(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2
|
|
|
- Quentin Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2 Miyamoto (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS (56) References Cited AND LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS CONTROL METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,825,201 A * 4, 1989 Watanabe et al (75) Inventor: Tsuneo Miyamoto, Tokyo (JP) 5,359,345 A* 10/1994 Hunter ,102 6,188,380 B1 2/2001 Kawashima et al. ck (73) Assignee: NEC Display Solutions, Ltd., Tokyo 7%. 338 R.A.O.S: (JP) 7,777,945 B2* 8/2010 Whitehead et al /443 (Continued) FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 732 days. EP A2 6/2006 JP , 1988 (21) Appl. No.: 12/312,187 (Continued) (86). PCT No.: PCT/UP2007/ Notice of Reasons for Rejection dated Sep. 7, 2010, with English translation. S371 (c)(1), (2), (4) Date: Sep. 14, 2009 (Continued) (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2O08/ Primary Examiner William Boddie Assistant Examiner Mansour M Said PCT Pub. Date: May 15, 2008 (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm McGinn IP Law Group, PLLC (65) Prior Publication Data US 2010/ A1 Mar. 4, 2010 (57) ABSTRACT A liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present (30) Foreign Application Priority Data invention includes: a liquid crystal panel; a backlight pro vided on a rear face of the liquid crystal panel; a detector Nov. 7, 2006 (JP) which detects RGB output light levels of the backlight; a first controller which controls backlight current for driving the (51) Int. Cl. backlight so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on G09G 5/00 ( ) the RGB output light levels detected by the detector; and a (52) U.S. Cl. second controller which controls display signals Supplied to USPC /207:345/87; 34.5/102 the liquid crystal panel so that a prescribed chromaticity is (58) Field of Classification Search /22, attained based on the RGB output light levels detected by the 345/39, 48, 50, 82-84, 87 88, 204, , detector. 34.5/214, 699 See application file for complete search history. 3 Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets 8 A/D CONVERTER CURRENT-VOLTAGE CONVERTER NVERTER CIRCUI DISPLAY SIGNALS SIGNAL PROCESSOR 11
2 US 8, B2 Page 2 U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS JP , ,800,822 B2 * 9/2010 Whitehead et al / /2006 7,830,358 B2 * 1 1/2010 Seetzen /102 JP , ,872,659 B2* 1/2011 Seetzen ,690 WO WO 2005/ A1 6, / A1* 6/2002 Bruning et al , , A1* 7, 2005 Whitehead et al / A1 8/2005 Konno et al. OTHER PUBLICATIONS 2006/ A1 5/2006 Ng et al. European Search Report dated Nov. 18, / A1 4/2007 Sakuda , O A1* 7, 2008 Whitehead et al. 345,694 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS JP , 1998 * cited by examiner
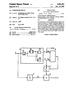
3 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 1 of 6 US B2 FIG. 1 8 A/D CONVERTER CURRENT-VOLTAGE CONVERTER NVERTER CIRCUIT DISPLAY SIGNALS SIGNAL PROCESSOR 11
4 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 2 of 6 US B2 FIG. 2A 3OO 4OO 5OO 6OO 7OO 8OO WAVELENGTH (nm) SPECTRUM OF SENSORS FIG. 2B O.O 7 OO6 O.O2 - X A a o --- J/XA i.n. 35O 350 Zoo 450 5OO so 6OO so 7OO 75O 8OO WAVELENGTH (nm) TRIST MULUS VALUES
5 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 3 of 6 US B2 FIG. 3 O 1 OO 200 3OO 4OO 5OO 6OO LUMINANCE OF FRONTAL SURFACE (cd/m2) FIG. 4 -ae's OF SENSOR VALUE LV-Y AND EXPECTED WALUE LW-) BACKLIGHT or.
6 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 4 of 6 US B2 FIG. 5 CHROMATICITY AT TIME OF SHIPMENT OCURRENT CHROMATICITY (xcyc) FIG. 6 CHROMATICITY AT TIME OF SHIPMENT OCURRENT CHROMATICTY (XCyc)
7 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 5 of 6 US B2 FIG. 7 y CURRENT CHROMATICITY O (xcyc) CHROMATICITY AT TIME OF SHIPMENT - FIG. 8 y CURRENT CHROMATICTY O. (XCyC) - CHROMATICITY -A AT TIME OF SHIPMENT
8 U.S. Patent Apr. 23, 2013 Sheet 6 of 6 US B2 FIG 9A -25O -24O 2OO-21 O BEFORE LUMINANCE UNIFORMITY CORRECTION FIG. 9B N 24O -25O x21o-22o AFTER LUMINANCE UNIFORMITY CORRECTION
9 1. LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS AND LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS CONTROL METHOD TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention pertains to a liquid crystal display apparatus having a backlight, and relates to a liquid crystal display device with controllable luminance and color, and a control method for a liquid crystal display apparatus. Priority is claimed on Japanese Patent Application No filed Nov. 7, 2006, the content of which is incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND ART Conventionally, for purposes of controlling the backlight of a liquid crystal display apparatus, there is a technology of controlling the lamp current of the backlight according to output information of luminance sensors pertaining to light leaked from a reflecting plate of the backlight (see, e.g., Patent document 1). In the conventional art, light leaked from the reflecting plate of a liquid crystal module is detected by sensors, and luminance control signals are outputted while monitoring this detected output so that the luminance set by the user is attained, thereby enabling maintenance of optimal display conditions. In addition, there is a technology in which a liquid crystal panel is controlled using a look-up table in accordance with output information of color sensors pertaining to the chroma ticity of the backlight, so that AEab* is minimized (see, e.g., Patent document 2). In the conventional technology, the chro maticity of the illuminating light of the liquid crystal module is detected by sensors, and display signals of the liquid crystal panel are controlled so that color differences relative to preset chromaticity information are minimized. Patent document 1 Japanese Patent Publication No (Page 3, FIG. 1) Patent document 2 Japanese Unexamined Patent Applica tion, First Publication No (Page 14, FIG. 4) DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION Problem to be Solved by the Invention Incidentally, with respect to a liquid crystal display appa ratus using a CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) in the backlight, it is known that deterioration in the luminous effi ciency of blue fluorescent material over time is quicker than that of red and green fluorescent material. That is, the white points of the liquid crystal display apparatus assume a yel lowish tint as time passes. In terms of fields of application of liquid crystal display apparatuses, temporal variation in color is particularly problematic in the medical field which com pares past diagnostic images and current diagnostic photo graphs, and in the graphics design field which requires con cordance of actual colors and display colors. In the above-described prior art (Patent document 1), the brightness of the backlight is fixed by detecting the intensity of the light of the backlight with luminance sensors, and controlling the current of the backlight. There is the problem that this is for control of luminance alone, and does not further enable adjustment of chromaticity. Moreover, in the above-described prior art (Patent docu ment 2), variable display signals are Supplied to the liquid crystal panel based on chromaticity information outputted from color sensors that measure the chromaticity of illumi US 8,427,462 B nating light Supplied from the backlight. However, the prior technology uses a method that obtains color differences AEab*, and conducts control according to a look-up table, and there is the problem that it is not possible to simulta neously control chromaticity and luminance without impair ing the gradation properties of the signals. The present invention has conceived in light of these cir cumstances, and its object is to offer a liquid crystal display apparatus and a control method for a liquid crystal display apparatus which enable achievement of constant and stable luminance and chromaticity. Means for Solving the Problem In order to solve the above-described problems, a liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention includes: a liquid crystal panel; a backlight provided on a rear face of the liquid crystal panel; a detector which detects RGB output light levels of the backlight; a first controller which controls backlight current for driving the backlight so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on the RGB output light levels detected by the detector; and a second controller which controls display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that a prescribed chromaticity is attained based on the RGB output light levels detected by the detector. The liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention may include: a first converter which con verts the RGB output light levels detected by the detector into tristimulus values; and a second converter which converts the tristimulus values into a luminance value and chromaticity values, the first controller may control the backlight current for driving the backlight based on the luminance value con verted by the second converter, and the second controller may control the display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel based on the chromaticity values converted by the second converter. In the liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention, the first controller may control the back light current so that the luminance value converted by the second converter matches a prescribed expected value. In the liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention, the second controller may control the dis play signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that the chromaticity values converted by the second converter match prescribed expected values or initial values. The liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention may include a corrector which corrects the prescribed expected value when the first controller controls the backlight current for driving the backlight, in order to prevent luminance variation in the liquid crystal panel pro duced when the second controller controls the display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel. In order to solve the above-described problems, a liquid crystal display control method according to the present inven tion is for a liquid crystal display apparatus including a liquid crystal panel and a backlight provided on a rear face of the liquid crystal panel, and includes the steps of detecting a RGB output light levels of the backlight; controlling back light current for driving the backlight so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on the detected RGB output light levels; and controlling display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that a prescribed chromaticity is attained based on the detected RGB output light levels. Effects of the Invention According to the present invention, RGB output light lev els of the backlight are detected by a detector, backlight
10 3 current for driving the backlight is controlled by a first con troller so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on the RGB output light levels, and display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel are controlled by a second controller so that a prescribed chromaticity is attained based on the RGB output light levels. Consequently, it is possible to achieve constant and stable luminance and chromaticity. With respect to the place of measurement, light that leaks from a reflecting plate on the backface may be measured, or light that is guided by an optical guide plate may be measured. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the detected RGB output light levels are converted into tristimu lus values by a first converter, the tristimulus values are con Verted into a luminance value and chromaticity values by a second converter, the backlight current for driving the back light is controlled based on the luminance values, and display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel are controlled based on the chromaticity values. Consequently, it is possible to obtain accurate tristimulus values from the RGB output light levels of the backlight, and achieve a more constant and stable luminance and chromaticity. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the backlight current is controlled by a first controller so that the luminance value converted by the second converter match a prescribed expected value. Consequently, it is possible to obtain a desired luminance that is preset at a stage prior to factory shipment. According to an embodiment of the present invention, display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel are con trolled by a second controller so that chromaticity values converted by the second converter match prescribed expected values or initial values. Consequently, it is possible to obtain a desired chromaticity that is preset at the stage prior to factory shipment. According to an embodiment of the present invention, in order to prevent luminance variation in the liquid crystal panel produced when the second controller controls display signals that are Supplied to the liquid crystal panel, a pre scribed expected value is corrected by a corrector when the first controller controls backlight current for driving the back light. Consequently, it is possible to prevent luminance varia tion in the liquid crystal panel arising due to chromaticity control. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a block diagram which shows the configuration of a liquid crystal display apparatus according to an embodi ment of the present invention. FIG. 2A is a schematic view which shows the chromaticity spectral properties of sensors 5, 6, and 7, and the spectral properties of tristimulus values XYZ in the present embodi ment. FIG. 2B is a schematic view which shows the chromaticity spectral properties of the sensors 5, 6, and 7, and the spectral properties of tristimulus values XYZ in the present embodi ment. FIG. 3 is a schematic view which shows irregularity in the sensitivities of the sensors 5, 6, and 7. FIG. 4 is a schematic view which serves to describe a control method according to the present embodiment. FIG. 5 is a schematic view for the case whereyc andyfare matched by reducing Bp, whenyc is less than yf. FIG. 6 is a schematic view for the case whereyc andyfare matched by reducing Bp, whenyc is less than yf. FIG. 7 is a schematic view for the case whereyc andyfare matched by reducing Gp, whenyc is greater than yf. US 8,427,462 B FIG. 8 is a schematic view for the case where ye and yfare matched by reducing Gp, whenyc is greater than yf. FIG.9A is a schematic view which shows luminance prop erties before luminance uniformity correction. FIG.9B is a schematic view which shows luminance prop erties after luminance uniformity correction. REFERENCE SYMBOLS 1 liquid crystal panel 2 backlight 3 cold cathode fluorescent lamp 4 inverter circuit (first controller) 5, 6, and 7 sensor (detector) 8 current voltage converter 9 A/D converter 10 CPU (first controller, second controller, first converter, second converter, corrector) 11 signal processor (second controller) BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION Below, the liquid crystal display apparatus according to one embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to drawings. FIG. 1 is a block diagram which shows the configuration of a liquid crystal display apparatus of an embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1, 1 is a liquid crystal panel, which has a color filter divided into RGB, and which displays the respective gradations of RGB by controlling signal levels corresponding to RGB. 2 is a backlight system (hereinafter, simply backlight'), which converts the gradations of the liquid crystal panel 1 into luminance. The backlight 2 includes a plurality of cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) 3, and an inverter circuit 4 which controls the current thereof. The luminance of the liquid crystal panel 1 is increased or decreased by controlling the current of the plurality of cold cathode fluorescent lamps 3. The sensors 5, 6, and 7 detect the light (R,G,B) that leaks or that is guided and extracted from the backlight 2, convert it into current corresponding to the respective light quantity, and supply this to the current-voltage converter 8. The cur rent-voltage converter 8 converts the current from the sensors 5, 6, and 7 into voltage, and supplies it to the CPU 10. The CPU 10 has an A/D converter 9, which converts the voltage from the aforementioned current-voltage converter 8 into digital data (hereinafter, RGB data). After CPU 10 conducts prescribed arithmetic computation relative to RGB data converted by the A/D converter 9 that is, RGB data corresponding to the light quantity of the light (R,G,B) that leaks or that is guided and extracted from the backlight 2 it generates control signals S1, S2 for control ling the current of the backlight 2 and for controlling the signal levels of the liquid crystal panel according to the results of the arithmetic computation to supply them to the inverter circuit 4 and signal processor 11 respectively. The inverter circuit 4 controls the current of the backlight 2 according to the aforementioned control signal S1. The signal processor 11 controls the signal levels of the liquid crystal panel 1 accord ing to the aforementioned control signal S2. According to the above-described configuration, after con version of the light that leaks or is guided and extracted from the backlight 2 into current by the three RGB sensors 5, 6, and 7, the current is converted into voltage by the current-voltage converter 8, and the voltage is converted into RGB data by the A/D converter 9. In the CPU 10, prescribed arithmetic com
11 5 putation is conducted relative to the digitalized RGB data, and control signals S1 and S2 for controlling the current of the backlight 2 and for controlling the signal levels of the liquid crystal panel 1 are generated. Control signal S1 is a control signal based on the luminance of the backlight 2 detected by the sensors 5, 6, and 7. Control signal S2 is a control signal based on the color temperatures of the backlight 2 detected by the sensors 5, 6, and 7. In the inverter circuit 4, the current of the backlight 2 is controlled according to the aforementioned control signals S1. In the signal processor 11, the signal levels of the liquid crystal panel 1 is controlled according to the aforementioned control signals S2. Next, the arithmetic processing of the aforementioned CPU 10 is described. The CPU 10 converts the digitalized RGB data into tris timulus signals XYZ which measure the surface of the liquid crystal panel 1. This is because, as shown by FIG. 2A and FIG.2B, the chromaticity spectral properties of the respective sensors 5, 6, and 7 of RGB do not completely match the spectral properties of the tristimulus values X, Y, and Z. The CPU 10 converts the RGB data into the tristimulus values X, Y. and Zaccording to the below formulae (1), (2), and (3). Formula 1 X=aRS+b GS-CBS-d (1) Formula 2) Formula 3 In the above formulae (1), (2), and (3), RS, Gs, and Bs are output values of the sensors 5, 6, and 7: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i. j, k, and 1 are fixed constants proper to each model; and X, Y, and Z are tristimulus values. With respect to all models, if it is assumed that the ratios of RS, Gs, and BS in the respective tristimulus values are equal, the above formulae (1), (2), and (3) would be expressed by the below formulae (4), (5), and (6). Formula 4 Formula 5 Formula 6 In the above formulae (4) (6), b', c', f, g, j', and k'are fixed constants common to all models. For each model, the variables a, d, e, h, i, and 1 of formulae (4), (5), and (6) are found by obtaining the measurement values of the tristimulus values X, Y, and Z of the liquid crystal panel Surface at the maximum luminance and mini mum luminance of a prescribed luminance range, and the sensor values RS, Gs, and Bs at that time. By this means, it is possible to calibrate irregularities in the sensitivities of the sensors 5, 6, and 7 like those shown in FIG. 3, and also to adopt tracking in their luminance ranges. As stated above, the sensor values RS, Gs, and Bs, which are obtained by detecting the three-wavelength optical output of the backlight 2 with the respective sensors 5, 6, and 7 of RGB, is correlated with the tristimulus values X, Y, and Z of US 8,427,462 B the liquid crystal surface. From these tristimulus values X,Y, and Z, it is also possible to obtain a luminance value LV and chromaticity values X, y in accordance with the below formu lae (7), (8), and (9). Formula 7 L=Y (7) Formula 8 Formula 9 As stated above, if sensor values RS, Gs, and Bs are known, the tristimulus values X,Y, and Z of the liquid crystal surface are found in a certain luminance range. Consequently, it is possible to conduct control so that the luminance value LV is the expected value Lv' by controlling the backlight current. That is, a loop like that shown in FIG. 4 is configured. With respect to chromaticity, as it is difficult to cause variation in the color temperature of the backlight 2, the chromaticity of the liquid crystal panel 1 is fixed by having the signal processor 11 cause variation in the levels of the display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel 1 in accordance with the control signals S2 (i.e., control signals based on information relating to the color temperature of the backlight 2 detected by the sensors 5, 6, and 7) from the CPU 10. The levels of the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel 1 are expressed as Rp, Gp, and Bp. With white points as the reference, there exist the relations of: decrease in Rp->X of the Xy coordinates decreases, y does not change; decrease in Gp->X of the Xy coordinates does not change, y decreases; decrease in Bp->X of the Xy coordinates increases, y increases. For example, this yields: Ax=0.0004xARp Ay=0xARp. The levels of Rp, Gp, and Bp are controlled according to how much deviation has occurred from the reference color temperature values X and y measured at a time of factory shipment. The method is shown below. Current color tem perature values X and y are expressed as Xc and yc, and reference color temperature values Xandy are expressed as Xf andyf. (1) The case where ye is less thanyf, and Xc is greater than Xf yc and yfare matched by decreasing Bp. The amount of change in Xandy relative to change in Bp is as follows. Ay= xABp Ax= xABp AY=0.0764xY( )xABp/255 Furthermore, Xc and Xfare matched by decreasing Rp. The amount of change in Xandy relative to change in Rp is as follows. Ay=0 Ax=0.0004xARp AY=0.338xY( )xARp/255
12 7 FIG. 5 is a schematic view for the cases whereycandyfare matched by decreasing Bp whenyc is less thanyf, and where Xc and Xfare matched by decreasing Rp when Xc is greater than Xf. (2) The case where ye is less thanyf, and Xc is less than Xf yc and yfare matched by decreasing Bp. The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Bp is as follows. Ay= xABp Ax= xABp AY=0.6691xY( )xABp/255 Furthermore, Xc and Xfare matched by decreasing Bp and Gp. The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Bp and Gp is as follows. Ax= xABpGp Ay= xABpGp AY=0.7309xY( )xABpGp/255 FIG. 6 is a schematic view for the cases whereycandyfare matched by decreasing Bp whenyc is less thanyf, and where Xc and Xfare matched by decreasing Bp and Gp when Xc is less than Xf. (3) The case where ye is greater than yf, and Xc is greater than Xf ye and yfare matched by decreasing Gp The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Gp is as follows. Ax= xAGp Ay=0.0003xAGp AY=0.6691xY( )xAGp/255 Furthermore, Xc and Xfare matched by decreasing Rp. The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Rp is as follows. Ay=0 Ax=0.0004xARp AY=0.338xY( )xARp/255 FIG. 7 is a schematic view for the cases whereycandyfare matched by decreasing Gp when ye is greater than yf, and where Xc and Xf are matched by decreasing Rp when Xc is greater than Xf. (4) The case where ye is greater thanyf, and Xc is less than Xf yc and yfare matched by decreasing Gp The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Rp and Gp is as follows. Ay= xARpGp Ax=0.0003xARpGp AY=0.6691x Y( )xARpGp/255 Furthermore, Bp and Gp are decreased. The amount of change in X and y relative to change in Bp and Gp is as follows. Ax= xABpGp Ay= xABpGp AY=0.7309xY( )xABpGp/255 US 8,427,462 B FIG. 8 is a schematic view for the cases where ye andyfare matched by decreasing Gp when ye is greater than yf and where Xc and Xfp are matched by decreasing Bp and Gp when Xc is less than Xf. In the foregoing (1) (4), when the entirety of RGB is less than 255, a change is made so that the highest color is 255. The levels of the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel 1 ordinarily adopt a maximum value of 255 when resolution is 8 bits. As stated above, when chromaticity is adjusted by changing display signal levels, luminance LV decreases. Luminance variation at the time of change in the respective display signal levels of RGB are therefore mea Sured in advance to calculate how much luminance falls when chromaticity is adjusted. An example thereof is expressed by AY in the above (1) (4). Luminance is fixed by adding the AY to an expected value Lv'. It is possible to conceive of a variety of applications with respect to a method which fixes the luminance value LV by adding the reduction in luminance produced by changing the RGB levels of the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel 1 to the expected value Lv'. As one example, there is a method which changes the RGB levels to change the screen color temperature of the liquid crystal panel 1. For example, in the case of a liquid crystal panel in which the maximum levels of all RGB (in the case of 8 bits, R=255, G=255, and B-255) is 6500 K (kelvin), for a setting of 9300 K, it would have R=180, G=197 and B-255, and luminance would decrease to 33%. By adding this decreased portion to the expected value LV", it is possible to change color temperature without changing luminance. As another example, as a method for improving luminance uniformity and color uniformity of a liquid crystal panel, there is a method which changes RGB levels according to portions of the screen. Liquid crystal panels are generally made so that luminance is higher in the central part where the human eye focuses to give the screen a bright appearance. In order to satisfy standards for luminance/color uniformity for medical uses and so on, there is a method which reduces peripheral luminance differences to improve luminance/color uniformity by reducing RGB levels at the center of the screen. Since it is common to conduct measurement at the central part of the screen with respect to definition of the luminance of a screen, a reduction in luminance occurs when luminance? color uniformity is improved. By adding this decreased por tion to the expected value Lv', it is possible to improve lumi nance/color uniformity without changing luminance. Here, FIG.9A is a schematic view which shows luminance properties before the luminance uniformity correction of the present embodiment, and FIG.9B is a schematic view which shows luminance properties after conducting the luminance uniformity correction of the present embodiment. Prior to luminance uniformity correction, as shown in FIG.9A, it is clear that luminance is highest at the central part, and lower toward the periphery. In contrast, after luminance uniformity correction, as shown in FIG.9B, it is clear that luminance is approximately uniform. According to the foregoing embodiment, in the liquid crys tal display apparatus, the optical output of the backlight 2 is detected by the respective sensors 5, 6, and 7 of RGB, the luminance value LV and color temperature X and y are obtained from these values, and the display signal levels to the liquid crystal panel 1 is controlled so that the expected value Lv' of luminance and the color differences X and y at the time of factory shipment are attained, and thereby it is possible to achieve a constant and stable luminance and chromaticity. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention can be applied to a liquid crystal display apparatus having a backlight. According to the liquid
13 crystal display apparatus and the liquid crystal display appa ratus control method of the present invention, it is possible to achieve constant and stable luminance and chromaticity. The invention claimed is: 1. A liquid crystal display apparatus comprising: a liquid crystal panel; a backlight provided on a rear face of the liquid crystal panel; a detector which detects RGB output light levels of the backlight; a first controller which controls backlight current for driv ing the backlight so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on the RGB output light levels detected by the detector; a second controller which controls display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that a prescribed chroma ticity is attained based on the RGB output light levels detected by the detector; a first converter which converts the RGB outputlight levels detected by the detector into tristimulus values: a second converter which converts the tristimulus values into a luminance value and chromaticity values, wherein the first controller controls the backlight current for driving the backlight based on the luminance value converted by the second converter, and the second con troller controls the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel based on the chromaticity values converted by the second converter, and wherein the first controller controls the backlight current so that the luminance value converted by the second con Verter matches a prescribed expected value; and a corrector which corrects the prescribed expected value when the first controller controls the backlight current for driving the backlight, in order to prevent luminance Variation in the liquid crystal panel produced when the Second controller controls the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel. US 8,427,462 B The liquid crystal display apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the second controller controls the display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that the chromaticity values converted by the second converter match prescribed expected values or initial values. 3. A liquid crystal display control method for a liquid crystal display apparatus including a liquid crystal panel and a backlight provided on a rear face of the liquid crystal panel, the method comprising: detecting RGB output light levels of the backlight; controlling backlight current for driving the backlight so that a prescribed luminance is attained based on the detected RGB output light levels: controlling display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel so that a prescribed chromaticity is attained based on the detected RGB output light levels; converting the detected RGB output light levels into tris timulus values; converting the tristimulus values into a luminance value and chromaticity values, wherein, in the controlling of the backlight current, the backlight current for driving the backlight is controlled based on the converted luminance value, in the controlling of the display signals, the display signals Supplied to the liquid crystal panel are controlled based on the converted chromaticity values, and in the controlling of the backlight current, the backlight current is controlled so that the converted luminance value matches a prescribed expected value, the method further comprising: correcting the prescribed expected value when the back light current for driving the backlight is controlled in the controlling of the backlight current, in order to prevent luminance variation in the liquid crystal panel produced when the display signals supplied to the liquid crystal panel are controlled in the controlling of the display signals.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
Assistant Examiner Kari M. Horney 75 Inventor: Brian P. Dehmlow, Cedar Rapids, Iowa Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Kyle Eppele; James P.
 USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005
 (19) United States US 2005O28O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0280851A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) COLOR SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2005O28O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0280851A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) COLOR SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
Monitor QA Management i model
 Monitor QA Management i model 1/10 Monitor QA Management i model Table of Contents 1. Preface ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 2.
Monitor QA Management i model 1/10 Monitor QA Management i model Table of Contents 1. Preface ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 2.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/20
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 43 301 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/20 (1) Int Cl.: G02F 1/1337 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11103.3 (22) Date of filing: 22.02.2011
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 43 301 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/20 (1) Int Cl.: G02F 1/1337 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11103.3 (22) Date of filing: 22.02.2011
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Evanicky et al. USOO6448955B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH ENHANCED BACKLIGHT BRIGHTNESS AND SPECIALLY SELECTED
(12) United States Patent Evanicky et al. USOO6448955B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH ENHANCED BACKLIGHT BRIGHTNESS AND SPECIALLY SELECTED
III. United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 5,329,314. Jul. 12, ) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: FILTER FILTER P2B AVERAGER
 United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0057484A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0057484A1 Diefenbaugh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC IMAGE LUMINANCE (22) Filed: Sep.
US 2005.0057484A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0057484A1 Diefenbaugh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC IMAGE LUMINANCE (22) Filed: Sep.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7916217B2 (12) United States Patent Ono (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Kenichiro Ono, Kanagawa (JP) (73) (*) (21) (22) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo
USOO7916217B2 (12) United States Patent Ono (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Kenichiro Ono, Kanagawa (JP) (73) (*) (21) (22) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al.
 (12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,020,022 B2. Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited
 United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. Venkatraman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014
 US 20140028364A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0028364 A1 Venkatraman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) CRITICAL PATH MONITOR HARDWARE Publication
US 20140028364A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0028364 A1 Venkatraman et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) CRITICAL PATH MONITOR HARDWARE Publication
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Jun. 28, 2005 (JP) LEVEL DETECTION CIRCUIT IMAGE DATA
 (19) United States US 20070064162A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0064162 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20070064162A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0064162 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,786 B1
 USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7760213B2 (12) United States Patent Aoki et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Apr. 5, 2002 (51) (52) (58) CONTRASTADJUSTING CIRCUITRY AND VIDEO DISPLAY APPARATUS USING SAME Inventors:
USOO7760213B2 (12) United States Patent Aoki et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Apr. 5, 2002 (51) (52) (58) CONTRASTADJUSTING CIRCUITRY AND VIDEO DISPLAY APPARATUS USING SAME Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1
 USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
OPTIMIZED LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (LED) DEVICES THAT HAVE A HIGH COLOR RENDERING INDEX (CRI) FOR LIGHTING APPLICATIONS
 The contents of U.S. Patent Pub. No. 20100001648, entitled LED lighting that has continuous and adjustable color temperature (CT), while maintaining a high CRI, published on January 7, 2010 is based in
The contents of U.S. Patent Pub. No. 20100001648, entitled LED lighting that has continuous and adjustable color temperature (CT), while maintaining a high CRI, published on January 7, 2010 is based in
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
Color measurement and calibration of professional display devices
 White Paper Color measurement and calibration of professional display devices Abstract: With the advance of display technologies using LED light sources, the problems of color consistency, accuracy and
White Paper Color measurement and calibration of professional display devices Abstract: With the advance of display technologies using LED light sources, the problems of color consistency, accuracy and
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nishijima et al. US005391.889A 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 1995 54) OPTICAL CHARACTER READING APPARATUS WHICH CAN REDUCE READINGERRORS AS REGARDS A CHARACTER
United States Patent (19) Nishijima et al. US005391.889A 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 1995 54) OPTICAL CHARACTER READING APPARATUS WHICH CAN REDUCE READINGERRORS AS REGARDS A CHARACTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O125411A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0125411A1 Tonami et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2004 (54) METHOD OF, APPARATUS FOR IMAGE Publication Classification
US 2004O125411A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0125411A1 Tonami et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2004 (54) METHOD OF, APPARATUS FOR IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9369636B2 (12) United States Patent Zhao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2016 (54) VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD AND CAMERADEVICE (71) Applicant: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen
USOO9369636B2 (12) United States Patent Zhao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2016 (54) VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD AND CAMERADEVICE (71) Applicant: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2. Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016
 USOO938913 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2 Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016 (54) ASSEMBLY, SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR G01L 5/042; G01L 5/06; G01L 5/10; A01 K CABLE
USOO938913 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2 Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016 (54) ASSEMBLY, SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR G01L 5/042; G01L 5/06; G01L 5/10; A01 K CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
