(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
|
|
|
- Chad Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
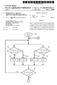
1 US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application Priority Data ADJUSTINGVIEWING ANGLE THEREOF May 25, 2009 (KR) May 25, 2009 (KR) (75) Inventors: Dong-Hyun IIM Gyeonggi-do May 25, 2009 (KR) (KR); Woo-Sik JUNG, Gyeonggi-do (KR); Dong-Hyun Publication Classification HAM, Gyeonggi-do (KR); (51) Int. Cl. Seong-Hwan KIM, Gyeonggi-do G09G 5/00 ( ) (KR) GO2B 27/28 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /204; 359/484 Correspondence Address: (57) ABSTRACT FSH & RICHARDSON P.C. P.O. BOX 1022 MINNEAPOLIS, MN (US) A display device for selectively adjusting a viewing angle thereof and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereofare provided. The display device comprises: a display unit dis playing an input image based on a determined viewing angle; (73) Assignee: LG Electronics Inc., Seoul (KR) and a controlling unit determining a viewing angle of the display unit according to a predetermined viewing condition and controlling to display the input image with the deter (21) Appl. No.: 12/758,052 mined viewing angle, wherein the viewing condition is one of a viewer position condition, an image type condition, and a (22) Filed: Apr. 12, 2010 viewer setting condition. O 130 POLARZNGELEMENT 2O DISPLAY ELEMENT 160 MENUSCREEN GENERATING UNIT 140 CONTROLLING UNT POSITON DETECNG UNIT 70 MEMORY UNIT
2 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure 1) O 30 POLARZING ELEMEN 2O DISPLAY ELEMENT 160 MENUSCREEN GENERATING UNIT 140 CONTROLLING UNT POSITON DETECTING UNIT 70 MEMORY UNIT OO Figure 2) FIRST POLARIZING ELEMENT SECONO POLARANG ELEMENT
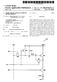
3 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 2 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure 3) 300 (Figure 4) 400
4 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 3 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure 5) 500 WEWING ANGLE SETTING X SET PREFERRED WEWING ANGLE. MOVIE: INTERNET ; TEXT : 2O/2O (Figure 6) 600 WENING ANGE SETING : SET WEWING ANGLE APPED TO TYPE OF INPUT IMAGE.. INPUT IMAGE TYPE: PICTURE(STILL IMAGE,.jpg) VIEWING ANGLE : 60/60 CONFERM
5 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 4 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure WEWING ANGLE SETTING : SET PREFERRED WEWING ANGLE 710 N.. LEFT VIEWING ANGLE : N. RIGHT VIEWING ANGLE : 90" (Figure 8) 800 WEWING ANGLE SETTING : SET REGON FOR WEWING ANGLE BLOCKING. RIGHT CONFIRM CANCEL
6 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 5 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure 9) S900 START CAPTURE IMAGE ABOUT PERPHERAL REGION OF DISPLAY SCREEN CONFIRM USER POSITON S9 O S93O CONFIRM S920 Playo NO S960 USERS YES CONFIRM OUTERMOST INFORMATION ABOUT POSITIONS OF PLURALITY OF USERS SET WEWING ANGLE OF DISPLAY UNIT USNGWENG ANGLE CORRESPONDING TO USER POSETION SET LEFT AND RIGHT WEWENG ANGLES USING CONFIRMED OUTERMOST INFORMATION DSPLAY INPUT IMAGE WITH SET VENING ANGLE S940 S950 END
7 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 6 of 7 US 2010/ A1 Figure 10) NPUT IMAGE SIGNAL SOOO RECOGNIZE TYPE OF INPUTTED IMAGE SIGNAL S1 OO VIEWING ANGE NFORMATION CORRESPONDING TO RECOGNIZED TYPE EXIST? S1020 NO SiO30 DISPLAY MENUSCREEN FOR SETTING YES WENGANGECORRESPONDING TO S1060 FXTRACT WIEWING ANGLE INFORMATION CORRESPONDING TO YPE OF INPUT IMAGE SIGNAL SiO40 ADJUST VIEWING ANGLE CORRESPONDING TO TYPE OF INPUT MAGE SIGNAL TYPE OF INPUT IMAGE SIGNAL SET W WING ANGLE SiO70 DISPLAY INPUT IMAGE SGNAL WH ADJUSTED WENG ANGLE STORE AND APPLY SETWEWING ANGLE-S1080 END
8 Patent Application Publication Nov. 25, 2010 Sheet 7 of 7 US 2010/ A1 (Figure 11) S1 OO S1110 Si2O S1130 ADJUST VENING ANGLE OF DISPLAY UNIT ACCCRONG TO CETERMINED LEFT AND RIGHT WEWING ANGLES DISPLAY INPUT IMAGE WITH ADJUSTED WEWING ANGLE END
9 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, 2010 DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF ADJUSTINGVIEWING ANGLE THEREOF CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS The present application claims priority under 35 U.S.C. 119 and 35 U.S.C. 365 to Korean Patent Application Nos , and (filed on 25 May, 2009), which are hereby incorpo rated by reference in their entirety. BACKGROUND 0002 The present disclosure relates to a display device, and more particularly, to a display device for selectively adjusting a viewing angle thereof according to various view ing environments and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof A display device includes a monitor. The monitor may be used for a display terminal of a computer device and also used for a display device of an image device Such as a television and a video recorder and player A related art monitor typically includes a cathode ray tube (CRT) display device, but due to its bulky volume, high power consumption, and a heavyweight, a thin film type display device is increasingly used as the latest technology image display device A liquid crystal display (LCD) or a plasma display panel (PDP) is used for the thin film type display device In relation to basic principles of the above LCD, liquid crystal is disposed between two thin glass Substrates to which a transparent conductive layer is attached and an elec tric filed is applied to the transparent conductive layer through a matrix electrode. Then, the LCD uses a light scattering phenomenon in a liquid crystal layer according to a change of the electric field and displays images to a user by projecting a reflected light or a transmitted light on the liquid crystal layer In addition, a general display device cannot adjust an arbitrary viewing angle. Accordingly, according an angle that a viewer watches a display device, others may easily peep at Screen contents being displayed on the display device Moreover, since various personal multimedia ser vices are gradually more used through the latest satellite reception technology, a viewer should be aware of others during a personal multimedia service due to a wide viewing angle of a display device On the contrary, if a viewing angle of a display device is narrow, although many people want to use the same multimedia service through one display device, it is impos sible due to its narrow viewing angle Accordingly, required is a method of selectively adjusting a viewing angle of a display device according to viewing environments. SUMMARY 0011 Embodiments provide a display device for protect ing view's privacy by adjusting a viewing angle thereof according to various viewing environments and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof Embodiments also provide a display device capable of automatically adjusting a viewing angle thereof according to a viewer position and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof Embodiments also provide a display device capable of automatically adjusting a viewing angle thereof according to a type of contents that a viewer watches and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof Embodiments also provide a display device capable of separately adjusting a left viewing angle and a right view ing angle thereof and a method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof In one embodiment, a display device comprises: a display unit displaying an input image based on a determined viewing angle; and a controlling unit determining a viewing angle of the display unit according to a predetermined view ing condition and controlling to display the input image with the determined viewing angle, wherein the viewing condition is one of a viewer position condition, an image type condition, and a viewer setting condition In another embodiment, a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device, the method comprising: detecting a position of a viewer, determining a viewing angle of a display screen where an input image is displayed accord ing to the position of the detected viewer, and displaying the input image with the determined viewing angle In further another embodiment, a method of adjust ing a viewing angle of a display device, the method compris ing: inputting an image signal; determining a type of the inputted image signal; determining a viewing angle of a dis play Screen where the image signal is displayed, based on the type of the determined image signal; and displaying the input ted image signal based on the determined viewing angle In still further another embodiment, a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device, the method comprising: displaying a viewing angle setting screen; setting a viewing angle of an image displayed through a display screen in the displayed viewing angle setting screen; and displaying the image based on the set viewing angle The details of one or more embodiments are set forth in the accompanying drawings and the description below. Other features will be apparent from the description and drawings, and from the claims. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0020 FIG. 1 is a view illustrating a configuration of a display device according to an embodiment FIG. 2 is a detailed view of a polarizing element of FIG FIG. 3 is a view illustrating an outermost informa tion confirming method according to a first embodiment FIG. 4 is a view illustrating an outermost informa tion confirming method according to a second embodiment FIG. 5 is a view illustrating one example of a view ing angle setting screen according to an embodiment FIG. 6 is a view illustrating another example of a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment FIG. 7 is a view illustrating another example of a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment FIG. 8 is a view illustrating a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjust ing a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a first embodiment. (0029 FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a second embodiment.
10 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a third embodiment. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS 0031 Preferred embodiments will be described In embodiments, terms that will be used are cur rently extensive general terms in use, but may be arbitrarily selected terms in a specific case. In that case, their meanings are specifically described in the detailed description of the embodiments below. Thus, the embodiments should be understood with the meaning of the terms not the simple naming of the terms That is, during description below, a term include does not exclude components or operations different from listed components or operations FIG. 1 is a view illustrating a configuration of a display device according to an embodiment. 0035) Referring to FIG. 1, the display device 100 includes a display unit 110, a controlling unit 140, a position detecting unit 150, a menu screen generating unit 160, and a memory unit 170.The display unit 110 may Includes a display element 120 and a polarizing element The display unit 110 displays an image signal pro vided from an external according to a viewing angle deter mined by the controlling unit 140 that will be described later Here, the display unit 110 includes the display ele ment 120 where an actual image is displayed and the polar izing element 120 that is attached to one side of the display element 120 and performs a polarizing function optically according to an electric control signal provided from the controlling unit FIG. 2 is a detailed view of the polarizing element 120 of FIG Referring to FIG. 2, the polarizing element 120 includes a first polarizing element 132 and a second polariz ing element 134. Here, the first polarizing element 132 is attached to the left region and the second polarizing element 134 is attached to the right region, based on the middle of the display element In the embodiment, the polarizing element 132 includes two polarizing elements, but this is just one example. It is apparent that the number of polarizing elements 132 varies according to the segmented region of the display SCC The controlling unit 140 provides an electric control signal to the polarizing element 120 and adjusts a polarization degree based on a viewing angle determined by a predeter mined viewing condition Here, the controlling unit 140 predetermines a polarization degree (for example, a narrow viewing angle or a wide viewing angle), and then adjusts a polarization degree of the polarizing element 120 through a switching method for simply turning on/off an electric control signal. For example, when the controlling unit 140 turns on a Switch, a polarization degree of the polarizing element 120 may be adjusted to a wide viewing angle. On the contrary, when the controlling unit 140 turns off a switch, a polarization degree of the polar izing element 120 may be adjusted to a narrow viewing angle That is, if it is assumed that there is a mobile com munication terminal with a mounted display device of an adjustable viewing angle, when a viewer presses a predeter mined button to adjust a viewing angle, the controlling unit 140 provides an electric control signal corresponding to on Switching to the polarizing element 120 according to a des ignated algorithm. Then, the polarizing element 120 performs a polarizing function optically and transmits a light having directivity according to an electric control signal provided through the controlling unit Accordingly, a viewing angle of the display unit 110 becomes narrow and thereby, an image displayed through the display unit 110 is provided to only viewers who watch the display unit 110 in the front On the contrary, if an electric control signal corre sponding to off-switching is provided through the controlling unit 140, the polarizing element 120 does not perform a polarizing function and thereby, an image displayed through the display unit 110 is provided with a viewing angle degree set through a basic property of the display unit 110. Of course, it is apparent that the on/off function may be interchangeable. 0046) However, the controlling unit 140 is allowed to adjust a polarization degree of the polarizing element 120 by a predetermined angle, like adjusting the brightness of the display element 120, because an electric control signal applied to the polarizing element 120 may be minutely adjusted That is, in this embodiment, the controlling unit 140 provides the above-mentioned predetermined viewing angle (on Switching on, off switching) and also minutely adjusts an intensity of an electric control signal applied to the polarizing element 120, such that a viewing angle of the display unit 110 is adjusted within the maximum and minimum viewing angle range Here, the maximum and minimum viewing angle range is as follows The maximum viewing angle is determined by a basic property of the display element 120. That is, the maxi mum viewing angle is not a specific value that is identically applied to all display devices but is determined by a condition applied when the display element 120 is manufactured Additionally, the minimum viewing angle is 0 degree. That is, if the set viewing angle is 0 degree, the controlling unit 140 provides an electric control signal corre sponding to the set viewing angle to the polarizing element 120. Then, the polarizing element 120 blocks all lights based on the electric control signal of the controlling unit Here, as mentioned above, the polarizing element 120 includes the first polarizing element 132 for adjusting a viewing angle of the left screen and the second polarizing element 134 for adjusting a viewing angle of the right screen In addition, the polarizing element 120 may be sepa rately set on the top surface of the display element 120 or may be set being inserted and integrated into the inside of the display element 120. The configuration of the polarizing ele ment 120 may vary according to determination of display device manufacturers and may be controlled by an algorithm described below The controlling unit 140 determines a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a predetermined viewing condition, provides an electric control signal corresponding to the determined viewing angle to the polarizing element 120, and adjusts a viewing angle of an image being displayed through a display screen The viewing condition may include a viewer posi tion condition, an image type condition, and a viewer setting condition. The viewer position condition is for determining a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a position
11 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, 2010 of a viewer who watches the display unit 110. The image type condition is for determining a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a type of animage displayed through the display unit 110. The viewer setting condition is for deter mining a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a viewing angle set by a viewer through a viewing angle setting SCC Hereinafter, a view angle determining operation of the display unit 110 according to each viewing condition will be described in more detail The viewing condition of a first embodiment is a viewer position condition and the controlling unit 140 deter mines a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a position of a viewer who watches the display unit For this, the position detecting unit 150 is included in the display device 100 according to the first embodiment The position detecting unit 150 detects a position of a viewer to determine a viewing angle of the display unit 110. Here, the position detecting unit 150 may be realized with an infrared sensor and an image capturing unit. However, the position detecting unit 150 may include an image capturing unit for detecting a position of the viewer The position detecting unit 150 is disposed at one side of the display device 100 and captures an image about a front region of the display unit 110. Here, the position detect ing unit 150 is disposed at the middle of the display unit 110 and may capture a front image for detecting a position of the viewer. That is, the position detecting unit 150 is an image capturing device and may include a Web cam The position detecting unit 150 captures an image about a front region of the display unit 110 and analyzes the captured image to detect a position of the viewer in the image. Then, the position detecting unit 150 confirms viewer posi tion outermost information based on the detected viewer posi tion A method of confirming the outermost information of the position detecting unit 150 will be described in more detail FIG. 3 is a view illustrating an outermost informa tion confirming method according to a first embodiment. FIG. 4 is a view illustrating an outermost information confirming method according to a second embodiment Referring to FIG. 3, the position detecting unit 150 captures an image about a front region. Then, once the image is captured, the position detecting unit 150 divides the cap tured image 300. Here, a reference for dividing the captured image 300 is determined by a configuration of the polarizing element That is, the polarizing element 120 is set for each of the left region and the right region based on the middle of the display element 120, such that the captured image 300 is divided into a left image and a right image based on the middle. Here, the divided left image is used for determining a viewing angle of the first polarizing element 132 and the divided right image is used for determining a viewing angle of the second polarizing element If the captured image 300 is divided as above, the position detecting unit 150 analyzes each of the divided left and right images, so as to detect a position of a viewer. For example, if a viewer is included in the captured image, since a region where the viewer is captured has a specific brightness level, a position of the viewer in the captured image is detected by analyzing a brightness level of the captured image If the position of the viewer is detected, the position detecting unit 150 confirms outermost information for deter mining a viewing angle based on the position of the detected viewer. Here, the outermost information is divided into left outermost information about the left image and right outer most information about the right image That is, as shown in FIG. 3, if a position 310 of a viewer is detected in the captured image 300, the position detecting unit 150 confirms the outermost information 320 and X about the left image and outermost information 330 and y about the right image based on the position 310 of the detected viewer As mentioned above, the position detecting unit 150 provides the confirmed outermost information to the control ling unit 140 and the controlling unit 140 determines the viewing angle by using the provided outermost information. That is, the controlling unit 140 uses the outermost informa tion for the left image to determine a polarization degree of the first polarizing element 132 and uses the outermost infor mation about the right image to determine a polarization degree of the second polarizing element 134. Substantially, the X degree is a left viewing angle according to the polariza tion degree of the first polarizing element 132 and they degree is a right viewing angle according to a polarization degree of the second polarizing element Here, a viewer who watches the current display device 100 may be in plurality. (0070 That is, referring to FIG.4, if there are a first viewer 410, a second viewer 420, and a third viewer 430 in a captured image 400, the position detecting unit 150 detects a viewer position based on a viewer at the leftmost and a viewer at the rightmost among the first to third viewers 410 to 430. (0071. That is, since the viewer at the leftmost is the first viewer 410, the position detecting unit 150 confirms left outermost information 440 and X based on a position of the first viewer 410. That is, since the viewer at the rightmost is the third viewer 430, the position detecting unit 150 confirms right outermost information 450 and y based on a position of the third viewer 430. The controlling unit 140 uses the outer most information to adjust a polarization degree of the first and second polarizing elements 132 and In addition, if there is no viewer in the divided left or right image, an image may not be provided to the left or right of the display unit 110 by adjusting a polarization degree of the first polarizing element 132 or the second polarizing ele ment A viewing condition of the second embodiment is an image type condition and the controlling unit 140 deter mines a viewing angle of the display unit 110 according to a type of an image displayed through the display unit For this, the display device 100 includes the menu screen generating unit 160 and the memory unit 170 accord ing to the second embodiment The menu screen generating unit 160 generates a menu screen for setting a viewing angle according to each type of an input image signal. The generated menu screen is outputted through the display element 120. Then, a viewer sets a viewing angle corresponding to each type of an input image in the menu screen outputted through the display ele ment 120. At this point, when the menu screen is displayed, if a predetermined viewing angle is a narrow viewing angle, the viewing angle may be adjusted to a wide viewing angle while the menu screen is displayed.
12 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, FIG. 5 is a view illustrating one example of a view ing angle setting screen according to an embodiment Referring to FIG. 5, the viewing angle setting screen 500 includes a viewing angle setting region 510 for setting a viewing angle corresponding to each type of an input image. Then, a vieweruses the viewing angle setting region 510 to set a viewing angle corresponding to each input image. At this point, the viewing angle setting region 510 includes a left viewing angle setting region for setting a left viewing angle and a right viewing angle setting region for setting a right viewing angle according to types of an input image The memory unit 170 is a storage unit for storing various data and may be set with an Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) In addition, a driving program necessary for adjust ing a viewing angle of the display unit 110 and viewing angle information related to types of an input image set by a user are stored in the memory unit Here, the image may a broadcast program inputted through an antenna and a cable connector, an external device signal inputted through an external interface unit, or a per sonal computer (PC) signal inputted through a PC In addition, if a viewer does not set a viewing angle separately, a default value is applied to adjust a viewing angle That is, an image such as a movie or internet screen does not require special security generally, such that the view ing angle is set with the maximum viewing angle. However, an image Such as a secrete text screen requires security because personal word processing is in progress. Accord ingly, the image signal Such a movie or internet Screen allows viewers to watch the screen at the side and front by applying the maximum viewing angle, and the image such as a text screen allows only a specific viewer who performs personal word processing to watch the screen only at the front by applying the minimum viewing angle (not 0 degree) Once an image is inputted, the controlling unit 140 recognizes types of the inputted image and extracts viewing angle information corresponding to the recognized type from the memory unit 170. Then, the controlling unit 140 uses the extracted viewing angle information to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit In addition, if the viewing angle information corre sponding to a type of the inputted image is not stored in the memory unit 170, the controlling unit 140 controls to display a menu screen for setting a viewing angle corresponding to a type of the image FIG. 6 is a view illustrating another example of a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment. I0086 Referring to FIG. 6, the viewing angle setting screen 600 displays information corresponding to a type of the input image and includes a viewing angle setting region 610 for setting a viewing angle corresponding to a type of the input image Moreover, the controlling unit 140 stores the set image type information and viewing angle information in the memory unit 170 through the viewing angle setting screen 600 and applies the set viewing angle to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit Moreover, there may be a plurality of images dis played on the display element Accordingly, when a plurality of images are dis played on the display unit 110 (that is, a plurality of image signals are inputted from an external), the controlling unit 140 adjusts a viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using viewing angle information corresponding to a type of cur rently activated image Moreover, when a plurality of images are displayed in a picture out picture (POP) form through the display ele ment 120, the controlling unit 140 adjusts a left viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using viewing angle information corresponding to a type of an image displayed at the left region and adjusts a right viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using viewing angle information corresponding to a type of an image displayed at the right region That is, the controlling unit 140 extracts viewing angle information corresponding to a type of an image dis played at the left region, from the memory unit 170. Then, the controlling unit 140 uses the extracted viewing angle infor mation to adjust a polarization degree of the first polarizing element 132. In addition, the controlling unit 140 extracts viewing angle information corresponding to a type of an image displayed at the right region, from the memory unit 170.Then, the controlling unit 140 uses the extracted viewing angle information to adjust a polarization degree of the sec ond polarizing element In the display device according to the second embodiment, if important personal data or secrete items need to be displayed, a display screen image is outputted at a front angle Such that security about user information can be main tained and personal word processing can be effectively per formed. I0093. A viewing condition of a third embodiment is a viewer setting condition and the controlling unit 140 uses a viewing angle set by a viewer to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit For this, the menu screen generating unit 160 is included in the display device 100 according to the third embodiment. (0095. The controlling unit 140 of the third embodiment controls the menu screen generating unit 160 to generate a viewing angle setting screen and controls the display element 120 to display the generated viewing angle setting screen. At this point, the viewing angle setting screen may be displayed by a viewer command, or may be displayed only if specific conditions are satisfied. For example, the viewing angle set ting screen may be displayed when a power-on condition, an input mode Switching condition, of a channel Switching con dition occurs FIG. 7 is a view illustrating another example of a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment As shown in FIG.7, the viewing angle setting screen 700 includes a first viewing angle setting region 710 for setting a left viewing angle and a second viewing angle setting region 720 for setting a right viewing angle. In addition, viewing angle information, which is currently set within an adjustable range, is displayed in the first viewing angle setting region 710 and the second viewing angle setting region 720. Moreover, a viewer uses up and down direction keys to increase or decrease the displayed viewing angle information such that a viewing angle that the viewer himself or herself wants can be set That is, the displayed viewing angle setting screen 700 provides a menu screen through which a viewer can separately set the left viewing angle and the right viewing angle The controlling unit 140 uses a viewing angle set through the first viewing angle setting region 710 to adjust a
13 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, 2010 polarization degree of the first polarizing element 132. In addition, the controlling unit 140 uses a viewing angle set through the second viewing angle setting region 720 to adjust a polarization degree of the second polarizing element FIG. 8 is a view illustrating a viewing angle setting screen according to an embodiment As shown in FIG. 8, the viewing angle setting screen 800 includes an output blocking setting region 810 to set a region that a viewer wants to block an image output among the left and right regions. That is, once a display device is installed, when a first viewer is positioned at the left of the display device and a second viewer is positioned at the right of the display device, if the second viewer does not want to watch the display device anymore, the first viewer may set to block a viewing angle about the right region in the viewing angle setting screen The controlling unit 140 sets a viewing angle of the side (where the viewing angle blocking is set) with the mini mum viewing angle and a viewing angle of the other side with the maximum viewing angle. For example, if output blocking about the left region is set in the viewing angle setting screen 800, the controlling unit 140 sets the left viewing angle of the display unit 110 with the minimum viewing angle (for example, 0 degree) and sets the right viewing angle of the display unit 110 with the maximum viewing angle FIG.9 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjust ing a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a first embodiment Referring to FIG. 9, an image about a peripheral region of a display screen is captured first in operation S900. That is, the position detecting unit 150 is a webcam equipped in a display device. The webcam captures a peripheral image of an installation region to detect a viewer position and deliv ers the detected viewer position to the controlling unit That is, the position detecting unit 150 captures a viewer to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit 110. Accordingly, an image inputted from a microlens mounted on the position detecting unit 150 is converted into optical signal and an image signal sequentially to generate image data using the captured image Then, the position detecting unit 150 confirms a viewer position by using the captured image in operation S910. Here, the user position recognizing method analyzes a brightness level of the captured image by each pixel and recognizes a user capturing position from the captured image based on the analyzed brightness level. Additionally, a user face image is captured and stored in advance and the stored user face image is compared to the captured image to recog nize a position where an actual user face is captured. The above method of recognizing a user position by using the captured image is apparent to those skilled in the art and thus its detailed description will be omitted In addition, during the recognizing of the user posi tion, an entire body of a user is not recognized but a specific face portion of the user may be recognized. That is, in general, a viewing angle of the display unit 110 should be determined by a position of an eye of a user not by a position of a user. That is, even ifa user stays at the same position, there may be a difference in an image provided to the user based on where an eye of a user is positioned, and accordingly, an eye position may be recognized as a user position in the captured image. In addition, besides the user face, various other portions such as an eyebrow, a nose, a mouth, and an ear may be used to recognize a user position The controlling unit 140 determines whether a plu rality of users are recognized or not in the captured image in operation S920. That is, it is determined that the number of viewers who watch a current display screen is one or more than two. This is confirmed through user position information obtained by analyzing the captured image If a plurality of users are recognized in the captured image, the controlling unit 140 confirms outermost informa tion about positions of the plurality of users in operation S930. That is, as shown in FIG. 4, if the plurality of users currently watch the same display screen, it is impossible to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit 110 based on one user. Accordingly, the controlling unit 140 confirms outer most information according to a user position in the captured image and adjusts a viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using the confirmed outermost information Here, the outermost information includes left outer most information and right outermost information. That is, the outermost information means position information of a user positioned at the rightmost and position information of a user positioned at the leftmost. That is, as shown in FIG. 4, based on the front region, the X degree about a user positioned at the leftmost is the outermost information about the left region and they degree about a user positioned at the right most is the outermost information about the right region The controlling unit 140 uses the outermost infor mation to set each of the left viewing angle and the right viewing angle of the display unit 110 in operation S940. That is, the controlling unit 140 uses the X degree to set the left viewing angle of the display unit 110 and uses they degree to set the right viewing angle of the display unit Next, the display element 120 displays an input image with a viewing angle determined by the controlling unit 140 in operation S950. That is, the controlling unit 140 outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the deter mined left viewing angle to the first polarizing element 132 and outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the determined right viewing angle to the second polarizing ele ment 134. Accordingly, the polarizing element 120 equipped in the display element 120 adjusts a polarization degree by an electric control signal outputted from the controlling unit 140 Such that a viewing angle about a screen displayed through the display element 120 can be adjusted In addition, if one user is recognized in the captured image, the controlling unit 140 sets a viewing angle of the display element 120 corresponding to a position of the rec ognized user in operation S FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a second embodiment As shown in FIG. 10, the viewing angle adjusting method of the display device according to the second embodi ment receives an image signal inputted from an external first in operation S1000. Here, the image signal may a broadcast program inputted through an antenna and a cable connector, an external device signal inputted through an external inter face unit, or a personal computer (PC) signal inputted through a PC The controlling unit 140 determines which type an image signal is inputted operation S1010. Here, if the input tedimage signal is a signal inputted from a PC, the controlling unit 140 receives information about the image signal inputted from the PC and recognizes a type of the inputted image
14 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, 2010 signal by using the received information. Here, the type of the image signal may be classified by a user or may be classified by a default condition That is, as shown in FIG. 5, the viewing angle setting screen 500 includes a viewing angle setting region 510 for setting a viewing angle corresponding to each type of the input image signal, and a user may set a viewing angle cor responding to each type of the image signal by using the viewing angle setting region 510. In addition, a viewing angle corresponding to each type of an image signal may be set by a default value That is, an image signal Such as a movie or internet screen does not require special security generally, Such that the viewing angle is set with the maximum viewing angle. However, an image signal Such as a text requires security because personal word processing is in process. Accordingly, the image signal Such as a movie or internet Screen allows users to watch the display at the side and front by applying the maximum viewing angle, and the image signal Such as a text allows only a specific user who performs a word processing to watch the display only at the front by applying the minimum viewing angle (not 0 degree) Once a type of the inputted image signal is recog nized, the controlling unit 140 recognizes whether viewing angle information corresponding to the recognized type is already stored in the memory unit 170 in operation S1020. That is, the controlling unit 140 determines whether the view ing angle information corresponding to the type of the recog nized image signal is set by a user or a default value in advance In addition, if the viewing angle information corre sponding to the type of the inputted image signal is stored in the memory unit 170 in advance, the pre-stored viewing angle information is extracted in operation S Then, the controlling unit 140 uses the extracted viewing angle information to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit 110 in operation S1040. That is, the controlling unit 140 outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the determined left viewing angle to the first polarizing ele ment 132 and outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the determined right viewing angle to the second polarizing element ) The display unit 110 displays an input image with a viewing angle adjusted by the controlling unit 140 in opera tion That is, the polarizing element 120 equipped in the display unit 110 adjusts apolarization degree using an electric control signal outputted from the controlling unit 140 Such that a viewing angle about a screen displayed through the display element 120 can be adjusted In addition, if the viewing angle information corre sponding to the type of the inputted image signal is not stored in the memory unit 170, the controlling unit 140 controls to display a menu screen for setting a viewing angle for the type of the image signal in operation S That is, as shown in FIG. 6, displayed is the viewing angle setting screen 600 for displaying information about a type of the inputted image and including a viewing angle setting region 610 for setting a viewing angle corresponding to a type of the inputted image The controlling unit 140 sets a viewing angle corre sponding to the type of the inputted image signal according to a command inputted from a user in operation S Then, the controlling unit 140 stores the type infor mation of the inputted image signal and the set viewing angle information in the memory unit 170 and applies the set view ing angle to adjust a viewing angle of the display unit 110. I0127. Moreover, there may be a plurality of image signals displayed on the display element Accordingly, when a plurality of image signals are displayed on the display element 120 (that is, a plurality of image signals are inputted from an external), the controlling unit 140 adjusts a viewing angle of the display unit 110 by applying a viewing angle corresponding to a type of currently activated image signal. I0129. Moreover, when a plurality of images are displayed in a picture out picture (POP) form through the display ele ment 120, the controlling unit 140 adjusts a left viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using viewing angle information corresponding to an image signal displayed at the left region and adjusts a right viewing angle of the display unit 110 by using viewing angle information corresponding to an image signal displayed at the right region Moreover, if the inputted image signal is in plurality, the controlling unit 140 devices divides the display element 120 based on a display region of the image signal and deter mines each viewing angle that will be applied to the divided region. I0131 Likewise, in relation to the display device according to the second embodiment, a viewing angle of a display device is arbitrarily adjusted depending on user needs Such that user convenience can be improved and also a personal display screen can be protected from others. In addition, when personally important data or items that require security need to be displayed, a display Screen image is outputted at a front angle Such that privacy information can be maintained and word processing can be effectively performed. I0132 FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating a method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device step by step according to a third embodiment As shown in FIG. 11, a viewing angle setting screen is displayed first in operation S1100. At this point, the view ing angle setting screen may be displayed by a user instruc tion, or may be displayed only if specific conditions are satisfied. Here, the specific condition may include a power-on condition, an input mode Switching condition, and a channel Switching condition At this point, the displayed viewing angle setting screen may be displayed according to two embodiments. I0135. As shown in FIG.7, the viewing angle setting screen including a first viewing angle setting region 710 for setting a left viewing angle and a second viewing angle setting region 720 for setting a right viewing angle may be displayed. View ing angle information, which is currently set within an adjust able range, is displayed in the first viewing angle setting region 710 and the second viewing angle setting region 720. Or, a user uses up and down direction keys to increase or decrease the displayed viewing angle As shown in FIG. 8, the viewing angle setting screen 800 including the output blocking setting region 810 to set a region that a user wants to block among the left and right regions may be displayed. That is, once a display device is installed, when a first user is positioned at the left of the display device and a second user is positioned at the right of the display device, if the second user does not want to watch the display device, the first user can set to block a viewing angle about the right region in the viewing angle setting Screen 800.
15 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, The controlling unit 140 determines the left viewing angle and the right viewing angle that will be applied to the display unit 110 according to a user instruction on the menu screen in operation S That is, the controlling unit 140 determines viewing angles set by the first viewing angle setting region 710 and the second viewing angle setting region 720 as the left viewing angle and the right viewing angle, respectively In addition, the controlling unit 140 sets a viewing angle of the side (where the viewing angle blocking is set) with the minimum viewing angle and sets a viewing angle of the other side with the maximum viewing angle. For example, if blocking about the left viewing angle is set in the viewing angle setting screen 800, the controlling unit 140 sets the left viewing angle of the display unit 110 with the minimum viewing angle (for example, 0 degree) and sets the right viewing angle with the maximum viewing angle The controlling unit 140 adjusts a viewing angle of the display unit 110 based on the determined left and right viewing angles in operation S1120. That is, the controlling unit 140 outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the determined left viewing angle to the first polarizing ele ment 132 and outputs an electric control signal corresponding to the determined right viewing angle to the second polarizing element The display unit 110 displays an input image with a viewing angle adjusted by the controlling unit 140 in opera tion That is, the polarizing element 120 equipped in the display unit 110 adjusts a polarization degree by using an electric control signal outputted from the controlling unit 140 Such that a viewing angle about a screen displayed through the display element 120 can be adjusted As mentioned above, in relation to the display device of the third embodiment, a viewing angle of the dis play device is arbitrarily depending on user needs such the user convenience can be improved and personal display screen can be protected from others. In addition, for other people who do not want to watch a screen, a viewing angle for a specific direction is completely blocked such that a viewer can watch the screen without interference to others According to the display device and the method of adjusting a viewing angle thereof, a viewing angle of the display device is adjusted based on viewing environments, Such that viewer convenience can be improved and personal display Screen can be protected from others In addition, a viewing angle of a display device is automatically adjusted according to a position of a viewer, Such that eye fatigue of a viewer can be alleviated and an optimized quality image can be provided to a viewer Moreover, if important personal data or secrete items need to be displayed, a display Screen image is output ted at a front angle Such that security about user information can be maintained and personal word processing can be effec tively performed Although embodiments have been described with reference to a number of illustrative embodiments thereof, it should be understood that numerous other modifications and embodiments can be devised by those skilled in the art that will fall within the spirit and scope of the principles of this disclosure. More particularly, various variations and modifi cations are possible in the component parts and/or arrange ments of the Subject combination arrangement within the Scope of the disclosure, the drawings and the appended claims. In addition to variations and modifications in the component parts and/or arrangements, alternative uses will also be apparent to those skilled in the art. What is claimed is: 1. A display device comprising: a display unit displaying an input image based on a deter mined viewing angle; and a controlling unit determining a viewing angle of the dis play unit according to a predetermined viewing condi tion and controlling to display the input image with the determined viewing angle, wherein the viewing condition is one of a viewer position condition, an image type condition, and a viewer setting condition. 2. The display device according to claim 1, wherein the display unit comprises: a display element displaying the input image; and a polarizing element attached to one side of the display unit and receiving an electric control signal inputted through the controlling unit to perform a polarizing function optically, wherein the controlling unit applies an electric control signal corresponding to the determined viewing angle to the polarizing element. 3. The display device according to claim 2, wherein the polarizing element comprises: a first polarizing element attached to the left based on the middle of the display element; and a second polarizing element attached to the right based on the middle point of the display element. 4. The display device according to claim 1, comprising a position detecting unit detecting a position of a viewer posi tioned around the display unit. 5. The display device according to claim 4, wherein the controlling unit confirms outermost position information of a viewer based on the detected viewer position and determines a viewing angle of the display unit based on the confirmed outermost position information. 6. The display device according to claim 1, comprising a memory unit that stores viewing angle information corre sponding to a type of an input image, wherein the controlling unit extracts viewing angle information corresponding to the type of the input image from the memory unit to determine a viewing angle of the display unit. 7. The display device according to claim 6, wherein the viewing angle information stored in the memory unit is set by a viewer. 8. The display device according to claim 6, wherein, if the input image is in plurality, the controlling unit determines a viewing angle of the display unit by using viewing angle information corresponding to a type of a currently activated image. 9. The display device according to claim 1, comprising a menu screen generating unit generating a viewing angle set ting screen for setting a viewing angle, wherein the control ling unit determines a viewing angle of the display device based on a viewer setting condition set through the viewing angle setting screen. 10. The display device according to claim 9, wherein the viewing angle setting screen comprises a first setting region for setting a left viewing angle of the display unit and a second setting region for setting a right viewing angle of the display unit.
16 US 2010/ A1 Nov. 25, The display device according to claim 3, wherein: the determined viewing angle is at least one of a left view ing angle and a right viewing angle; and the controlling unit outputs respectively different electric control signals to the first polarizing element and the second polarizing element based on the determined left and right viewing angles. 12. A method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device, the method comprising: detecting a position of a viewer, determining a viewing angle of a display screen where an input image is displayed according to the position of the detected viewer; and displaying the input image with the determined viewing angle. 13. The method according to claim 12, the detecting of the position of the viewer comprises obtaining outermost posi tion information corresponding to a viewer position by cap turing a peripheral image of the display Screen. 14. The method according to claim 13, wherein the deter mining of the viewing angle comprises determining at least one of a left viewing angle and a right viewing angle of the display screen based on the obtained outermost position information. 15. A method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device, the method comprising: inputting an image signal; determining a type of the inputted image signal; determining a viewing angle of a display screen where the image signal is displayed, based on the type of the deter mined image signal; and displaying the inputted image signal based on the deter mined viewing angle. 16. The method according to claim 15, comprising storing viewing angle information for each type of an image signal set through a viewing angle setting screen. 17. The method according to claim 16, if a viewing angle corresponding to the type of the determined image signal is not set, comprising displaying a viewing angle setting screen for setting a viewing angle corresponding to a type of the image signal. 18. The method according to claim 15, wherein, if the inputted image signal is in plurality, the viewing angle is determined a type of a currently activated image signal. 19. The method according to claim 15, wherein the deter mining of the viewing angle comprises: if the inputted image signal is in plurality, dividing the display screen based on a display region of the image signal; and determining viewing angles applied to the divided display regions, respectively. 20. The method according to claim 19, wherein: the display Screen is divided into a left region and a right region based on the middle of the display Screen; and the determined viewing angles are a left viewing angle corresponding to the left region and a right viewing angle corresponding to the right region. 21. A method of adjusting a viewing angle of a display device, the method comprising: displaying a viewing angle setting screen; setting a viewing angle of an image displayed through a display screen in the displayed viewing angle setting Screen; and displaying the image based on the set viewing angle. 22. The method according to claim 21, wherein the viewing angle setting screen comprises a first viewing angle setting region for setting a left viewing angle and a second viewing angle setting region for setting a right viewing angle. 23. The method according to claim 21, wherein the viewing angle setting screen comprises a first viewing angle blocking region for blocking an output of a left display region and a second viewing angle blocking region for blocking an output of a right display region. c c c c c
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
Assistant Examiner Kari M. Horney 75 Inventor: Brian P. Dehmlow, Cedar Rapids, Iowa Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Kyle Eppele; James P.
 USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
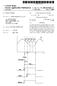 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl O : --- I. all T
 (19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014
 (19) United States US 2014O108943A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0108943 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR BROWSING INTERNET OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O108943A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0108943 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR BROWSING INTERNET OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O155728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0155728A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) CONTROL APPARATUS OPERATIVELY (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O155728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0155728A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) CONTROL APPARATUS OPERATIVELY (30) Foreign Application
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0027408 A1 Liu et al. US 20160027408A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0027408 A1 Liu et al. US 20160027408A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl. M M 110 / <E
 (19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
File Edit View Layout Arrange Effects Bitmaps Text Tools Window Help
 USOO6825859B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,825,859 B1 Severenuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2004 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROCESSING 5,564,004 A 10/1996 Grossman et al. CONTENT
USOO6825859B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,825,859 B1 Severenuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2004 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROCESSING 5,564,004 A 10/1996 Grossman et al. CONTENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2
 USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2
 US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2
 US007620287B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2 Appenzeller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 17, 2009 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS HOUSING WITH 5,167,001. A 1 1/1992 Debortoli et al....
US007620287B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2 Appenzeller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 17, 2009 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS HOUSING WITH 5,167,001. A 1 1/1992 Debortoli et al....
CAUTION: RoAD. work 7 MILEs. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0303458 A1 Schuler, JR. US 20120303458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) GPS CONTROLLED ADVERTISING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0303458 A1 Schuler, JR. US 20120303458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) GPS CONTROLLED ADVERTISING
