(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
|
|
|
- Marion Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
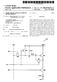
1 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR INCLUDING THE SAME (75) Inventor: Masatoshi Kokubun, Kawasaki (JP) Correspondence Address: ARENT FOX KINTNER PLOTKIN & KAHN 1050 CONNECTICUT AVENUE, N.W. SUTE 400 WASHINGTON, DC (US) (73) Assignee: Fujitsu Limited (21) Appl. No.: 10/337,436 (22) Filed: Jan. 2, 2003 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Feb. 7, 2002 (JP) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl.... H01L 27/00 (52) U.S. Cl /208.1 (57) ABSTRACT A correlated double Sampling circuit that reduces a shift in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side pro duced by reset operation. A reset signal RST is turned to H and then is turned to "L. By doing So, a photodiode begins integration according to the intensity of light. This detected signal is sent to a CDS circuit. An SW1 and a connection Switch for sampling in the CDS circuit are turned to ON to accumulate the detected Signal according to integration time in C1 and C2 as electric charges. After a certain period of time elapsed, the SW1 and connection Switch for Sampling are turned to OFF to hold the detected signal sampled. Next, the RST is turned again to H and the SW1 is turned to ON. Then the RST is turned to L and the SW1 is turned to OFF. By doing So, reset noise is Sampled and held in the C1. AS a result, only a signal component can be extracted from the detected Signal. After that a connection Switch for outputting SW3 and a connection Switch for reading are turned to ON to transfer an output voltage Signal according to the Signal component included in the detected Signal to an output bus line O PIXEL SECTION a O > CA) O r 25 O of o E g 9 fi - ge - t U n A - CDS CIRCUIT SW22-1 SW22-2 SW22-7 SW22-8 e TG SW3-1 SW3-2 SW3-7 CIRCUIT FE
2
3 Patent Application Publication Aug. 7, Sheet 2 of 7 US 2003/ A OPIXEL SECTION RST-k SLCTsk TG CIRCUIT X CDS CIRCUIT SW22-1 SW22-2 SW22-7 SW22-8 I HORIZONTAL SCANNING SHIFT REGISTER V 32 FIG. 2
4 Patent Application Publication Aug. 7, Sheet 3 of 7 US 2003/ A1 _LOTIS WAS LZWAS L ZAVAS Z.Z.NAS / ZZ WAS 8 ZZAWS 9 WAS Z SWAS WAS 8-9 WAS
5 Patent Application Publication Aug. 7, Sheet 4 of 7 US 2003/ A1 i DUMMY SW MAIN SW 21 FIG. 4
6 Patent Application Publication Aug. 7, 2003 Sheet 5 of 7 US 2003/ A1 C) CD. O O? C) C O t s
7
8 Patent Application Publication Aug. 7, Sheet 7 of 7 US 2003/ A1 SCHEMATIC VIEW OF LAYOUT 61 SWITCHING ELEMENT REFERENCE VOLTAGE 62 SIGNAL LINE a cro Ho Soo CONTROL SIGNAL FOR COMMON OPERATION /\ /\ /\ 64 ON/OFF CONTROL SIGNAL s SW2 SWITCH ON/OFF GENERATION SECTION 63 CONTROL CIRCUIT PRIOR ART FIG. 7A REFERENCE VOLTAGE SIGNAL LINE Vref PRIOR ART FIG. 7B
9 US 2003/O A1 Aug. 7, 2003 CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR INCLUDING THE SAME CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is based upon and claims priority of Japanese Patent Application No , filed on Feb. 7, 2002, the contents being incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002 (1) Field of the Invention This invention relates to a correlated double sam pling circuit and a CMOS image Sensor and, more particu larly, to a correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from a pixel Section where Solid-state image Sensing devices are arranged like a matrix and a CMOS image Sensor including Such a correlated double Sampling circuit. 0004) (2) Description of the Related Art 0005 Solid-state image sensing devices used now for digital cameras, digital video cameras, and the like include image sensors using charge coupled devices (CCDS) and image Sensors using complementary metal oxide Semicon ductor (CMOS) sensors. CMOS image sensors have merits. For example, CMOS image Sensors consume a Smaller amount of power than CCDs, CMOS image Sensors can be driven by a single power Source, and peripheral circuits, Such as a timing generation circuit and read circuit, can be formed so that they will be one with CMOS image sensors. Therefore, CMOS image sensors have been used widely in recent years ACMOS image sensor comprises a pixel section where unit pixels including a photodiode are arranged like a matrix, a Scanning circuit for Scanning unit pixels in order, and a correlated double sampling (CDS) circuit for process ing Signals output from the pixel Section This CDS circuit will now be described with ref erence to drawings. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of a unit pixel and CDS circuit A unit pixel 11 includes a photodiode D1, a reset transistor M1, a drive transistor M2, and a selection tran sistor M3. A plurality of unit pixels 11 each having the above Structure are arranged like a matrix to form a pixel Section. The pixel Section is Scanned in order by a vertical Scanning shift register for Scanning in a vertical direction and a horizontal Scanning shift register for Scanning in a horizontal direction There is a CDS circuit 60 for each column in the pixel section. The CDS circuit 60 processes a signal output from a unit pixel in a row Selected by the vertical Scanning shift register from among unit pixels in a column to which the CDS circuit 60 is connected. The CDS circuit 60 includes a first capacitor C1, a Second capacitor C2, a power Source VREF for generating reference potential Vref, ampli fiers AMP1 and AMP2 for amplifying signals, a Switch SW1, being a Switching element, for controlling connection with the unit pixel 11, a Switch SW2, being a Switching element, for connecting one end of the Second capacitor C2 to the first capacitor C1 and power source VREF, and a Switch SW3, being a Switching element, for outputting output signals to an output bus Acurrent source I1 is located to make the transistor M2 in the unit pixel 11 function as an amplifier Now, the operation of the above unit pixel and CDS circuit will be described. FIG. 6 is a timing chart of a CDS circuit First, a selection signal SLCT1 for selecting pixels in the first row is turned to ON by the vertical scanning shift register (the selection signal SLCT1 changes to the H level). Then a reset signal RST1 for resetting pixels in the first row is kept H for a certain period of time to perform the first reset called an initial reset. At this time the potential on the cathode side of the photodiode D1 is VR (constant). After the reset time ended, the reset signal RST1 is turned to L. By doing So, the photodiode D1 begins integration accord ing to the intensity of light. Then by turning the Switch SW2 (it is assumed that there are eight columns of unit pixels and therefore switches SW2-1 through SW2-8) and switch SW1 in the CDS circuit 60 located for each column to ON, detected Signals according to time during which the photo diode D1 integrates are accumulated as electric charges not only in the first capacitor C1 but also in the Second capacitor C2. After a certain period of time elapsed, the Switch SW1 and switches SW2-1 through SW2-8 are turned to OFF to hold the detected Signals Sampled. Subsequently, the reset signal RST1 is kept H for a certain period of time as the second reset and the switch SW1 is turned to ON during this time. By doing So, reset noise is accumulated in the first capacitor C1. After a predetermined period of time elapsed, the Switch SW1 is turned to OFF. As a result, the potential at node VC2 of the second capacitor C2 is given by the following equation (1) Vief-((detected signal+reset noise)-reset noise) (1) 0013 Therefore, only signal components can be extracted. After that the Signals are transferred to the output bus line by turning the Switch SW2 and Switch SW3 in each CDS circuit (the switch SW2-1 and switch SW3-1, the Switch SW2-2 and Switch SW3-2,..., and the Switch SW2-8 and switch SW3-8) to ON in synchronization with a Scanning Signal from the horizontal Scanning shift register With conventional CDS circuits, however, a Switching element for Sampling detected Signals is also used as a Switching element for reading. Therefore, node potential on the reference Voltage Side, being reference, will shift at the time of the Switch being turned to OFF, so that there will be differences in brightness among output images As described above, when detected signals accord ing to time during which the photodiode D1 integrates are accumulated in the first capacitor C1 and Second capacitor C2 as electric charges to Sample the detected Signals, the Switches SW1 and SW2 in the CDS circuit 60 are turned to ON and are turned to OFF after a certain period of time. When the Switch SW2 is turned to OFF, node potential on the reference Voltage Side, being reference, will shift by the influence of parasitic capacitance between the gate and Source of a Switching element, being the Switch SW2, and between the gate and drain Moreover, there will be a shift in node potential caused by a layout. FIGS. 7A, B shows a schematic of a
10 US 2003/O A1 Aug. 7, 2003 layout and changes in reference Voltage. FIG. 7A is a schematic of a layout. FIG. 7B is a simple view showing changes in reference Voltage corresponding to the Switches SW2-1 through SW In reference to FIG. 7A, the switch SW2 serving both as a Switching element for Sampling Signals output from the unit pixel 11 and as a Switching element for reading to the output bus is included in a CDS circuit located for each column. Switching elements 61 (SW2-1 through SW2 8, for example) are arranged in a row and are connected to a common reference Voltage Signal line 62. Each of the Switching elements SW2-1 through SW2-8 is controlled by an SW2 Switch on/off control circuit 63. When a control signal for common operation is input to the SW2 Switch on/off control circuit 63, an on/off control Signal generation Section 64 corresponding to each Switching element 61 generates a control Signal. As a result, the Switching ele ments SW2-1 through SW2-8 perform common operation. The Switching elements SW2-1 through SW2-8 turn to ON/OFF in this way by a control signal for common operation, but in reality delays will occur. Therefore, when the SW2 turns to ON/OFF, reference voltage will fluctuate by the influence of the capacitance of a CDS circuit. If the SW2-1 through SW2-8 are turned to OFF in that order, a shift in reference Voltage will gradually become great due to fluctuations in the reference Voltage, the wiring resistance of the reference Voltage Signal line 62, and the like. It is assumed that a dashed line in FIG. 7B indicates ideal reference voltage (reference potential Vref). Then almost ideal reference voltage is obtained at the SW2-1, but refer ence voltage at the SW2-8 is lower than the ideal reference potential (Vref) by the influence of capacitance, wiring resistance, and the like. Such fluctuations in reference Volt age will lead to a shift in the potential VC2 of a node on the reference Voltage Side. As a result, a shift in the number of electric charges accumulated in the Second capacitor C2 will occur and differences in brightness will arise among results obtained when the CDS circuit 60 reads detected signals. It is assumed that pixels corresponding to the SW2-1 through SW2-8 output detected signals indicative of the same bright ness. Then in the case of FIG. 7B, a pixel corresponding to the SW2-8 is duller than a pixel corresponding to the SW2-1. That is to say, a difference in brightness arises. A case where reference voltage at the SW2-8 is lower than the ideal reference potential (Vref) has been described. How ever, reference voltage at the SW2-8 may exceed the ideal reference potential (Vref), depending on how to control the Switches. In this case, differences in brightness will also arise among the corresponding pixels Pixel sections have become minute, so the rate at which Signals output from the pixel Sections are read must be increased. Therefore, the width of a gate on the Switching element SW2 used at read time must be widened to reduce its ON-state resistance. However, widening gate width will Strengthen the influence of parasitic capacitance produced there and make a shift in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side great Ashift in output signal caused by such a shift in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side is amplified by an amplifier located at the next stage of a CDS circuit. Therefore, even if a shift in signals output from a CDS circuit is Small, differences in brightness will eventually arise among images. If an amplifier with an amplification factor of, for example, 16 is located at the next Stage, a shift of 1 mv will be amplified to 16 mv. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention was made under the back ground circumstances as described above. An object of the present invention is to provide a correlated double Sampling circuit for reducing a shift in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side produced by reset operation and a CMOS image sensor including such a correlated double Sampling circuit In order to achieve the above object, a correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from a pixel Section where Solid-state image Sensing devices are arranged like a matrix is provided. This correlated double Sampling circuit comprises a first capacitor for Sampling and holding reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by resetting the pixel Section, a Second capacitor for Sam pling and holding detected Signals obtained by a photoelec tric conversion in the pixel Section, a connection Switch for Sampling for controlling connection between predetermined power Supply which generates predetermined potential to Sample the detected Signals with the predetermined potential as reference and the Second capacitor, and a connection Switch for reading for controlling reading of output signals according to a difference between the detected Signals and the reset level Signals obtained from electric charges Sampled and held in the Second capacitor and the first capacitor Furthermore, in order to achieve the above object, a CMOS image Sensor comprising a pixel Section where unit pixels including a photodiode and transistors are arranged like a matrix, a Scanning circuit for Scanning the pixels, and a correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from the pixel Section are provided. The correlated double Sampling circuit in this CMOS image Sensor includes a first capacitor for Sampling and holding reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by resetting the pixel Section, a Second capacitor for Sampling and holding detected Signals obtained by a photoelectric conversion in the pixel Section, a connection Switch for Sampling for controlling connection between predetermined power Sup ply which generates arbitrary potential to Sample the detected Signals with the arbitrary potential as reference and the Second capacitor, and a connection Switch for reading for controlling reading of output Signals according to a differ ence between the detected Signals and the reset level Signals obtained from electric charges Sampled and held in the Second capacitor and the first capacitor The above and other objects, features and advan tages of the present invention will become apparent from the following description when taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings which illustrate preferred embodi ments of the present invention by way of example. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0024 FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a CDS circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention FIG. 2 is a view showing the basic structure of a CMOS image sensor FIG. 3 is a timing chart of a CDS circuit section in a CMOS image Sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention.
11 US 2003/O A1 Aug. 7, FIG. 4 is a view showing the structure of a connection Switch for Sampling according to the present invention. 0028) circuit. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of a unit pixel and CDS 0029) FIG. 6 is a timing chart of a CDS circuit FIGS. 7A,B show a schematic of a layout and changes in reference Voltage. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Embodiments of the present invention will now be described with reference to the drawings FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of a CDS circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention. 0033) A CDS circuit 20 inputs signals output from a plurality of unit pixels 11 arranged in horizontal and Vertical directions and processes them The unit pixel 11 includes a photodiode D1 and three n-channel MOS transistors M1 through M3. A cathode of the photodiode D1 is connected to a source of the transistor M1 and a gate of the transistor M2. A gate of the transistor M1, being a reset transistor, is connected to a reset line where a reset Signal RST is Supplied, and a drain of the transistor M1 is connected to a power Supply line where reference Voltage VR is Supplied. A drain of the transistor M2, being a drive transistor, is connected to the power Supply line where reference Voltage VR is Supplied. This is the same with the transistor M1. A Source of the transistor M2 is connected to a drain of the transistor M3. A gate of the transistor M3, being a Selection transistor, is connected to a column Selection line where a Selection Signal SLCT is Supplied. A Source of the transistor M3 is connected to a current Source I1 and a Switch SW1 in the CDS circuit ). Now, operation in the unit pixel 11 will be described. When a reset signal RST turns to H, the potential on the cathode side of the photodiode D1 becomes VR (constant). Subsequently, the reset signal RST turns to L, then light strikes the photodiode D1. As a result, electric charges are produced in the photodiode D1 accord ing to the intensity of light. These electric charges will change potential at VPD, that is to Say, the Voltage of the gate of the transistor M2. When a selection signal SLCT turns to H, an electrical Signal according to potential at VPD at that time is sent via the transistor M3 to the CDS circuit ) The CDS circuit 20 includes the connection switch for inputting SW1 for controlling input of Signals output from the unit pixel 11, first and second capacitors C1 and C2 for Sampling and holding Signals output from the unit pixel 11, power Supply VREF for generating reference potential Vref, a connection Switch for Sampling 21 for connecting the Second capacitor C2 and the power Supply VREF at Sam pling time, a connection Switch for reading 22 for connect ing the Second capacitor C2 and the power Supply VREF at reading time, amplifiers AMP1 and AMP2, and a connection Switch for outputting SW3 for controlling output to an output bus in response to a signal from the horizontal Scanning Side The connection Switch for inputting SW1 is con nected to the current Source I1, the Source of the Selection transistor M3 in the unit pixel 11, and one end of the first capacitor C1 in the CDS circuit 20 and imports signals detected by the unit pixel 11 into the CDS circuit One end of the first capacitor C1 is connected to an output terminal of the unit pixel 11 via the SW1 and to the amplifier AMP1 and the other end is connected to the power supply VREF and to one end of the second capacitor C2 via the connection Switch for Sampling 21. The first capacitor C1 Samples and holds detected Signals according to the intensity of light detected by the photodiode D1 which are output from the unit pixel 11 after the initial reset, and Samples and holds reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by a reset when a Second reset is performed One end of the second capacitor C2 is connected to the amplifier AMP1 and the other end is connected to the amplifier AMP2 and to the power Supply VREF and first capacitor C1 via the connection Switch for Sampling 21 and connection Switch for reading 22. When the initial reset is performed, the Second capacitor C2 connects via the con nection switch for sampling 21 with the power supply VREF and first capacitor C1 and Samples and holds detected Signals output from the unit pixel 11. When a Second reset is performed, potential at node VC2 is given by equation (1). Then the connection Switch for reading 22 and connection Switch for outputting SW3 turn to ON and output signals according to potential at node VC2 are transferred One end of the connection switch for sampling 21 is connected to one end of the Second capacitor C2 and the other end of the connection Switch for Sampling 21 is connected to one end of the first capacitor C1 and the power supply VREF. At sampling time the connection Switch for Sampling 21 turns to ON to connect the Second capacitor C2 to the first capacitor C1 and power Supply VREF. When Sampling ends, the connection Switch for Sampling 21 turns to OFF to disconnect the second capacitor C2 from the first capacitor C1 and power supply VREF. As will be described later, there is Sufficient time to Sample. Therefore, compared with the width of a gate of the connection Switch for reading 22, the width of a gate of the connection Switch for Sampling 21 can be narrowed. For example, the minimum width that can be realized by a technology used in the Semiconductor production process may be Selected. As a result, hold operation can be completed without being Significantly influenced by parasitic capacitance between the gate and Source and between the gate and drain One end of the connection Switch for reading 22 is connected to one end of the Second capacitor C2 and the other end of the connection Switch for reading 22 is con nected to one end of the first capacitor C1 and the power supply VREF. Together with the connection Switch for outputting SW3, the connection switch for reading 22 turns to ON/OFF to transfer output signals according to the potential of node VC2. A pixel section 10 has become minute, So a read rate must be increased. Therefore, the width of a gate of the connection Switch for reading 22 must be widened The connection switch for outputting SW3 turns to ON in Synchronization with a horizontal Scanning Signal to transfer only signal components which the CDS circuit 20 generates by removing noise from Signals detected by the unit pixel 11 to an output bus line.
12 US 2003/O A1 Aug. 7, The CDS circuit 20 described above is incorpo rated into a CMOS image sensor. FIG. 2 is a view showing the basic structure of a CMOS image sensor. Sections which are the same as those in FIG. 1 are denoted with the same numbers and descriptions of them will be omitted A CMOS image sensor comprises a pixel section 10 where unit pixels 11 are arranged like a matrix, a CDS circuit 20 for processing Signals output from the pixel Section 10, a Scanning circuit including a vertical Scanning shift register/reset control circuit 31 for Scanning the pixel Section 10 in a vertical direction and for controlling reset Signals and a horizontal Scanning shift register 32 for controlling horizontal Scanning, and a timing generation circuit (TG circuit) 40 for generating timing Signals for Scanning and Sampling The TG circuit 40 generates a selection signal SLCT for selecting a row in a pixel section 10, a reset Signal RST, and a control Signal for controlling Switches SW1-** and SW21-** which connect the pixel section 10 and CDS circuit 20, where * indicates an arbitrary row and **** indicates an arbitrary row and column. 0046) The CDS circuit 20 is located for each column. The CDS circuit 20 outputs in order signals detected by the unit pixel 11 in a row Selected by the Vertical Scanning shift register/reset control circuit 31 in compliance with a hori Zontal Scanning Signal output from the horizontal Scanning shift register An amplifier 50 amplifies signals, which are output from the CDS circuit 20 and which are transferred to an output bus line, and transfers them to the next circuit Now, operation in a CDS circuit having the above structure and a CMOS image sensor having the above structure will be described. FIG. 3 is a timing chart of a CDS circuit Section in a CMOS image Sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention A selection signal SLCT is turned to ON, and a row in the pixel Section 10 is Selected by the vertical Scanning shift register/reset control circuit 31. In FIG. 3, SLCT1 is turned to ON and row 1 is selected. The moment or after SLCT1 is selected, an RST terminal is turned to ON and RST1 changes to H. As a result, the potential of a cathode of a photodiode D1 is reset to initial potential VR. After reset time ends, the RST terminal is turned to OFF and RST1 changes to L. When RST1 changes to L, the photodiode D1 begins integration according to the intensity of light Then a connection switch for inputting SW1 and a connection switch for sampling 21 (SW21) in the CDS circuit 20 are turned to ON to accumulate detected signals according to integration time in a first capacitor C1 as electric charges. At this time electric charges are also accu mulated in a Second capacitor C2. After a certain period of time elapsed, the SW1 and connection Switch for Sampling 21 (SW21) are turned to OFF to hold the detected signals sampled. The width of a gate of the connection switch for Sampling 21 is narrow, So this hold operation will be completed without being Significantly influenced by para Sitic capacitance between the gate and a Source and between the gate and a drain. A connection Switch for reading 22 (SW22-1 through SW22-8) is kept in the OFF state during this time Next, to accumulate reset noise in the first capaci tor C1, the RST terminal is turned again to ON and the SW1 is turned to ON. After a certain period of time elapsed, the RST terminal is turned to OFF and the SW1 is also turned to OFF. As a result of this operation electric charges corre sponding to the reset noise are accumulated in the first capacitor C1. Therefore, as shown by equation (1), the potential at a node of the Second capacitor C2 is given by (Vref-detected signal) and only signal components can be extracted Then signals are transferred to the output bus line by turning a connection switch for outputting SW3 (SW3-1 through SW3-8) and the connection switch for reading 22 (SW22-1 through SW22-8) to ON in order in synchroniza tion with a horizontal Scanning Signal As stated above, by locating the connection switch for Sampling 21 for connecting the Second capacitor C2 and power Supply VREF in the case of performing Sampling and by narrowing the width of its gate, fluctuations in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side can be reduced. By performing a process by the use of Signals in which fluctuations in reference Voltage are reduced in this way, a difference in brightness can be made Small among output images Moreover, the connection Switch for reading 22 is located Separately from the connection Switch for Sampling 21. As a result, the width of a gate of the connection Switch for reading 22 can be widened with an increase in read rate. 0055) Furthermore, the connection switch for sampling 21 described above consists of a proper Switching element. However, an additional dummy Switching element can be connected. FIG. 4 is a view showing the structure of a connection Switch for Sampling according to the present invention. Sections which are the same as those in FIG. 1 are denoted with the same numbers and descriptions of them will be omitted A drain and source of a main Switching element (main SW) 211 are connected to power supply VREF and a drain of a dummy Switching element (dummy SW) 212 respectively. A gate of the main SW211 is connected to a control signal for controlling ON/OFF of the main SW211 and dummy SW A source of the dummy Switching element 212 is connected to one end of a Second capacitor C2 and its drain. The drain of the dummy Switching element 212 is connected to the source of the main SW211. A gate of the dummy SW212 is connected to a signal obtained by inverting a control signal for controlling ON/OFF of the main SW AS has been described in the foregoing, a CDS circuit according to the present invention includes a capaci tor for holding electric charges Sampled with arbitrary potential as reference and a connection Switch for Sampling for Sampling and holding Signals detected by a pixel Section and a connection Switch for reading for reading output Signals as Switching elements for connecting or disconnect ing power Supply for generating the arbitrary potential. This reduces fluctuations in the potential of a node on the reference Voltage Side caused by turning a Switch to OFF at the time of Sampling being ended With a CMOS image sensor including such a CDS circuit according to the present invention, output signals in
13 US 2003/O A1 Aug. 7, 2003 which fluctuations in reference Voltage are Small in the case of extracting Signals detected by the pixel Section can be obtained by the CDS circuit. As a result, good output images among which a difference in brightness is Small can be obtained The foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the present invention. Further, Since numer ous modifications and changes will readily occur to those skilled in the art, it is not desired to limit the invention to the exact construction and applications shown and described, and accordingly, all Suitable modifications and equivalents may be regarded as falling within the Scope of the invention in the appended claims and their equivalents. What is claimed is: 1. A correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from a pixel Section where Solid-state image Sensing devices are arranged like a matrix, the circuit comprising: a first capacitor for Sampling and holding reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by resetting the pixel Section; a Second capacitor for Sampling and holding detected Signals obtained by a photoelectric conversion in the pixel Section; a connection Switch for Sampling for controlling connec tion between predetermined power Supply which gen erates predetermined potential to Sample the detected Signals with the predetermined potential as reference and the Second capacitor; and a connection Switch for reading for controlling reading of output signals according to a difference between the detected Signals and the reset level Signals obtained from electric charges Sampled and held in the Second capacitor and the first capacitor. 2. The correlated double Sampling circuit according to claim 1, wherein a width of a gate of a Switching element included in the connection Switch for Sampling is narrower than a width of a gate of a Switching element included in the connection Switch for reading. 3. The correlated double Sampling circuit according to claim 1, wherein a width of a gate of a Switching element included in the connection Switch for Sampling is a mini mum width formed in a Semiconductor production process. 4. The correlated double Sampling circuit according to claim 1, wherein a Switching element included in the con nection Switch for Sampling is connected to a dummy Switching element, a gate of the dummy Switching element being provided with a signal with a phase reverse to a phase of an input signal provided to a gate of the Switching element included in the connection Switch for Sampling and a Source and drain of the dummy Switching element being connected to each other. 5. A correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from a pixel Section where Solid-state image Sensing devices are arranged like a matrix, the circuit comprising: a first capacitor for Sampling and holding reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by resetting the pixel Section, a first terminal of the first capacitor being connected to an output terminal of the pixel Section at Sampling time, and a Second terminal of the first capacitor being connected to predetermined power Supply for generating predetermined reference poten tial for Sampling, and a Second capacitor connected in parallel with the first capacitor and connected via a connection Switch for Sampling and a connection Switch for reading located in parallel with the connection Switch for Sampling to the Second terminal of the first capacitor and the predeter mined power Supply for Sampling and holding detected Signals obtained by a photoelectric conversion in the pixel Section, wherein: the connection Switch for Sampling connects the Second capacitor to the first capacitor and the predetermined power Supply while the Second capacitor Samples the detected Signals, and the connection Switch for reading connects the Second capacitor to the first capacitor and the predetermined power Supply while output Signals according to a difference between the detected Signals and the reset level Signals obtained from electric charges Sampled and held in the Second capacitor and the first capacitor are read. 6. The correlated double Sampling circuit according to claim 5, wherein a width of a gate of a Switching element included in the connection Switch for Sampling is narrower than a width of a gate of a Switching element included in the connection Switch for reading. 7. A CMOS image sensor comprising: a pixel Section where unit pixels including a photodiode and transistors are arranged like a matrix; a Scanning circuit for Scanning the pixels, and a correlated double Sampling circuit for processing Signals output from the pixel Section, the circuit including: a first capacitor for Sampling and holding reset level Signals corresponding to noise produced by resetting the pixel Section, a Second capacitor for Sampling and holding detected Signals obtained by a photoelectric conversion in the pixel Section, a connection Switch for Sampling for controlling con nection between predetermined power Supply which generates arbitrary potential to Sample the detected Signals with the arbitrary potential as reference and the Second capacitor, and a connection Switch for reading for controlling reading of output signals according to a difference between the detected Signals and the reset level Signals obtained from electric charges Sampled and held in the Second capacitor and the first capacitor.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,733,141 B2
 USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US B2
 USOO87240O2B2 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 8.724.002 B2 9 9 Rajasekaran (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) IMAGING PIXELS WITH DUMMY 6,535,247 B1 3/2003 Kozlowski et al. TRANSISTORS
USOO87240O2B2 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 8.724.002 B2 9 9 Rajasekaran (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) IMAGING PIXELS WITH DUMMY 6,535,247 B1 3/2003 Kozlowski et al. TRANSISTORS
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1
 USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
? Me ???????? ?????? & > Dec. 14, ??? 2,455,992 ???.. ????? T. T. GOLDSMITH, Jr., ET AL CATHODE-RAY TUBE AMUSEMENT DEVICE. Filed Jan, 25, 1947
 Dec. 14, 1948. Filed Jan, 25, 1947 T. T. GOLDSMITH, Jr., ET AL CATHODE-RAY TUBE AMUSEMENT DEVICE 2,455,992 $?* do??? (TD S Y O s??????????? & > 8+ N zz +aosz No.O2 ---- g s S ÀY vr N???..??????? Me V)??
Dec. 14, 1948. Filed Jan, 25, 1947 T. T. GOLDSMITH, Jr., ET AL CATHODE-RAY TUBE AMUSEMENT DEVICE 2,455,992 $?* do??? (TD S Y O s??????????? & > 8+ N zz +aosz No.O2 ---- g s S ÀY vr N???..??????? Me V)??
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LOURIE ETAL 3,143,664
 Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al.
 United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040041173A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0041173 A1 Takahashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEMICONDUCTOR STORAGE AND ITS REFRESHING METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20040041173A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0041173 A1 Takahashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEMICONDUCTOR STORAGE AND ITS REFRESHING METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,616 B1. Nakano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004
 USOO6765616B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nakano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) ELECTRIC CAMERA 6,529.236 B1 3/2003 Watanabe... 348/230.1 6,580,457 B1 * 6/2003 Armstrong
USOO6765616B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nakano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) ELECTRIC CAMERA 6,529.236 B1 3/2003 Watanabe... 348/230.1 6,580,457 B1 * 6/2003 Armstrong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu
 United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
AND9191/D. KAI-2093 Image Sensor and the SMPTE Standard APPLICATION NOTE.
 KAI-09 Image Sensor and the SMPTE Standard APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The KAI 09 image sensor is designed to provide HDTV resolution video at 0 fps in a progressive scan mode. In this mode, the sensor
KAI-09 Image Sensor and the SMPTE Standard APPLICATION NOTE Introduction The KAI 09 image sensor is designed to provide HDTV resolution video at 0 fps in a progressive scan mode. In this mode, the sensor
United States Patent (19) Stein
 United States Patent (19) Stein 54) PULSE GENERATOR FOR PRODUCING FIXED WIDTH PUISES (75) Inventor: Marc T. Stein, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 967,769 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Stein 54) PULSE GENERATOR FOR PRODUCING FIXED WIDTH PUISES (75) Inventor: Marc T. Stein, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 967,769 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
