Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Circuit Analysis
|
|
|
- Reynard Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 March 13, 2006 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Circuit Analysis For questions, comments, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor technology, please call Sales at Chipworks Richmond Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: Fax:
2 Some of the information in this report may be covered by patents, mask and/or copyright protection. This report should not be taken as an inducement to infringe on these rights Chipworks Incorporated This report is provided exclusively for the use of the purchasing organization. It can be freely copied and distributed within the purchasing organization, conditional upon the accompanying Chipworks accreditation remaining attached. Distribution of the entire report outside of the purchasing organization is strictly forbidden. The use of portions of the document for the support of the purchasing organization's corporate interest (e.g., licensing or marketing activities) is permitted, as defined by the fair use provisions of the copyright act. Accreditation to Chipworks must be attached to any portion of the reproduced information.
3 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Table of Contents Introduction... Page 1 Brief Functional Description... Page 2 List of Figures... Page 5 Device Summary Sheet... Page 24 Top Level Diagram...Tab 1 Data Path...Tab 2 Address Path...Tab 3 Control Clocks...Tab 4 Voltage Generators...Tab 5 Row Redundancy...Tab 6 Column Redundancy...Tab 7 Test/Calibration Modes...Tab 8 Mode Registers...Tab 9 Self Refresh...Tab 10 Signal Cross-Reference List...Tab 11 Signal Naming Conventions...Tab 12 Report Evaluation...Tab 13
4 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page 5 List of Figures Package Markings Package X-Ray Die Markings Die Photograph Annotated Die Photograph Die Architecture Pin Configuration Annotated X-Ray Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Standard Cells Definition Latch Definitions Latch Definitions Latch Definitions Latch Definitions Latch Definitions Latch Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions
5 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Flip-Flop Definitions Symbol Definitions for Delay Line Definitions Symbol Definitions for Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions
6 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Delay Line Definitions Level Shifter Definitions Top Level Diagram Data Path Memory Cell Access Cells and Bitline Sense Amplifiers Local Data Bus Access Data Bus Sense & Drive Data Bus Sense Amplifier Data Bus Write Driver Data Line Latches and Drivers I Data Line Switch Data Line Latches and Drivers II Data Output Registers Data Output Register Data Output Buffers Data Output Buffer Data Output Driver Pull-Up Strength Control Pull-Down Strength Control {DQ} Bus On-Die Termination {DQ} On-Die Termination
7 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Adjustable Termination Resistors Resistor Value Control Data Input Buffers Data Input Buffer Data Input Registers Data Input Register Read Multibit Test Multibit Test Comparators Multibit Test Logic I Multibit Test Logic II Multibit Test Output Latch Multibit Test Output Select Write Multibit Test Register Address Path Address Input Buffers Address Buffer I Address Buffer II Address Buffer III Bank Address Buffer Address Input Latch Row Address Register I Row Address Path Row Address Register II Address Bit [13] Gated Buffers Block Decoder Block/Row Select X-Block Select Row Predecoder Row Factor Decoder Row Factor Drivers Master Row Decoder
8 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Wordline Drivers Sense/Precharge Select Load Unlink Drivers Load Unlink Driver (Edge) Sense/Precharge Controls Sense/Precharge Controls (Edge) SP/SN~ Drivers Column Address Register Column Address [0] Register Column Address [2:1] Register Column Address [8:3] Register Column Address [9] Register Column Address [11] Register Column Bank Address Register Column Bank Address Decoder Auto-Precharge Address Register Address Latency Register I Address Latency Register II A Address Latency Register II B Column Address Path Column Address Latch Sector Decoder Sector Select Column Predecoder Column Factor Decoder Column Decoder Data Address Path Read Data Address Register Read Data Address Register Cell Write Data Address Register I Write Data Address Register II Data Line Drive/Switch Enables
9 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Data Line Drive Control I Data Line Switch Control Data Address [1,0] Predecoder Data Address [13,11] Predecoder X16 Switch Control Decoder X16/X8 Switch Control Decoder X16/X4 Switch Control Decoder X8 Switch Control Decoder X8/X4 Switch Control Decoder I X8/X4 Switch Control Decoder II X4 Switch Control Decoder Data Line Drive Control II Refresh Counter Refresh Counter Cell Control Clocks Internal Clock / Power-Down System Active {CK/CK~} Buffer Standby {CK/CK~} Buffer Clock Frequency Divider Clock Gated Buffers Internal Clock Generator I Internal Clock Splitter Internal Clock Generator II {CKE} Input Buffer CKE Pass Circuit Power-Down / Self Refresh Controller Power-Down Control Register CKE Setup Timer Sleep Signal Generator DLL Status Monitor Clock Frequency Divider
10 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page System Clock Input Control Power-Down Mode Exit Control Power-Down Mode Clocks Clock Generator Options Delay Locked Loop DLL Control Signal Generation DLL Enable Generator DLL Reset Pulse Generator DLL Clocks DLL Clock Input Buffer Internal DLL Clocks Generator Clock Shape & Latch I Clock Shape & Latch II Phase Detector Clock Jitter Filter Up/Down Counter I Up/Down Counter Cell Up/Down Counter II Start Up Comparator I Mode Select Decoder Start Up Counter Control Clock Stabilizer Delay Comparator II Start-Up Circuit Start-Up Circuit II Jitter Filter Stop Generator Adjustable Delay Lines Control DLL Test Input Buffer Counter Control Bit Up/Down Counter
11 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Fine Delay Adjust Decoders Coarse Delay Adjust Decoders Adjustable Delay Lines Fine Delay Fine Adjustable Delay Line Coarse Delay Counter Clock Generator Feedback Delay Line Clock Output Select Command Controller {RAS~} Input Buffer {CAS~} Input Buffer {WE~} Input Buffer {CS~} Input Buffer Command Decoder Command Register Test [45H] Command Decoder Test [06H] Command Decoder Row Activation/Refresh Controller Device Initialization/Refresh Clocks Bank Activation/Precharge Control Single Bank Activate/Precharge Single Bank Activate/Precharge Control Write Recovery Delay Register Auto-Precharge Pulse Generator Programmable Delay Line Bank Auto-Deactivation Activate/Precharge Select Bank Status Monitor Row Activation Path Sub-Bank Activation Programmable Inverting Delay
12 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page X-Block Select Enable Sense Amplifier Activation Delay Line I Delay Line II Programmable Delay Delay Control Delay Line III Unused Delay Line Block Activation/Precharge Controls Bitline Sense Delay Emulator Rising Edge Delay Delay Register Programmable Delay Line Programmable Capacitor I Programmable Capacitor II Refresh Disable Signal Generator Read/Write Burst Controller Read/Write Additive Latency Additive Latency Clocks R/W Command Additive Latency Column Address Register Clocks R/W Bank Select Read/Write Clocks I Write Latency Timer Read/Write Active Detector Write Latency Clocks Write Latency Register Write Burst Length Counter Actual Write Start Detector I Actual Write Start Detector II CAC/Write Control I CAC Control II
13 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Local Data Line Drive Clock Read/Write Clocks II R/W Status Monitor I R/W Column Access Enable Column Address Transfer Clock Column Access Enable Latch R/W Status Monitor II R/W Status Monitor III Read Burst Trigger DQ/DQS/DM Input Control Input Buffer Enable OCD Adjust/Write Latency OCD Adjust Additive Latency Auto-Precharge Feature Detector Read/Write Test Clocks Data Bus Sense and Drive Clocks Sense and Drive Start Delay Sense and Drive Enable Sense and Drive Select Data Path Clocks Data Sense and Prefetch Emulator Sense Start Delay Emulator Sense Enable Emulator Data Bus Sense Amplifier Emulator Data Bus Write Driver Emulator Data Prefetch Delay Emulator Data Output Control Counters Data Output Register Load Decoder Data Output Register Flush Decoder Double Data Rate Clocks Read Latency Control Latency Shift Register
14 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Data Output Enable Data Output Clocks Data Strobe Input/Output Output Strobe Generators Output Strobe Generator Data Strobe Output Buffers Data Strobe Output Buffer Data Strobe Output Driver Pull-Up Strength Control Pull-Down Strength Control Data Strobes ODT {DQS} On-Die Termination Adjustable Termination Resistors Resistor Value Control Write Data Strobe Generator Data Strobe Input Buffer Write Data Strobe Driver Data Strobe Input Control Data Output Power-Down Power-Down Delay Write Data Mask Path {LDM} Input Buffer {UDM} Input Buffer {LDM} Register {UDM} Register Write Data Mask Switch Write Data Mask Drivers Local Data Mask Select {DM} On-Die Termination Adjustable Termination Resistors Resistor Value Control On-Die Termination Control
15 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page {ODT} Input Buffer ODT Register Voltage Generators Low Voltage Pump System VBB Detector Voltage Divider Voltage Comparator I Voltage Comparator II VAUXL Detector Voltage Divider Voltage Comparator III Voltage Divider Voltage Comparator IV Ring Oscillator Low Voltage Clocks Low Voltage Pump VBB Pull-Up VBB Test Clamp VAUXL Test Clamp Level Shifter Sense Voltage Generators Sense Voltage Generator VSP Control Circuit VSP Bank Generator Enable VCP/VBLP Generator VCP Generator I VCP Generator II VCP Signal Margin Voltage Generator VCP Signal Margin Decoder VBLP Generator VBLP Signal Margin Voltage Generator
16 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page VBLP Signal Margin Decoder VCP/VBLP Power Mode Control Bias Voltage Generator Bias Wake-Up Circuit High Voltage Generators High Voltage Generators (Bottom) High Voltage Generators (Top) High Voltage Pump System High Voltage Pump Charge Pump Charge Pump Driver Ring Oscillator Ring Oscillator Control VAUXH Level Detector Hold Latch VAUXH Pump Enable Latch Voltage Comparator VAUXH Start-Up Pull-Up VPP Start-Up Pull-Up Charge Pumps Control VPP Level Detector VPP Enable Latch Voltage Comparator Pulse Generator Voltage Comparator Voltage Divider Unused VAUXH Detector VPP Detector DVCC Generator Reference Voltage Generators Bandgap Voltage Generator Rest of Bandgap Voltage Generator
17 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Primary Bias Voltage Generator Programmable Voltage Divider Bias Voltage Generator Open Drain Operational Amplifier Programmable Voltage Divider Bias Generator Variable Current Source Variable Resistor Load and Decoupling Auxilliary Sense Voltage Generator Self Refresh Bias Generator Power-Up Circuitry VCC Power-Up Detector VREF1 Power-Up Detector Power-Up Circuit VCP and Low Voltages Test Circuit Power-Up Sequencer Redundancy Power-Up Circuitry Redundancy Test Preset Redundancy Power-Up MUX Redundancy Power-Up Chain Row Redundancy Row Redundancy Fuse Programming Row Redundancy Programming Cell Row Address Match Detector Redundant Master Row Drivers Redundant Wordline Drivers Normal Row Disable Column Redundancy Bitline Block Decoder
18 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Column Redundancy Sector Column Redundancy Fuse Programming Column Address Match Detector Redundant Column Driver Normal Column Disable Test/Calibration Modes Test Address Buffer and Latches Address Buffer Test Address Latch Test Address Latch Test Address Latch Test Mode Control Input Address Buffers I Input Address Register I Test Address Predecoder I Test Mode Registers I Test Mode Register I-a Test Mode Latch I-b Test Mode Latch I-c Test Mode Register I-d Test Mode Register I-e Input Address Buffers II Input Address Register II Test Address Predecoder II Test Mode Registers II Test Mode Register II-a Tets Mode Register II-b Test Mode Register II-c Test Address Buffers III Test Address Register III Test Address Predecoder III
19 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Test Mode Registers III Test Mode Latch III-a Test Mode Register III-b Test Mode Register III-c Test Mode Register III-d Test Mode Entry Test Mode Reset Test Setting Registers Test [2FH] Setting Register I Test [40H] Setting Register I Test [2FH] Setting Register III Test [40H] Setting Register III Test [30H] Setting Register Test [8BH] Setting Register Test [5FH] Setting Register Test [5EH] Setting Register Test [4BH] and [0CH] Setting Register Test [6eh] Setting Register Test [65h] Setting Register Multibit Test Setting Registers Test [31h] and [34h] Setting Register Multibit Test Setting Register I Multibit Setting Register II Test Setting Register Test [32H] Setting Register Multibit Test Setting Register III Test Mode Address Input Test Mode Address Load Sequencer Test Mode Address Register Test Clock Buffer Test Address Generator Address Scrambler Logic
20 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Scrambler Logic I Scrambler Logic II Scrambler Logic III Scrambler Logic IV Scrambler Logic V Scrambler Logic VI Address Negators Register I Register II Register III State Machine Mode Register I Mode Register II Mode Selector Register Hashing Signals Generator Register Enable Generator Test Address Registers Scrambler First Stage Scrambler & Register I Scrambler & Register II Output Register Test Bank Address Generator Multibit Test Pattern Generators Multibit Control Set Signal Generator Delay Selector Read Multibit Test Patern Generator Write Multibit Test Patern Generator OCD Impedance Controller Self Refresh Test Output Signature Control Signature Circuit
21 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page OCD Program Decoder OCD Control Logic OCD Calibration Machine OCD Clock Buffer Data Line Signal Register Calibration Step Pulse Generator OCD Impedance Calibration Counter Test Multiplexer Programming Circuitry Programming Circuitry I Programming Circuitry II Programming Circuitry III Programming Cell I Programming Circuitry IV Programming Cell II Programming Circuitry V Memory Organization Options Supply Test Output Switch I Supply Test Output Switch II Mode Registers Mode Address Register Mode Register Set Basic Mode Register Extended Mode Register I Extended Mode Register II Extended Mode Register III Write Recovery Decoder CAS Latency Decoders OCD Adjust Mode Decoder Additive Latency Decoder ODT Resistance Value Decoder
22 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM Page Self Refresh Self Refresh Oscillator Programmable Capacitor Oscillator Frequency Divider Self Refresh Timer Self Refresh Pulse Generator A.1.0 Symbol Conventions - 1 A.1.1 Symbol Conventions - 2 A.1.2 Symbol Conventions - 3 A.2.0 Symbol Definitions - 1 A.2.1 Symbol Definitions - 2 A.2.2 Symbol Definitions - 3 A.2.3 Symbol Definitions - 4 A.3.0 Transistor Size Notation A.4.0 Capacitor Size Notation A.5.0 Resistor Size Notation
23 Infineon HYB18T512160AF-3.7 DDR2 SDRAM CAR Report Evaluation We value your business relationship at Chipworks. Your feedback is very important to help us better serve your future needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this evaluation to let us know if you were satisfied with this report. The information you provide will be used to strengthen our service quality program. Please rate Chipworks on this report at the following: On-Line Evaluation Form Or use the attached Report Evaluation Fax Back version on the next page. Rev Feb. 6, 06 13:02 Y:\Reports_Public\Infineon\HYB18T512160AF-3.7\CAR \CAR-report_evaluation.doc
Nan Ya NT5DS32M8AT-7K 256M DDR SDRAM
 Nan Ya NT5DS32M8AT-7K 256M DDR SDRAM Circuit Analysis 3685 Richmond Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613.829.0414 Fax: 613.829.0515 www.chipworks.com Nan Ya NT5DS32M8AT-7K 32Mx8 DDR SDRAM
Nan Ya NT5DS32M8AT-7K 256M DDR SDRAM Circuit Analysis 3685 Richmond Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613.829.0414 Fax: 613.829.0515 www.chipworks.com Nan Ya NT5DS32M8AT-7K 32Mx8 DDR SDRAM
Texas Instruments OMAP1510CGZG2 Dual-Core Processor Partial Circuit Analysis
 October 11, 2005 Texas Instruments OMAP1510CGZG2 Dual-Core Processor Partial Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction...Page 1 List of Figures...Page 4 Device Summary Sheet...Page 7 Schematics...
October 11, 2005 Texas Instruments OMAP1510CGZG2 Dual-Core Processor Partial Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction...Page 1 List of Figures...Page 4 Device Summary Sheet...Page 7 Schematics...
Texas Instruments TNETE2201 Ethernet Transceiver Circuit Analysis
 October 31, 2003 Texas Instruments TNETE2201 Ethernet Transceiver Circuit Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Introduction...Page 4 Device Summary Sheet...Page 6 Top Level Diagram...Tab
October 31, 2003 Texas Instruments TNETE2201 Ethernet Transceiver Circuit Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Introduction...Page 4 Device Summary Sheet...Page 6 Top Level Diagram...Tab
Samsung VTU11A0 Timing Controller
 Samsung VTU11A0 1891 Robertson Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613-829-0414 chipworks.com Some of the information in this report may be covered by patents, mask and/or copyright protection.
Samsung VTU11A0 1891 Robertson Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613-829-0414 chipworks.com Some of the information in this report may be covered by patents, mask and/or copyright protection.
Lucent ORCA OR2C15A-2S208 FPGA Circuit Analysis
 August 12, 1999 Lucent ORCA OR2C15A-2S208 FPGA Circuit Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Device Summary Sheet...Page 4 Introduction...Page 6 PLC Architecture...Tab 1 Programmable Function
August 12, 1999 Lucent ORCA OR2C15A-2S208 FPGA Circuit Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Device Summary Sheet...Page 4 Introduction...Page 6 PLC Architecture...Tab 1 Programmable Function
NXP t505f Smart Card RFID Die Embedded NOR Flash Die From Smart Card World MIFARE Ultralight C
 NXP t505f Smart Card RFID Die Die From Smart Card World MIFARE Ultralight C Custom Process Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs
NXP t505f Smart Card RFID Die Die From Smart Card World MIFARE Ultralight C Custom Process Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs
OV µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor
 OmniVision OV5642 1.4 µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor Circuit Analysis of the Pixel Array, Row Control, Column Readout, Analog Front End, and Pipelined A/D Converter
OmniVision OV5642 1.4 µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor Circuit Analysis of the Pixel Array, Row Control, Column Readout, Analog Front End, and Pipelined A/D Converter
A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER
 A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER Item Type text; Proceedings Authors CONN, RAYMOND; BREEDLOVE, PHILLIP Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER Item Type text; Proceedings Authors CONN, RAYMOND; BREEDLOVE, PHILLIP Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
MediaTek MSD95C0H DTV SoC
 MediaTek MSD95C0H Basic Functional Analysis 1891 Robertson Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613-829-0414 www.chipworks.com Basic Functional Analysis 2 Some of the information in this report
MediaTek MSD95C0H Basic Functional Analysis 1891 Robertson Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H 5B7 Canada Tel: 613-829-0414 www.chipworks.com Basic Functional Analysis 2 Some of the information in this report
Freescale SPC5604BF1CLL6 Embedded NOR Flash with M27V Die Markings 32 Bit Power Architecture Automotive Microcontroller 90 nm Logic Process
 Freescale SPC5604BF1CLL6 Embedded NOR Flash with M27V Die Markings 32 Bit Power Architecture Automotive Microcontroller 90 nm Logic Process Process Review 3685 Richmond Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H
Freescale SPC5604BF1CLL6 Embedded NOR Flash with M27V Die Markings 32 Bit Power Architecture Automotive Microcontroller 90 nm Logic Process Process Review 3685 Richmond Road, Suite 500, Ottawa, ON K2H
Hardware Design I Chap. 5 Memory elements
 Hardware Design I Chap. 5 Memory elements E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Why memory is required? To hold data which will be processed with designed hardware (for storage) Main memory, cache, register, and
Hardware Design I Chap. 5 Memory elements E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Why memory is required? To hold data which will be processed with designed hardware (for storage) Main memory, cache, register, and
Combinational vs Sequential
 Combinational vs Sequential inputs X Combinational Circuits outputs Z A combinational circuit: At any time, outputs depends only on inputs Changing inputs changes outputs No regard for previous inputs
Combinational vs Sequential inputs X Combinational Circuits outputs Z A combinational circuit: At any time, outputs depends only on inputs Changing inputs changes outputs No regard for previous inputs
A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1
 A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1 J. M. Bussat 1, G. Bohner 1, O. Rossetto 2, D. Dzahini 2, J. Lecoq 1, J. Pouxe 2, J. Colas 1, (1) L. A. P. P. Annecy-le-vieux, France (2) I. S. N. Grenoble,
A FOUR GAIN READOUT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT : FRIC 96_1 J. M. Bussat 1, G. Bohner 1, O. Rossetto 2, D. Dzahini 2, J. Lecoq 1, J. Pouxe 2, J. Colas 1, (1) L. A. P. P. Annecy-le-vieux, France (2) I. S. N. Grenoble,
MUHAMMAD NAEEM LATIF MCS 3 RD SEMESTER KHANEWAL
 1. A stage in a shift register consists of (a) a latch (b) a flip-flop (c) a byte of storage (d) from bits of storage 2. To serially shift a byte of data into a shift register, there must be (a) one click
1. A stage in a shift register consists of (a) a latch (b) a flip-flop (c) a byte of storage (d) from bits of storage 2. To serially shift a byte of data into a shift register, there must be (a) one click
IT T35 Digital system desigm y - ii /s - iii
 UNIT - III Sequential Logic I Sequential circuits: latches flip flops analysis of clocked sequential circuits state reduction and assignments Registers and Counters: Registers shift registers ripple counters
UNIT - III Sequential Logic I Sequential circuits: latches flip flops analysis of clocked sequential circuits state reduction and assignments Registers and Counters: Registers shift registers ripple counters
55:131 Introduction to VLSI Design Project #1 -- Fall 2009 Counter built from NAND gates, timing Due Date: Friday October 9, 2009.
 55:131 Introduction to VLSI Design Project #1 -- Fall 2009 Counter built from NAND gates, timing Due Date: Friday October 9, 2009 Introduction In this project we will create a transistor-level model of
55:131 Introduction to VLSI Design Project #1 -- Fall 2009 Counter built from NAND gates, timing Due Date: Friday October 9, 2009 Introduction In this project we will create a transistor-level model of
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Computer Hardware Design ECSE Report. Lab Three Xilinx Richards Controller and Logic Analyzer Laboratory
 RPI Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Computer Hardware Design ECSE 4770 Report Lab Three Xilinx Richards Controller and Logic Analyzer Laboratory Name: Walter Dearing Group: Brad Stephenson David Bang
RPI Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Computer Hardware Design ECSE 4770 Report Lab Three Xilinx Richards Controller and Logic Analyzer Laboratory Name: Walter Dearing Group: Brad Stephenson David Bang
Chapter 2. Digital Circuits
 Chapter 2. Digital Circuits Logic gates Flip-flops FF registers IC registers Data bus Encoders/Decoders Multiplexers Troubleshooting digital circuits Most contents of this chapter were covered in 88-217
Chapter 2. Digital Circuits Logic gates Flip-flops FF registers IC registers Data bus Encoders/Decoders Multiplexers Troubleshooting digital circuits Most contents of this chapter were covered in 88-217
16 Stage Bi-Directional LED Sequencer
 16 Stage Bi-Directional LED Sequencer The bi-directional sequencer uses a 4 bit binary up/down counter (CD4516) and two "1 of 8 line decoders" (74HC138 or 74HCT138) to generate the popular "Night Rider"
16 Stage Bi-Directional LED Sequencer The bi-directional sequencer uses a 4 bit binary up/down counter (CD4516) and two "1 of 8 line decoders" (74HC138 or 74HCT138) to generate the popular "Night Rider"
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring Lecture Outline
 Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 03 February 09, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Registers and Counters Chapter 12 2 Course Admin 3 Administrative Admin for tonight Syllabus
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 03 February 09, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Registers and Counters Chapter 12 2 Course Admin 3 Administrative Admin for tonight Syllabus
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 11: Decoders and Delay Estimation
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 11: Decoders and Delay Estimation David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 11: Decoders and Delay Estimation David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University
Chapter 18. DRAM Circuitry Discussion. Block Diagram Description. DRAM Circuitry 113
 DRAM Circuitry 113 Chapter 18 DRAM Circuitry 18-1. Discussion In this chapter we describe and build the actual DRAM circuits in our SK68K computer. Since we have already discussed the general principles
DRAM Circuitry 113 Chapter 18 DRAM Circuitry 18-1. Discussion In this chapter we describe and build the actual DRAM circuits in our SK68K computer. Since we have already discussed the general principles
SDA 3302 Family. GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses
 GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
Digital Circuits 4: Sequential Circuits
 Digital Circuits 4: Sequential Circuits Created by Dave Astels Last updated on 2018-04-20 07:42:42 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Sequential Circuits Onward Flip-Flops R-S Flip Flop Level
Digital Circuits 4: Sequential Circuits Created by Dave Astels Last updated on 2018-04-20 07:42:42 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Sequential Circuits Onward Flip-Flops R-S Flip Flop Level
HIGH PERFORMANCE MEMORY DESIGN TECHNIQUE FOR THE MC68000
 MOTOROLA Semiconductor Products nc. AN-838 Application Note HGH PERFORMANCE MEMORY DESGN TECHNQUE FOR THE MC68000 This application note presents a technique for interfacing a 256K byte semi-transparent
MOTOROLA Semiconductor Products nc. AN-838 Application Note HGH PERFORMANCE MEMORY DESGN TECHNQUE FOR THE MC68000 This application note presents a technique for interfacing a 256K byte semi-transparent
CSE115: Digital Design Lecture 23: Latches & Flip-Flops
 Faculty of Engineering CSE115: Digital Design Lecture 23: Latches & Flip-Flops Sections 7.1-7.2 Suggested Reading A Generic Digital Processor Building Blocks for Digital Architectures INPUT - OUTPUT Interconnect:
Faculty of Engineering CSE115: Digital Design Lecture 23: Latches & Flip-Flops Sections 7.1-7.2 Suggested Reading A Generic Digital Processor Building Blocks for Digital Architectures INPUT - OUTPUT Interconnect:
PESIT Bangalore South Campus
 SOLUTIONS TO INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date : 8/11/2016 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Analog and Digital Electronics (15CS32) Section: III A and B Name of faculty: Deepti.C Time : 11:30 am-1:00 pm Note:
SOLUTIONS TO INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date : 8/11/2016 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Analog and Digital Electronics (15CS32) Section: III A and B Name of faculty: Deepti.C Time : 11:30 am-1:00 pm Note:
HD66766 Rev. 1.0 / 30 November 2001 HD (132 x 176-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors)
 HD66766 Rev.. / 3 November 2 HD66766 (32 x 76-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors) Rev.. November, 2 Description The HD66766, color-graphics LCD controller and driver LSI, displays 32-by-76-dot
HD66766 Rev.. / 3 November 2 HD66766 (32 x 76-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors) Rev.. November, 2 Description The HD66766, color-graphics LCD controller and driver LSI, displays 32-by-76-dot
Experiment # 4 Counters and Logic Analyzer
 EE20L - Introduction to Digital Circuits Experiment # 4. Synopsis: Experiment # 4 Counters and Logic Analyzer In this lab we will build an up-counter and a down-counter using 74LS76A - Flip Flops. The
EE20L - Introduction to Digital Circuits Experiment # 4. Synopsis: Experiment # 4 Counters and Logic Analyzer In this lab we will build an up-counter and a down-counter using 74LS76A - Flip Flops. The
DIFFERENTIAL CONDITIONAL CAPTURING FLIP-FLOP TECHNIQUE USED FOR LOW POWER CONSUMPTION IN CLOCKING SCHEME
 DIFFERENTIAL CONDITIONAL CAPTURING FLIP-FLOP TECHNIQUE USED FOR LOW POWER CONSUMPTION IN CLOCKING SCHEME Mr.N.Vetriselvan, Assistant Professor, Dhirajlal Gandhi College of Technology Mr.P.N.Palanisamy,
DIFFERENTIAL CONDITIONAL CAPTURING FLIP-FLOP TECHNIQUE USED FOR LOW POWER CONSUMPTION IN CLOCKING SCHEME Mr.N.Vetriselvan, Assistant Professor, Dhirajlal Gandhi College of Technology Mr.P.N.Palanisamy,
psasic Timing Generator
 psasic Timing Generator Fukun Tang psasic Design Review July 1-2 2009 University of Chicago 1 Diagram of 40Gs/s Sampling Chip CLOCK (80MHz) IN(1:32) Timing Generator with 2 DLLs interleaved PD CP LF φ1
psasic Timing Generator Fukun Tang psasic Design Review July 1-2 2009 University of Chicago 1 Diagram of 40Gs/s Sampling Chip CLOCK (80MHz) IN(1:32) Timing Generator with 2 DLLs interleaved PD CP LF φ1
Digital Systems Laboratory 3 Counters & Registers Time 4 hours
 Digital Systems Laboratory 3 Counters & Registers Time 4 hours Aim: To investigate the counters and registers constructed from flip-flops. Introduction: In the previous module, you have learnt D, S-R,
Digital Systems Laboratory 3 Counters & Registers Time 4 hours Aim: To investigate the counters and registers constructed from flip-flops. Introduction: In the previous module, you have learnt D, S-R,
MBI5050 Application Note
 MBI5050 Application Note Foreword In contrast to the conventional LED driver which uses an external PWM signal, MBI5050 uses the embedded PWM signal to control grayscale output and LED current, which makes
MBI5050 Application Note Foreword In contrast to the conventional LED driver which uses an external PWM signal, MBI5050 uses the embedded PWM signal to control grayscale output and LED current, which makes
DIGITAL CIRCUIT LOGIC UNIT 9: MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES
 DIGITAL CIRCUIT LOGIC UNIT 9: MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES 1 Learning Objectives 1. Explain the function of a multiplexer. Implement a multiplexer using gates. 2. Explain the
DIGITAL CIRCUIT LOGIC UNIT 9: MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES 1 Learning Objectives 1. Explain the function of a multiplexer. Implement a multiplexer using gates. 2. Explain the
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
BABAR IFR TDC Board (ITB): requirements and system description
 BABAR IFR TDC Board (ITB): requirements and system description Version 1.1 November 1997 G. Crosetti, S. Minutoli, E. Robutti I.N.F.N. Genova 1. Timing measurement with the IFR Accurate track reconstruction
BABAR IFR TDC Board (ITB): requirements and system description Version 1.1 November 1997 G. Crosetti, S. Minutoli, E. Robutti I.N.F.N. Genova 1. Timing measurement with the IFR Accurate track reconstruction
R.G.O. 32 BIT CAMAC COUNTER MODULE USER MANUAL
 R.G.O. 32 BIT CAMAC COUNTER MODULE USER MANUAL C.S. Amos / D.J. Steel 16th August 1993 Copyright R.G.O. August 1993 1. General description. 3 2. Encoder formats 3 2.1 A quad B type encoders... 3 2.2 Up/down
R.G.O. 32 BIT CAMAC COUNTER MODULE USER MANUAL C.S. Amos / D.J. Steel 16th August 1993 Copyright R.G.O. August 1993 1. General description. 3 2. Encoder formats 3 2.1 A quad B type encoders... 3 2.2 Up/down
WINTER 15 EXAMINATION Model Answer
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
0 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 1 1 Stop bits. 11-bit Serial Data format
 Applications of Shift Registers The major application of a shift register is to convert between parallel and serial data. Shift registers are also used as keyboard encoders. The two applications of the
Applications of Shift Registers The major application of a shift register is to convert between parallel and serial data. Shift registers are also used as keyboard encoders. The two applications of the
DDR2 Application Note
 DDR2 ODT(On Die Termination) Control March 2006 Engineering Team MEMORY DIVISION SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS Co., LTD DDR2 ODT (On Die Termination) On board termination resistance is integrated inside of Motherboard
DDR2 ODT(On Die Termination) Control March 2006 Engineering Team MEMORY DIVISION SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS Co., LTD DDR2 ODT (On Die Termination) On board termination resistance is integrated inside of Motherboard
DM Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
SEQUENTIAL LOGIC. Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur
 SEQUENTIAL LOGIC Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com OSCILLATORS Oscillators is an amplifier which derives its input from output. Oscillators
SEQUENTIAL LOGIC Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com OSCILLATORS Oscillators is an amplifier which derives its input from output. Oscillators
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Fundamentals Of Digital Logic 1 Our Goal Understand Fundamentals and basics Concepts How computers work at the lowest level Avoid whenever possible Complexity Implementation
Computer Systems Architecture Fundamentals Of Digital Logic 1 Our Goal Understand Fundamentals and basics Concepts How computers work at the lowest level Avoid whenever possible Complexity Implementation
IMS B007 A transputer based graphics board
 IMS B007 A transputer based graphics board INMOS Technical Note 12 Ray McConnell April 1987 72-TCH-012-01 You may not: 1. Modify the Materials or use them for any commercial purpose, or any public display,
IMS B007 A transputer based graphics board INMOS Technical Note 12 Ray McConnell April 1987 72-TCH-012-01 You may not: 1. Modify the Materials or use them for any commercial purpose, or any public display,
List of the CMOS 4000 series Dual tri-input NOR Gate and Inverter Quad 2-input NOR gate Dual 4-input NOR gate
 List of the CMOS 4000 series 4000 - Dual tri-input NOR Gate and Inverter 4001 - Quad 2-input NOR gate 4002 - Dual 4-input NOR gate 4006-18 stage Shift register 4007 - Dual Complementary Pair Plus Inverter
List of the CMOS 4000 series 4000 - Dual tri-input NOR Gate and Inverter 4001 - Quad 2-input NOR gate 4002 - Dual 4-input NOR gate 4006-18 stage Shift register 4007 - Dual Complementary Pair Plus Inverter
V6118 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
S6B CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
Chapter Contents. Appendix A: Digital Logic. Some Definitions
 A- Appendix A - Digital Logic A-2 Appendix A - Digital Logic Chapter Contents Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix A: Digital Logic A. Introduction A.2 Combinational
A- Appendix A - Digital Logic A-2 Appendix A - Digital Logic Chapter Contents Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix A: Digital Logic A. Introduction A.2 Combinational
Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic
 EEA091 - Digital Logic 數位邏輯 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 吳俊興國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 2006 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 7-1 Introduction 7-2 Random-Access Memory 7-3 Memory Decoding 7-4 Error
EEA091 - Digital Logic 數位邏輯 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 吳俊興國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 2006 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 7-1 Introduction 7-2 Random-Access Memory 7-3 Memory Decoding 7-4 Error
Memory Interfaces Data Capture Using Direct Clocking Technique Author: Maria George
 Application Note: Virtex-4 Family R XAPP701 (v1.4) October 2, 2006 Memory Interfaces Data Capture Using Direct Clocking Technique Author: Maria George Summary This application note describes the direct-clocking
Application Note: Virtex-4 Family R XAPP701 (v1.4) October 2, 2006 Memory Interfaces Data Capture Using Direct Clocking Technique Author: Maria George Summary This application note describes the direct-clocking
DM Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 DM9368 7-Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
Layout Analysis Analog Block
 Layout Analysis Analog Block Sample Report Analysis from an HD Video/Audio SoC For any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor and electronics technology, please call Sales at Chipworks. 3685
Layout Analysis Analog Block Sample Report Analysis from an HD Video/Audio SoC For any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor and electronics technology, please call Sales at Chipworks. 3685
82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
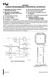 Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
ECE 372 Microcontroller Design
 E.g. Port A, Port B Used to interface with many devices Switches LEDs LCD Keypads Relays Stepper Motors Interface with digital IO requires us to connect the devices correctly and write code to interface
E.g. Port A, Port B Used to interface with many devices Switches LEDs LCD Keypads Relays Stepper Motors Interface with digital IO requires us to connect the devices correctly and write code to interface
Principles of Computer Architecture. Appendix A: Digital Logic
 A-1 Appendix A - Digital Logic Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix A: Digital Logic A-2 Appendix A - Digital Logic Chapter Contents A.1 Introduction A.2 Combinational
A-1 Appendix A - Digital Logic Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix A: Digital Logic A-2 Appendix A - Digital Logic Chapter Contents A.1 Introduction A.2 Combinational
Logic Gates, Timers, Flip-Flops & Counters. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Logic Gates, Timers, Flip-Flops & Counters Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Logic Gates Transistor NOT Gate Let I C be the collector current.
Logic Gates, Timers, Flip-Flops & Counters Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Logic Gates Transistor NOT Gate Let I C be the collector current.
Keysight B4623 LPDDR Bus Decoder. User s Guide
 Keysight B4623 LPDDR Bus Decoder User s Guide Notices Keysight Technologies 2001-2014 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or
Keysight B4623 LPDDR Bus Decoder User s Guide Notices Keysight Technologies 2001-2014 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or
PICOSECOND TIMING USING FAST ANALOG SAMPLING
 PICOSECOND TIMING USING FAST ANALOG SAMPLING H. Frisch, J-F Genat, F. Tang, EFI Chicago, Tuesday 6 th Nov 2007 INTRODUCTION In the context of picosecond timing, analog detector pulse sampling in the 10
PICOSECOND TIMING USING FAST ANALOG SAMPLING H. Frisch, J-F Genat, F. Tang, EFI Chicago, Tuesday 6 th Nov 2007 INTRODUCTION In the context of picosecond timing, analog detector pulse sampling in the 10
PHYSICS 5620 LAB 9 Basic Digital Circuits and Flip-Flops
 PHYSICS 5620 LAB 9 Basic Digital Circuits and Flip-Flops Objective Construct a two-bit binary decoder. Study multiplexers (MUX) and demultiplexers (DEMUX). Construct an RS flip-flop from discrete gates.
PHYSICS 5620 LAB 9 Basic Digital Circuits and Flip-Flops Objective Construct a two-bit binary decoder. Study multiplexers (MUX) and demultiplexers (DEMUX). Construct an RS flip-flop from discrete gates.
Microprocessor Design
 Microprocessor Design Principles and Practices With VHDL Enoch O. Hwang Brooks / Cole 2004 To my wife and children Windy, Jonathan and Michelle Contents 1. Designing a Microprocessor... 2 1.1 Overview
Microprocessor Design Principles and Practices With VHDL Enoch O. Hwang Brooks / Cole 2004 To my wife and children Windy, Jonathan and Michelle Contents 1. Designing a Microprocessor... 2 1.1 Overview
BUSES IN COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 BUSES IN COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE The processor, main memory, and I/O devices can be interconnected by means of a common bus whose primary function is to provide a communication path for the transfer of data.
BUSES IN COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE The processor, main memory, and I/O devices can be interconnected by means of a common bus whose primary function is to provide a communication path for the transfer of data.
DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port
 DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port General Description The DP8212 DP8212M is an 8-bit input output port contained in a standard 24-pin dual-in-line package The device which is fabricated using Schottky
DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port General Description The DP8212 DP8212M is an 8-bit input output port contained in a standard 24-pin dual-in-line package The device which is fabricated using Schottky
VU Mobile Powered by S NO Group
 Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one A 8-bit serial in / parallel out shift register contains the value 8, clock signal(s) will be required to shift the value completely out of the register.
Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one A 8-bit serial in / parallel out shift register contains the value 8, clock signal(s) will be required to shift the value completely out of the register.
Physics 120 Lab 10 (2018): Flip-flops and Registers
 Physics 120 Lab 10 (2018): Flip-flops and Registers 10.1 The basic flip-flop: NAND latch This circuit, the most fundamental of flip-flop or memory circuits, can be built with either NANDs or NORs. We will
Physics 120 Lab 10 (2018): Flip-flops and Registers 10.1 The basic flip-flop: NAND latch This circuit, the most fundamental of flip-flop or memory circuits, can be built with either NANDs or NORs. We will
COMP2611: Computer Organization. Introduction to Digital Logic
 1 COMP2611: Computer Organization Sequential Logic Time 2 Till now, we have essentially ignored the issue of time. We assume digital circuits: Perform their computations instantaneously Stateless: once
1 COMP2611: Computer Organization Sequential Logic Time 2 Till now, we have essentially ignored the issue of time. We assume digital circuits: Perform their computations instantaneously Stateless: once
Introduction. NAND Gate Latch. Digital Logic Design 1 FLIP-FLOP. Digital Logic Design 1
 2007 Introduction BK TP.HCM FLIP-FLOP So far we have seen Combinational Logic The output(s) depends only on the current values of the input variables Here we will look at Sequential Logic circuits The
2007 Introduction BK TP.HCM FLIP-FLOP So far we have seen Combinational Logic The output(s) depends only on the current values of the input variables Here we will look at Sequential Logic circuits The
BASIC LINEAR DESIGN. Hank Zumbahlen Editor Analog Devices, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 BASIC LINEAR DESIGN Hank Zumbahlen Editor A 2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All Rights Reserved Preface: This work is based on the work of many other individuals who have been involved with applications and
BASIC LINEAR DESIGN Hank Zumbahlen Editor A 2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All Rights Reserved Preface: This work is based on the work of many other individuals who have been involved with applications and
Name Of The Experiment: Sequential circuit design Latch, Flip-flop and Registers
 EEE 304 Experiment No. 07 Name Of The Experiment: Sequential circuit design Latch, Flip-flop and Registers Important: Submit your Prelab at the beginning of the lab. Prelab 1: Construct a S-R Latch and
EEE 304 Experiment No. 07 Name Of The Experiment: Sequential circuit design Latch, Flip-flop and Registers Important: Submit your Prelab at the beginning of the lab. Prelab 1: Construct a S-R Latch and
An Asynchronous Fully Digital DLL for DDR SDRAM Data Recovery
 An Asynchronous Fully Digital DLL for DDR SDRAM Data Recovery Jim Garside et al. University The problem Contents Why asynchronous Some asynchronous bits and pieces Dynamic switching and glitches Overall
An Asynchronous Fully Digital DLL for DDR SDRAM Data Recovery Jim Garside et al. University The problem Contents Why asynchronous Some asynchronous bits and pieces Dynamic switching and glitches Overall
DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) COUNTERS
 COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) COUNTERS One common requirement in digital circuits is counting, both forward and backward. Digital clocks and
COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) COUNTERS One common requirement in digital circuits is counting, both forward and backward. Digital clocks and
Analogue Versus Digital [5 M]
![Analogue Versus Digital [5 M] Analogue Versus Digital [5 M]](/thumbs/93/111640168.jpg) Q.1 a. Analogue Versus Digital [5 M] There are two basic ways of representing the numerical values of the various physical quantities with which we constantly deal in our day-to-day lives. One of the ways,
Q.1 a. Analogue Versus Digital [5 M] There are two basic ways of representing the numerical values of the various physical quantities with which we constantly deal in our day-to-day lives. One of the ways,
UNIT V 8051 Microcontroller based Systems Design
 UNIT V 8051 Microcontroller based Systems Design INTERFACING TO ALPHANUMERIC DISPLAYS Many microprocessor-controlled instruments and machines need to display letters of the alphabet and numbers. Light
UNIT V 8051 Microcontroller based Systems Design INTERFACING TO ALPHANUMERIC DISPLAYS Many microprocessor-controlled instruments and machines need to display letters of the alphabet and numbers. Light
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design
 Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Summer 29 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Summer 29 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
VLSI Design: 3) Explain the various MOSFET Capacitances & their significance. 4) Draw a CMOS Inverter. Explain its transfer characteristics
 1) Explain why & how a MOSFET works VLSI Design: 2) Draw Vds-Ids curve for a MOSFET. Now, show how this curve changes (a) with increasing Vgs (b) with increasing transistor width (c) considering Channel
1) Explain why & how a MOSFET works VLSI Design: 2) Draw Vds-Ids curve for a MOSFET. Now, show how this curve changes (a) with increasing Vgs (b) with increasing transistor width (c) considering Channel
Flip-Flops. Because of this the state of the latch may keep changing in circuits with feedback as long as the clock pulse remains active.
 Flip-Flops Objectives The objectives of this lesson are to study: 1. Latches versus Flip-Flops 2. Master-Slave Flip-Flops 3. Timing Analysis of Master-Slave Flip-Flops 4. Different Types of Master-Slave
Flip-Flops Objectives The objectives of this lesson are to study: 1. Latches versus Flip-Flops 2. Master-Slave Flip-Flops 3. Timing Analysis of Master-Slave Flip-Flops 4. Different Types of Master-Slave
Memory, Latches, & Registers
 Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) How to save a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers L13 Memory 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis
Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) How to save a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers L13 Memory 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis
Modeling Digital Systems with Verilog
 Modeling Digital Systems with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 6-1 Composition of Digital Systems Most digital systems can be partitioned into two types
Modeling Digital Systems with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 6-1 Composition of Digital Systems Most digital systems can be partitioned into two types
EECS 270 Group Homework 4 Due Friday. June half credit if turned in by June
 EES 270 Group Homework 4 ue Friday. June 1st @9:45am, half credit if turned in by June 1st @4pm. Name: unique name: Name: unique name: Name: unique name: This is a group assignment; all of the work should
EES 270 Group Homework 4 ue Friday. June 1st @9:45am, half credit if turned in by June 1st @4pm. Name: unique name: Name: unique name: Name: unique name: This is a group assignment; all of the work should
D Latch (Transparent Latch)
 D Latch (Transparent Latch) -One way to eliminate the undesirable condition of the indeterminate state in the SR latch is to ensure that inputs S and R are never equal to 1 at the same time. This is done
D Latch (Transparent Latch) -One way to eliminate the undesirable condition of the indeterminate state in the SR latch is to ensure that inputs S and R are never equal to 1 at the same time. This is done
Counters. The simplest circuit for binary counting is a multibit divider.
 Counters The simplest circuit for binary counting is a multibit divider. +5 CL 0 1 2 3 Each bit toggles on the downward edge of the preceding bit. The timing is asynchronous. This particular circuit is
Counters The simplest circuit for binary counting is a multibit divider. +5 CL 0 1 2 3 Each bit toggles on the downward edge of the preceding bit. The timing is asynchronous. This particular circuit is
16-BIT LOAD CELL/DUAL STATUS INPUT
 16-BIT LOAD CELL/DUAL STATUS INPUT On-board Excitation. +5VDC, (120mA). State-of-the-art Electromagnetic Noise Suppression Circuitry. Ensures signal integrity even in harsh EMC environments. Optional Excitation
16-BIT LOAD CELL/DUAL STATUS INPUT On-board Excitation. +5VDC, (120mA). State-of-the-art Electromagnetic Noise Suppression Circuitry. Ensures signal integrity even in harsh EMC environments. Optional Excitation
110 MHz 256-Word Color Palette 15-, 16-, and 24-Bit True Color Power-Down RAMDAC
 110 MHz 256-Word Color Palette 15-, 16-, and 24-Bit True Color Power-Down RAMDAC Designed specifically for high-performance color graphics, the RAM- DAC supports three true-color modes: 15-bit (5:5:5,
110 MHz 256-Word Color Palette 15-, 16-, and 24-Bit True Color Power-Down RAMDAC Designed specifically for high-performance color graphics, the RAM- DAC supports three true-color modes: 15-bit (5:5:5,
STMicroelectronics LSM330DLC inemo Inertial Module: 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope. MEMS Package Analysis
 STMicroelectronics LSM330DLC inemo Inertial Module: 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope MEMS Package Analysis STMicroelectronics LSM330DLC 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope 2 Some of the information in this
STMicroelectronics LSM330DLC inemo Inertial Module: 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope MEMS Package Analysis STMicroelectronics LSM330DLC 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope 2 Some of the information in this
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous)
 Subject Code: 17320 Model Answer Page 1 of 32 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17320 Model Answer Page 1 of 32 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Chapter 3: Sequential Logic Systems
 Chapter 3: Sequential Logic Systems 1. The S-R Latch Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you should be able to: design a Set-Reset latch based on NAND gates; complete a sequential truth table
Chapter 3: Sequential Logic Systems 1. The S-R Latch Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you should be able to: design a Set-Reset latch based on NAND gates; complete a sequential truth table
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, Karur District UNIT-III SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District DEPARTMENT OF ELETRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE NOTES SUBJECT: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS CLASS: II YEAR ECE SUBJECT CODE: EC2203
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District DEPARTMENT OF ELETRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE NOTES SUBJECT: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS CLASS: II YEAR ECE SUBJECT CODE: EC2203
MUX AND FLIPFLOPS/LATCHES
 MUX AN FLIPFLOPS/LATCHES BY: SURESH BALPANE Multiplexers 2:1 multiplexer chooses between two inputs S 1 0 Y 0 X 0 0 0 0 0 X 1 1 1 0 X 0 1 1 X 1 1 1 S Y @BALPANECircuits and Slide 2 Gate-Level Mux esign
MUX AN FLIPFLOPS/LATCHES BY: SURESH BALPANE Multiplexers 2:1 multiplexer chooses between two inputs S 1 0 Y 0 X 0 0 0 0 0 X 1 1 1 0 X 0 1 1 X 1 1 1 S Y @BALPANECircuits and Slide 2 Gate-Level Mux esign
Introduction to Microprocessor & Digital Logic
 ME262 Introduction to Microprocessor & Digital Logic (Sequential Logic) Summer 2 Sequential Logic Definition The output(s) of a sequential circuit depends d on the current and past states of the inputs,
ME262 Introduction to Microprocessor & Digital Logic (Sequential Logic) Summer 2 Sequential Logic Definition The output(s) of a sequential circuit depends d on the current and past states of the inputs,
DM Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits to drive
7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits to drive
A Tour of PLDs. PLD ARCHITECTURES. [Prof.Ben-Avi]
![A Tour of PLDs. PLD ARCHITECTURES. [Prof.Ben-Avi] A Tour of PLDs. PLD ARCHITECTURES. [Prof.Ben-Avi]](/thumbs/95/124179913.jpg) [Prof.Ben-Avi]. (We shall now take a quick initial tour through the land of PLDs... the devices selected for this introductory tour have been chosen either because they are/were extremely popular or because
[Prof.Ben-Avi]. (We shall now take a quick initial tour through the land of PLDs... the devices selected for this introductory tour have been chosen either because they are/were extremely popular or because
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 6. Latches/Flip-Flops and Registers/Counters 서강대학교 전자공학과
 EEE235 Digital Logic Design Chapter 6. Latches/Flip-Flops and Registers/Counters 서강대학교 전자공학과 . Delay and Latches ) Signal Storage a. as voltage level static memory b. as charges dynamic memory 2) Delays
EEE235 Digital Logic Design Chapter 6. Latches/Flip-Flops and Registers/Counters 서강대학교 전자공학과 . Delay and Latches ) Signal Storage a. as voltage level static memory b. as charges dynamic memory 2) Delays
Logic Devices for Interfacing, The 8085 MPU Lecture 4
 Logic Devices for Interfacing, The 8085 MPU Lecture 4 1 Logic Devices for Interfacing Tri-State devices Buffer Bidirectional Buffer Decoder Encoder D Flip Flop :Latch and Clocked 2 Tri-state Logic Outputs
Logic Devices for Interfacing, The 8085 MPU Lecture 4 1 Logic Devices for Interfacing Tri-State devices Buffer Bidirectional Buffer Decoder Encoder D Flip Flop :Latch and Clocked 2 Tri-state Logic Outputs
Keysight LPDDR Bus Decoder. User s Guide
 Keysight LPDDR Bus Decoder User s Guide Notices Keysight Technologies 2001-2015 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or translation
Keysight LPDDR Bus Decoder User s Guide Notices Keysight Technologies 2001-2015 No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or translation
Application Note. A Collection of Application Hints for the CS501X Series of A/D Converters. By Jerome Johnston
 AN08 Application Note A Collection of Application Hints for the CS501X Series of A/D Converters By Jerome Johnston Jam ADC into Coarse Charge for High Slew Signals Single Control Input Acts as a "Start
AN08 Application Note A Collection of Application Hints for the CS501X Series of A/D Converters By Jerome Johnston Jam ADC into Coarse Charge for High Slew Signals Single Control Input Acts as a "Start
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION
 Subject Code: 17320 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17320 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS THE RELAY CIRCUIT
 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS THE RELAY CIRCUIT This circuit is one big circle. The main switch is open and the flexible contact is closed. Note: A closed inverter (NOT gate) circuit performs the same function.
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS THE RELAY CIRCUIT This circuit is one big circle. The main switch is open and the flexible contact is closed. Note: A closed inverter (NOT gate) circuit performs the same function.
(CSC-3501) Lecture 7 (07 Feb 2008) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) CSC S.J. Park. Announcement
 Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 7 (07 Feb 2008) 1 Announcement 2 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic Combinational Logic Memoryless Outputs
Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 7 (07 Feb 2008) 1 Announcement 2 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic Combinational Logic Memoryless Outputs
MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM
 MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL DVM-1000 DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM MULTIDYNE Electronics, Inc. Innovations in Television
MULTIDYNE INNOVATIONS IN TELEVISION TESTING & DISTRIBUTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL DVM-1000 DIGITAL VIDEO, AUDIO & DATA FIBER OPTIC MULTIPLEXER TRANSPORT SYSTEM MULTIDYNE Electronics, Inc. Innovations in Television
L11/12: Reconfigurable Logic Architectures
 L11/12: Reconfigurable Logic Architectures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University of California, Berkeley,
L11/12: Reconfigurable Logic Architectures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University of California, Berkeley,
