2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch AD723
|
|
|
- Collin Owens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 a FEATURES Low Cost, Fully Integrated Solution for NTSC/PAL Composite and Y/C (S-Video) Outputs Current Output Drives 75 Loads DC-Coupled: Supports TV Load Detect No Large AC-Coupling Capacitors at Output Self-Power-Down of Unloaded Output Drivers Triple Switch to Enable RGB Termination Integrated Delay Line and Auto-Tuned Filters Y-Trap to Eliminate Cross Color Artifacts 3 V Supply Operation: Low Power < 00 mw: Composite Active (Typical) < 50 mw: S-Video Active (Typical) < A: Power-Down Current APPLICATIONS TV Out for Personal Computers/Laptops Digital Cameras Set-Top Boxes Video Games Internet Appliances PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The AD723 is a low cost RGB-to-NTSC/PAL encoder that converts analog red, green, and blue color component signals into their corresponding luminance and chrominance signals for display on an NTSC or PAL television. Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C) signals are available individually for S-video, 2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch AD723 or combined for composite video (CV). All outputs are available separately and optimized for driving 75 Ω loads. Active termination is used for lower power consumption. A smart load detect feature powers down unused outputs and can be used to monitor the continuing presence or absence of an external TV. This enables plug-and-play operation. In addition, a logic controlled triple switch at the input solves the applications problem of differing load conditions when an RGB monitor is disconnected. When an RGB monitor is not present, the R, G, and B terminations are enabled by the user. This solution ensures no loss of video bandwidth when the RGB monitor is in operation. In PC applications, flicker filter support is provided by the graphics controller, which has direct access to memory. Underscan compensation, necessary for uses other than video or DVD, is supported through choice of RGB output clocks and sync intervals. An optional luminance trap (YTRAP) provides a means of reducing cross color artifacts due to subcarrier frequency information in the Y signal. The AD723 is available in a 28-lead TSSOP package and is capable of operation from supplies of 2.7 V to 5.5 V. FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM TRIPLE INPUT TERMINATION RIN RT GND GIN GT BIN BT TERM GND GND 4FSC HSYNC VSYNC DC CLAMP DC CLAMP DC CLAMP RGB-TO-YUV ENCODING MATRIX Y U V QUADRATURE DECODER SYNC SEPARATOR 4-POLE LPF CSYNC 4-POLE LPF BURST 4-POLE LPF BURST FSC BURST CSYNC SIN 8FSC CLK LUMA DELAY LINE BALANCED MODULATORS COS STND 4-POLE LPF 4-POLE LPF AD723 CE CURRENT OUTPUT DRIVERS WITH SMART LOAD DETECT LUMA TRAP TV DETECT LUMINANCE COMPOSITE CHROMINANCE GAIN SET RESISTORS Y Y TRAP CV C YSET CSET CVSET Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. One Technology Way, P.O. Box 906, Norwood, MA , U.S.A. Tel: 78/ World Wide Web Site: Fax: 78/ Analog Devices, Inc., 2000
2 * PRODUCT PAGE QUICK LINKS Last Content Update: 02/23/207 COMPARABLE PARTS View a parametric search of comparable parts. EVALUATION KITS AD723 Evaluation Board DOCUMENTATION Application Notes AN-205: Video Formats and Required Load Terminations Data Sheet AD723: 2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch Data Sheet SOFTWARE AND SYSTEMS REQUIREMENTS AD72X Evaluation Board Software DESIGN RESOURCES AD723 Material Declaration PCN-PDN Information Quality And Reliability Symbols and Footprints DISCUSSIONS View all AD723 EngineerZone Discussions. SAMPLE AND BUY Visit the product page to see pricing options. TECHNICAL SUPPORT Submit a technical question or find your regional support number. DOCUMENT FEEDBACK Submit feedback for this data sheet. This page is dynamically generated by Analog Devices, Inc., and inserted into this data sheet. A dynamic change to the content on this page will not trigger a change to either the revision number or the content of the product data sheet. This dynamic page may be frequently modified.
3 SPECIFICATIONS (V S = 3, T A = 25 C, using 4FSC synchronous clock unless otherwise noted. Signal inputs terminated with 75. Outputs configured in active termination mode, 75 external load.) Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit SIGNAL INPUTS (RIN, GIN, BIN) Input Amplitude Full-Scale 74 mv p-p Clamp Level 400 mv Input Resistance RIN, GIN, BIN MΩ Input Capacitance 5 pf TERMINATION SWITCH CHARACTERISTICS (RT, GT, BT) Input Capacitance VIN = 0 V 6 pf Switch On Resistance VIN = 0 V 5.2 Ω LOGIC INPUTS (STND, SA, CE, TERM, SYNC, 4FSC) Logic LO Input Voltage V Logic HI Input Voltage 2 V Logic LO Input Current (DC) µa Logic HI Input Current (DC) µa VIDEO OUTPUTS Luminance (Y) 3 db Bandwidth, NTSC Mode NTSC 4.7 MHz PAL 6. MHz Gain Error Direct Input Termination % Switch Input Termination 0.7 % Gain Nonlinearity 0.3 % Sync Amplitude NTSC mv PAL mv DC Black Level NTSC 450 mv PAL 450 mv Chrominance (C) Burst Amplitude NTSC mv p-p PAL mv p-p Chroma Level Error Switch Input Termination 4 % Chroma Phase Error 2 ± 3 Degree Color Burst Width NTSC 2.5 µs PAL 2.26 µs Chroma/Luma Time Alignment 9 ns Chroma Feedthrough RGB = mv p-p DC Black Level NTSC 66 mv PAL 608 mv Composite (CV) Gain Error Direct Input Termination % Switch Input Termination 0.75 % Gain Error wrt LUMA Direct Input Termination 0.4 % Differential Gain Error wrt CRMA 0.9 % Differential Phase Error wrt CRMA 0.95 Degree DC Black Level NTSC 456 mv PAL 440 mv Luminance Trap (YTRAP) Output Resistance.4 kω LOGIC OUTPUT (TVDET) LO Output Voltage 0.02 V HI Output Voltage 2.98 V POWER SUPPLIES Operating Voltage Range Single Supply V Current Consumption Quiescent No External Loads Present 6 9 ma Composite Output Connected 3 75 Ω Load, Active Termination, ma S-Video Inactive S-Video Output Connected 3 75 Ω Load, Active Termination, 4 49 ma Composite Output Inactive Power-Down Current µa NOTES Difference between ideal and actual color-bar subcarrier amplitudes. 2 Difference between ideal and actual color-bar subcarrier phase. 3 Current consumption is larger in standard termination mode. Current values shown for 50% average picture level. Larger current consumption possible for other levels. Specifications subject to change without notice. 2
4 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS* Supply Voltage, AVDD to AGND V Supply Voltage, DVDD to DGND V AVDD to DVDD V to +0.3 V AGND to DGND V to +0.3 V Inputs DGND 0.3 to DVDD V Internal Power Dissipation mw Operating Temperature Range C to +85 C Storage Temperature Range C to +25 C Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) C *Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS 28-lead TSSOP package: θ JA = 67.7 C/W. Thermal Resistance measured on SEMI standard 4-layer board. PIN CONFIGURATION STND SA CE TERM RIN AGND 27 YSET 26 Y 25 AVDD 24 CSET GIN 6 AD C BIN 7 TOP VIEW 22 AVDD AGND RT 8 9 (Not to Scale) 2 YTRAP 20 CV GT 0 BT TGND 2 DVDD 3 DGND 4 9 CVSET 8 TVDET 7 4FSC 6 VSYNC 5 HSYNC ORDERING GUIDE Temperature Package Package Model Range Description Option AD723ARU 40 C to +85 C 28-Lead TSSOP RU-28 AD723ARU-REEL 40 C to +85 C 28-Lead TSSOP RU-28 AD723-EVAL Evaluation Board CAUTION ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD723 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality. WARNING! ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE 3
5 PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS Pin Mnemonic Description Equivalent Circuit STND Encoding Standard Pin. A Logic HIGH signal is used for NTSC encoding, a Logic LOW Circuit A signal signifies PAL. 2 SA When SA is high, phase alternation accompanies NTSC bandwidths and timing for Circuit A support of PAL (M) and combination N standards used in South America. 3 CE Chip Enable. A Logic HIGH input enables the encode function. A Logic LOW input Circuit A powers down the chip when not in use. Requires active HSYNC signal to activate. Can be raised briefly to perform power-down load check. 4 TERM Terminate. A Logic HIGH enables terminate function. RT, GT, and BT terminals are Circuit A tied to the termination ground, TGND. A Logic Low leaves these terminals floating. 5 RIN Red Component Video Input. 0 mv to 74 mv ac-coupled. Circuit B 6 GIN Green Component Video Input. 0 mv to 74 mv ac-coupled. Circuit B 7 BIN Blue Component Video Input. 0 mv to 74 mv ac-coupled. Circuit B 8 AGND Analog Ground Connection. (Main Ground Connection.) 9 RT Input Terminal for RED Termination Switch. Can be left unconnected when switchable Circuit F input termination option is not used. 0 GT Input Terminal for GREEN Termination Switch. Can be left unconnected when switchable Circuit F input termination option is not used. BT Input Terminal for BLUE Termination Switch. Can be left unconnected when switchable Circuit F input termination option is not used. 2 TGND Termination Switch Ground Connection. 3 DVDD Digital Positive Supply Connection. 4 DGND Digital Ground Connection. 5 HSYNC Horizontal Sync Signal (or CSYNC signal). Circuit A 6 VSYNC Vertical Sync Signal. Circuit A 7 4FSC 4FSC Clock Input. For NTSC: MHz, for PAL: MHz. Circuit A 8 TVDET Output Flag for TV Presence Detection. LOW signal signifies no TV present. Circuit E 9 CVSET Composite Video Gain Setting Resistor. Circuit C 20 CV Composite Video Output. Circuit C 2 YTRAP Luminance Trap Filter Tap. Attach L-C resonant network to reduce cross-color artifacts. Circuit D 22 AVDD Analog Positive Supply Connection. 23 C Chrominance Output. Circuit C 24 CSET Chrominance Gain Setting Resistor. Circuit C 25 AVDD Analog Positive Supply Connection. 26 Y Luminance Output (with CSYNC). Circuit C 27 YSET Luminance Gain Setting Resistor. Circuit C 28 AGND Analog Ground Connection. APOS APOS APOS POS POS DPOS DGND Circuit A Circuit B Circuit C Circuit D APOS AGND AGND k AGND 2 DPOS DPOS k TGND DGND DGND Circuit E Circuit F Figure. Equivalent Circuits 4
6 Typical Performance Characteristics AD723 3V TEKTRONIX TG2000 SIGNAL GENERATION PLATFORM GENLOCK COMPOSITE SYNC RGB 3 AD723 RGB-TO- NTSC/PAL ENCODER 4FSC COMPOSITE VIDEO SONY MONITOR MODEL PVM-354Q FSC ( MHz OR MHz) OSCILLATOR FSC HP334A 4 PLL TEKTRONIX VM700A WAVEFORM MONITOR TPC. Evaluation Setup VOLTS IRE VOLTS APL = 5.2% 525 LINE NTSC NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.63 s 50 APL = 5.2% 625 LINE PAL NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.72 s µs TPC 2. 00% Color Bars, NTSC s TPC 4. 00% Color Bars, PAL NOISE REDUCTION: 5.05dB APL = 50.7% SYSTEM LINE L47 F ANGLE (DEG) 0.0 GAIN dB 525 LINE NTSC BURST FROM SOURCE NOISE REDUCTION: 5.05dB APL = 5.0% SYSTEM LINE L29 ANGLE (DEG) 0.0 GAIN dB 625 LINE PAL BURST FROM SOURCE DISPLAY +V AND V SETUP 7.5% SOUND IN SYNC OFF TPC 3. 00% Color Bars on Vector Scope, NTSC TPC 5. 00% Color Bars on Vector Scope, PAL 5
7 .0 APL = 46.6% 525 LINE NTSC NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.63 s 00.0 APL = 34.8% 625 LINE PAL NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.72 s VOLTS 50 IRE VOLTS s TPC 6. Modulated Pulse and Bar, NTSC s TPC 8. Modulated Pulse and Bar, PAL 200mV s 200mV s TPC 7. Zoom on Modulated Pulse, NTSC TPC 9. Zoom on Modulated Pulse, PAL 6
8 .0 APL = 48.2% 525 LINE NTSC NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.63 s 00.0 APL = 5.3% 625 LINE PAL NO FILTERING SLOW CLAMP TO 6.72 s VOLTS IRE VOLTS s TPC 0. Multiburst, NTSC s TPC 3. Multiburst, PAL H TIMING MEASUREMENT RS 70A (NTSC) FIELD = LINE = s 4.70 s 9.30 s 9.0 CYCLES H TIMING (PAL) LINE = s 4.67 s 2.24 s 87ns 35 IRE 69ns 25mV 95ns 36.7 IRE 72ns 277mV AVERAGE 256 TPC. Horizontal Timing, NTSC AVERAGE 256 TPC 4. Horizontal Timing, PAL DG DP (NTSC) FIELD = LINE = 25 (SYNC = EXT) Wfm > MOD 5 STEP DIFFERENTIAL GAIN (%) MIN = 0.00 MAX = 0.6 p-p/max = DIFFERENTIAL PHASE (deg) MIN = 0.00 MAX = 0.24 pk-pk = ST 2ND 3RD 4TH 5TH 6TH TPC 2. Composite Output Differential Phase and Gain, NTSC DG DP (PAL) Wfm > MOD 5 STEP DIFFERENTIAL GAIN (%) MIN = 0.08 MAX = 0.8 p-p/max = DIFFERENTIAL PHASE (deg) MIN = 0.00 MAX = 0.4 pk-pk = ST 2ND 3RD 4TH 5TH 6TH TPC 5. Composite Output Differential Phase and Gain, PAL 7
9 THEORY OF OPERATION The AD723 is a predominantly analog design, with digital logic control of timing. This timing logic is driven by an external frequency reference at four times the color subcarrier frequency, input into the 4FSC pin of the AD723. This frequency should be MHz for NTSC encoding, and MHz for PAL encoding. The 4FSC input accepts standard 3 V CMOS logic levels. The duty cycle of this input clock is not critical, but a fast-edged clock should be used to prevent excessive jitter in the timing. The AD723 accepts two common sync standards, composite sync or separate horizontal and vertical syncs. To use an external composite sync, a logic high signal is input to the VSYNC pin and the composite sync is input to the HSYNC pin. If separate horizontal and vertical syncs are available, the horizontal sync can be input to the HSYNC pin and vertical sync to the VSYNC pin. Internally, the device XNORs the two sync inputs to combine them into one negative-going composite sync. The AD723 detects the falling sync pulse edges, and times their width. A sync pulse of standard horizontal width will cause the insertion of a colorburst vector into the chroma modulators at the proper time. A sync pulse outside the detection range will cause suppression of the color burst, and the device will enter its vertical blanking mode. During this mode, the on-chip RC time constants are verified using the input frequency reference, and the filter cutoff frequencies are retuned as needed. The component color inputs, RIN, GIN, and BIN, receive analog signals specifying the desired active video output. The full-scale range of the inputs is 0.74 mv (for either NTSC or PAL operation). External black level is not important as these inputs are terminated externally, and then ac-coupled to the AD723. The AD723 contains on-chip RGB input clamps to restore the dc level on-chip to match its single supply signal path. This dc restore timing is coincident with the burst flag, starting approximately 5.5 ms after the falling sync edge and lasting for 2.5 ms. During this time, the device should be driven with a black input. Following the dc clamps, the RGB inputs are buffered and split into two signal paths for constructing the luminance and chrominance outputs. Luminance Signal Path The luminance path begins with the luma (Y) matrix. This matrix combines the RGB inputs to form the brightness information in the output video. The inputs are combined by the standard transformation Y = R G B This equation describes the sensitivity of the human eye to the individual component colors, combining them into one value of brightness. The equation is balanced so that full-scale RGB inputs give a full-scale Y output. Following the luma matrix, the composite sync is added. The user-supplied sync (from the HSYNC and VSYNC inputs) is latched into the AD723 at half the master clock rate, gating a sync pulse into the luminance signal. With the exception of transitioning on the clock edges, the output sync timing will be in the same format as the input sync timing. In order to be time-aligned with the filtered chrominance signal path, the luma signal must be delayed before it is output. The AD723 uses a sampled delay line to achieve this delay. Following the luma matrix, and prior to this delay line, a prefilter removes higher frequencies from the luma signal to prevent aliasing by the sampled delay line. This four-pole Bessel lowpass filter has a 3 db frequency of 8 MHz for NTSC, 0 MHz for PAL. This bandwidth is high to leave margin for subsequent filters which combine to set the overall luma 3 db bandwidth. A fourth order filter ensures adequate rejection at high frequencies. TRIPLE INPUT TERMINATION RIN RT GND GIN GT BIN BT TERM GND GND 4FSC HSYNC VSYNC DC CLAMP DC CLAMP DC CLAMP RGB-TO-YUV ENCODING MATRIX Y U V QUADRATURE DECODER SYNC SEPARATOR 4-POLE LPF CSYNC 4-POLE LPF BURST 4-POLE LPF BURST FSC BURST CSYNC SIN 8FSC CLK LUMA DELAY LINE BALANCED MODULATORS COS STND 4-POLE LPF 4-POLE LPF AD723 CE CURRENT OUTPUT DRIVERS WITH SMART LOAD DETECT LUMA TRAP TV DETECT LUMINANCE COMPOSITE CHROMINANCE GAIN SET RESISTORS Y Y TRAP CV C YSET CSET CVSET Figure 2. Functional Block Diagram 8
10 After the luma prefilter, the bandlimited luma signal is sampled onto a set of capacitors at twice the master reference clock rate. After an appropriate delay, the data is read from the delay line, reconstructing the luma signal. The 8FSC oversampling of this delay line limits the amount of jitter in the reconstructed sync output. The clocks driving the delay line are reset once per video line during the burst flag. The output of the luma path will remain unchanged during this period and will not respond to changing RGB inputs. The reconstructed luma signal is then smoothed with a 4-pole low-pass filter. This filter has a 3 db bandwidth of 7.5 MHz for NTSC (9 MHz for PAL), and is of a modified Bessel form with some high frequency boost introduced to compensate for Sinx/x roll-off in the sampled delay line. A final current mode buffer provides current drive for the LUMA output pin. The combined response of the luma input filter, delay line, and output filter has a bandwidth of 4.7 MHz for NTSC and 6. MHz for PAL. Chrominance Signal Path The chrominance path begins with the U and V color-difference matrices. The AD723 uses U and V modulation vectors for NTSC and PAL (+U being defined as 0 degrees phase), simplifying the design compared to I and Q designs. The U and V matrices combine the RGB inputs by the standard transformations: U = (B Y) V = (R Y) The Y signal in these transformations is provided by the luminance matrix. Before modulation, the U and V signals are prefiltered to prevent aliasing. These 4-pole modified Bessel low-pass filters have a 3 db bandwidth of.2 MHz for NTSC and.5 MHz for PAL. Between the prefilters and the modulators, the colorburst vectors are added to the U and V signals. The colorburst levels are defined according to the encoding standard. For NTSC, the colorburst is in the U direction (with no V component) with a resultant amplitude of 286 mv (40 IRE) at 80 degrees phase. For PAL, the colorburst has equal parts of U and ± V vectors (changing V phase every line) for a resultant amplitude of 300 mv alternating between 35 and 225 degrees phase. The burst gate timing is generated by waiting a certain number of reference clock cycles following the falling sync edge. If the sync pulsewidth is measured to be outside the standard horizontal width, it is assumed that the device is in an h/2 period (vertical blanking interval) and the burst is suppressed. The U and V signals are used to modulate a pair of quadrature clocks (sine and cosine) at one-fourth the reference frequency input ( MHz for NTSC, MHz for PAL). For PAL operation, the phase of the cosine (V) clock is changed after each falling sync edge is detected. This will change the V-vector phase in PAL mode every horizontal line. By driving the AD723 with an odd number of sync edges per field, any individual line will flip phase each field as required by the standard. In order to suppress the carriers in the chrominance signal, the U and V modulators are balanced. Once per horizontal line the offsets in the modulators are cancelled in order to minimize residual subcarrier when the RGB inputs are equal. This offset cancellation also provides a dc restore for the U and V signal paths, so it is important that the RGB inputs be held at black level during this time. The offset cancellation occurs after each falling sync edge, approximately 8.4 µs after the falling sync edge, lasting for a period of.0 µs. If the inputs are unbalanced during this time (for example, if a sync-on-green RGB input were used), there will be an offset in this chrominance response of the inputs during the remainder of the horizontal line, including the colorburst. The U signal is sampled by the sine clock and the V signal is sampled by the cosine clock in the modulators, after which they are summed to form the chrominance (C) signal. The chrominance signal then passes through a final 4-pole modified Bessel low-pass filter to remove the harmonics of the switching modulation. This filter has a 3 db frequency of 6 MHz for NTSC and 8 MHz for PAL. A final buffer provides current drive for the CRMA output pin. Composite Output To provide a composite video output, the separate (S-Video) luminance and chrominance signal paths are summed. Prior to summing, however, an optional filter tap for removing crosscolor artifacts in the receiver is provided. The luminance path contains a resistor, output pin (YTRAP), and buffer prior to entering the composite summing amplifier. By connecting an inductor and capacitor on this pin, an R-L-C series-resonant circuit can be tuned to null out the luminance response at the chrominance subcarrier frequency ( MHz for NTSC, MHz for PAL). The center frequency (f C ) of this filter will be determined by the external inductor and capacitor by the equation: f C = 2 π LC It can be seen from this equation that the center frequency of the trap is entirely dependent on external components. The ratio of center frequency to bandwidth of the notch (Q = f C / BW) can be described by the equation: Q = 000 When choosing the Q of the filter, it should be kept in mind that the sharper the notch, the more critical the tolerance of the components must be in order to target the subcarrier frequency. Additionally, higher Q notches will exhibit a transient response with more ringing after a luminance step. The magnitude of this ringing can be large enough to cause visible shadowing for Q values much greater than.5. L C 9
11 Current Mode Output Drivers In order to deliver a full swing video signal from a supply voltage as low as 2.7 V, the AD723 uses current mode output drivers. Bright colors like fully saturated yellow can reach peak amplitudes as high as.4 V when measured from the bottom of the sync pulse. A conventional output driver, with series reverse termination, would require a 2.8 V internal swing, or more. However, a current mode output stage, like those used in many D/A converters, can deliver current into a shunt reverse terminated load with half the swing requirements. This approach requires an additional resistor to set the analog gain, see Figure 3. A gain setting resistor of 50 Ω is used so that the full output voltage swing can be developed across the parallel 75 Ω loads at the output terminal, CV. This resistor is kept external since the gain accuracy depends on using like resistors for RL and RSET. The use of a shunt reverse termination resistor, as in Figure 3, results in higher current consumption when compared to series termination. To reduce the current in a current-mode output stage to levels comparable to a traditional voltage-mode output stage, active termination can be employed, see Figure 4. In this case, a gain setting resistor of 300 Ω is used, enough to supply the current needed to drive the remote 75 Ω termination. No current flows across the 375 Ω resistor between the CV and CVSET terminals in steady state. This is the preferred output configuration mode. INTERNAL CV SIGNAL + CVSET RSET 50 :4 CV RL AVDD REMOTE LOAD Figure 3. Output Configuration for Standard Termination Mode, Shown Here for CV Output INTERNAL CV SIGNAL + CVSET RSET 300 :4 RA 3 CV AVDD REMOTE LOAD Figure 4. Output Configuration for Active Termination Mode, Shown Here for CV Output The small signal resistance seen looking into the CV terminal can be shown to be 75 Ω due to the action of the output driver feedback loop. This is true from dc to high frequencies. At frequencies approaching 00 MHz and beyond the output impedance gets larger, as the bandwidth of the feedback loop is reached, and then smaller as the effects of shunt capacitance come into play (as they do in the standard termination mode as well). With the wide loop bandwidth of the output drivers, the output impedance is kept close to 75 Ω for frequencies well beyond the bandwidth of RS-70 video signals. This ensures proper reverse termination of reflections on the line. A further step toward reducing power consumption in the AD723 involves self-power-down of unused outputs. For those times when a user loads the composite video output or the S-video outputs, but not both, power can be saved by shutting down the unloaded channel. The AD723 accomplishes this by periodically checking for the presence of a load at the luma (Y) and composite video (CV) outputs. If an external load is added or removed to either port the driver is turned on and off accordingly. The chroma output (C) is turned on and off with luma (Y). Load Check and TV Presence Detection The provision for self-power-down of unused outputs just described, is actually part of a more comprehensive load-checking system. The AD723 is capable of checking for a load while in several different states of operation, and is also capable of reporting the presence of a load through the TVDET pin. Awake-Mode Load Checking When CE is high and an output driver is active, the continuing presence of the load is verified by comparing the dc level at the output to an internal reference. If the load is removed then the voltage on the output pin (CV or Y) will become twice as high, for standard termination, or even higher for active termination. When CE is held high this checking is performed once at the beginning of every 64th field of video (approximately once per second), just after the first vertical sync pulse. If the absence of a load is detected, the TVDET flag goes low for that output and that output stage is turned off. Load checking is shown in Figure 5. R, G, and B inputs should remain constant during this interval. Sleep-Mode Load Checking When CE is high and an output driver is not active (i.e., sleep mode), the AD723 needs to check for the addition of a new load to the output. Rather than power up the output stage, a special test current can be applied to compare the impedances on the CV and CVSET pins (or Y and YSET) instead. This is referred to as sleep-mode load checking. Since a small test current is applied, there is little draw on the power supply to cause interference with other, possibly active, outputs. This check is also made at the beginning of every 64th field of video, just after the first vertical sync pulse. If a load is detected, the output stage is activated and the TVDET flag is raised high. 0
12 Power-Down Load Checking One of the main uses of the TVDET signal is for plug-and-play operation. When this feature is used, a VGA controller or other IC polls the AD723 at regular intervals (such as once per second) to see if a load has been attached to either output. If a load is found, active video and sync signals can be generated for TV encoding if CE is held. To facilitate this use, the AD723 supports sleep-mode load checking while powered down. This feature is activated with the timing sequence shown in Figure 5. CE is temporarily raised high while a single full-width horizontal sync pulse followed by a single half-width horizontal sync pulse are applied. The spacing between these two pulses should nominally be one H. Load checking is performed just after the half-width pulse (this simulates the beginning of the vertical blanking interval) and the TVDET signal becomes valid approximately 8 µs after the pulse s leading edge (for both NTSC and PAL). CE is held high until TVDET is valid and is then pulled low to avoid powering up the rest of the chip. To make this mode possible, the AD723 is designed to activate only the digital and sleep mode load check sections of the IC when CE is initially pulled high. The rest of the chip is only activated when CE remains high for four consecutive rising edges of CSYNC. CE = HIGH (AWAKE/SLEEP) CE (POWER DOWN) H = 63.5 s CSYNC TVDET LOAD CHECK TEST CURRENT LOAD CHECK EVAL PULSE 4.7 s TIME LEGEND:NTSC (PAL) 8.2 s (8.2 s) 2.3 s 8 s 5.9 s (4.3 s) Figure 5. Timing Diagram for Load Check 9. s (7.3 s). s (0.9 s) The advantage of this two-tiered power-up sequence is that the total time required to poll for TV presence is kept short, and standby power is kept low. When the entire chip is powered up, a settling time as long as 00 ms may be required before the load check signal becomes valid, due to settling of the input clamp. If this settling time was part of the plug-and-play update loop, then an on-time duty cycle of 0% would result for a load check interval of once per second. This would result in substantial current consumption. With power-down load checking, and reasonable duty cycle, a standby current less than µa can be maintained. Some important points to keep in mind when using the TVDET signal are as follows. When power-down load check is used, the TVDET pin reflects the status at the time of checking. The addition or removal of loads afterwards is not be reflected without checking again. When CE is high, however, the TVDET output will be updated about once per second, provided a valid CSYNC signal is applied (or HSYNC and VSYNC). The TVDET output is the logical OR of the TVDET flags for the Y and CV outputs. Another important consideration when using the TVDET signal is that it is temporarily invalid at full power-up while the input dc restore circuit settles. The settling time can be up to 00 ms for large input coupling capacitors. This means that it is not advisable to use the TVDET signal to directly gate CE. This arrangement may lead to a limit cycle. Suitable delay should be included after turning the AD723 on before deciding to turn it off again because no load is detected. DC-Coupled Outputs The video outputs of the AD723 (Y, C and CV) are all dccoupled. The advantages of this are two-fold. First, the need for large ac-coupling capacitors (220 µf typically) at the output is eliminated. Second, it becomes possible to perform load checking. The disadvantage with dc-coupled outputs is that there is more dc current to dissipate. Reducing the supply voltage to 3 V can minimize this. Here, the typical power consumption will be similar to ac-coupled voltage drivers. As a result of dissipating dc current, there are two different power consumption numbers: one for a typical picture, and one for a worst-case all-white screen. The all-white screen requires a significant amount of power to be dissipated, but it is very uncommon for both RGB computer graphics and video to be in this condition.
13 HSYNC/VSYNC (USER INPUTS) t SW RIN/GIN BIN (USER INPUTS) t SB MODULATOR RESTORE t SM INPUT CLAMPS t SR t RW t MW BURST FLAG/ DELAY LINE RESET t SD t DW Y t SS t BY t BC C t SC Figure 6. Timing Diagram (Not to Scale) Table I. Timing Description (See Figure 6) Symbol Name Description NTSC PAL 2 t SW Sync Width Input valid sync width for burst Min 2.8 µs Min 3.3 µs insertion (user-controlled). Max 5.3 µs Max 5.4 µs t SB Sync to Blanking Minimum sync to color delay End (user-controlled). Min 8.2 µs Min 8. µs t SM Sync to Modulator Delay to modulator clamp start. 8.4 µs 8.3 µs Restore t MW Modulator Restore Length of modulator offset clamp. µs 0.9 µs Width (no chroma during this period). t SR Sync to RGB DC Delay to input clamping start. 5.4 ms 5.6 ms Restore t RW DC Restore Width Length of input clamp (no RGB 2.5 µs 2.3 µs response during this period). t SD Sync to Delay Line Delay to start of delay line 5.7 µs 5.8 µs Reset clock reset. t DW Delay Line Reset Length of delay line clock reset 2.5 µs 2.3 µs Width (no luma response during this period), also burst gate. t SS Sync Input to Luma Delay from sync input assertion Typ 30 ns Typ 265 ns Sync Output to sync in LUMA output. t BY Blanking End to Delay from RGB input assertion Typ 340 ns Typ 280 ns LUMA Start to LUMA output response. t SC Sync to Colorburst Delay from valid horizontal sync Typ 5.8 µs Typ 5.9 µs start to CRMA colorburst output. t BC Blanking End to Delay from RGB input assertion CRMA Start to CRMA output response. Typ 360 ns Typ 300 ns NOTES Input clock = MHz, STND pin = logic high. 2 Input clock = MHz, STND pin = logic low. 2
14 APPLYING THE AD723 Inputs RIN, BIN, GIN are analog inputs that should be terminated to ground with 75 Ω in close proximity to the IC. These connect directly to ground for direct input termination as in Figure 7. For switched input termination, these resistors connect to RT, GT, BT respectively, as in Figure 8. The horizontal blanking interval should be the most negative part of each signal. The inputs should be held at the input signal s black level during the horizontal blanking interval. The internal dc clamps will clamp this level during color burst to a reference that is used internally as the black level. Any noise present on the RIN, GIN, BIN, or AGND pins during this interval will be sampled onto the input capacitors. This can result in varying dc levels from line to line in all outputs or, if imbalanced, subcarrier feedthrough in the CV and C outputs. For increased noise rejection, larger input capacitors are desired. A capacitor of 0. µf is usually adequate. Similarly, the U and V clamps balance the modulators during an interval shortly after the falling CSYNC input. Noise present during this interval will be sampled in the modulators, resulting in residual subcarrier in the CV and C outputs. HSYNC and VSYNC are two logic level inputs that are combined internally to produce a composite sync signal. If a composite sync signal is to be used, it can be input to HSYNC while VSYNC is pulled to logic HI (> 2 V). The form of the input sync signal(s) will determine the form of the composite sync on the composite video (CV) and luminance (Y) outputs. If no equalization or serration pulses are included in the HSYNC input there will not be any in the outputs. Although sync signals without equalization and serration pulses do not technically meet the video standards specifications, many monitors do not require these pulses in order to display good pictures. The decision whether to include these signals is a system tradeoff between cost and complexity and adhering strictly to the video standards. The HSYNC and VSYNC logic inputs have a small amount of built-in hysteresis to avoid interpreting noisy input edges as multiple sync edges. This is critical to proper device operation, as the sync pulsewidths are measured for vertical blanking interval detection. The logic inputs have been designed for VIL <.0 V and VIH > 2.0 V for the entire temperature and supply range of operation. This allows the AD723 to directly interface to TTL- or 3 V CMOS-compatible outputs, as well as 5 V CMOS outputs where VOL is less than.0 V for 5 V operation. The NTSC specification calls for a frequency accuracy of ±0 Hz from the nominal subcarrier frequency of MHz. While maintaining this accuracy in a broadcast studio might not be a severe hardship, it can be quite expensive in a low-cost consumer application. The AD723 will operate with subcarrier frequencies that deviate quite far from those specified by the TV standards. In general, however, the monitor will not be quite so forgiving. Most monitors can tolerate a subcarrier frequency that deviates several hundred Hz from the nominal standard without any degradation in picture quality. These conditions imply that the subcarrier frequency accuracy is a system specification and not a specification of the AD723 itself. The STND pin is used to select between NTSC and PAL operation. Various blocks inside the AD723 use this input to program their operation. Most of the more common variants, with the exception of NTSC 4.43, of NTSC and PAL are supported. The PAL(M) and Combination N standards used in South America can be enabled by setting the STND pin HIGH, and the SA pin LOW. The 4FSC input frequency, line (H), and field (V) rates should be chosen appropriately for these standards. Layout Considerations The AD723 is an all-cmos mixed-signal part. It has separate pins for the analog and digital 3 V and ground power supplies. Both the analog and digital ground pins should be tied to the ground plane by a short, low inductance path. Each power supply pin should be bypassed to ground by a low inductance 0. µf capacitor and a larger tantalum capacitor of about 0 µf. If the termination switches are used, TGND should be connected to the same ground plane as AGND and DGND. The R SET resistors should be located close to the pins of the AD723. If active termination is used, the RA resistors should also be closely placed. 3
15 Basic Connections Some simple applications will not require use of all of the features of the AD723. In such a case, some of the pins must be connected to appropriate levels such that the rest of the device can operate. Figure 7 is a schematic of a very basic connection of the AD723. R, G, B FROM SOURCE 0 F + HIGH FOR NTSC LOW FOR PAL 3V HSYNC AND VSYNC OR CSYNC AND POLARITY (SEE TEXT) 4.388MHz-NTSC MHz-PAL 0. F 0. F 0. F NC NC NC 0. F NC = NO CONNECT DVDD STND SA 3V CE TERM RIN GIN BIN RT GT BT HSYNC VSYNC 3V AVDD AD723 3V 0. F AVDD TVDET CV CVSET YTRAP CSET YSET 4FSC AGND TGND DGND AGND C Y 0. F NC NC + 0 F TO TEMINATION TO TEMINATION TO TEMINATION 374 Figure 7. Basic Connection (Using Direct Input Termination) The following pins do not require any connection and can be left open circuited if their function is not needed: Pin 9, RT Pin 0, GT Pin, BT Pin 8, TVDET Pin 2, YTRAP Inputs to a CMOS device should never be left floating, even if their function is ignored. The following inputs should be dealt with accordingly: Pin, STND can be hard-wired either high or low, if only either NTSC or PAL output is desired. Pin 2, SA For most systems, this pin should be tied low (ground). Some of the video standards used in South America can be enabled by a high logic level on this pin. Pin 3, CE If continuous enabled operation is desired, this pin can be hard-wired to a high logic level. Pin 4, TERM This signal should be tied low (ground) if the on-chip termination switches are not used. 30 Most systems will use only one output type at a time either composite video or S-video. In such a case, it is desirable that unused outputs go to their power-down state. The only component necessary for these outputs is a resistor of 300 Ω from the appropriate XSET pin to ground. If no load is detected on the output pin, the corresponding output stage will be powered down to minimum current. PC Graphics Interface The AD723 has an extended feature set that simplifies the task of generating composite TV output signals from a PC from the conventional RGB and sync outputs. In order for this to function, however, the RGB output scanning must be interlaced and at the proper scanning frequencies for either NTSC or PAL operation. Figure 8 shows the connections for interfacing to a PC graphics chipset. The RGB signals now must serve two different destinations and two different termination conditions. There is a direct path from the RGB signals to the RGB monitor. This is the conventional path, and the presence of the AD723 should not interfere with it. The RGB signals are doubly shuntterminated by the 75 Ω resistors near the graphics chip and the 75 Ω terminations in the monitor. This situation does not require any additional termination, so the TERM pin of the AD723 should be low so that the termination switches are turned off. If the TV output is desired, there are two possibilities: either the RGB monitor will be plugged in or, since it is not necessary, it can be removed. The case where it is plugged in has the same termination scheme as above, so the TERM signal should be low to prevent switching in any additional termination. However, if the RGB monitor is unplugged, there is only one set of shunt terminations on the RGB signals. In this case, TERM should be switched high (3 V). This will provide the second termination by switching the three 75 Ω resistors to ground. General-purpose outputs (GPO) are used from the I/O controller device to control the logic inputs to the AD723: TERM, CE, SA, and STND. Any of these can be hardwired in the desired state if it is not going to be changed in normal operation. A general-purpose input (GPI) can be used to monitor TVDET if this feature is used. The RGB signals are ESD-protected by the diodes to the supplies. The Pi networks on these signal lines prevent EMI from radiating from the monitor cable. Low Cost Crystal Oscillator A low cost oscillator can be made that provides a CW clock that can be used to drive both the AD723 4FSC and other devices in the system that require a clock at this frequency. Figure 9 shows a circuit that uses one inverter of a 74HC04 package to create a crystal oscillator and another inverter to buffer the oscillator and drive other loads. The logic family must be a CMOS type that can support the frequency of operation, and it must NOT be a Schmitt trigger type of inverter. Resistor R from input to output of UA linearizes the inverter s gain such that it provides useful gain and a 80 degree phase shift to drive the oscillator. 4
16 ESD PROTECTION V CC PI FILTER GRAPHICS SUBSYSTEM RED GREEN BLUE HSYNC VSYNC DDCSCL 5V DDCSDL 5V V CC V CC VGA CONNECTOR SVGA MONITOR 0. F 0. F 0. F I/O CONTROLLER GPO GPO GPI GPO GPO 4FSC CE TERM TVDET SA STND RIN RT GIN GT BIN BT AD723 HSYNC VSYNC Y YSET C CSET S-VIDEO (Y/C VIDEO) YTRAP TGND AGND DGND 0. F DVDD AVDD AVDD CV CVSET 3V COMPOSITE VIDEO TELEVISION 0. F 3V 0. F + OPTIONAL 0 F Figure 8. PC Interface (Using Switch Input Termination) C3 ~5pF (OPT) C 47pF R M HC04 UA Y R2 200 C2 60pF UB HC04 TO PIN 7 OF AD723 TO OTHER DEVICE CLOCKS Figure 9. Low Cost Crystal Oscillator The crystal should be a parallel resonant type at the appropriate frequency (NTSC/PAL, 4FSC). The series combination of C and C2 should be approximately equal to the crystal manufacturer s specification for the parallel capacitance required for the crystal to operate at its specified frequency. C will usually want to be a somewhat smaller value because of the input parasitic capacitance of the inverter. If it is desired to tune the frequency to greater accuracy, C can be made still smaller and a parallel adjustable capacitor can be used to adjust the frequency to the desired accuracy. Resistor R2 serves to provide the additional phase shift required by the circuit to sustain oscillation. It can be sized by R2 = /(2 π f C2). Other functions of R2 are to provide a lowpass filter that suppresses oscillations at harmonics of the fundamental of the crystal and to isolate the output of the inverter from the resonant load that the crystal network presents. The basic oscillator described above is buffered by UB to drive the AD723 4FSC pin and other devices in the system. For a system that requires both an NTSC and PAL oscillator, the circuit can be duplicated by using a different pair of inverters from the same package. Dot Crawl Numerous distortions are apparent in the presentation of composite signals on TV monitors. These effects will vary in degree, depending on the circuitry used by the monitor to process the signal and on the nature of the image being displayed. It is generally not possible to produce pictures on a composite monitor that are as high quality as those produced by standard quality RGB, VGA monitors. 5
17 One well-known distortion of composite video images is called dot crawl. It shows up as a moving dot pattern at the interface between two areas of different color. It is caused by the inability of the monitor circuitry to adequately separate the luminance and chrominance signals. One way to prevent dot crawl is to use a video signal that has separate luminance and chrominance. Such a signal is referred to as S-video or Y/C-video. Since the luminance and chrominance are already separated, the monitor does not have to perform this function. The S-video outputs of the AD723 can be used to create higher quality pictures when an S-video input is available on the monitor. Flicker In a VGA conversion application, where the software-controlled registers are correctly set, two techniques are commonly used by VGA controller manufacturers to generate the interlaced signal. Each of these techniques introduces a unique characteristic into the display created by the AD723. The artifacts described below are not due to the encoder or its encoding algorithm as all encoders will generate the same display when presented with these inputs. They are due to the method used by the controller display chip to convert a noninterlaced output to an interlaced signal. The first interlacing technique outputs a true interlaced signal with odd and even fields (one each to a frame, Figure 0a). This provides the best picture quality when displaying photography, CD video, and animation (games, etc.). However, it will introduce a defect commonly referred to as flicker into the display. Flicker is a fundamental defect of all interlaced displays and is caused by the alternating field characteristic of the interlace technique. Consider a one pixel high black line that extends horizontally across a white screen. This line will exist in only one field and will be refreshed at a rate of 30 Hz (25 Hz for PAL). During the time that the other field is being displayed the line will not be displayed. The human eye is capable of detecting this, and the display will be perceived to have a pulsating or flickering black line. This effect is highly content-sensitive and is most pronounced in applications where text and thin horizontal lines are present. In applications such as CD video, photography, and animation, portions of objects naturally occur in both odd and even fields and the effect of flicker is imperceptible. The second commonly-used technique is to output an odd and even field that are identical (Figure 0b). This ignores the data that naturally occurs in one of the fields. In this case the same one-pixel-high line mentioned above would either appear as a two-pixel-high line, (one pixel high in both the odd and even field) or not appear at all if it is in the data that is ignored by the controller. Which of these cases occurs is dependent on the placement of the line on the screen. This technique provides a stable (i.e., nonflickering) display for all applications, but small text can be difficult to read and lines in drawings (or spreadsheets) can disappear. As above, graphics and animation are not particularly affected although some resolution is lost. There are methods to dramatically reduce the effect of flicker and maintain high resolution. The most common is to ensure that display data never exists solely in a single line. This can be accomplished by averaging/weighting the contents of successive/ multiple noninterlaced lines prior to creating a true interlaced output (Figure 0c). In a sense, this provides an output that will lie between the two extremes described above. The weight or percentage of one line that appears in another, and the number of lines used, are variables that must be considered in developing a system of this type. If this type of signal processing is performed, it must be completed prior to the data being presented to the AD723 for encoding. NONINTERLACED ODD FIELD EVEN FIELD = a. Conversion of Noninterlace to Interlace NONINTERLACED ODD FIELD EVEN FIELD = b. Line-Doubled Conversion Technique NONINTERLACED ODD FIELD EVEN FIELD = c. Line Averaging Technique Figure 0. Vertical Scaling In addition to converting the computer-generated image from noninterlaced to interlaced format, it is also necessary to scale the image down to fit into NTSC or PAL format. The most common vertical lines/screen for VGA display are 480 and 600 lines. NTSC can only accommodate approximately 400 visible lines/frame (200 per field), PAL can accommodate 576 lines/ frame (288 per field). If scaling is not performed, portions of the original image will not appear in the television display. This line reduction can be performed by merely eliminating every Nth (6th line in converting 480 lines to NSTC or every 25th line in converting 600 lines to PAL). This risks generation of jagged edges and jerky movement. It is best to combine the scaling with the interpolation/averaging technique discussed above to ensure that valuable data is not arbitrarily discarded in the scaling process. Like the flicker reduction technique mentioned above, the line reduction must be accomplished prior to the AD723 encoding operation. There is a new generation of VGA controllers on the market specifically designed to utilize these techniques to provide a crisp and stable display for both text- and graphics-oriented applications. In addition, these chips rescale the output from the computer to fit correctly on the screen of a television. A list of known devices is available through Analog Devices Applications group, but the most complete and current information will be available from the manufacturers of graphics controller ICs. 6
2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch AD723
 查询 AD723 供应商 捷多邦, 专业 PCB 打样工厂,24 小时加急出货 a 2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch AD723 FEATURES Low Cost, Fully Integrated Solution for NTSC/PAL Composite
查询 AD723 供应商 捷多邦, 专业 PCB 打样工厂,24 小时加急出货 a 2.7 V to 5.5 V RGB-to-NTSC/PAL Encoder with Load Detect and Input Termination Switch AD723 FEATURES Low Cost, Fully Integrated Solution for NTSC/PAL Composite
Low Cost RGB to NTSC/PAL Encoder with Luma Trap Port AD725
 a FEATURES Composite Video Output: Both NTSC and PAL Chrominance and Luminance (S-Video) Outputs Luma Trap Port to Eliminate Cross Color Artifacts TTL Logic Levels Integrated Delay Line and Auto-Tuned
a FEATURES Composite Video Output: Both NTSC and PAL Chrominance and Luminance (S-Video) Outputs Luma Trap Port to Eliminate Cross Color Artifacts TTL Logic Levels Integrated Delay Line and Auto-Tuned
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM DELAYED C-SYNC CLOCK AT 8FSC. 5MHz 4-POLE LP PRE-FILTER DC RESTORE AND C-SYNC INSERTION. 5MHz 2-POLE LP POST- FILTER
 a FEATURES Composite Video Output Chrominance and Luminance (S-Video) Outputs No External Filters or Delay Lines Required Drives 75 Ω Reverse-Terminated Loads Compact 28-Pin PLCC Logic Selectable NTSC
a FEATURES Composite Video Output Chrominance and Luminance (S-Video) Outputs No External Filters or Delay Lines Required Drives 75 Ω Reverse-Terminated Loads Compact 28-Pin PLCC Logic Selectable NTSC
RGB to NTSC/PAL Encoder AD724
 a FEATURES Low Cost, Integrated Solution +5 V Operation Accepts FSC Clock or Crystal, or 4FSC Clock Composite Video and Separate Y/C (S-Video) Outputs Luma and Chroma Outputs Are Time Aligned Minimal External
a FEATURES Low Cost, Integrated Solution +5 V Operation Accepts FSC Clock or Crystal, or 4FSC Clock Composite Video and Separate Y/C (S-Video) Outputs Luma and Chroma Outputs Are Time Aligned Minimal External
MAX11503 BUFFER. Σ +6dB BUFFER GND *REMOVE AND SHORT FOR DC-COUPLED OPERATION
 19-4031; Rev 0; 2/08 General Description The is a low-power video amplifier with a Y/C summer and chroma mute. The device accepts an S-video or Y/C input and sums the luma (Y) and chroma (C) signals into
19-4031; Rev 0; 2/08 General Description The is a low-power video amplifier with a Y/C summer and chroma mute. The device accepts an S-video or Y/C input and sums the luma (Y) and chroma (C) signals into
CXA1645P/M. RGB Encoder
 MATRIX CXA1645P/M RGB Encoder Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite
MATRIX CXA1645P/M RGB Encoder Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite
RGB Encoder For the availability of this product, please contact the sales office. VIDEO OUT Y/C MIX DELAY CLAMP
 MATRIX Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite video outputs and
MATRIX Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite video outputs and
ML6428. S-Video Filter and 75Ω Line Drivers with Summed Composite Output. Features. General Description. Block Diagram Σ BUFFER.
 www.fairchildsemi.com ML S-Video Filter and Line Drivers with Summed Composite Output Features.MHz Y and C filters, with CV out for NTSC or PAL cable line driver for Y, C, CV, and TV modulator db stopband
www.fairchildsemi.com ML S-Video Filter and Line Drivers with Summed Composite Output Features.MHz Y and C filters, with CV out for NTSC or PAL cable line driver for Y, C, CV, and TV modulator db stopband
4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter
 19-2948; Rev 1; 1/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video
19-2948; Rev 1; 1/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video
MAX7461 Loss-of-Sync Alarm
 General Description The single-channel loss-of-sync alarm () provides composite video sync detection in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM standard-definition television (SDTV) systems. The s advanced detection circuitry
General Description The single-channel loss-of-sync alarm () provides composite video sync detection in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM standard-definition television (SDTV) systems. The s advanced detection circuitry
DATASHEET EL1883. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Demo Board. Pinout. Sync Separator with Horizontal Output. FN7010 Rev 2.
 DATASHEET EL883 Sync Separator with Horizontal Output FN7 Rev 2. The EL883 video sync separator is manufactured using Elantec s high performance analog CMOS process. This device extracts sync timing information
DATASHEET EL883 Sync Separator with Horizontal Output FN7 Rev 2. The EL883 video sync separator is manufactured using Elantec s high performance analog CMOS process. This device extracts sync timing information
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET. TDA4510 PAL decoder. Product specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 March 1986 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a colour decoder for the PAL standard, which is pin sequent compatible with multistandard decoder
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 March 1986 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a colour decoder for the PAL standard, which is pin sequent compatible with multistandard decoder
Quadruple, 2:1, Mux Amplifiers for Standard-Definition and VGA Signals
 9-4457; Rev ; 2/9 Quadruple, 2:, Mux Amplifiers for General Description The MAX954/MAX9542 are quadruple-channel, 2: video mux amplifiers with input sync tip clamps. These devices select between two video
9-4457; Rev ; 2/9 Quadruple, 2:, Mux Amplifiers for General Description The MAX954/MAX9542 are quadruple-channel, 2: video mux amplifiers with input sync tip clamps. These devices select between two video
DATASHEET EL4583A. Features. Applications. Pinout. Ordering Information. Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT. FN7503 Rev 2.
 DATASHEET Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT FN7503 Rev 2.00 The extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non-standard formats, or from computer graphics operating
DATASHEET Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT FN7503 Rev 2.00 The extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non-standard formats, or from computer graphics operating
EL4583. Features. Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, H OUT. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinout FN Data Sheet March 28, 2013
 Data Sheet FN7173.4 Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, H OUT The EL4583 extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non standard formats, or from computer graphics operating
Data Sheet FN7173.4 Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, H OUT The EL4583 extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non standard formats, or from computer graphics operating
V6118 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
Chrontel CH7015 SDTV / HDTV Encoder
 Chrontel Preliminary Brief Datasheet Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Features 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION VGA to SDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 104x768 Analog YPrPb or YCrCb outputs for
Chrontel Preliminary Brief Datasheet Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Features 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION VGA to SDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 104x768 Analog YPrPb or YCrCb outputs for
Component Analog TV Sync Separator
 19-4103; Rev 1; 12/08 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Component Analog TV Sync Separator General Description The video sync separator extracts sync timing information from standard-definition (SDTV), extendeddefinition
19-4103; Rev 1; 12/08 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Component Analog TV Sync Separator General Description The video sync separator extracts sync timing information from standard-definition (SDTV), extendeddefinition
Complete 10-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9943
 a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
GS1881, GS4881, GS4981 Monolithic Video Sync Separators
 GS11, GS1, GS91 Monolithic Video Sync Separators DATA SHEET FEATURES noise tolerant odd/even flag, back porch and horizontal sync pulse fast recovery from impulse noise excellent temperature stability.5
GS11, GS1, GS91 Monolithic Video Sync Separators DATA SHEET FEATURES noise tolerant odd/even flag, back porch and horizontal sync pulse fast recovery from impulse noise excellent temperature stability.5
BTV Tuesday 21 November 2006
 Test Review Test from last Thursday. Biggest sellers of converters are HD to composite. All of these monitors in the studio are composite.. Identify the only portion of the vertical blanking interval waveform
Test Review Test from last Thursday. Biggest sellers of converters are HD to composite. All of these monitors in the studio are composite.. Identify the only portion of the vertical blanking interval waveform
Complete 10-Bit/12-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9943/AD9944
 a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit (AD9943), 12-Bit (AD9944), 25 MSPS
a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit (AD9943), 12-Bit (AD9944), 25 MSPS
2 MHz Lock-In Amplifier
 2 MHz Lock-In Amplifier SR865 2 MHz dual phase lock-in amplifier SR865 2 MHz Lock-In Amplifier 1 mhz to 2 MHz frequency range Dual reference mode Low-noise current and voltage inputs Touchscreen data display
2 MHz Lock-In Amplifier SR865 2 MHz dual phase lock-in amplifier SR865 2 MHz Lock-In Amplifier 1 mhz to 2 MHz frequency range Dual reference mode Low-noise current and voltage inputs Touchscreen data display
OBSOLETE. CMOS 80 MHz Monolithic (18) Color Palette RAM-DACs ADV478/ADV471
 a FEATURES Personal System/2* Compatible 80 MHz Pipelined Operation Triple 8-Bit (6-Bit) D/A Converters 256 24(18) Color Palette RAM 15 24(18) Overlay Registers RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Outputs Sync on
a FEATURES Personal System/2* Compatible 80 MHz Pipelined Operation Triple 8-Bit (6-Bit) D/A Converters 256 24(18) Color Palette RAM 15 24(18) Overlay Registers RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Outputs Sync on
4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video
 19-2951; Rev 2; 2/7 4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video applications
19-2951; Rev 2; 2/7 4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video applications
DATASHEET EL4583. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinout. Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT. FN7173 Rev 4.
 DATASHEET EL4583 Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT The EL4583 extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non standard formats, or from computer graphics operating at
DATASHEET EL4583 Sync Separator, 50% Slice, S-H, Filter, HOUT The EL4583 extracts timing from video sync in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM systems, and non standard formats, or from computer graphics operating at
CVOUT Vcc2 TRAP SWITCH Y/C MIX INTERNAL TRAP DELAY LPF LPF SIN-PULSE NPIN SCIN
 R G B SC NP BFOUT MATRIX GND2 ROUT GOUT BOUT CVOUT Vcc2 Y YOUT COUT RGB Encoder CXA20M Description The CXA20M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals a composite video signal. This IC has various
R G B SC NP BFOUT MATRIX GND2 ROUT GOUT BOUT CVOUT Vcc2 Y YOUT COUT RGB Encoder CXA20M Description The CXA20M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals a composite video signal. This IC has various
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945
 Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
SingMai Electronics SM06. Advanced Composite Video Interface: HD-SDI to acvi converter module. User Manual. Revision 0.
 SM06 Advanced Composite Video Interface: HD-SDI to acvi converter module User Manual Revision 0.4 1 st May 2017 Page 1 of 26 Revision History Date Revisions Version 17-07-2016 First Draft. 0.1 28-08-2016
SM06 Advanced Composite Video Interface: HD-SDI to acvi converter module User Manual Revision 0.4 1 st May 2017 Page 1 of 26 Revision History Date Revisions Version 17-07-2016 First Draft. 0.1 28-08-2016
192-Bit, 360 MHz True-Color Video DAC with Onboard PLL ADV7129
 a FEATURES 192-Bit Pixel Port Allows 2048 2048 24 Screen Resolution 360 MHz, 24-Bit True-Color Operation Triple 8-Bit D/A Converters 8:1 Multiplexing Onboard PLL RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Analog Outputs
a FEATURES 192-Bit Pixel Port Allows 2048 2048 24 Screen Resolution 360 MHz, 24-Bit True-Color Operation Triple 8-Bit D/A Converters 8:1 Multiplexing Onboard PLL RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Analog Outputs
Interfaces and Sync Processors
 Interfaces and Sync Processors Kramer Electronics has a full line of video, audio and sync interfaces. The group is divided into two sections Format Interfaces and Video Sync Processors. The Format Interface
Interfaces and Sync Processors Kramer Electronics has a full line of video, audio and sync interfaces. The group is divided into two sections Format Interfaces and Video Sync Processors. The Format Interface
Graphics Video Sync Adder/Extractor
 19-0602; Rev 2; 1/07 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Graphics Video Sync Adder/Extractor General Description The chipset provides a 3-wire (RGB) interface for 5-wire (RGBHV) video by adding and extracting the
19-0602; Rev 2; 1/07 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Graphics Video Sync Adder/Extractor General Description The chipset provides a 3-wire (RGB) interface for 5-wire (RGBHV) video by adding and extracting the
Synchronization circuit with synchronized vertical divider system for 60 Hz TDA2579C
 FEATURES Synchronization and horizontal part Horizontal sync separator and noise inverter Horizontal oscillator Horizontal output stage Horizontal phase detector (sync to oscillator) Triple current source
FEATURES Synchronization and horizontal part Horizontal sync separator and noise inverter Horizontal oscillator Horizontal output stage Horizontal phase detector (sync to oscillator) Triple current source
MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM
 MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL DVM-1000 DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM MULTIDYNE Electronics, Inc. Innovations in Television
MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL DVM-1000 DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM MULTIDYNE Electronics, Inc. Innovations in Television
CDK3402/CDK bit, 100/150MSPS, Triple Video DACs
 CDK3402/CDK3403 8-bit, 100/150MSPS, Triple Video DACs FEATURES n 8-bit resolution n 150 megapixels per second n ±0.2% linearity error n Sync and blank controls n 1.0V pp video into 37.5Ω or load n Internal
CDK3402/CDK3403 8-bit, 100/150MSPS, Triple Video DACs FEATURES n 8-bit resolution n 150 megapixels per second n ±0.2% linearity error n Sync and blank controls n 1.0V pp video into 37.5Ω or load n Internal
DVM-3000 Series 12 Bit DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO and 8 CHANNEL BI-DIRECTIONAL DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER for SURVEILLANCE and TRANSPORTATION
 DVM-3000 Series 12 Bit DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO and 8 CHANNEL BI-DIRECTIONAL FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER for SURVEILLANCE and TRANSPORTATION Exceeds RS-250C Short-haul and Broadcast Video specifications. 12 Bit
DVM-3000 Series 12 Bit DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO and 8 CHANNEL BI-DIRECTIONAL FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER for SURVEILLANCE and TRANSPORTATION Exceeds RS-250C Short-haul and Broadcast Video specifications. 12 Bit
NTE1416 Integrated Circuit Chrominance and Luminance Processor for NTSC Color TV
 NTE1416 Integrated Circuit Chrominance and Luminance Processor for NTSC Color TV Description: The NTE1416 is an MSI integrated circuit in a 28 Lead DIP type package designed for NTSC systems to process
NTE1416 Integrated Circuit Chrominance and Luminance Processor for NTSC Color TV Description: The NTE1416 is an MSI integrated circuit in a 28 Lead DIP type package designed for NTSC systems to process
Video Filter Amplifier with SmartSleep and Y/C Mixer Circuit
 19-535; Rev 2; 2/9 Video Filter Amplifier with SmartSleep General Description The video filter amplifier with SmartSleep and Y/C mixer is ideal for portable media players (PMPs), portable DVD players,
19-535; Rev 2; 2/9 Video Filter Amplifier with SmartSleep General Description The video filter amplifier with SmartSleep and Y/C mixer is ideal for portable media players (PMPs), portable DVD players,
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945
 Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
LMH0344 3Gbps HD/SD SDI Adaptive Cable Equalizer
 3Gbps HD/SD SDI Adaptive Cable Equalizer General Description The 3Gbps HD/SD SDI Adaptive Cable Equalizer is designed to equalize data transmitted over cable (or any media with similar dispersive loss
3Gbps HD/SD SDI Adaptive Cable Equalizer General Description The 3Gbps HD/SD SDI Adaptive Cable Equalizer is designed to equalize data transmitted over cable (or any media with similar dispersive loss
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET. TDA8501 PAL/NTSC encoder. Preliminary specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 April 1993 FEATURES Two input stages: R, G, B and (R Y), (B Y), Y with multiplexing Chrominance processing, highly integrated, includes
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 April 1993 FEATURES Two input stages: R, G, B and (R Y), (B Y), Y with multiplexing Chrominance processing, highly integrated, includes
Power Supply and Watchdog Timer Monitoring Circuit ADM9690
 a FEATURES Precision Voltage Monitor (4.31 V) Watchdog Timeout Monitor Selectable Watchdog Timeout 0.75 ms, 1.5 ms, 12.5 ms, 25 ms Two RESET Outputs APPLICATIONS Microprocessor Systems Computers Printers
a FEATURES Precision Voltage Monitor (4.31 V) Watchdog Timeout Monitor Selectable Watchdog Timeout 0.75 ms, 1.5 ms, 12.5 ms, 25 ms Two RESET Outputs APPLICATIONS Microprocessor Systems Computers Printers
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver with Selectable Slew Rate TOP VIEW +3.3V. 10nF IN+ IN- MAX3812 SD/HD GND RSET +3.
 19-3571; Rev ; 2/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver General Description The is a multirate SMPTE cable driver designed to operate at data rates up to 1.485Gbps, driving one or
19-3571; Rev ; 2/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver General Description The is a multirate SMPTE cable driver designed to operate at data rates up to 1.485Gbps, driving one or
GS4882, GS4982 Video Sync Separators with 50% Sync Slicing
 GS488, GS498 Video Sync Separators with 50% Sync Slicing DATA SHEET FEATUES precision 50% sync slicing internal color burst filter ±5 ns temperature stability superior noise immunity robust signal detection/output
GS488, GS498 Video Sync Separators with 50% Sync Slicing DATA SHEET FEATUES precision 50% sync slicing internal color burst filter ±5 ns temperature stability superior noise immunity robust signal detection/output
AD9884A Evaluation Kit Documentation
 a (centimeters) AD9884A Evaluation Kit Documentation Includes Documentation for: - AD9884A Evaluation Board - SXGA Panel Driver Board Rev 0 1/4/2000 Evaluation Board Documentation For the AD9884A Purpose
a (centimeters) AD9884A Evaluation Kit Documentation Includes Documentation for: - AD9884A Evaluation Board - SXGA Panel Driver Board Rev 0 1/4/2000 Evaluation Board Documentation For the AD9884A Purpose
GaAs, MMIC Fundamental Mixer, 2.5 GHz to 7.0 GHz HMC557A
 FEATURES Conversion loss: db LO to RF isolation: db LO to IF isolation: 3 db Input third-order intercept (IP3): 1 dbm Input second-order intercept (IP2): dbm LO port return loss: dbm RF port return loss:
FEATURES Conversion loss: db LO to RF isolation: db LO to IF isolation: 3 db Input third-order intercept (IP3): 1 dbm Input second-order intercept (IP2): dbm LO port return loss: dbm RF port return loss:
Dan Schuster Arusha Technical College March 4, 2010
 Television Theory Of Operation Dan Schuster Arusha Technical College March 4, 2010 My TV Background 34 years in Automation and Image Electronics MS in Electrical and Computer Engineering Designed Television
Television Theory Of Operation Dan Schuster Arusha Technical College March 4, 2010 My TV Background 34 years in Automation and Image Electronics MS in Electrical and Computer Engineering Designed Television
CLC011 Serial Digital Video Decoder
 CLC011 Serial Digital Video Decoder General Description National s Comlinear CLC011, Serial Digital Video Decoder, decodes and descrambles SMPTE 259M standard Serial Digital Video datastreams with serial
CLC011 Serial Digital Video Decoder General Description National s Comlinear CLC011, Serial Digital Video Decoder, decodes and descrambles SMPTE 259M standard Serial Digital Video datastreams with serial
SingMai Electronics SM06. Advanced Composite Video Interface: DVI/HD-SDI to acvi converter module. User Manual. Revision th December 2016
 SM06 Advanced Composite Video Interface: DVI/HD-SDI to acvi converter module User Manual Revision 0.3 30 th December 2016 Page 1 of 23 Revision History Date Revisions Version 17-07-2016 First Draft. 0.1
SM06 Advanced Composite Video Interface: DVI/HD-SDI to acvi converter module User Manual Revision 0.3 30 th December 2016 Page 1 of 23 Revision History Date Revisions Version 17-07-2016 First Draft. 0.1
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LMH1251 YP B P R to RGBHV Converter and 2:1 Video Switch General Description
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LMH1251 YP B P R to RGBHV Converter and 2:1 Video Switch General Description
EL1881. Features. Sync Separator, Low Power. Applications. Pinout. Demo Board. Data Sheet September 15, 2011 FN7018.2
 EL1881 Data Sheet FN7018.2 Sync Separator, Low Power The EL1881 video sync separator is manufactured using Elantec s high performance analog CMOS process. This device extracts sync timing information from
EL1881 Data Sheet FN7018.2 Sync Separator, Low Power The EL1881 video sync separator is manufactured using Elantec s high performance analog CMOS process. This device extracts sync timing information from
Maintenance/ Discontinued
 CCD Delay Line Series MNS NTSC-Compatible CCD Video Signal Delay Element Overview The MNS is a CCD signal delay element for video signal processing applications. It contains such components as a shift
CCD Delay Line Series MNS NTSC-Compatible CCD Video Signal Delay Element Overview The MNS is a CCD signal delay element for video signal processing applications. It contains such components as a shift
CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 10-Bit high Speed Video DAC ADV7123
 CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 10-Bit high Speed Video DAC ADV7123 FEATURES 330 MSPS throughput rate Triple 10-bit digital-to-analog converters (DACs) SFDR 70 db at fclk = 50 MHz; fout = 1 MHz 53 db at fclk = 140
CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 10-Bit high Speed Video DAC ADV7123 FEATURES 330 MSPS throughput rate Triple 10-bit digital-to-analog converters (DACs) SFDR 70 db at fclk = 50 MHz; fout = 1 MHz 53 db at fclk = 140
Features. Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units
 Typical Applications The is ideal for: Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multi-Point Radios Military Radar, EW & ELINT Satellite Communications Features Conversion Gain: db Image Rejection: dbc Input Third-Order
Typical Applications The is ideal for: Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multi-Point Radios Military Radar, EW & ELINT Satellite Communications Features Conversion Gain: db Image Rejection: dbc Input Third-Order
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Digital Delay / Pulse Generator DG535 Digital delay and pulse generator (4-channel)
 Digital Delay / Pulse Generator Digital delay and pulse generator (4-channel) Digital Delay/Pulse Generator Four independent delay channels Two fully defined pulse channels 5 ps delay resolution 50 ps
Digital Delay / Pulse Generator Digital delay and pulse generator (4-channel) Digital Delay/Pulse Generator Four independent delay channels Two fully defined pulse channels 5 ps delay resolution 50 ps
Representative Block Diagram. Outputs. Sound Trap/Luma Filter/Luma Delay/ Chroma Filter/PAL and NTSC Decoder/Hue and Saturation Control
 Order this document by MC44/D The Motorola MC44, a member of the MC44 Chroma 4 family, is designed to provide RGB or YUV outputs from a variety of inputs. The inputs can be composite video (two inputs),
Order this document by MC44/D The Motorola MC44, a member of the MC44 Chroma 4 family, is designed to provide RGB or YUV outputs from a variety of inputs. The inputs can be composite video (two inputs),
HMC613LC4B POWER DETECTORS - SMT. SUCCESSIVE DETECTION LOG VIDEO AMPLIFIER (SDLVA), GHz
 v.54 HMC6LC4B AMPLIFIER (SDLVA),. - GHz Typical Applications The HMC6LC4B is ideal for: EW, ELINT & IFM Receivers DF Radar Systems ECM Systems Broadband Test & Measurement Power Measurement & Control Circuits
v.54 HMC6LC4B AMPLIFIER (SDLVA),. - GHz Typical Applications The HMC6LC4B is ideal for: EW, ELINT & IFM Receivers DF Radar Systems ECM Systems Broadband Test & Measurement Power Measurement & Control Circuits
IQDEC01. Composite Decoder, Synchronizer, Audio Embedder with Noise Reduction - 12 bit. Does this module suit your application?
 The IQDEC01 provides a complete analog front-end with 12-bit composite decoding, synchronization and analog audio ingest in one compact module. It is ideal for providing the bridge between analog legacy
The IQDEC01 provides a complete analog front-end with 12-bit composite decoding, synchronization and analog audio ingest in one compact module. It is ideal for providing the bridge between analog legacy
Specifications. Reference Documentation. Performance Conditions
 The material in this section is organized into two main groupings: the specification tables and the supporting figures. The specification tables include: 1. PAL general and test signal specifications 2.
The material in this section is organized into two main groupings: the specification tables and the supporting figures. The specification tables include: 1. PAL general and test signal specifications 2.
Complete 14-Bit, 56 MSPS Imaging Signal Processor AD9941
 Complete 14-Bit, 56 MSPS Imaging Signal Processor AD9941 FEATURES Differential sensor input with 1 V p-p input range 0 db/6 db variable gain amplifier (VGA) Low noise optical black clamp circuit 14-bit,
Complete 14-Bit, 56 MSPS Imaging Signal Processor AD9941 FEATURES Differential sensor input with 1 V p-p input range 0 db/6 db variable gain amplifier (VGA) Low noise optical black clamp circuit 14-bit,
Camera Interface Guide
 Camera Interface Guide Table of Contents Video Basics... 5-12 Introduction...3 Video formats...3 Standard analog format...3 Blanking intervals...4 Vertical blanking...4 Horizontal blanking...4 Sync Pulses...4
Camera Interface Guide Table of Contents Video Basics... 5-12 Introduction...3 Video formats...3 Standard analog format...3 Blanking intervals...4 Vertical blanking...4 Horizontal blanking...4 Sync Pulses...4
TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller
 TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller With the widespread conversion of the TV transmission and coding standards, from the early analog (NTSC, PAL, SECAM) systems to the modern digital formats
TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller With the widespread conversion of the TV transmission and coding standards, from the early analog (NTSC, PAL, SECAM) systems to the modern digital formats
LM MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with OSD
 LM1279 110 MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with OSD General Description The LM1279 is a full featured and low cost video amplifier with OSD (On Screen Display). 8V operation for low power and increased
LM1279 110 MHz RGB Video Amplifier System with OSD General Description The LM1279 is a full featured and low cost video amplifier with OSD (On Screen Display). 8V operation for low power and increased
MACROVISION RGB / YUV TEMP. RANGE PART NUMBER
 NTSC/PAL Video Encoder NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT contact our Technical Support Center at 1-888-INTERSIL or www.intersil.com/tsc September 2003 DATASHEET FN4284 Rev 6.00
NTSC/PAL Video Encoder NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT contact our Technical Support Center at 1-888-INTERSIL or www.intersil.com/tsc September 2003 DATASHEET FN4284 Rev 6.00
SDA 3302 Family. GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses
 GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY TECHNICAL BULLETIN CALIBRATION PROCEDURE FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO CORRECTOR TEKTRONIX, MODEL 1440 (NSN )
 DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY TECHNICAL BULLETIN TB 11-5820-861-35 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO CORRECTOR TEKTRONIX, MODEL 1440 (NSN 5820-00-570-1978) Headquarters, Department of the Army, Washington,
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY TECHNICAL BULLETIN TB 11-5820-861-35 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE FOR AUTOMATIC VIDEO CORRECTOR TEKTRONIX, MODEL 1440 (NSN 5820-00-570-1978) Headquarters, Department of the Army, Washington,
WVR500 Waveform/Vector Monitor
 Service Manual WVR500 Waveform/Vector Monitor 070-8897-01 Warning The servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To avoid personal injury, do not perform any servicing unless you are
Service Manual WVR500 Waveform/Vector Monitor 070-8897-01 Warning The servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To avoid personal injury, do not perform any servicing unless you are
Instruction Manual. SMS 8601 NTSC/PAL to 270 Mb Decoder
 Instruction Manual SMS 8601 NTSC/PAL to 270 Mb Decoder 071-0421-00 First Printing: November 1995 Revised Printing: November 1998 Contacting Tektronix Customer Support Product, Service, Sales Information
Instruction Manual SMS 8601 NTSC/PAL to 270 Mb Decoder 071-0421-00 First Printing: November 1995 Revised Printing: November 1998 Contacting Tektronix Customer Support Product, Service, Sales Information
COMPOSITE VIDEO LUMINANCE METER MODEL VLM-40 LUMINANCE MODEL VLM-40 NTSC TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 COMPOSITE VIDEO METER MODEL VLM- COMPOSITE VIDEO METER MODEL VLM- NTSC TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION MANUAL VLM- NTSC TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION MANUAL INTRODUCTION EASY-TO-USE VIDEO LEVEL METER... SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY...
COMPOSITE VIDEO METER MODEL VLM- COMPOSITE VIDEO METER MODEL VLM- NTSC TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION MANUAL VLM- NTSC TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION MANUAL INTRODUCTION EASY-TO-USE VIDEO LEVEL METER... SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY...
CH7021A SDTV / HDTV Encoder
 Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Brief Datasheet Features VGA to SDTV/EDTV/HDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 1600x1200 HDTV support for 480p, 576p, 720p, 1080i and 1080p Support for NTSC,
Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Brief Datasheet Features VGA to SDTV/EDTV/HDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 1600x1200 HDTV support for 480p, 576p, 720p, 1080i and 1080p Support for NTSC,
Application Note Component Video Filtering Using the ML6420/ML6421
 April 1998 Application Note 42035 Component Video Filtering Using the ML6420/ML6421 INTRODUCTION This Application Note provides the video design engineer with practical circuit examples of Micro Linear
April 1998 Application Note 42035 Component Video Filtering Using the ML6420/ML6421 INTRODUCTION This Application Note provides the video design engineer with practical circuit examples of Micro Linear
TSG 90 PATHFINDER NTSC Signal Generator
 Service Manual TSG 90 PATHFINDER NTSC Signal Generator 070-8706-01 Warning The servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To avoid personal injury, do not perform any servicing unless
Service Manual TSG 90 PATHFINDER NTSC Signal Generator 070-8706-01 Warning The servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To avoid personal injury, do not perform any servicing unless
SM02. High Definition Video Encoder and Pattern Generator. User Manual
 SM02 High Definition Video Encoder and Pattern Generator User Manual Revision 0.2 20 th May 2016 1 Contents Contents... 2 Tables... 2 Figures... 3 1. Introduction... 4 2. acvi Overview... 6 3. Connecting
SM02 High Definition Video Encoder and Pattern Generator User Manual Revision 0.2 20 th May 2016 1 Contents Contents... 2 Tables... 2 Figures... 3 1. Introduction... 4 2. acvi Overview... 6 3. Connecting
ESI VLS-2000 Video Line Scaler
 ESI VLS-2000 Video Line Scaler Operating Manual Version 1.2 October 3, 2003 ESI VLS-2000 Video Line Scaler Operating Manual Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...4 2. INSTALLATION AND SETUP...5 2.1.Connections...5
ESI VLS-2000 Video Line Scaler Operating Manual Version 1.2 October 3, 2003 ESI VLS-2000 Video Line Scaler Operating Manual Page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...4 2. INSTALLATION AND SETUP...5 2.1.Connections...5
CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 8-Bit High Speed Video DAC ADV7125
 CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 8-Bit High Speed Video DAC ADV75 FEATURES 330 MSPS throughput rate Triple 8-bit DACs RS-343A-/RS-70-compatible output Complementary outputs DAC output current range:.0 ma to 6.5 ma
CMOS, 330 MHz Triple 8-Bit High Speed Video DAC ADV75 FEATURES 330 MSPS throughput rate Triple 8-bit DACs RS-343A-/RS-70-compatible output Complementary outputs DAC output current range:.0 ma to 6.5 ma
Complete 10-Bit and 12-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processors AD9943/AD9944
 Complete 10-Bit and 12-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processors AD9943/AD9944 FEATURES 25 MSPS correlated double sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-bit variable gain amplifier (VGA) Low noise optical black clamp
Complete 10-Bit and 12-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processors AD9943/AD9944 FEATURES 25 MSPS correlated double sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-bit variable gain amplifier (VGA) Low noise optical black clamp
Maintenance/ Discontinued
 CCD Delay Line Series MN390S NTSC-Compatible CCD H Video Signal Delay Element Overview The MN390S is a H image delay element of a f SC CMOS CCD and suitable for video signal processing applications. It
CCD Delay Line Series MN390S NTSC-Compatible CCD H Video Signal Delay Element Overview The MN390S is a H image delay element of a f SC CMOS CCD and suitable for video signal processing applications. It
FMS6417A Selectable RGB (YUV) HD/SD Video Filter Driver with Y, C, Composite, and Modulator Outputs
 FMS6417A Selectable RGB (YUV) HD/SD Video Filter Driver with Y, C, Composite, and Modulator Outputs Features YUV/RGB filters 2:1 Mux inputs for multiple RGB/YUV inputs Selectable 8MHz or 3MHz 6th order
FMS6417A Selectable RGB (YUV) HD/SD Video Filter Driver with Y, C, Composite, and Modulator Outputs Features YUV/RGB filters 2:1 Mux inputs for multiple RGB/YUV inputs Selectable 8MHz or 3MHz 6th order
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET. TDA8304 Small signal combination IC for colour TV. Preliminary specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Small signal combination IC for colour TV File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 September 1991 FEATURES Gain controlled vision IF amplifier Synchronous demodulator for negative
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Small signal combination IC for colour TV File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 September 1991 FEATURES Gain controlled vision IF amplifier Synchronous demodulator for negative
ZXFV4583 SYNC SEPARATOR WITH VARIABLE FILTER
 SYNC SEPARATOR WITH VARIABLE FILTER DEVICE DESCRIPTION The ZXFV4583 provides the ability to separate out video synchronization signals for a wide variety of TV and CRT display systems, standard and non-standard.
SYNC SEPARATOR WITH VARIABLE FILTER DEVICE DESCRIPTION The ZXFV4583 provides the ability to separate out video synchronization signals for a wide variety of TV and CRT display systems, standard and non-standard.
Features. PFD Output Voltage 2000 mv, Pk - Pk. PFD Gain Gain = Vpp / 2π Rad khz 100 MHz Square Wave Ref.
 HMC98LP5 / 98LP5E Typical Applications The HMC98LP5(E) is ideal for: Satellite Communication Systems Point-to-Point Radios Military Applications Sonet Clock Generation Functional Diagram Features Ultra
HMC98LP5 / 98LP5E Typical Applications The HMC98LP5(E) is ideal for: Satellite Communication Systems Point-to-Point Radios Military Applications Sonet Clock Generation Functional Diagram Features Ultra
NTSC color TV signal encoder
 NTSC color TV signal encoder The comprises an RGB signal matrix circuit, balanced modulator circuit (rectangular 2-phase modulation), oscillator circuit (VCXO) for a 3.58MHz subcarrier synchronized with
NTSC color TV signal encoder The comprises an RGB signal matrix circuit, balanced modulator circuit (rectangular 2-phase modulation), oscillator circuit (VCXO) for a 3.58MHz subcarrier synchronized with
FMS3810/3815 Triple Video D/A Converters 3 x 8 bit, 150 Ms/s
 Triple Video D/A Converters 3 x 8 bit, 150 Ms/s Features 8-bit resolution 150 megapixels per second 0.2% linearity error Sync and blank controls 1.0V p-p video into 37.5Ω or 75Ω load Internal bandgap voltage
Triple Video D/A Converters 3 x 8 bit, 150 Ms/s Features 8-bit resolution 150 megapixels per second 0.2% linearity error Sync and blank controls 1.0V p-p video into 37.5Ω or 75Ω load Internal bandgap voltage
A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1
 A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1 J. M. Bussat 1, G. Bohner 1, O. Rossetto 2, D. Dzahini 2, J. Lecoq 1, J. Pouxe 2, J. Colas 1, (1) L. A. P. P. Annecy-le-vieux, France (2) I. S. N. Grenoble,
A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1 J. M. Bussat 1, G. Bohner 1, O. Rossetto 2, D. Dzahini 2, J. Lecoq 1, J. Pouxe 2, J. Colas 1, (1) L. A. P. P. Annecy-le-vieux, France (2) I. S. N. Grenoble,
Software Analog Video Inputs
 Software FG-38-II has signed drivers for 32-bit and 64-bit Microsoft Windows. The standard interfaces such as Microsoft Video for Windows / WDM and Twain are supported to use third party video software.
Software FG-38-II has signed drivers for 32-bit and 64-bit Microsoft Windows. The standard interfaces such as Microsoft Video for Windows / WDM and Twain are supported to use third party video software.
LMH0002 SMPTE 292M / 259M Serial Digital Cable Driver
 SMPTE 292M / 259M Serial Digital Cable Driver General Description The SMPTE 292M / 259M serial digital cable driver is a monolithic, high-speed cable driver designed for use in SMPTE 292M / 259M serial
SMPTE 292M / 259M Serial Digital Cable Driver General Description The SMPTE 292M / 259M serial digital cable driver is a monolithic, high-speed cable driver designed for use in SMPTE 292M / 259M serial
Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL. Model: FC Analog Video to SDI Converter
 Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL Model: FC-7501 Analog Video to SDI Converter Contents Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Getting Started 1 3 Overview 2 4 Your Analog Video to SDI Converter 3 5 Using Your
Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL Model: FC-7501 Analog Video to SDI Converter Contents Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Getting Started 1 3 Overview 2 4 Your Analog Video to SDI Converter 3 5 Using Your
To discuss. Types of video signals Analog Video Digital Video. Multimedia Computing (CSIT 410) 2
 Video Lecture-5 To discuss Types of video signals Analog Video Digital Video (CSIT 410) 2 Types of Video Signals Video Signals can be classified as 1. Composite Video 2. S-Video 3. Component Video (CSIT
Video Lecture-5 To discuss Types of video signals Analog Video Digital Video (CSIT 410) 2 Types of Video Signals Video Signals can be classified as 1. Composite Video 2. S-Video 3. Component Video (CSIT
Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s)
 OCTAL BUS TRANSCEIVER/REGISTER WITH 3 STATE OUTPUTS HIGH SPEED: f MAX = 60 MHz (TYP.) at V CC = 4.5V LOW POWER DISSIPATION: I CC = 4µA(MAX.) at T A =25 C COMPATIBLE WITH TTL OUTPUTS : V IH = 2V (MIN.)
OCTAL BUS TRANSCEIVER/REGISTER WITH 3 STATE OUTPUTS HIGH SPEED: f MAX = 60 MHz (TYP.) at V CC = 4.5V LOW POWER DISSIPATION: I CC = 4µA(MAX.) at T A =25 C COMPATIBLE WITH TTL OUTPUTS : V IH = 2V (MIN.)
3 V/5 V, CMOS, 500 A Signal Conditioning ADC AD7714
 a FEATURES Charge Balancing ADC 24 Bits No Missing Codes 0.0015% Nonlinearity Five-Channel Programmable Gain Front End Gains from 1 to 128 Can Be Configured as Three Fully Differential Inputs or Five Pseudo-Differential
a FEATURES Charge Balancing ADC 24 Bits No Missing Codes 0.0015% Nonlinearity Five-Channel Programmable Gain Front End Gains from 1 to 128 Can Be Configured as Three Fully Differential Inputs or Five Pseudo-Differential
4 MHz Lock-In Amplifier
 4 MHz Lock-In Amplifier SR865A 4 MHz dual phase lock-in amplifier SR865A 4 MHz Lock-In Amplifier 1 mhz to 4 MHz frequency range Low-noise current and voltage inputs Touchscreen data display - large numeric
4 MHz Lock-In Amplifier SR865A 4 MHz dual phase lock-in amplifier SR865A 4 MHz Lock-In Amplifier 1 mhz to 4 MHz frequency range Low-noise current and voltage inputs Touchscreen data display - large numeric
Presented by: Amany Mohamed Yara Naguib May Mohamed Sara Mahmoud Maha Ali. Supervised by: Dr.Mohamed Abd El Ghany
 Presented by: Amany Mohamed Yara Naguib May Mohamed Sara Mahmoud Maha Ali Supervised by: Dr.Mohamed Abd El Ghany Analogue Terrestrial TV. No satellite Transmission Digital Satellite TV. Uses satellite
Presented by: Amany Mohamed Yara Naguib May Mohamed Sara Mahmoud Maha Ali Supervised by: Dr.Mohamed Abd El Ghany Analogue Terrestrial TV. No satellite Transmission Digital Satellite TV. Uses satellite
LM16X21A Dot Matrix LCD Unit
 LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 12.5Gbps Settable Receive Equalizer +2.5V +3.3V V CC1 V CC. 30in OF FR-4 STRIPLINE OR MICROSTRIP TRANSMISSION LINE SDI+ SDI-
 19-2713; Rev 1; 11/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 12.5Gbps Settable Receive Equalizer General Description The driver with integrated analog equalizer compensates up to 20dB of loss at 5GHz. It is designed
19-2713; Rev 1; 11/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 12.5Gbps Settable Receive Equalizer General Description The driver with integrated analog equalizer compensates up to 20dB of loss at 5GHz. It is designed
Color TV Signal Encoder
 Color TV Signal Encoder The converts analog RGB signals into color TV signals in the NTSC and PAL formats. From inputs of analog RGB signals, a composite synch signal, burst pulses and a color carrier,
Color TV Signal Encoder The converts analog RGB signals into color TV signals in the NTSC and PAL formats. From inputs of analog RGB signals, a composite synch signal, burst pulses and a color carrier,
Multimedia Systems Video I (Basics of Analog and Digital Video) Mahdi Amiri April 2011 Sharif University of Technology
 Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Video I (Basics of Analog and Digital Video) Mahdi Amiri April 2011 Sharif University of Technology Video Visual Effect of Motion The visual effect of motion is due
Course Presentation Multimedia Systems Video I (Basics of Analog and Digital Video) Mahdi Amiri April 2011 Sharif University of Technology Video Visual Effect of Motion The visual effect of motion is due
Digital PC to TV Encoder 2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION LINE MEMORY TRUE SCALE SCALING & DEFLICKERING ENGINE SYSTEM CLOCK PLL
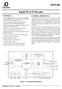 Chrontel CHRONTEL Digital PC to TV Encoder 1. FEATURES Universal digital interface accepts YCrCb (CCIR601 or 656) or RGB (15, 16 or 24-bit) video data in both non-interlaced and interlaced formats True
Chrontel CHRONTEL Digital PC to TV Encoder 1. FEATURES Universal digital interface accepts YCrCb (CCIR601 or 656) or RGB (15, 16 or 24-bit) video data in both non-interlaced and interlaced formats True
LMH1981 Multi-Format Video Sync Separator
 Multi-Format Video Sync Separator General Description The LMH1981 is a high performance multi-format sync separator ideal for use in a wide range of video applications, such as broadcast and professional
Multi-Format Video Sync Separator General Description The LMH1981 is a high performance multi-format sync separator ideal for use in a wide range of video applications, such as broadcast and professional
CCD Signal Processor For Electronic Cameras AD9801
 a FEATURES 10-Bit, 18 MSPS A/D Converter 18 MSPS Full-Speed CDS Low Noise, Wideband PGA Internal Voltage Reference No Missing Codes Guaranteed +3 V Single Supply Operation Low Power CMOS: 185 mw 48-Pin
a FEATURES 10-Bit, 18 MSPS A/D Converter 18 MSPS Full-Speed CDS Low Noise, Wideband PGA Internal Voltage Reference No Missing Codes Guaranteed +3 V Single Supply Operation Low Power CMOS: 185 mw 48-Pin
