(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013
|
|
|
- John Malcolm Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
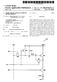
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP /2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i; JP /2004 (75) Inventor: Yang-Wan KlIIl, Suwon-s1 (KR) JP 2005_ /2005 (73) _ JP /2005 Asslgnee: Samsung Display C0., Ltd., Yong1n-s1 JP /2005 (KR) JP /2005 JP /2006 ( * ) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this JP 2007' /2007 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 (Continued) U.S.C. 154(b) by 870 days. (21) Appl. No.: 12/419,875 OTHER PUBLICATIONS _ European Search Report dated Aug. 12, 2009, for corresponding (22) Flled3 APr- 7: 2009 European Patent application (65) Prior Publication Data (Continued) US 2009/ A1 Dec. 17, 2009 Primary Examiner * Sumati LeikowitZ R1 th.s.a l' t' D t e a e PP lea Ion a a Assistant Examineri Jonathan Horner (60) PrOV1slonal apphcatlon No. 61/060,749,?led on Jun. (74) Attorney) Agent) or Firm ichristie, Parker & Hales 11, LLP (51) Int. Cl. G09G 3/30 ( ) (57) ABSTRACT G09G 3/10 ( ) (52) us. Cl /76; 345/77; 315/1693 An organic light emitting display includesr_ scan lines for (58) Field of Classi?cation Search /76483; applylng scan Slgnals; control for applylng control 51% 315/1693; 377/34, 70i73 nals; and data lines for applying data signals. The organic See apphcatlon - -?le for complete search h1story. - li t emittin g dis p la y further _ includes: _ ixels cou _ p led to the scan, control and data 11nes for d1splay1ng an 1mage; power (56) References Cited supply lines coupled to the pixels; and a data driver for sup plying the data signals of the image to the data lines. The US, PATENT DOCUMENTS organic light emitting display also includes: a power supply 2002/ A1 8/2002 Bu driver for swinging a voltage at the power supply lines 2006/ A1 7/2006 Choi et a1, between a?rst level and a second level; a sensing unit includ 2007/ A1 * 2/2007 Chung et al /76 ing a current sink for sinking a?rst current from the pixels and * Egrasg! e: 345/212 a current source for supplying a second current to the pixels; CN CN EP JP 1ras 1 e FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS and a switching unit for selectively electrically coupling the pixels to at least one of the data driver, the current source or the current sink A 6/ A 6/ A2 8/ / Claims, 11 Drawing Sheets D a t a 1 /180 " m T 150 r """""""""""""""" $9" 7*. 1 / 182 / 181 \E 713 : 1111ng i _ Sensing 1. controller 1' controuerr Memory ii ADC circuit H'P/, 140 L... "H ; L ".1: SW2; Data2 I 2. jbit \ : : Plxe] 120 i i / E 1 Data driver {=/ 1 1%-121 J
2 US 8,405,582 B2 Page 2 JP JP JP JP JP JP JP JP KR KR KR KR KR W0 W0 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS / A A A WO 2009/ A1 WO 2010/ A1 3/2007 8/ / /2007 5/2008 3/2009 3/ /2009 7/2005 6/ / /2007 2/2010 7/2009 1/2010 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Korea Of?ce action dated Sep. 28, 2011, for Korean Patent Applica tion No , which claims priorities of the corre sponding U.S. Appl. No. 61/060,749 and US. Appl. No. 12/419,875; 1 page. Japanese Of?ce action dated Dec. 27, 2011, for corresponding Japa nese Patent application , 4 pages. Japanese Of?ce action dated Jul. 3, 2012, for corresponding Japanese Patent application , (4 pages). SIPO Patent Gazette dated Jun. 27, 2012, for corresponding Chinese Patent application , W/English translation ofp. 1, (3 pages). * cited by examiner
3 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 1 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 (RELATED ART) PEG. 1 / 122an
4 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 2 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 150 D t 1 T, / Data2 a 1 'ming L _ 5;? controller j/bit Data di Lcomml Sensin unijt F4180 block 4 { g _ 1 Y T90 Switching unit ~170 D1 D2 Dm l 31 a me CLIJE i - T - r i '&] with ' 110m (12 83 it] L. L -.. l 5 Poweir = ' J L ngw PP? Scan CL3 : L T T ; hpe driver g 0! I H I - pi g driver H Sn 5 5 T :VLn CLn i l I l 5 ELVSS
5 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 3 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 149?riw--MJ 320mm /77
6 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 4 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 Datal lblt \\ Timing _ E :- d controller i i 240 DataZ """""\""""""". jbit \ P1er Data driver
7 U.S. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 5 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B / : Current sink unit \WQ... ADC i 5 Current source unit -- -o/@-_
8
9 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 7 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 811._J (3111 j B High SW1 SW2 SW3 High High Low Sn CLn l VLn SW1 SW2 swa High Low High LOW High
10 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet 8 0f 11 US 8,405,582 B2 FIG. 7C Sn CLn VLII High High.1..._... SW1 LOW SW2 High 3% High
11 US. Patent Mar. 26, 2013 Sheet90f11 US 8,405,582 B2 NM Hg \\\ mem H a», N; _ a! é 6\o..?nd..Emt?u mugom } _ mm: /. _ v P ol w x \:5. vim E % %8 52 mxm NBQQ / A L_r l\t 55% 22 6: mm Em M /?g 58 5% ENE m:. 352 N2 5 N2 05 E \ gm é i,
12 US. Patent h4ar.26,2013 Sheet100f11 US 8,405,582 B2 Q M; 55 mwim hi! 5 gm. a: 33 m2 NE 2 é We as \ 2w N \ lu\o HE: Em E226 1v. Sana. >88»: 22 6: > E3350 a; $812.? E % 1L N35 / w P 53% 52 5% YIIJ us?g 32% 1 gm Em f / =52 53 ENE / EH
13 US. Patent h4ar.26,2013 Sheetllrofll US 8,405,582 B2 g H. 5?. ET > hi a; Velma: EESU 35% 1. g was M. 5% we / 3 F 55m?g 3 E 515% Y a 5 / Ea 5% 5s 52 g,. l, Es Q: 5 N \#5. EM 525 la L. E \ 2w DE hwzobgu 5
14 1 ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION This application claims priority to and the bene?t of US. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/060,749?led Jun. 11, 2008, the entire content of which is incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to an organic light emitting display and a driving method thereof. 2. Discussion of RelatedArt Recently, various?at panel display devices having reduced weight and volume in comparison to cathode ray tubes (CRTs) have been developed. Types of?at panel display devices include a liquid crystal display (LCD), a?eld emis sion display (FED), a plasma display panel (PDP), and an organic light emitting display, etc. An organic light emitting display displays an image using organic light emitting diodes that generate light through recombination of electrons and holes. The organic light emit ting display has an advantage over other?at panel display devices in that it has a high response speed and is driven with low power consumption. FIG. 1 is a circuit view showing a pixel of a conventional organic light emitting display. Referring to FIG. 1, a pixel 4 of a conventional light emit ting display includes an organic light emitting diode (OLED) and a pixel circuit 2 coupled to a data line Dm and a scan line Sn to control the organic light emitting diode (OLED). An anode electrode of the organic light emitting diode (OLED) is coupled to the pixel circuit 2 and a cathode elec trode of the OLED is coupled to a second power supply ELVSS. The pixel circuit 2 controls an amount of current supplied to the OLED in accordance with a data signal sup plied to the data line Dm when a scan signal is supplied to the scan line Sn. To this end, the pixel circuit 2 includes a second transistor M2 coupled between a?rst power supply ELVDD and the OLED, a?rst transistor M1 coupled between the second transistor M2, the data line Dm, and the scan line Sn, and a storage capacitor Cst coupled between a gate electrode and a?rst electrode of the second transistor M2. A gate electrode of the?rst transistor M1 is coupled to the scan line Sn and a?rst electrode of the?rst transistor M1 is coupled to the data line Dm. Further, a second electrode of the?rst transistor M1 is coupled to one terminal of the storage capacitor Cst. Here, the?rst electrode may be either a source electrode or a drain electrode and the second electrode may be the other one of the source electrode or the drain electrode. For example, if the?rst electrode is the source electrode, the second electrode is the drain electrode. The?rst transistor M1 is turned on when the scan signal is applied at its gate to supply the data signal supplied from the data line Dm to the storage capacitor Cst At this time the storage capacitor Cst charges a voltage corresponding to the data signal. The gate electrode of the second transistor M2 is coupled to one side of the storage capacitor Cst and the?rst electrode of the second transistor M2 is coupled to the other side of the storage capacitor Cst and the?rst power supply ELVDD. Further, a second electrode of the second transistor M2 is coupled to the anode electrode of the OLED. The second transistor M2 controls the amount of current?owing from the US 8,405,582 B ?rst power supply ELVDD to the second power supply ELVSS via the OLED in accordance with the voltage value stored in the storage capacitor Cst. At this time, the OLED generates light corresponding to the amount of current sup plied from the second transistor M2. The conventional organic light emitting display may not display an image with desired luminance due to the change in ef?ciency according to the deterioration of the OLED. In practice, the OLED is deteriorated over time so that light with gradually low luminance is generated in response to the same data signal supplied through the data line Dm. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Therefore, it is an aspect according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention to provide an organic light emitting display and a driving methodthereof capable of compensating for a deterioration of organic light emitting diodes and a non-uniform threshold voltage/mobility among driving transistors in different pixel circuits. In an exemplary embodiment according to the present invention, an organic light emitting display includes: a plu rality of scan lines for applying scan signals; a plurality of control lines for applying control signals; a plurality of data lines for applying data signals, the data lines crossing the scan lines and the control lines; a plurality of pixels for displaying an image, the pixels coupled to the scan lines, the control lines and the data lines; a plurality of power supply lines coupled to the pixels; a data driver for supplying the data signals of the image to the plurality of data lines; a power supply driver for swinging a voltage at the power supply lines between a?rst level and a second level; a sensing unit including a current sink con?gured to sink a?rst current from the pixels and a current source con?gured to supply a second current to the pixels; and a switching unit for selectively electrically cou pling the plurality of pixels to at least one of the data driver, the current source or the current sink. Each of the pixels may include: a driving transistor and an organic light emitting diode coupled in series between a cor responding one of the power supply lines and a power source, the organic light emitting diode having an anode coupled to the driving transistor and a cathode coupled to the second power source; a data switch between a corresponding one of the data lines and a control electrode of the driving transistor, the data switch having a control electrode coupled to a cor responding one of the scan lines; a capacitor coupled between the?rst power source and the control electrode of the driving transistor for storing a corresponding one of the data signals; and a control switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the anode of the organic light emitting diode, the control switch having a control electrode coupled to a corresponding one of the control lines. The switching unit may include: a?rst switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the data driver, the?rst switch being adapted to turn on when the data driver supplies the corresponding one of the data signals to the corresponding one of the data lines; a second switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the current source, the second switch being adapted to turn on when the current source supplies the?rst current to the corresponding one of the data lines; and a third switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the current sink, the third switch being adapted to turn on when the current sink receives the second current from the corresponding one of the data lines.
15 3 The current sink may be adapted to detect a?rst voltage corresponding to the?rst current, and the current source may be adapted to detect a second voltage corresponding to the second current. The organic light emitting display may further include a memory for storing the?rst voltage and the second voltage. The organic light emitting display may further include a timing controller adapted to receive external data signals, wherein the timing controller is con?gured to convert the external data signals to the data signals in accordance with the?rst voltage and the second voltage. The?rst voltage may correspond to threshold voltage/ mobility information of the driving transistor. The second voltage may correspond to deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode. The sensing unit may further include an analog-to-digital converter for converting the?rst voltage and the second volt age to digital data prior to storing them in the memory. The voltage applied to the power supply lines while the?rst current?ows may have a level higher than that of a voltage applied to the power supply lines while the second current?ows. In another exemplary embodiment according to the present invention, a method of adjusting luminance of an image dis played on an organic light emitting display is provided. The organic light emitting display includes a plurality of pixels coupled to a plurality of data lines, each of the pixels includ ing a driving transistor and an organic light emitting diode. The method includes: sensing a?rst voltage while a?rst current?ows through the driving transistor of a pixel among the plurality of pixels to a current sink via a corresponding one of the data lines while a?rst voltage is being supplied to a corresponding one of the pixels; sensing a second voltage while a second current?ows from a current source through the organic light emitting diode of the pixel via the corre sponding one of the data lines while a second voltage that is lower than the?rst voltage is being supplied to the corre sponding one of the pixels; and converting external data to a data signal to be applied to the pixel in accordance with the?rst voltage and the second voltage. In another exemplary embodiment according to the present invention, an organic light emitting display includes: a plu rality of pixels coupled to a plurality of data lines, each of the pixels including a driving transistor and an organic light emit ting diode; a current sink for sensing a?rst voltage corre sponding to a?rst current that?ows through the driving transistor of a pixel among the plurality of pixels to the current sink via a corresponding one of the data lines; a current source for sensing a second voltage corresponding to a second cur rent that?ows from the current source through the organic light emitting diode of the pixel via the corresponding one of the data lines; a timing controller for adjusting a data signal to be applied to the pixel in accordance with the?rst voltage and the second voltage; and a power supply line driver for sup plying power to the pixels, wherein the power supplied while the?rst voltage is being sensed has a higher voltage than that of the power supplied while the second voltage is being sensed. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The accompanying drawings, together with the speci?ca tion, illustrate exemplary embodiments of the present inven tion, and, together with the description, serve to explain the principles of the present invention. FIG. 1 is a view showing a pixel of a conventional organic light emitting display; US 8,405,582 B FIG. 2 is a view showing an organic light emitting display according to an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion; FIG. 3 is a view showing an embodiment of a pixel shown in FIG. 2; FIG. 4 is a view showing in detail a switching unit, a sensing unit, and a control block shown in FIG. 2; FIG. 5 is a view showing a sensing circuit shown in FIG. 4; FIG. 6 is a view showing a data driver shown in FIG. 2; FIGS. 7A, 7B and 7C are views showing a driving wave form supplied to a pixel and a switching unit in an exemplary embodiment according to the present invention; and FIGS. 8A, 8B and 8C are views that show a data driver, a timing controller, a control block, a sensing unit, a switching unit, and a pixel, and a current?ow corresponding to the waveforms of FIGS. 7A, 7B and 7C, respectively. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, certain exemplary embodiments according to the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. Here, when a?rst element is described as being coupled to a second element, the?rst element may be directly coupled to the second element, or may be indirectly coupled to the second element via a third element. Further, some of the elements that are not essential to the complete understanding of the invention are omitted for clarity. Also, like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout. Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying draw mgs. FIG. 2 is a view showing an organic light emitting display according to an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion. Referring to FIG. 2, the organic light emitting display according to an exemplary embodiment of the present inven tion includes a display unit 130 having pixels positioned at crossing regions of scan lines S1 to Sn and data lines D1 to Dm; a scan driver 110 for driving scan lines S1 to Sn and control lines CL1 to CLn; a power supply line driver 160 for driving power supply lines VL1 to VLn; a data driver 120 for driving data lines D1 to Dm; and a timing controller 150 for controlling the scan driver 110, the data driver 120 and the power supply line driver 160. The organic light emitting display also includes a sensing unit 180 for extracting deterioration information of an organic light emitting diode included in each pixel 140 and threshold voltage/mobility information of a driving transistor; a switch ing unit 170 for selectively coupling the sensing unit 180 and the data driver 120 to the data lines D1 to Dm; and a control block 190 for storing information sensed by the sensing unit 180. The display unit 130 includes the pixels 140 positioned at the crossing regions of the scan lines S1 to Sn and the data lines D1 to Dm. The pixels 140 are supplied with?rst power ELV L)L) through the power supply lines VB and are supplied with second power ELVSS from the outside. Each of the pixels 140 supplied with the?rst power ELVDD and the second power ELVSS controls the amount of current supplied from the?rst power ELVDD to the second power ELVSS via the organic light emitting diode. Then, light with luminance corresponding to the current is generated in the organic light emitting diode. The scan driver 110 drives the scan lines S1 to Sn and the control lines CL1 to CLn in accordance with the control by
16 5 the timing controller 150. Also, the data driver 120 supplies data signals to the data lines D1 to Dm in accordance with the control by the timing controller 150. The data signals may have values ranging from +8V to +13V in one embodiment, for example. The switching unit 170 selectively couples the sensing unit 180 and the data driver 120 to the data lines D1 to Dm. To this end, the switching unit 170 includes at least one switching device coupled (to each of the data lines D1 to Dm. In other words, at least one switching device is provided per channel (or data line) to selectively couple the sensing unit 180 or the data driver 120 to the data line. The sensing unit 180 extracts the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode included in each pixel 140 and supplies the extracted deterioration information to the control block 190. Also, the sensing unit 180 extracts the threshold/mobility information of the driving transistor included in each pixel 140 and supplies the extracted thresh old voltage/mobility information to the control block 190. To this end, the sensing unit 180 includes the sensing circuit coupled to each of the data lines D1 to Dm. In other words, the sensing unit 180 may have a sensing circuit per channel (e.g., per data line). The control block 190 stores the deterioration information and the threshold voltage/mobility information supplied from the sensing unit 180. In one embodiment, the control block 190 stores the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode and the threshold voltage/mobility informa tion of the driving transistor included in each of the pixels. To this end, the control block 190 in one embodiment includes a memory and a controller for transferring the information stored in the memory to the timing controller 150. The timing controller 150 controls the data driver 120, the scan driver 110, and the control line driver 160. Also, the timing controller 150 generates second data Data2 by con verting bit value of?rst data Data1 input from the outside, in accordance with the information supplied from the control block 190. In one embodiment, the number of bits in the?rst data Data1 is i (i is a natural number) and the number of bits in the second data Data2 is j (j is a natural number having a value of i or more). In one embodiment, i:8; in other embodi ments, i may be 6, 8 or 10. In one embodiment, j:8 or 10; in other embodiments,j may be 6, 8, 10 or 12. The second data Data2 generated by the timing controller 150 is supplied to the data driver 120. Then, the data driver 120 uses the second data Data2 to generate the data signal and supplies the generated data signal to the pixels 140. The power supply line driver 160 supplies voltage of a high-level?rst power ELVDD or a low-level?rst power ELVDD to the power supply lines VL1 to VLn. Although the power supply line driver 160 is coupled to the power supply lines VL1 to VLn positioned in parallel with the scan lines S1 to Sn in FIG. 2, the present invention is not limited thereto. For example, the power supply lines VL1 to VLn may be coupled to the power supply line driver 160 and be in parallel wi e a a ines o m. FIG. 3 is a view showing an embodiment of a pixel 140 shown in FIG. 2. For convenience of description, FIG. 3 shows a single pixel coupled to an m data lines Dm and an nth scan line Sn. Referring to FIG. 3, the pixel 140 according to one embodi ment of the present invention includes an OLED and a pixel circuit 142 for supplying current to the OLED. The anode electrode of the OLED is coupled to the pixel circuit 142 and the cathode electrode of the OLED is coupled US 8,405,582 B to the second power supply ELVSS. The OLED generates light having luminance corresponding to current supplied by the pixel circuit 142. The pixel circuit 142 is supplied with the data signal from the data line Dm when the scan signal is supplied to the scan line Sn. Also, the pixel circuit 142 provides at least one of the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED or the threshold voltage/mobility information of the driving transistor (i.e., the second transistor M2) when the control signal is supplied to the control line CLn. To this end, the pixel circuit 142 includes three transistors M1, M2 and M3 and a storage capacitor Cst. A gate electrode of the?rst transistor M1 is coupled to the scan line Sn and a?rst electrode of the?rst transistor M11 is coupled to the data line Dm. Further, a second electrode of the?rst transistor M1 is coupled to a?rst terminal of the storage capacitor Cst. The?rst transistor M1 is turned on when the scan signal is supplied to the scan line Sn. Here, the scan signal is supplied in a period (e.g., a?rst period) where the threshold voltage/mobility information is sensed and in a period (e.g., a third period) where the data signal is supplied to the storage capacitor Cst. A gate electrode of the second transistor M2 is coupled to the?rst terminal of the storage capacitor Cst and a?rst elec trode of the second transistor M2 is coupled to the second terminal of the storage capacitor Cst and the power supply line VLn. The second transistor M2 controls the amount of current that?ows from the high-level?rst power supply ELVDD to the second power supply ELVSS via the organic light emitting diode OLED in accordance with the value of the voltage stored in the storage capacitor Cst. The OLED generates light corresponding to the amount of current sup plied from the second transistor M2. A gate electrode of the third transistor M3 is coupled to the control line CLn and a?rst electrode of the third transistor M3 is coupled to a second electrode of the second transistor M2. Also, a second electrode of the third transistor M3 is coupled to the data line Dm. The third transistor M3 is turned on when the control signal is supplied to the control line CLn (i.e., when a low level control signal is applied at its gate). When the control signal is not supplied, the third transistor M3 is turned off. Here, the control signal is supplied during a period (e.g., a second period) in which the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED is sensed and a period (e.g., the?rst period) in which the threshold voltage/ mobility information of the second transistor M2 is sensed. FIG. 4 further illustrates the switching unit 170, the sensing unit 180, and the control block 190 shown in FIG. 2. For convenience of description, FIG. 4 shows a connection con?guration of the switching unit 170, the sensing unit 180, and the control block 190 with the mth data line Dm and one of the pixels 140 coupled to the mth data line Dm. Referring to FIG. 4, three switching devices SW1, SW2 and SW3 are provided in each channel of the switching unit 170. Further, each channel of the sensing unit 180 includes a sensing circuit 181 and an analog-digital converter (herein after, referred to as ADC ) 182. In this and other embodi mens,eac may es are yapuraiyo cannesor a single ADC may be shared by all of the channels. Also, the control block 190 includes a memory 191 and a controller 192. The number of bits of sensed data generated by ADC may be 8 in one embodiment. The?rst switching device SW1 is positioned between the data driver 120 and the data line Dm. The?rst switching device SW1 is turned on when the data signal is supplied from the data driver 120. In other words, the?rst switching device SW1 maintains the tum-on state at least during a period (e. g.,
17 7 the third period) in which the data signal is provided to the pixel 140 (or while the organic light emitting display displays an image). The sensing circuit 181 includes a current sink 185 and a current source 186 as shown in FIG. 5. The current sink 185 sinks a?rst current from the pixel 140 when the high-level?rst power supply ELVDD is supplied to the power supply line VLn and supplies a corresponding voltage generated in the data line Dm to the ADC 182 when the?rst current is sunk. Here, the?rst current is sunk via the second transistor M2 included in the pixel 140. Therefore, the voltage (i.e., a?rst voltage) of the data line Dm generated by the current sink 185 has the threshold voltage/mobility infor mation of the second transistor M2. The?rst voltage may have a value of between 5V and 8V, for example. The current value of the?rst current may be set variously to apply a reference voltage (e. g., a predetermined voltage) within a de?ned time (e.g., 4 us). For example, the?rst current may be set to the value of a current (e.g., l ua) to be?owed to the OLED when the pixel 140 is light-emitted at maximum lumi nance. The current source 186 supplies a second current to the pixel 140 when the low-level?rst power supply ELVDD is supplied to the power supply line VLn and supplies a second voltage generated across the OLED to the ADC 182 when the second current is supplied. The second voltage may be between 8V and 10V, for example. Here, since the second current is supplied via the OLED, the second voltage has the deterioration information of the OLED. In more detail, as the OLED is deteriorated, the resistance value of the OLED is changed (e.g., increased). Therefore, the voltage value of the second voltage is changed corresponding to the deterioration of the OLED so that the deterioration information of the OLED can be extracted. In the described embodiment, the current value of the second current is experi mentally determined to be able to apply a predetermined voltage prior to the deterioration. For example, in one exem plary embodiment, the second current may be set to have the same current value as the?rst current. The ADC 182 converts the?rst voltage supplied from the sensing circuit 181 to a?rst digital value and converts the second voltage to a second digital value. The memory 191 of the control block 190 stores the?rst digital value and the second digital value supplied from the ADC 182. In practice, the memory 191 stores the threshold voltage/mobility information of the second transistor M2 and the deterioration information of the OLED of each of the pixels 140 included in the display unit 130. The controller 192 transfers the?rst digital value and the second digital value stored in the memory 191 to the timing controller 150. Here, the controller 192 transfers to the timing controller 150 the?rst digital value and the second digital value extracted from the pixel 140 that will receive the second data Data2 corresponding to the?rst data Data1 input to the timing controller 150. The timing controller 150 is supplied with the?rst data Data1 from the outside and the?rst digital value and the I value changes the bit value of the?rst data Data1 to the second data Data2 so that the image with uniform luminance can be displayed. In other words, in one embodi ment, the timing controller 150 converts the?rst data Data1 to the second data Data2 using the?rst and second digital values such that the?rst data Data1 having the same value will result in substantially the same luminance in each of the same color pixels 140 regardless of the variation in the threshold voltage/ mobility and over time regardless of the OLED deterioration. US 8,405,582 B For example, in one embodiment, the timing controller 150 decreases the bit value of the?rst data Data1 as the OLED is deteriorated based on the second digital value to generate the second data Data2. Then, the second data Data2 is generated re?ecting the deterioration information of the OLED and thus, the generation of light with low luminance resulting from the OLED deterioration is prevented. Also, the timing controller 150 generates the second data Data2 to compensate for the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 based on the?rst digital value so that the image with substan tially uniform luminance can be displayed regardless of the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2. The data driver 120 generates the data signal using the second data Data2 and supplies the generated data signal to the pixel 140. FIG. 6 is a view showing the data driver 120 according to one exemplary embodiment. Referring to FIG. 6, the data driver 120 includes a shift register unit 121, a sampling latch unit 122, a holding latch unit 123, a signal generator 124, and a buffer unit 125. The shift register unit 121 receives a source start pulse SSP and a source shift clock SSC from the timing controller 150. The shift register unit 121 then shifts the source start pulse SSP per one period of the source shift clock SSC to sequen tially generate m sampling signals. To this end, the shift register unit 121 includes m shift registers 1211 to 121m. The sampling latch unit 122 sequentially stores second data Data2 in response to the sampling signals sequentially supplied from the shift register unit 121. To this end, the sampling latch unit 122 includes m sampling latches 1221 to 121m in order to store m second data Data2. The holding latch unit 123 receives a source output enable signal SOE from the timing controller 150. The holding latch unit 123 then receives and stores second data Data2 from the sampling latch unit 122. Further, the holding latch unit 123 supplies the second data Data2 stored therein to the signal generator 124. To this end, the holding latch unit 123 includes m holding latches 1231 to 123m. The signal generator 124 receives the second data Data2 from the holding latch unit 123 and generates m data signals corresponding to the received second data Data2. To this end, the signal generator 124 includes m digital-analog converters (hereinafter, referred to as DAC ) 1241 to 124m. That is, the signal generator 124 generates the m data signals using the DACs 1241 to 124m each positioned at a corresponding chan nel and supplies the generated data signals to the buffer unit 125. The buffer unit 125 supplies the m data signals supplied from the signal generator 124 to each of m data lines D1 to Dm. To this end, the buffer unit 125 includes m buffers 1251 to 125m. FIGS. 7A to 7C are views showing driving waveforms supplied to a pixel and a switching unit. FIG. 7A shows a waveform diagram during the?rst period for sensing threshold voltage/mobility of the second transis tor M2 included in the pixels 140. The scan driver 1 10 sequen ' a Q a Q C I ' a sensing period of the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 included in the pixels 140. For example, the scan signals may have a high voltage of +l4v and a low voltage of 2V in one embodiment. Also, when the scan signal is supplied to k (k is a natural number) scan line Sk, the scan driver 110 supplies a control signal to a k control line CLk. For example, the control signals may have a high voltage of +l4v and a low voltage of 2V in one embodi ment.
18 The power supply line driver 160 supplies the voltage of the high-level?rst power supply ELVDD to the power supply lines VL1 to VL. Here, the voltage value (e.g., 12V) of the high-level?rst power supply ELVDD is set to a value higher than the voltage value (e. g., 0V) of the second power supply ELVSS so that current may?ow in the second transistor M2. Meanwhile, the third switching device SW3 maintains a tum on state during the sensing period of the threshold voltage/ mobility of the second transistor M2. An operation process will be described in detail with ref erence to FIGS. 7A and 8A. First, when the scan signal is supplied to the scan line Sn, the?rst transistor M1 is turned on. When the?rst transistor M1 is turned on, the gate elec trode of the second transistor M2 and the data line Dm are electrically coupled. And, the third transistor M3 is turned on by the control signal supplied to the control line CLn in synchronization with the scan signal. At this time, the current sink 185 sinks the?rst current (shown in FIG. 8A) from the?rst power supply ELVDD via the second transistor M2, the third transistor M3, and the third switching device SW3. When the?rst current is sunk in the?rst sink unit 185, the?rst voltage is applied to the current sink 185. Here, since the?rst current is sunk via the second transistor M2, information on the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 is included in the?rst voltage. For example, in one embodiment, the voltage applied to the gate electrode of the second transistor M2 is used as the?rst voltage. The?rst voltage applied to the current sink 185 is con verted to a?rst digital value in the ADC 182 to be supplied to the memory 191. Accordingly, the?rst digital value is stored in the memory 191. Through such a process, the?rst digital value including the information on the threshold voltage/ mobility of the second transistor M2 included in each of the pixels 140 is stored in the memory 191. In the described embodiment of the present invention, a process for sensing the threshold voltage/mobility of the sec ond transistor M2 may be performed more than once before the organic light emitting display is used. For example, before the organic light emitting display is shipped, it is possible to sense the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 to store it in the memory 191. Also, the process for sensing the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transis tor M2 may be performed at the time of user s designation. FIG. 7B shows a waveform diagram during the second period for sensing deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode included in each of the pixels. The scan driver 110 sequentially supplies the control sig nals to the control lines CL1 to CLn during a sensing period of the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED included in each of the pixels 140. The second switching device SW2 maintains a tum-on state during the sensing period of the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED. Also, the power supply line driver 160 supplies the low-level?rst power ELVDD to the power supply lines VL1 to VLn during the sensing period of the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED. Here, the low-level?rst power ELVDD is set to a voltage capable of turning off the second transistor M2. For example, the low level?rst power ELVDD may be set to the same voltage as the second power ELVSS. An operation process will be described in detail with ref erence to FIGS. 7B and 8B. First, when the control signal is supplied to the control line CLn, the third transistor M3 is turned on. When the third transistor M3 is turned on, the organic light emitting diode OLED and the data line Dm are electrically coupled to each other. US 8,405,582 B In this case, the second current supplied by the current source 186 is supplied to the organic light emitting diode OLED via the second switching device SW2 and the third transistor M3. At this time, when the second current is sup plied, the current source 186 senses the second voltage applied to the organic light emitting diode OLED and sup plies the sensed second voltage to the ADC 182. The ADC 182 converts the second voltage supplied from the current source 186 to a second digital value to supply it to the memory 191. Accordingly, the second digital value is stored in the memory 191. Through such a process, the second digital value including deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED included in each of the pixels 140 is stored in the memory 191. In the described embodiment of the present invention, the process for sensing the organic light emitting diode OLED may be performed at a time prede?ned by a designer. For example, the deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode OLED may be sensed whenever power is supplied to the organic light emitting display. FIG. 7C shows a waveform diagram for the third period for performing a normal display operation. During the normal display operation period, the scan driver 110 sequentially supplies the scan signals to the scan lines S1 to Sn, and does not supply the control signals to the control lines CL1 to CLn. During the normal display operation period, the power line driver 160 supplies the high-level?rst power ELVDD to the power supply lines VL1 to VLn. Fur ther, during the normal display operation period, the?rst switching device SW1 maintains the turn-on state. An operation process will be described in detail with ref erence to FIGS. 7C and 8C. First, the?rst data Data1 to be supplied to the pixel 140 coupled to the data line Dm and the scan line Sn is supplied to the timing controller 150. At this time, the controller 192 supplies the?rst digital value and the second digital value extracted from the pixel 140 coupled to the data line Dm and the scan line Sn to the timing controller 150. After receiving the?rst and second digital values, the tim ing controller 150 modi?es a bit value of the?rst data Data1 to generate the second data Data2. Here, the second data Data2 is set so that the deterioration of the organic light emitting diode OLED and the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 may be compensated for. For example, when the?rst data of is input, the timing controller 150 can generate the second data Data2 of so that the deterioration of the organic light emitting diode OLED may be compensated for. In this case, since the data signal for displaying the image of a high lumi nance is generated corresponding to the second data Data2, the deterioration of the organic light emitting diode OLED may be compensated for. Likewise, the timing controller 150 controls the bit value of the second data Data2 so that the deviation in the thresholdvoltage/mobility of the second tran sistor may be compensated for. The second data Data2 generated by the timing controller 150 is supplied to the DAC 124m via the sampling latch 122m and the hold latch 123m. In this case, the DAC 124m gener ates the data signal using the second data Data2 and supplies the generated data signal to the data line Dm via the buffer 125m. Here, since the scan signal is supplied to the scan line Sn so that the?rst transistor M1 is turned on, the data signal sup plied to the data line Dm is supplied to the gate electrode of the second transistor M2. At this time, the storage capacitor Cst is charged with the voltage corresponding to the data signal.
19 11 Thereafter, the supply of the scan signal is stopped so that the?rst transistor M1 is turned off. At this time, the second transistor M2 supplies the current corresponding to the volt age charged in the storage capacitor Cst to the organic light emitting diode OLED. In this case, the organic light emitting diode OLED generates light with a luminance corresponding to the amount of current supplied thereto. Here, the current supplied to the organic light emitting diode OLED is set so that the deterioration of the organic light emitting diode OLED and the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 may be compensated for. Therefore, it is possible to uniformly display the image with a desired luminance. In other words, in one embodiment, the same color OLED would generate substantially the same lumi nance corresponding to the same data Data1 regardless of the threshold voltage/mobility of the second transistor M2 and the deterioration status of the OLED. While the present invention has been described in connec tion with certain exemplary embodiments, it is to be under stood that the present invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but, on the contrary, is intended to cover vari ous modi?cation and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit and scope of the appended claims, and equivalents thereof. What is claimed is: 1. An organic light emitting display comprising: a plurality of scan lines for applying scan signals; a plurality of control lines for applying control signals; a plurality of data lines for applying data signals, the data lines crossing the scan lines and the control lines; a plurality of pixels for displaying an image, the pixels coupled to the scan lines, the control lines and the data lines; a plurality of power supply lines coupled to the pixels; a data driver for supplying the data signals of the image to the plurality of data lines; a power supply driver for swinging a voltage at the power supply lines between a?rst level and a second level; a sensing unit comprising a current sink con?gured to sink a?rst current from the pixels and a current source con?gured to supply a second current to the pixels, the current source being separate from the current sink and the power supply driver; and a switching unit for selectively electrically connecting the plurality of pixels to the data driver, the current source and the current sink to allow a current to?ow between the pixels and the connected one of the data driver, the current source, and the current sink, wherein the voltage applied to the power supply lines while the?rst current?ows has a level higher than that of a voltage applied to the power supply lines while the sec ond current?ows. 2. The organic light emitting display of claim 1, wherein each of the pixels comprises: a driving transistor and an organic light emitting diode coupled in series between a corresponding one of the power supply lines and a power source, the organic light emitting diode having an anode coupled to the driving transistor and a cathode coupled to the second power source; a data switch between a corresponding one of the data lines and a control electrode of the driving transistor, the data switch having a control electrode coupled to a corre sponding one of the scan lines; a capacitor coupled between a?rst power source and the control electrode of the driving transistor for storing a corresponding one of the data signals; and US 8,405,582 B a control switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the anode of the organic light emitting diode, the control switch having a control electrode coupled to a corresponding one of the control lines. 3. The organic light emitting display of claim 2, wherein the switching unit comprises: a?rst switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the data driver, the?rst switch being adapted to turn on when the data driver supplies the corresponding one of the data signals to the corresponding one of the data lines; a second switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the current source, the second switch being adapted to turn on when the current source supplies the?rst current to the corresponding one of the data lines; and a third switch between the corresponding one of the data lines and the current sink, the third switch being adapted to turn on when the current sink receives the second current from the corresponding one of the data lines. 4. The organic light emitting display of claim 1, wherein the current sink is adapted to detect a?rst voltage correspond ing to the?rst current, and the current source is adapted to detect a second voltage corresponding to the second current. 5. The organic light emitting display of claim 4, further comprising a memory for storing the?rst voltage and the second voltage. 6. The organic light emitting display of claim 4, further comprising a timing controller adapted to receive external data signals, wherein the timing controller is con?gured to convert the external data signals to the data signals in accor dance with the?rst voltage and the second voltage. 7. The organic light emitting display of claim 4, wherein the?rst voltage corresponds to threshold voltage/mobility information of a driving transistor. 8. The organic light emitting display of claim 4, wherein the second voltage corresponds to deterioration information of the organic light emitting diode. 9. The organic light emitting display of claim 4, wherein the sensing unit further comprises an analog-to-digital con verter for converting the?rst voltage and the second voltage to digital data prior to storing them in a memory. 10.Amethod of adjusting luminance of an image displayed on an organic light emitting display comprising a plurality of pixels coupled to a plurality of data lines, each of the pixels comprising a driving transistor and an organic light emitting diode, the method comprising: sensing a?rst sensed voltage while a?rst current?ows through the driving transistor of a pixel among the plu rality of pixels to a current sink via a corresponding one of the data lines while a?rst supply voltage is being supplied to a corresponding one of the pixels; sensing a second sensed voltage while a second current?ows from a current source through the organic light emitting diode of the pixel via the corresponding one of the data lines while a second supply voltage that is lower than the?rst supply voltage is being supplied to the corresponding one of the pixels; and converting external data to a data signal to be applied to the pixel in accordance with the?rst sensed voltage and the second sensed voltage. 11. The method according to claim 10, further comprising converting the?rst sensed voltage and the second sensed voltage to digital data and storing the digital data in a memory. 12. The method according to claim 10, wherein the organic light emitting display further comprises a switching unit coupled to the data lines, the switching unit comprising a
20 US 8,405,582 B plurality of switches for selectively electrically coupling the through the organic light emitting diode of the pixel via data lines to at least one of a sensing unit for sensing the?rst the corresponding one of the data lines; and second sensed voltages or a data driver for supplying the a timing controller for adjusting a data signal to be applied data Signal to the pixe1_ to the pixel in accordance with the?rst voltage and the 13 An organic light emitting display comprising" ' ' 5 second VOltage;-and - - a power supply line dr1ver for supply1ng power to the a plurality of pixels coupled to a plurality of data lines, each 0f the PixelS comprising a driving IraHSiSIOI and an Organic light emitting diode; a current sink for sensing a?rst voltage corresponding to a 10?rst current that?ows through the driving transistor of a pixel among the plurality of pixels to the current sink via a corresponding one of the data lines;. rality of data lines. a current source for sens1ng a second voltage correspond ing to a second current that?ows from the current source * * * * * pixels, wherein the power supplied Wh?e the?rst volt age is being sensed has a higher voltage than that of the power supplied while the second voltage is being sensed 14- The organic light emitting display Of Claim 13> further COmPr 15mg a data driver for supplying the adjuswd data Sig nal to a data line corresponding to the pixel among the plu
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
III. United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 5,329,314. Jul. 12, ) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: FILTER FILTER P2B AVERAGER
 United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
United States Patent 19
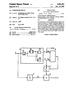 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. KO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008
 US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al.
 (12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis
 IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017.0024602A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0024602A1 HAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2017 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR INTEGRATED TYPE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2017.0024602A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0024602A1 HAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2017 (54) FINGERPRINT SENSOR INTEGRATED TYPE (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2. Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013
 USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2
 USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,020,022 B2. Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited
 United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(73) Assignee. SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO.,LTD.(KR) ' ' ' ' " Gools
 USOO9420363B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.420,363 B2 Seo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2016 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USPC... 381/333 See application file for complete search history.
USOO9420363B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.420,363 B2 Seo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2016 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USPC... 381/333 See application file for complete search history.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,733,141 B2
 USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O295827A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0295827 A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
