terminal of the driving transistor M1, and maintains the voltage even after the switching transistor M2 is turned off The organic light emitting element may be realized by an organic light emitting diode (OLED). The organic light emitting element has the cathode terminal receiving the sec ond driving voltage ELVSS. The organic light emitting ele ment displays an image by emitting light with different inten sities according to a current I, that is supplied by the driving transistor M1. Generally, the organic light emitting element deteriorates overdriving time such that the resistance thereof is increased. When the resistance is increased, the amount of light emitted is decreased for the same current. The decrease in amount of light emitted occurs according to the deterioration degree The luminance is used as a factor representing the light emitting amount of the organic light emitting element. The resistance of the organic light emitting element is increased according to the deterioration of the organic light emitting element. Thus, the luminance for the same current is decreased. The resistance of the organic light emitting ele ment is increased Such that the sensing Voltage Vol. between the anode terminal and the cathode terminal is increased. The V between the anode terminal and the cathode terminal is generated when the driving current I flows in the organic light emitting element The organic light emitting diode (OLED) display of an exemplary embodiment determines the deterioration degree of the organic light emitting element according to the driving time by using the sensing Voltage Vol of the
7 dummy pixel PX D. The organic light emitting diode (OLED) display compensates the size of the driving current Io, flowing in the organic light emitting element accord ing to image data DR, DG, and DB, by the deterioration degree in an analog driving method The organic light emitting diode (OLED) display compensates the light emitting time of the organic light emit ting element, according to the image data DR, DG, and DB, by the deterioration degree in a digital driving method. Thus, the organic light emitting diode (OLED) display may com pensate the luminance decreasing according to the deteriora tion of the organic light emitting element. The organic light emitting diode (OLED) display according to the present embodiment uses the image data DR, DG, and DB corre sponding to the plurality of pixels PX to determine the dete rioration degree of each organic light emitting element of the plurality of pixels PX. The detailed description will be described below with reference to FIG Although the driving transistor M1 and the switch ing transistor M2 are shown as p-channel field effect transis tors (FETs) in FIG. 2, the embodiment is not limited thereto. For example, at least one of the driving transistor M1 and the switching transistor M2 may be an n-channel field effect transistor. Furthermore, the connection relationship of the driving transistor M1, the Switching transistor M2, the capaci tor Cst, and the organic light emitting diode (OLED) may be changed. The dummy pixel PX D shown in FIG. 2 is one example of one pixel of the display device. Thus, pixels of different types, including at least two transistors and at least one capacitor, may be used. The configuration of the pixel PX shown in FIG. 1 is the same as that of the dummy pixel PX D shown in FIG.2. Therefore, the description thereof is omitted Referring back to FIG. 1, the scan driver 200 is connected to the scan line S1 to Sn of the display unit 100, and sequentially applies the scan signals S1 to Sn in accordance with a scan control signal CONT1. The scan signal includes a gate-on Voltage Von that can turn on the Switching transistor M2 and a gate-off voltage Voff that can turn off the switching transistor M2. When the switching transistor M2 is the p-channel field effect transistor, the gate-on Voltage Von and the gate-off voltage Voff are a low Voltage and a high Voltage, respectively Also, the scan driver 200, according to an exemplary embodiment, is connected to a dummy Scanline SD. The scan driver 200 applies the dummy Scan signal to the dummy Scan line SD. The dummy Scan signal applied to the dummy Scan line SD maintains the gate-on Voltage Von The data driver 300 is connected to the data lines D1 to Dm of the display unit 100, and converts compensation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB input from the signal con troller 400 into data voltages and applies them to the data lines D1 to Dm in accordance with a data control signal CONT2. The data driver 300 according to an exemplary embodiment is driven by the digital driving method. The data driver 300 controls the pulse width of the data voltage to represent the grayscale of the compensation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB The data driver 300 is connected to the dummy data line Dd of the dummy pixel PX D. The data driver 300 applies the dummy data Voltage having the pulse width cor responding to a full white grayscale to the dummy data line Dd The signal controller 400 receives input signals R, G, and B, a horizontal synchronization signal HSync, a verti cal synchronization signal VSync, and a main clock signal MCLK from the outside to generate the image data DR, DG, and DB, the scan control signal CONT1, and the data control signal CONT The scan control signal CONT1 includes a scan start signal STV directing scan starting and at least one clock signal for controlling an output cycle of the gate-on voltage Von. The scan control signal CONT1 may include an output enable signal OE defining a running time of the gate-on Voltage Von The data control signal CONT2 includes a horizon tal synchronization start signal STH indicating a transmission start of the compensation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB for the pixel PX of one row to the data driver 300 and a load signal LOAD indicating application of the plurality of data voltage to the data lines D1 to Dm The compensation image data generator 500 calcu lates the compensation amount according to the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element by using the resistance and the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel PX D, determines the compensation amount according to each accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element of the plurality of pixels PX, and compen sates the image data DR, DG, and DB corresponding each pixel PX according to the determined compensation amount. The image data signals DR, DG, and DB compensated in the compensation image data generator 500 are referred to as compensation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB. 0044) The compensation image data generator 500 according to an exemplary embodiment senses the resistance every time the accumulation light emitting of the organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel is increased by a pre determined compensation unit time. The compensation image data generator 500 determines the compensation amount corresponding to every time that the accumulation light emitting is increased by a predetermined compensation unit time The compensation image data generator 500, as illustrated in FIG. 3, includes a memory 510, a timer 520, compensation amount calculator 530, a lookup table 540, a data sum unit 550, and an image data compensator 560. The memory 510 stores the decreasing amount of the luminance of the organic light emitting element corresponding to the sensing Voltage Vol. The decreasing amount of luminance is the degree that the luminance is decreased compared with the initial predetermined luminance. The luminance occurs when the predetermined driving current I, flows in the organic light emitting element An exemplary embodiment is operated according to the digital driving method, and the magnitude of the driving current I flowing in the plurality of pixels PX is the same regardless of the image data DR, DG, and DB. The timer 520 measures the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel PX D and trans mits it to the compensation amount calculator The compensation amount calculator 530 calculates the compensation amount of the image data DR, DG, and DB according to the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element by using the resistance of the organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel PX D and the accumulation light emitting time. The compensation amount calculator 530 stores the calculated compensation amount in the lookup table 540 according to the accumulation
8 light emitting time. The compensation amount calculator 530 receives the sensing Voltage V and detects the decreas ing amount of the luminance corresponding to the input sens ing Voltage V from the memory The compensation amount calculator 530 calculates the increasing amount of the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element to change it into the compensation amount. The compensation amount will com pensate the decreasing amount of luminance of the organic light emitting element. The relationship between the increas ing amount of the accumulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element and the decreasing amount of the luminance of the organic light emitting element may be represented by a function F(t). The function F(t) is based on experimental data In an exemplary embodiment, the function F(t) rep resents the increasing amount of the pulse width of the data Voltage corresponding to the image data DR, DG, and DB to compensate the decreasing amount of the luminance accord ing to the accumulation light emitting time. The increasing amount of the application time of the data Voltage to the decreasing amount of the luminance may have a proportional relationship. The light emitting time of the organic light emit ting element may be 20 hours. Therefore, the function F(t), when the decreasing amount of the luminance is 0.1%, increases the application time of the data Voltage correspond ing to the image data DR, DG, and DB by 0.1%. Thus, the function F(t) calculates the application time of the data volt age. The data Voltage is the compensation amount to be main tained for the luminance corresponding to the predetermined grayscale of the image data DR, DG, and DB The data sum unit 550 receives the image data DR, DG, and DB. The data sum unit 550 accumulates and sums each image data DR, DG, and DB of the plurality of pixels PX for each pixel PX. The image data DR, DG, and DB accumu lated and summed for each pixel PX is the information cor responding to the accumulation light emitting time of each pixel PX. The data sum unit 550 generates the information for the accumulation light emitting time corresponding to the accumulated and summed image data DR, DG, and DB of the plurality of pixel PX The image data compensator 560 senses each accu mulation light emitting time of the organic light emitting element of the plurality of pixels PX to detect the compensa tion amount from the lookup table 540 according to the accu mulation light emitting time. The image data compensator 560 modulates the image data DR, DG, and DB according to the detected compensation amount. The image data compen sator 560 detects the compensation amount every time that the compensation unit time is passed to modulate the image data DR, DG, and DB. The image data compensator 560, according to an exemplary embodiment, generates the com pensation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB by using Equa tion 1 below: DATAP-DATAP-F(t)'p In the above Equation 1, DATA, represents the pulse width of the data Voltage corresponding to the compen sation image data CDR, CDG, and CDB, i.e., the application time of the data Voltage. DATA represents the application of the data Voltage corresponding to the image data DR, DG, and DB. A factor p represents the predetermined initial lumi nance value In an exemplary embodiment, there is an upward normalization method and a downward normalization method for compensating the image data DG, DB, and DR. The upward normalization method is a method determining the factor p as a predetermined value, for example "0.7, and increasing the luminance of each pixel PX to 1. The down ward normalization method is a method determining the fac tor Pas '1', and decreasing the luminance of the neighboring pixel PX corresponding to the pixel PX having deteriorated luminance. In the case of the downward normalization method, the function F(t) represents the decreasing amount of the pulse width of the data Voltage corresponding to the image data DR, DG, and DB. The decreasing amount of the pulse width of the data Voltage will compensate the decreasing amount of luminance according to the total light emitting time. As a result, the image data compensator 560 controls the entire luminance of the display unit 100 to be constant. Thus, image Sticking may be prevented By way of summation and review, according to embodiments described above, the display device may be capable of preventing image sticking due to luminance dete rioration without employing an additional photosensor Exemplary embodiments have been disclosed herein, and although specific terms are employed, they are used and are to be interpreted in a generic and descriptive sense only and not for purpose of limitation. Accordingly, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that various changes in form and details may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention as set forth in the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A display device comprising: a display unit including a plurality of pixels connected to a plurality of scan lines and a plurality of data lines, the plurality of pixels emitting light according to corre sponding image data; a dummy pixel connected to a dummy Scan line and a dummy data line, the dummy pixel including a first organic light emitting element and each pixel including a second organic light emitting element; and a compensation image data generator configured to: calculate a compensation amount according to an accumu lation light emitting time of the first organic light emit ting element; detect the compensation amount corresponding to each accumulation light emitting time of the plurality of sec ond organic light emitting elements using a decreasing amount of luminance corresponding to a resistance of the first organic light emitting element according to an accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element of the dummy pixel; and compensate the corresponding image data according to the detected compensation amount. 2. The display device as claimed in claim 1, wherein: the compensation image data generator configured to sense resistance of the first organic light emitting element according to a sensing Voltage generated to both termi nals of the first organic light emitting element when a predetermined current flows in the first organic light emitting element.
9 3. The display device as claimed in claim 2, wherein the compensation image data generator includes: a memory storing the decreasing amount of luminance of the first organic light emitting element corresponding to the sensing Voltage; a timer measuring the accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; a data sum unit accumulating and Summing the image data respectively corresponding to the plurality of pixels per each pixel; a compensation amount calculator calculating the compen sation amount of the corresponding image data accord ing to the accumulation light emitting time by using the resistance of the first organic light emitting element and the accumulation light emitting time; and an image data compensator sensing each accumulation light emitting time of the plurality of second organic light emitting elements and modulating the correspond ing image data into the compensation amount corre sponding to the accumulation light emitting time. 4. The display device as claimed in claim 3, wherein the compensation amount calculator detects the decreasing amount of luminance corresponding to the sensing Voltage and calculates the increasing amount of the accumulation light emitting time corresponding to the detected decreasing amount of luminance as the compensation amount. 5. The display device as claimed in claim 3, further com prising: a lookup table storing the compensation amount time cal culated from the compensation amount calculator according to the accumulation light emitting time. 6. The display device as claimed in claim 3, wherein: the image data compensator modulates the corresponding image data for the predetermined compensation unit time. 7. The display device as claimed in claim 1, wherein: the dummy pixel receives a dummy data Voltage corre sponding to a full white grayscale through the dummy data line. 8. A method for driving a display device including a dummy pixel including a first organic light emitting element and a plurality of pixels respectively including a second organic light emitting element, the method comprising: calculating a compensation amount according to an accu mulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element by using a decreasing amount of lumi nance corresponding to resistance of the first organic light emitting element according to the accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; determining a compensation amount corresponding to the accumulation light emitting time of each second organic light emitting element; and compensating the image data respectively corresponding to the plurality of pixels according to the calculated compensation amount. 9. The method as claimed in claim 8, wherein calculating the compensation amount includes: detecting the sensing Voltage between both terminals of the first organic light emitting element when a predeter mined current flows to the first organic light emitting element; measuring the accumulation light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element; and calculating the increasing amount of the light emitting time of the first organic light emitting element corresponding to the decreasing amount of the luminance by using the decreasing amount of luminance of the first organic light emitting element corresponding to the sensing Voltage. 10. The method as claimed in claim 8, wherein: compensating the image data is executed every predeter mined compensation unit time. 11. The method as claimed in claim 8, further comprising: applying a dummy data Voltage corresponding to a full white grayscale to the dummy pixel. c c c c c
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
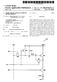 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. KO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008
 US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013
 USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
United States Patent 19 11) 4,450,560 Conner
 United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1
 USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011
 US 2011 0193817A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0193817 A1 BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS Publication Classification
US 2011 0193817A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0193817 A1 BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,760,165 B2
 USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
-/9. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 POWER.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl O : --- I. all T
 (19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0057484A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0057484A1 Diefenbaugh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC IMAGE LUMINANCE (22) Filed: Sep.
US 2005.0057484A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0057484A1 Diefenbaugh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC IMAGE LUMINANCE (22) Filed: Sep.
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,501,230 B1
 USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0379551A1 Zhuang et al. US 20160379551A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) WEAR COMPENSATION FOR ADISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0379551A1 Zhuang et al. US 20160379551A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) WEAR COMPENSATION FOR ADISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080225.036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0225036A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Hong Sung
(19) United States US 20080225.036A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0225036A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Hong Sung
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu
 United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
