(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1
|
|
|
- Justin Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al /102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE 6, B1 * 10/2001 Someya et al /102 6,323,847 B1 11/2001 Kaneko et al /204 (75) Inventor: Tatsuya Shiki, Tokyo (JP) 6,337,676 B1 1/2002 Anai et al /89 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (73) Assignee: NEC LCD Technologies, Ltd., Kanagawa (JP) JP S /1985 JP S /1986 (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this JP /1989 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 E. Hof: 21. U.S.C. 154(b) by 274 days. JP H /1998 (21) Appl. No.: 09/602,182 (22) Filed: Jun. 22, 2000 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jun. 25, 1999 (JP)... 11/ (51) Int. Cl."... G09G 5/00 (52) U.S. Cl /204; 345/87; 345/88; 34.5/589; 34.5/690; 348/674; 348/675; 348/677; 348/694; 358/518; 358/519 (58) Field of Search /87-90, 98, 345/99, 204, 63, 690, 77, 589, 590, 596; 348/222, 223, 241, 251, , 671, 673, , 683, 689, 719, 694; 358/518, 519, 521, 529, 530 (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS JP /1999 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner Richard Hjerpe Assistant Examiner-Henry N. Tran (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Scully, Scott, Murphy & Presser (57) ABSTRACT A clamping circuit for Supplying a clamped color Signal to a gamma-correction circuit is provided with a clamping portion connected to a clamping Voltage generating circuit. The clamping Voltage generating circuit generates a clamp ing Voltage in response to an individual control Signal in Such a way that the black level of a color Signal coincides with the black level in an input/output characteristic of the gamma-correction circuit. The clamping portion adds this clamping voltage to the pedestal level of a color signal at a predetermined timing in response to a control Signal, So as to absorb variations in black levels of the clamping levels 5.255,080 A * 10/1993 Kageyama et al /675 and later-stage circuits including variation in the later-stage 5, A * 5/1998 Sato et al /209 circuits. 5,754,150 A 5/1998 Matsui / ,058 A * 8/1999 Koyama /89 9 Claims, 7 Drawing Sheets R / PR RC GAMMA RG o-h-54en crl 42 CLAPNG GENERANG G / clausing G GCGAMMA GG V O-H-IN O 5 CLAMP if" E log GENERAING CRCUt / o-h-55aen - SECTIONH-o B / CAMPNG PB BcSAMMA: BG 6 - clarific CLAMP UNI WOTAGE GENERANG CIRCUIt a 1-mm -w-m TT p o O
2 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 1 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 F.G. 1 (PRIOR ART) R / GAMMA- RG O- CLAMPNG CORRECTION PORTION 400 CLAMPNG SMP VOLTAGE GENERATING L. 8 CLAMPNG PORTION GAMMA- CORRECTION GG CLAMPNG PORTION GAMMA- CORRECTION BG 600 CLAMPNG CLAMP VOLTAGE 62O ÜNft" SENERATING CRCUIT LC-e
3 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 2 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 FG.2 (PRIOR ART) 420 VOD 423 N- 422 FR CR CD CC h O D FIG.3 (PRIOR ART) INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTIC OF GAMMA CORRECTION / 5 DC LEVEL OF BLACKLEVEL OF al GAMMA-CORRECTION d BLACKLEVEL OF CLAMPED COLOR SIGNAL RC INPUT VOLTAGE
4 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 3 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 vs room we were u v 7 41 R CLAMPING RC GAMMA- RG O- PORTION SECTION -o 4. CLAMPNG 42 SMP WOAGE QR SERATING LA : G / CLAMPNG GC GAMMA GG VI o- PORTION SETION--C 5- cc 5: CLAMP UNIT i CAMPNG VOLTAGE SEATING A 9 a s / PB B s GAMMA- BG camping BOCORRECTION O- PORTION 6 CLAMPENG CLAMP VOLTAGE UNIT GENERATING L.A.-
5 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 4 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 RA O- RC PR CLAMPNG VOLTAGE GENERATING FG DIA CONVERSION CR
6 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 5 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 FG.7 INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERSTC OF GAMMA- CORRECTION CERCUIT BLACKLEVEL OF GAMMA-CORRECTION CRCUIT (=BLACKLEVEL OF CLAMPED COLOR SIGNALRC) INPUT VOLTAGE
7
8 U.S. Patent Dec. 2, 2003 Sheet 7 of 7 US 6,657,619 B1 FG.9 RA -- PEDESTAL LEVEL PR -- LEVEL H - ) -L EVEL st - - FIG.10 R -setup LEVEL - PEDESTAL LEVEL
9 1 CLAMPING FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device, and more particularly to a clamping circuit for a large-screen and high-definition color liquid crystal display device of an active-matrix type. 2. Description of the Prior Art Since a liquid crystal display device (LCD) of an active matrix type using thin film transistors has advantages that it can drive two-dimensionally arranged pixel electrodes inde pendently of one another, can implement a large-screen, high-definition and fine-gradation image display device, can be made compact thanks to its flat panel, can be driven by a low Voltage and can be low in power consumption, the demand on it has been more and more expanded. Since a liquid crystal display device of this kind Sets a picture Signal at a Voltage Suitable for driving liquid crystal, a black level in a picture Signal is clamped to a predeter mined clamping Voltage. Furthermore, Since the character istic of transmissivity of liquid crystal to Voltage applied to the liquid crystal is Steep in the vicinity of the black level, the degree of gradation is lowered in the vicinity of the black level. To this end, So called gamma correction is performed, in which a picture Signal is amplified by changing the degree of amplification in response to a picture Signal level, which is called a gamma correction, is performed. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device clamps in general the black levels of analog RGB (Red, Green and Blue) picture Signals to the same Voltage. In recent years, however, incorrect operation of a gamma correction circuit and a coloring problem caused by varia tion in black level after a gamma correction are getting a great deal of attention as a problem to be Solved. On the other hand, in order to prevent the coloring problem caused by the difference in the characteristic of applied Voltage to brightness among R, G and B Signals of a LCD panel, a clamping circuit for a conventional liquid crystal display device described in Japanese Patent Laid Open Publication No.Sho 64-78,592 has proposed to set pedestal clamping levels So that at least one of them is different from the other according to R, G and B color Signals. Referring to FIG. 1, a conventional clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device is provided with three clamping circuits connected between three coupling capacitors and three gamma-correction circuits, respectively. The coupling capacitors 1, 2 and 3 are provided for receiving input color Signals R, G and B of a picture Signal VI to remove a direct current (DC) bias. Output signals from the coupling capaci tors 1, 2 and 3 are inputted into the clamp units 400, 500 and 600, respectively, to output clamped color signals RC, GC and BC to the gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9, respec tively. The clamped color signals RC, GC and BC are obtained by newly adding a predetermined clamping Voltage, which is the pedestal level of the picture Signal, to the AC component of each of the color signals R, G and B whose DC bias has been cut. The gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 perform a predetermined gamma correction and amplification on each of the clamped color Signals RC, GC and BC to output the respective output color Signals RG, GG and B.G. US 6,657,619 B The clamp unit 400 is provided with a clamping portion 410 for performing a clamping operation of adding a clamp ing Voltage to the AC component of an inputted color Signal R and outputting the clamped color Signal RC, and a clamping Voltage generating circuit 420 for generating and Supplying a predetermined clamping Voltage to the clamp unit 410. The clamp unit 500 is provided with a clamping portion 510 for performing a clamping operation of adding a clamp ing Voltage to the AC component of the inputted color Signal G and outputting the clamped color Signal G.C. The clamp unit 600 is provided with a clamping portion 610 for performing a clamping operation of adding a clamp ing Voltage to the AC component of an inputted color Signal B and outputting the clamped color Signal BC, and a clamping Voltage generating circuit 620 for generating and Supplying a predetermined clamping Voltage to the clamp units 510 and 610. The clamping Voltage generating circuits 420 and 620 are of the Same composition, and referring to FIG. 2 showing with a block diagram the composition of the clamping Voltage generating circuit 420 for the color Signal R as a representative, the clamping Voltage generating circuit 420 is provided with a variable resistor 423 for generating a divided voltage FR by dividing variably the voltage VDD of a power Source and a buffer circuit 422 consisting of a voltage follower circuit for buffer-amplifying the divided Voltage FR and outputting a clamping Voltage CR. In the same way, the clamping Voltage generating circuit 620 is provided with a variable resistor and a buffer circuit. Now, operation of a clamping circuit of a conventional liquid crystal display circuit is described with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2. The color signals R, G and B of the input picture Signal VI are Supplied to the respective Systems. The coupling capacitors 1, 2 and 3 are provided to eliminate only the DC components of the color signals R, G and B since the respective DC components are not constant. The AC com ponent of each of the color Signals R, G and B, in which the DC components are eliminated by the capacitors 1 to 3, varies in black level according to the kind of a picture Signal in a state of leaving as it is (for example, an inverse character display and a normal character display are different in black level), and therefore it is difficult to perform a later-stage process Such as a gamma correction and the like. Thereupon, in order to prevent the black level of a picture Signal from varying, pedestal level clamping circuits are provided for reproducing the DC components to the AC components of the color Signals R, G and B. The foregoing circuits are called the clamp units 400, 500 and 600. The processing System of the color Signal R is explained as a representative in the following. The clamping Voltage generating circuit 420 in the clamp unit 400 generating a divided Voltage FR corresponding to a desired clamping voltage CR by dividing a power voltage VDD by means of the variable resistor 423. The buffer circuit 422 buffer amplifies the divided Voltage, generates and Supplies a clamping Voltage CR to a clamping portion 410. The clamp ing portion 410 operates So as to Superpose the Supplied clamping Voltage CR on the pedestal level of the AC component of a color Signal R, namely, the black level of a color Signal R and outputs a clamped color Signal RC. This is a clamping operation. In the same way, clamped color Signals GC and BC are outputted by performing clamping operations in the Systems of color Signals G and B. In Such a way, in a conventional clamping circuit the clamped color signals RC, and GC and BC can set their
10 3 black levels independently. In this example the clamped color signals GC and BC are interlocked, but they can be composed So that they can be set independently of each other. However, once these clamped Voltages, namely, the black levels are Set, their Settings are fixed as they are. On the other hand, the black levels to be set of the gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 at a later Stage of the clamp units 4, 5 and 6 are ideally Set aiming at a predeter mined Voltage. As a matter of fact, however, the black levels vary among Signals R, G and B or even among the gamma correction circuits of the same color due to variation in accuracy of the gamma-correction circuits. As shown in FIG. 3 showing an example of the input/ output characteristic of a gamma-correction circuit, however, when the black level of an output of a clamping circuit is fixed, the black level of the output of the clamping circuit may become different from the black level of the gamma-correction circuit. In Such a State, therefore, a gamma correction cannot be correctly performed. If the black level of a gamma-correction circuit varies, a circuit at a later Stage of the gamma-correction circuit results in operating incorrectly due to that variation and for example the black level results in being corrected slightly toward the white Side. AS the result, a disadvantage that the display becomes whitish or poor in contrast occurs. Moreover, Since the clamping Voltages are Set individu ally but fixedly, there is a problem of deterioration in color reproductivity or degradation in gamma-correction curves due to a fact that the correction may become an inverse correction depending upon variation in a process at a later Stage of the clamping circuit. Since a clamping circuit for a conventional liquid crystal display device as described above can Set a clamping level for each of color Signals R, G and B but cannot change the clamping level So as to absorb variation in black level of gamma-correction circuits and the like at a later Stage of the clamping circuit, it has a disadvantage that if the black levels of a later-stage circuit vary, the later-stage circuit operates incorrectly due to that variation. Furthermore, Since the clamping Voltages are Set indi vidually but fixedly, there is a disadvantage of deterioration in color reproductivity or degradation of gamma-correction curves due to a fact that the correction may become an inverse correction depending upon variation in a later Stage of the clamping circuit. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION An object of the present invention is to provide a clamp ing circuit for a liquid crystal display device which performs prevention of a coloring phenomenon as well as optimiza tion of a gamma correction due to a circuit composition and prevention of deterioration in contrast by making it possible to adjust the black levels of clamping levels and the black levels of circuits at later Stages of the clamping circuits So as to absorb variation in black levels of these circuits including the later-stage circuits. According to the present invention, a clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device has a plurality of clamp units for receiving a plurality of input color Signals of an input picture Signal after deleting a DC bias from each of the input color Signals to produce a plurality of clamped color Signals, respectively, by adding a predetermined clamping Voltage corresponding to a pedestal level of the input picture Signal to each of the input color Signals. Furthermore, a plurality of gamma-correction circuits are connected to the clamp units for receiving the clamped color Signals, respectively, and for US 6,657,619 B performing a predetermined gamma correction and ampli fication on each of the clamped color Signals to produce output color Signals, respectively. Each of the clamp units is provided with a clamping portion for receiving the input color Signal and a clamping Voltage generating circuit for Supplying a clamping Voltage to the clamping portion So as to be controlled in response to an individual first control Signal Supplied thereto and generates the clamping Voltage Such that a black level of the clamped color Signal coincides with a black level in an input/output characteristic of the gamma-correction circuit. The clamping portion is Supplied with the clamping Voltage So as to add the clamping Voltage to the pedestal level of the input color Signal at a predeter mined timing in response to a Second control Signal Supplied thereto. The pedestal level may be a level corresponding to the black level of an input picture Signal, or the black level of a picture signal may correspond to a Setup level which is Slightly higher by a certain Voltage than the pedestal level. The clamping Voltage generating circuit may be provided with a D/A correction circuit for performing a digital-to analog (D/A) correction on a digital data signal contained in the first control Signal and outputting an analog Voltage Signal, and a buffer circuit for buffer-amplifying the analog Voltage Signal and outputting the clamping Voltage. The clamping portion may be provided with a Switch circuit for conducting or shutting a clamping Voltage in response to the level of the Second control Signal. Furthermore, it may be provided with a control means for outputting a first and a Second control Signal, and a memory means for memorizing data from Said control means and reading and Supplying the memorized data to the control CS. The first control Signal may be a Serial control Signal of a 3-line control method, and may have a digital data Signal corresponding to the clamping Voltages So as to be Supplied to three control lines thereof, a clock signal for Synchroni Zation of this digital data Signal and a Strobe Signal for Specifying a clamping Voltage generating circuit to be con trolled. The Second control Signal may be a Signal which comes to be at high level H for only a specific period of the pedestal level of a color Signal for one horizontal Scanning period which is one period of a horizontal Synchronizing Signal, and may be generated by Shifting the phase of the horizontal Synchronizing Signal by a predetermined time and inverting this shifted horizontal Synchronizing Signal. According to the present invention, a clamping circuit of a liquid crystal display device is provided with a clamping circuit for adding newly a predetermined clamping Voltage corresponding to the black level corresponding to a Setup level which is a level higher by a certain Voltage than the pedestal level of a picture Signal to a color Signal having a direct current (DC) bias cut for each color signal of the inputted picture Signal and outputting a clamped color Signal, and a gamma-correction circuit for performing a predetermined gamma correction and amplification on the Supplied clamped color Signal and outputting an output color Signal, wherein a clamping circuit for each color Signal is provided with a clamping Voltage generating circuit which is controlled in response to the individual first control Signal and generates a clamping Voltage Such that the black level of a clamped color Signal coincides with the black level in an input/output characteristic of a gamma-correction circuit, and a clamping portion which is Supplied with a clamping Voltage and adds the clamping Voltage to the pedestal level
11 S in a predetermined timing of a color Signal in response to the Second control Signal. And in case that the black level of a picture Signal corresponds to a Setup level higher by a certain Voltage than a pedestal level, the clamping Voltage generating circuit may Set the clamping level at the black level by Setting the value of a digital data Signal corresponding to a clamping Voltage contained in the first control Signal lower by the Setup level portion than the pedestal level. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of a clamping circuit of a conventional liquid crystal display device. FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram Showing the composition of a clamping Voltage generating circuit in FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is an input/output characteristic diagram showing an example of operation of a gamma-correction circuit according to a conventional example. FIG. 4 is a block diagram Showing an embodiment of a clamping circuit of a liquid crystal display device of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing the composition of a clamping portion in FIG. 4. FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing the composition of a clamping Voltage generating circuit in FIG. 4. FIG. 7 is an input/output characteristic diagram showing an example of operation of a gamma-correction circuit according to the present invention. FIG. 8 is a timing chart for explaining a Serial control Signal used in the present invention. FIG. 9 is a timing chart showing an example of operation of a clamping circuit of a liquid crystal display device according to the present invention. FIG. 10 is a timing chart showing an example of wave form of a color Signal containing a Setup level. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Referring to FIG. 4, a preferred embodiment of the present invention is described in which components com mon to FIG. 1 and FIG. 4 are given the common reference characters/numerals and are Similarly represented by blocks. A clamping circuit of a liquid crystal display device of this embodiment shown in FIG. 4 is provided with coupling capacitors 1, 2 and 3 each cutting a direct current (DC) bias in each of the color Signals R, G and B of an inputted picture Signal VI common to the conventional example, gamma correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 for performing predetermined gamma correction and amplification respectively on the clamped color Signals RC, GC and BC and outputting the output color Signals RG, GG and BG, and additionally, clamp units 4, 5 and 6 instead of the conventional clamp units 400, 500 and 600. The clamp units 4, 5 and 6 are respectively controlled by individual control signals PR, QR, PG, QG, PB and QB (hereinafter referred to as control Signals P and Q in case of collectively describing them) for the respective color Signals R, G and B and newly adding predetermined clamping Voltages being the pedestal level of a picture Signal to the AC components of the color Signals. R, G and B and outputting respectively the clamped color Signals RC, GC and BC. A control unit Such as a central processing unit (CPU) 10 generates and Supplies individual control signals PR, QR, PG, QG, PB and QB for the US 6,657,619 B respective color Signals R, G and B to the clamp units 4, 5 and 6 by means of a serial 3-line control method. A memory unit Such as a random access memory (RAM) 11 memorizes data Supplied from the CPU 10 and exchanges data with the CPU 10 by reading and supplying the memorized data to the CPU 10. The clamp unit 4 is provided with a clamping portion 41 controlled by a control Signal PR and a clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 controlled by a control Signal QR. The clamping portion 41 performs a clamping operation of adding a clamping Voltage CR to the AC component of an input color Signal R and outputs the clamped color Signal RC. The clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 generates and outputs a clamping Voltage CR to the clamping portion The clamp unit 5 is provided with a clamping portion 51 controlled by a control Signal PG and a clamping Voltage generating circuit 52 controlled by a control Signal QG. The clamping portion 51 performs a clamping operation of adding a clamping Voltage CG to the AC component of an inputted color Signal G and outputs a clamped color Signal GC. The clamping Voltage generating circuit 52 generates and outputs a clamping Voltage CG to the clamping portion 51. The clamp unit 6 is provided with a clamping portion 61 controlled by a control Signal PB and a clamping Voltage generating circuit 62 controlled by a control Signal QB. The clamping portion 61 performs a clamping operation of adding a clamping Voltage CB to the AC component of an inputted color Signal B and outputs a clamped color Signal BC. The clamping Voltage generating circuit 62 generates and Supplies a clamping Voltage CB to the clamping portion 61. The clamp units 4, 5 and 6 are of the same composition, and referring to FIG. 5 showing with a block diagram the composition of the clamping portion 41 of the clamp unit 4 for a color Signal R as a representative. The clamping portion 41 is provided with a Switch circuit 411 for turning on/off a clamping Voltage CR Supplied from the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 in response to the control of a control signal PR. In the same way, the clamping portions 51 and 61 are respectively provided with Switch circuits. Referring to FIG. 6, the composition of a clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 of the clamp unit 4 for a color Signal R is explained with a block diagram as a represen tative. This clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 is pro vided with a D/A conversion circuit 421 and a buffer circuit 422. D/A conversion circuit 421 is provided for performing a digital-to-analog (D/A) conversion on a digital data signal (hereinafter referred to as a data signal) contained in a control Signal QR and outputting a clamping Signal VR as an analog signal. The buffer circuit 422 has a Voltage follower circuit for buffer-amplifying a clamping Signal VR and outputting a clamping Voltage CR. In the same way, the clamping Voltage generating circuits 52 and 62 for color signals G and B are each provided with a D/A conversion circuit and a buffer circuit. Operation of this embodiment is described with reference to FIG. 4, FIG. 5 and FIG. 6. Here, as a representative, a System for a color Signal R is described. When a color Signal R forming an input picture Signal VI is Supplied, capacitor 1 cuts or deletes a DC bias from the color signal R and Supplies only the AC component (hereinafter referred to as a color Signal RA) of the color Signal R to the clamp unit 4. The clamp unit 4 reproduces the DC bias by clamping the pedestal level portion of the color Signal RA. The clamp unit
12 7 4 clamps the pedestal level Voltage, namely, the black level of the picture Signal R to a clamping Voltage CR from the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 to be given to the clamping portion 41 and then outputs a clamped color Signal RC. AS described later, the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 is composed So as to be able to vary the clamping voltage CR. Referring also to FIG. 7 showing with a graph an input/ output characteristic of the gamma-correction circuit 7, the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 adjusts this process of varying the clamping Voltage CR So that the black level Voltage of the clamped color Signal RC and the black level which the gamma-correction circuit 7 has coincide with each other in order to absorb variation in black level of the gamma-correction circuit 7 itself at a later Stage of the clamping portion 41. AS the result, the gamma-correction circuit 7 comes to be supplied with the black level voltage of a clamped color signal RC which has coincided with the black level which the gamma-correction circuit 7 has. The CPU 10 and the RAM 11 supply a control signal QR to the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 for a color Signal R and control a clamping Voltage CR outputted from the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42. And they Supply a control Signal PR to the clamping portion 41 and control its clamping operation. In the same way, the Systems for color Signals G and B are also of the same composition, reproduce DC bias and output respectively clamped color Signals GC and BC. A control signal Q supplied by the CPU 10 is a serial control Signal of a general 3-line control method as shown in FIG. 8, and is composed of a data Signal, a clock signal and a strobe Signal to be respectively Supplied to a control bus line. In this embodiment, it is assumed that the data Signal is digital data of 8 bits. AS publicly known, the clock Signal is used for Synchronization of the data Signals, and the Strobe Signal is a Selection signal for activating one of the clamping Voltage generating circuits 42, 52 and 62. Here, as described above, a Strobe Signal of a control Signal Q Selects a color Signal R System and this State is called a control Signal QR. Similarly, a State of Selecting a color Signal G System is called QG, and a State of Selecting a color Signal B System is called QB. Namely, a data Signal and a clock Signal are used commonly to R, G and B, and a Strobe Signal is controlled individually in such a way as QR, QG and QB. Referring to FIG. 6, the D/A conversion circuit 421 in the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 D/A-converts a data signal forming a control signal QR sent from the CPU and outputs a clamped color Signal VR. The D/A conversion circuit 421 is a D/A conversion circuit of 8 bits and its output dynamic range is set at 1.22 to 3.77 V. For example, assuming that a data Signal is 80 (Hex), the D/A conversion circuit 421 outputs as a clamping Signal VR a voltage of 2.5 V that is the central value of Said output dynamic range. The buffer circuit 422 is a Voltage follower circuit using a transistor having a Sufficiently large driving capability in its output Stage in order to Secure an output current driving capability for the clamping portion 41, namely, the gamma correction circuit 7 at a later Stage, and buffer-amplifies an inputted clamping Signal VR and outputs a clamping Voltage CR. The reference numeral 3 at the left-hand side of FIG. 6 represents a 3-line Structure composed of a data Signal, a clock signal and a strobe Signal, and it is a matter of course that the number of bits of the data signal out of them is 8 bits. In the same way, with respect to the Systems for the color Signals G and B also, the clamping Voltage generating circuits 52 and 62 operate as described above. Therefore, the US 6,657,619 B black level Voltages of the respective color Signals R, G and B can be controlled independently of one another. Operation of the clamping portion 41 is now described with reference to FIG. 5 and FIG. 9 showing waveform of each Signal of the clamping portion 41 with a timing chart. The clamping portion 41 turns on the Switch circuit 411 in response to the control of a control Signal PR Supplied from the CPU 10, and applies a clamping voltage CR from the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 to only a specific part shown in FIG. 9 of the pedestal level of a color signal RA. The color signal RA comes to be at level of high H for only Said Specific period of the pedestal level of the color Signal RA of one horizontal Scanning period which is one period of a horizontal Synchronizing Signal SH. The level H of a control signal PR to be generated by the CPU 10 can be easily generated by shifting the phase (timing) of the horizontal Synchronizing Signal SH by a predetermined time and inverting the shifted Signal by means of an inverter or the like. The part of the pedestal level is a part where the black level is inserted as a picture Signal in a non-display period of a picture Signal VI, namely, in a non-display period of a color signal RA. The Switch circuit 411 is turned on in response to the level H of a control signal PR. Accordingly, a clamping Voltage CR is Superposed on the black level of a color signal RA for a period where the Switch circuit 411 is on. In Such a way, for a period of the pedestal level of a color Signal R, a black level Voltage comes to be in a State where it is clamped to a fixed clamping Voltage, and is outputted as a clamped color Signal RC. On the other hand, a state where the Switch circuit 411 is turned off by level of low L of a control signal PR attempts to hold a clamping Voltage CR for a fixed period by means of a discharging current from the capacitor 1. However, the circuitry operation is intended to perform this clamping operation in each horizontal Scanning period. Therefore, the black level of a clamped color Signal RC can be always kept constant by optimizing the constant of the capacitor 1. Since the gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 are not directly related to the present invention, explanation of their detailed composition is omitted. Each of the gamma correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 processes as an analog signal each of Supplied clamped color signals RC, GC and BC according to an input/output characteristic curve shown in FIG. 7. The black levels of the gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9 are ideally Set aiming at a specific Voltage, but result in being actually varied among R, G and B or even among the gamma-correction circuits of the Same color due to variation in accuracy of the gamma-correction circuits. AS described in the prior art, therefore, when the black levels of clamped color signals RC, GC and BC are fixed, the black levels of the clamped color signals RC, GC and BC may be different from the black levels of the gamma-correction circuits (see FIG. 3). In Such a state, therefore, a gamma correction cannot be correctly performed. AS described above, however, in order to amend this disadvantage, this embodiment provides the clamping Volt age generating circuits 42, 52 and 62 respectively for the color Signals R, G and B independently of one another and makes it possible to individually adjust the clamping Volt ages CR, CG and CB by means of control signals QR, QG and QB (hereinafter referred to as Q) from the CPU 10 so that the black levels set by the clamp units 4, 5 and 6 can coincide with the black levels of the gamma-correction circuits 7, 8 and 9. More specifically, the RAM 11 is made to store the adjusted and changed digital data value of a control Signal Q
13 9 by combining the CPU 10 and the RAM 11. That is to say, at the beginning of using a display device, the clamping Voltages CR, CG and CB are adjusted by changing the data of a control signal Q So as to meet Said condition as initialization. After completion of the adjustment, each data of the control signal is stored in the RAM 11 as the initialization data. After this, even when power is repeatedly turned on/off, the CPU 10 uses the initialization data stored in the RAM 11 as the data of the control signal Q. Accordingly, it is possible to Solve the problems on display of variation in black level of gamma-correction circuits and Slippage in color caused by Setting of clamping Voltages or fixation of the clamping Voltages performed commonly to color Signals R, G and B. Hereinafter, operation of this embodiment in case that each of the color Signals R, G and B of an input picture Signal VI contains a Setup level is described. With reference to FIG. 10 showing in a timing chart an example of waveform in case that a color Signal R of an input picture Signal VI contains a Setup level, a picture Signal (a color signal R in this example) having a setup level refers to a picture Signal whose black level is Set at a level slightly higher than the pedestal level. Here also, operation of a color Signal R System is described as an example. When a color Signal R having Such a Setup level is inputted into a conventional clamping circuit as described earlier, the clamping portion 41 results in operating So as to clamp the pedestal level, and therefore a level lower than the black level of a gamma-correction circuit 7 results in being recognized as a black level, as described in FIG. 3. As the result, since the black level of a gamma-correction circuit 7 and the black level of a clamped color signal CR become different from each other, a gamma correction is not correctly performed. Furthermore, Since the output of the gamma-correction circuit 7, namely, the black level Voltage of the output color Signal RG becomes a black level slightly slipped toward the white level (whitish), the ratio of a white level to a black level (contrast ratio) results in a deteriorated State. In this embodiment, however, Since the value of a clamp ing Voltage CR to be Supplied to the clamping portion 41 can be changed by the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42, even if a color Signal R containing a Setup level is inputted it is possible to perform adjustment So as to make the black level of a clamped color signal RC and the black level of the gamma-correction circuit 7 coincide with each other. More Specifically, the data value of a control Signal QR to be given to the D/A conversion circuit 421 from the CPU 10 is set lower by a setup level than the pedestal level of a color Signal R, and a clamping Voltage CR outputted from the clamping Voltage generating circuit 42 is set lower by the Setup level. Since this results in clamping the pedestal level of a color signal R to a level lower by a setup level than the pedestal level of an ordinary color Signal R having no Setup level (FIG. 9), it is possible to make the same as each other the black level of a clamped color signal RC when a color Signal R containing this Setup level is inputted and the black level of the gamma-correction circuit 7 at a later Stage. The color Signal G and B Systems are processed in the same way. Accordingly, it is possible to prevent incorrect operation in a gamma-correction circuit and deterioration in contrast ratio. AS described above, according to the present invention, each clamp unit includes a clamping Voltage generating circuit and a clamping portion. The clamping Voltage gen erating circuit generates Such a clamping Voltage that the US 6,657,619 B black level of the above mentioned clamped color Signal coincides with the black level in an input/output character istic of a gamma-correction circuit in response to the first control Signal. The clamping Voltage is individually adjusted and Supplied to the clamping portion. This clamping Voltage is applied to the pedestal level of a color Signal at a predetermined timing in response to the Second control Signal. This makes it possible to perform adjustment So as to make the black level of a color Signal clamped by the clamping circuit coincide with the black level of the gamma correction circuit at a later Stage of the clamping circuit. Accordingly, even if the color signals of the gamma correction circuits vary in black level, it is possible to make the black levels of the clamping Voltages of these color signals R, G and B respectively coincide with the black levels of the respective gamma-correction circuits and thereby preventing incorrect operation of the gamma correction circuits caused by fixedly Setting the clamping Voltages. And Since the operation of making the black level of a clamping circuit and the black level of a gamma-correction circuit coincide with each other is performed by individually adjusting each of the color Signals R, G and B, it is possible to amend individually variation in black level of gamma correction circuits and avoid a coloring phenomenon caused by difference among black level Voltages. Furthermore, Since it is possible to perform a gamma correction correctly reproducing the black level, it is pos Sible to prevent deterioration in contrast caused by variation in black level. What is claimed is: 1. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device comprising: a plurality of clamp units for receiving a plu rality of input color Signals of an input picture Signal after deleting a DC bias from each of Said input color Signals to produce a plurality of clamped color Signals, respectively, by adding a predetermined clamping Voltage corresponding to a pedestal level of Said input picture Signal to each of Said input color Signals, and a plurality of gamma-correction circuits connected to Said clamp units for receiving Said clamped color Signals, respectively, and for performing a predetermined gamma correction and amplification on each of Said clamped color Signals to produce output color Signals, respectively; each of Said clamp units being pro Vided with a clamping portion for receiving Said input color Signal and a clamping Voltage generating circuit for Supply ing a clamping Voltage to Said clamping portion So as to be controlled in response to an individual first control Signal Supplied thereto and generates Said clamped color Signal Such that a black level of Said clamped color Signal coincides with a black level in an input/output characteristic of Said gamma-correction circuit, and Said clamping portion being Supplied with Said clamping Voltage So as to add Said clamping Voltage to Said pedestal level in a predetermined timing of Said input color Signal in response to a Second control Signal Supplied thereto. 2. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein; Said clamping Voltage generating circuit is provided with a digital-to-analog (D/A) conversion circuit for per forming a D/A conversion on a digital data Signal contained in Said first control Signal and outputting an analog Voltage Signal, and a buffer circuit for buffer amplifying Said analog Voltage Signal and outputting Said clamping Voltage. 3. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein;
14 11 Said clamping portion is provided with a Switch circuit for conducting or Shutting Said clamping voltage in response to the level of Said Second control Signal. 4. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, further comprising a control unit for outputting Said first and Second control Signals, and a memory unit for memorizing data from Said control unit and reading and Supplying Said memorized data to Said control unit. 5. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein; Said first control Signal is a Serial control Signal of a 3-line control method and has a digital data Signal corre sponding to Said clamping Voltage So as to be Supplied to three control lines thereof, a clock signal for Syn chronization of Said digital data Signal and a Strobe Signal for Specifying Said clamping Voltage generating circuit to be controlled. 6. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein; Said Second control Signal is a signal which becomes a high level (H) for only a specific period of Said pedestal level of Said input color Signal of one horizontal US 6,657,619 B1 1O Scanning period being one period of a horizontal Syn chronizing Signal, and is generated by Shifting the phase of Said horizontal Synchronizing Signal by a predetermined time and inverting this shifted horizon tal Synchronizing Signal. 7. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein; a black level of Said input picture Signal corresponds to Said pedestal level. 8. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 1, wherein; a black level of Said input picture Signal corresponds to a Setup level which is higher by a fixed voltage than Said pedestal level. 9. A clamping circuit for a liquid crystal display device according to claim 8, wherein; Said clamping Voltage generating circuit Sets Said clamp ing Voltage at Said black level by Setting a value of Said digital data Signal contained in Said first control Signal and corresponding to Said clamping Voltage, lower by Said Setup level than Said pedestal level. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
-/9. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 POWER.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999
 USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al.
 (12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
United States Patent 19
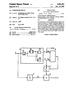 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7760213B2 (12) United States Patent Aoki et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Apr. 5, 2002 (51) (52) (58) CONTRASTADJUSTING CIRCUITRY AND VIDEO DISPLAY APPARATUS USING SAME Inventors:
USOO7760213B2 (12) United States Patent Aoki et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Apr. 5, 2002 (51) (52) (58) CONTRASTADJUSTING CIRCUITRY AND VIDEO DISPLAY APPARATUS USING SAME Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al.
 United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
(12) United States Patent
 US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
D-ILA PROJECTOR DLA-G15 DLA-S15
 D-ILA PROJECTOR DLA-G15 Outstanding Projection Im Breakthrough D-ILA projector offers high-contrast 350:1, 1500 ANSI lumen brightness and S-XGA resolution Large-size projection images with all the sharpness
D-ILA PROJECTOR DLA-G15 Outstanding Projection Im Breakthrough D-ILA projector offers high-contrast 350:1, 1500 ANSI lumen brightness and S-XGA resolution Large-size projection images with all the sharpness
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,733,141 B2
 USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu
 United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
United States Patent (19) Muramatsu 11 Patent Number 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 1989 54 COLOR VIDEO SIGNAL GENERATING DEVICE USNG MONOCHROME AND COLOR MAGE SENSORS HAVING DFFERENT RESOLUTIONS TO FORMA
