2-Wire Interfaced, 7-, 14-, and 16-Segment Alphanumeric Vacuum-Fluorescent Display Controller
|
|
|
- Sabina Pope
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
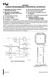
1 ; Rev 0; 1/03 2-Wire Interfaced, 7-, 14-, and 16-Segment Alphanumeric General Description The compact vacuum-fluorescent display (VFD) controller provides microprocessors with the multiplex timing for 7-segment, 14-segment, or 16-segment alphanumeric VFD displays up to 96 characters and controls industry-standard, shift-register, high-voltage grid/anode VFD tube drivers. The device supports display tubes using either one or two digits per grid, as well as universal displays. Hardware is included to simplify the generation of cathode bias and filament supplies and to provide up to five logic outputs, including a buzzer driver. The provides an internal crosspoint switch to match any tube-driver, shift-register grid/anode order, and is compatible with both chip-inglass and external tube drivers. The includes an ASCII 104-character font, multiplex scan circuitry, and static RAM that stores digit, cursor, and annunciator data, as well as font data for 24 user-definable characters. The display intensity can be adjusted by an internal 16-step digital brightness control. The device also includes separate annunciator and cursor control with automatic blinking, as well as a low-power shutdown mode. The provides timing to generate the PWM waveforms to drive the tube filament from a DC supply. The filament drive is synchronized to the display multiplexing to eliminate beat artifacts. For a high-speed SPI /QSPI /MICROWIRE interfaced version, refer to the MAX6850 data sheet. Display Modules Retail POS Displays Weight and Tare Displays Bar Graph Displays Applications Industrial Controllers White Goods Professional Audio Equipment Features 400kbps I 2 C-Compatible Serial Interface 2.7V to 3.6V Operation Controls Up to 48 Grids of 7-Segment, 14-Segment, or 16-Segment Alphanumeric Digits One Digit and Two Digits per Grid and Universal Displays Supported 16-Step Digital Brightness Control Built-In ASCII 104-Character Font 24 User-Definable Characters Up to Four Annunciators per Grid with Automatic Blinking Control Separate Cursor Control with Automatic Blinking Filament Drive Full-Bridge Waveform Synthesis Charge-Pump Drive Output to Generate Cathode Bias Supply Buzzer Tone Generator with Single-Ended or Push-Pull Driver Up to Five General-Purpose Logic Outputs 11µA Low-Power Shutdown (Data Retained) 16-Pin QSOP Package Ordering Information PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE AEE -40 C to +125 C 16 QSOP Typical Application Circuit CHIP-ON-GLASS VFD VFD SUPPLY VOLTAGE 0.1µF Pin Configuration and Functional Diagram appear at end of data sheet. SPI and QSPI are trademarks of Motorola, Inc. MICROWIRE is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corp. MICROCONTROLLER SDA SCL SDA SCL GND VFCLK VFDOUT VFLOAD VFBLANK OSC2 OSC1 56pF 10kΩ Maxim Integrated Products 1 For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at , or visit Maxim s website at
2 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Voltage (with respect to GND) V V to +4V ADO, SDA, SCL V to +5.5V All Other Pins V to (V V) Current V mA GND mA PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP...±150mA VFCLK, VFDOUT, VFLOAD, VFBLANK...±150mA SDA...15mA Continuous Power Dissipation (T A = +70 C) 16-Pin QSOP (derate at 8.34mW/ C above +70 C)...667mW Operating Temperature Range (T MIN, T MAX ) AEE C to +125 C Junction Temperature C Storage Temperature Range C to +150 C Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) C Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Typical Operating Circuit, V+ = 2.7V to 3.6V, T A = T MIN to T MAX, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 1) PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS Operating Supply Voltage V V Shutdown Supply Current I SHDN Shutdown mode, all digital inputs at V+ or GND Operating Supply Current I+ T A = T MIN to T MAX 85 T A = +25 C OSC = 4MHz T A = T MIN to 3.5 VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, T MAX VFBLANK, loaded 100pF T A = +25 C µa ma Master Clock Frequency (OSC Internal Oscillator) f OSC OSC1 fitted with C OSC = 56pF, OSC2 fitted with R OSC = 10kΩ; see the Typical Operating Circuit 4 MHz Master Clock Frequency (OSC External Oscillator) OSC1 overdriven with external f OSC 2 8 MHz Dead-Clock Protection Frequency 200 khz OSC High Time t CH 50 ns OSC Low Time t CL 50 ns Fast or Slow Segment Blink Duty Cycle LOGIC INPUTS AND OUTPUTS Input Leakage Current ADO, SDA, SCL Logic-High Input Voltage ADO, SDA, SCL Logic-Low Input Voltage ADO, SDA, SCL (Note 2) % I IH, I IL µa V IH 2.4 V V IL 0.6 V SDA Output Low Voltage V OLSDA I SINK = 4mA 0.5 V Input Capacitance C I (Note 2) 10 pf 2
3 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued) (Typical Operating Circuit, V+ = 2.7V to 3.6V, T A = T MIN to T MAX, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 1) PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS Output Rise and Fall Time PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP, VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, VFBLANK Output High-Voltage PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP, VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, VFBLANK t RFT C LOAD = 100pF 25 ns V OH I SOURCE = 10mA V V Output Low-Voltage PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP, VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, VFBLANK V OL I SINK = 10mA 0.4 V Output Short-Circuit Source Current PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP, VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, VFBLANK I OHSC Output programmed high, output short circuit to GND (Note 2) ma Output Short-Circuit Sink Current PHASE1, PHASE2, PORT0, PORT1, PUMP, VFLOAD, VFDOUT, VFCLK, VFBLANK I OLSC Output programmed low, output short circuit to V+ (Note 2) ma 2-WIRE SERIAL INTERFACE TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (Figure 8) Serial Clock Frequency f SCL 400 khz Bus Free Time Between a STOP and a START Condition t BUF 1.3 µs Hold Time (Repeated) START Condition Repeated START Condition Setup Time t HD,STA 0.6 µs t SU,STA 0.6 µs STOP Condition Setup Time t SU,STO 0.6 µs Data Hold Time t HD,DAT 0.9 µs Data Setup Time t HD,DAT (Note 3) 100 ns SCL Clock Low Period t LOW 1.3 µs SCL Clock High Period t HIGH 0.6 µs 3
4 DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued) (Typical Operating Circuit, V+ = 2.7V to 3.6V, T A = T MIN to T MAX, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 1) PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS Rise Time of Both SDA and SCL Signals, Receiving Fall Time of Both SDA and SCL Signals, Receiving t R (Notes 2, 4) t F (Notes 2, 4) C B 300 ns C B 300 ns 20 + Fall Time of SDA Transmitting t F (Notes 2, 5) 250 ns 0.1C B Pulse Width of Spike Suppressed t SP (Note 6) 50 ns Capacitive Load for Each Bus Line VFD INTERFACE TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (Figure 16) C B (Note 2) 400 pf VFCLK Clock Period t VCP (Note 2) ns VFCLK Pulse Width High t VCH (Note 2) 250 ns VFCLK Pulse Width Low t VCL (Note 2) 250 ns VFCLK Rise to VFD Load Rise Hold Time t VCSH (Note 2) 19 µs VFDOUT Setup Time t VDS (Note 2) 50 ns VFLOAD Pulse High t VCSW (Note 2) 245 ns Note 1: All parameters tested at T A = +25 C. Specifications over temperature are guaranteed by design. Note 2: Guaranteed by design. Note 3: A master device must provide a hold time of at least 300ns for the SDA signal (referred to V IL of the SCL signal) in order to bridge the undefined region of SCL s falling edge. Note 4: C B = total capacitance of one bus line in pf; t R and t F measured between 0.3V+ and 0.7V+. Note 5: I SINK 6mA; C B = total capacitance of one bus line in pf; t R and t F measured between 0.3V+ and 0.7V+. Note 6: Input filters on the SDA and SCL inputs suppress noise spikes less than 50ns. 4
5 Typical Operating Characteristics (Typical Application Circuit, V+ = 3.3V, T A = +25 C, unless otherwise noted.) ISUPPLY (ma) SUPPLY CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE T A = +125 C V+ (V) T A = -40 C toc01 ISUPPLY (µa) SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE OSC1 = T A = +25 C 3.1 V+ (V) T A = +125 C T A = -40 C toc02 SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT (µa) SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. OSC FREQUENCY FREQUENCY (MHz) toc03 OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE vs. I SINK OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE vs. I SINK OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE vs. I SINK V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc06 VOL (V) V+ = 3.6V VOL (V) V+ = 3.6V VOL (V) V+ = 3.6V T A = -40 C T A = +25 C T A = +125 C ISINK (ma) ISINK (ma) ISINK (ma) V+ - V OH vs. I SOURCE V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc V+ - V OH vs. I SOURCE V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc V+ - V OH vs. I SOURCE V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V toc09 V+ - VOH (V) V+ = 3.6V T A = -40 C V+ - VOH (V) V+ = 3.6V T A = +25 C V+ - VOH (V) V+ = 3.6V T A = +125 C ISOURCE (ma) ISOURCE (ma) ISOURCE (ma) 5
6 Typical Operating Characteristics (continued) (Typical Application Circuit, V+ = 3.3V, T A = +25 C, unless otherwise noted.) fosc (MHz) f OSC vs. TEMPERATURE V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.3V V+ = 3.6V toc10 FREQUENCY (MHz) DEAD-CLOCK OSC FREQUENCY vs. TEMPERATURE V+ = 3.3V V+ = 2.7V V+ = 3.6V toc TEMPERATURE ( C) TEMPERATURE ( C) Pin Description PIN NAME FUNCTION 1 VFCLK Serial-Clock Output to External Driver. Push-pull clock output to external display driver. On VFCLK s falling edge, data is clocked out of VFDOUT. 2 VFDOUT Serial-Data Output to External Driver. Push-pull data output to external display driver. 3 VFLOAD Serial-Load Output to External Driver. Push-pull load output to external display driver. Rising edge is used by external display driver to load serial data into display latch. 4 VFBLANK Display Blanking Output to External Driver. Push-pull blanking output to external display driver used for PWM intensity control. 5 PUMP Pump General-Purpose Output. User-configurable push-pull logic output. 6 PHASE1 Filament Drive PHASE1 Output and General-Purpose Output. User-configurable push-pull logic output can also be used as a driver for external filament bridge drive. 7 PHASE2 Filament Drive PHASE2 Output and General-Purpose Output. User-configurable push-pull logic output can also be used as a driver for external filament bridge drive. 8 V+ Positive Supply Voltage. Bypass V+ to GND with a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor. 9 GND Ground 10 PORT0 PORT0 General-Purpose Output. User-configurable push-pull logic output. 11 SCL Serial-Clock Input 12 SDA Serial-Data Input I/O 13 AD0 Address Input 0. Sets device slave address. Connect to GND, V+, SCL, or SDA to give four logic combinations. See Table PORT1 PORT1 General-Purpose Output. User-configurable push-pull logic output. 6
7 PIN NAME FUNCTION Pin Description (continued) 15 OSC1 Multiplex Clock Input 1. To use the internal oscillator, connect capacitor C OSC from OSC1 to GND. To use the external clock, drive OSC1 with a 2MHz to 8MHz CMOS clock. 16 OSC2 Multiplex Clock Input 2. Connect resistor R OSC from OSC2 to GND. GRID 1 GRID 2 GRID 3 GRID 4 GRID 5 GRID 6 GRID 7 GRID 8 GRID 9 GRID 10 GRID 11 GRID 12 GRID 13 GRID 14 GRID 15 GRID 16 Figure 1. Example of a One-Digit-per-Grid Display Detailed Description Overview of the The VFD controller generates the multiplex timing for the following VFD display types: Multiplexed displays with one digit per grid, and up to 48 grids (in 48/1 mode). Each grid can contain one 7-, 14-, or 16-segment character, a decimal place (DP) segment, a cursor segment, and four extra annunciator segments (Figure 1). Multiplexed displays with two digits per grid, and up to 48 grids (in 96/2 mode). Each grid can contain two 7-, 14-, or 16-segment characters, two DP segments, and two cursor segments. No annunciator segments are supported (Figure 2). Each digit can have a 7-, 14-, or 16-segment character, a DP segment, a cursor segment, and (for one-digitper-grid displays only) four annunciators (Figure 3). The 7, 14, or 16 segments use on-chip fonts that map the segments. The fonts comprise an ASCII 104-character fixed-font set, and 24 user-definable characters. The predefined characters follow the Arial font, with the addition of the following common symbols:,,,, µ, ±,, and. The 24 user-definable characters are uploaded by the user into on-chip RAM through the serial interface and are lost when the device is powered down. As well as custom 7- and 14-segment characters, the user-definable fonts can control up to 14 custom segments, bar graph characters, or graphics. Annunciator segments have individual, independent control, so any combination of annunciators can be lit. Annunciators can be off, lit, or blink either in phase or 7
8 GRID 1 GRID 2 GRID 3 GRID 4 GRID 5 GRID 6 GRID 7 GRID 8 Figure 2. Example of a Two-Digit-per-Grid Display C F ph mw 4 ANNUNCIATOR SEGMENTS 14-SEGMENT CHARACTER DECIMAL POINT (DP) SEGMENT CURSOR SEGMENT Figure 3. Digit Structure with 14-Segment Character, DP Segment, Cursor Segment, and Four Annunciators MICROCONTROLLER SDA SCL SDA SCL VFDOUT VFCLK VFLOAD VFBLANK VFD TUBE DRIVER VFDIN VFCLK VFLOAD VFBLANK GRID/ ANODE DRIVERS Figure 4. Connection of the to VFD Driver and VFD Tube VFD TUBE out of phase with the cursor. The blink-speed control is software selectable to be one or two blinks per second (OSC = 4MHz). DP segments can be lit or off, but have no blink control. A DP segment is set by the same command that writes the digit s 7-, 14-, or 16-segment character. The cursor segment is controlled differently. A single register selects one digit s cursor from the entire display, and that can be lit either continuously or blinking. All the other digits cursors are off. The designations of DP, cursor, and annunciator are interchangeable. For example, consider an application requiring only one DP lit at a time, but the DP needs to blink. The DP function does not have blink capability. Instead, the DP segments on the display are routed (using the output map) to the cursor function. In this case, the DP segments are controlled using the cursor register. The output of the controller is a 4-wire serial stream that interfaces to industry-standard, shift-register, high-voltage grid/anode VFD tube drivers (Figure 4). This interface uses three outputs to transfer and latch grid and anode data into the tube drivers, and a fourth output that enables/disables the tube driver outputs (Figure 6). The enable/disable control is modulated by the for both PWM intensity control and interdigit 8
9 f a g b f a h i j g1 g2 b f a1 a2 h i j g1 g2 b e d c dp e m l d k c dp e m d1 l k d2 c dp Figure 5. Segment Labeling for 7-, 14-, and 16-Segment Displays blanking, and disables the tube driver in shutdown. The controller multiplexes the display by enabling each grid of the VFD in turn for 100µs (OSC = 4MHz) with the correct segment (anode) data. The data for the next grid is transferred to the tube drivers during the display time of the current grid. The controller uses an internal output map to match any tube-driver s shift-register grid/anode order, and is therefore compatible with all VFD internal chip-in-glass or external tube drivers. The provides five high-current output ports, which can be configured for a variety of functions: The PUMP output can be configured as either an 80kHz (OSC = 4MHz) clock intended for DC-to-DC converter use, the 4-wire serial interface s DOUT data output, or a general-purpose logic output. The PHASE1 and PHASE2 outputs can be individually configured as either 10kHz PWM outputs (OSC = 4MHz) intended for filament driving, blink status outputs, or general-purpose logic outputs. The PORT0 and PORT1 outputs can be individually configured as either 625Hz, 1250Hz, or 2500Hz clocks (OSC = 4MHz) intended for buzzer driving, the 4-wire serial interface s DOUT data output, blink or shutdown status outputs, or general-purpose logic outputs. Figure 5 shows segment labeling for 7-, 14-, and 16-segment displays. Figure 6 is a block diagram of the VFD tube driver and VFD tube. VFCLK VFDIN VFLOAD VFBLANK O0 O0 O1 O1 VFD TUBE DRIVER SERIAL-TO-PARALLEL SHIFT REGISTER O2 O2 LATCHES VFD TUBE SIMPLIFIED On-2 On-2 On-1 On-1 On-0 On-0 Figure 6. Block Diagram of VFD Tube Driver and VFD Tube Display Modes The has two display modes (Table 1), selected by the M bit in the configuration register (Table 23). The display modes trade the maximum allowable number of digits (96/2 mode) against the availability of annunciator segments (48/1 mode). Table 2 is the register address map. Initial Power-Up On initial power-up, all control registers are reset, the display segment and annunciator data are cleared, intensity is set to minimum, and shutdown is enabled (Table 3). 9
10 Table 1. Display Modes DISPLAY MODE MAXIMUM NO. OF DIGITS 48/1 mode 48 digits, each with a DP segment and a cursor segment 96/2 mode 96 digits, each with a DP segment and a cursor segment MAXIMUM NO. OF ANNUNCIATORS MAXIMUM NO. OF GRIDS DIGITS COVERED BY EACH GRID 4 per digit 1 digit per grid 48 grids None 2 digits per grid Table 2. Register Address Map ADDRESS HEX REGISTER D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 CODE No-Op x00 VFBLANK polarity x01 Intensity x02 Grids x03 Configuration x04 User-defined fonts x05 Output map x06 Display test and device ID x07 PUMP register x08 Filament duty cycle x09 PHASE x0A PHASE x0B PORT x0C PORT x0D Shift limit x0E Cursor x0F Factory reserved. Do not write to register. X x10 Character Registers The uses 48 character registers (48/1 mode) (Table 4) or 96 character registers (96/2 mode) (Table 5) to store the 7-, 14-, and 16-segment characters (Table 6). Each digit is represented by 1 byte of memory. The data in the character registers does not control the character segments directly. Instead, the register data is used to address a character generator, which stores the data of the 128-character font (Table 7). The lower 7 bits of the character data (D6 to D0) select a character from the font table. The most significant bit (MSB) of the register data (D7) controls the DP segment of the digit; it is set to light the DP, cleared to leave it unlit. The character registers address maps are shown in Table 4 (48/1 mode) and Table 5 (96/2 mode). In 48/1 mode, the character registers use a single address range 0x20 to {0x20 + g}, where g is the value in the grids register (Table 28). The 48/1 mode upper address limit, when g is 0x2F, is therefore 0x4F. The address range 0x50 to 0x7F is used for annunciator data in 48/1 mode. In 96/2 mode, the character registers use two address ranges. The first row s address range is 0x20 to {0x20 + g}. The second row s address range is 0x50 to {0x50 + g}. Therefore, in 96/2 mode, the character registers are only one contiguous memory range when a 48- grid display is used. 10
11 Table 3. Initial Power-Up Register Status REGISTER VFBLANK polarity POWER-UP CONDITION VFBLANK is high to disable the display ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 0x01 X X X X X X 0 0 Intensity 1/16 (min on) 0x02 X X X X Grids Display has 1 grid 0x03 X X Configuration Shutdown enabled, configuration unlocked 0x User-defined font address pointer Address 0x80; pointing to the first user-defined font location 0x User-defined fonts Predefined for hex fonts See Table 11 for power-up patterns. Output map pointer Address 0x80; pointing to first entry address 0x Output map data Predefined for 40-digit display See Table 32 for power-up patterns. Display test Normal operation 0x07 X X X X X X X 0 PUMP General-purpose output, logic 0x Filament duty cycle Minimum duty cycle 0x PHASE1 General-purpose output, logic 0x0A PHASE2 General-purpose output, logic 0x0B PORT0 General-purpose output, logic 0x0C PORT1 General-purpose output, logic 0x0D Shift limit 1 output bit 0x0E X Cursor Off 0x0F Character and annunciator data Clear 0x UP TO UP TO Character and annunciator data Clear 0x7F Character Generator Font Mapping The font comprises 104 characters in ROM, and 24 user-definable characters. The selection from the total of 128 characters is represented by the lower 7 bits of the 8-bit digit registers. The MSB, shown as X in the ROM maps (Tables 7 and 8), controls the DP segment of the digit; it is set to light the DP. There are two font maps stored in the. One font map covers 14-segment displays (Table 8), and the other suits 16-segment displays (Table 7). The F bit in the configuration register (Table 20) selects between the two font maps. The F bit may be set either high or low for 7-segment displays; 7-segment displays use a subset of the 14- or 16-segment display described in two font maps (Figure 7). 7 SEGMENT 14/16 SEGMENTS f e a g d b c dp MAPS TO Figure and 16-Segment Fonts Map a Subset of Their 14 or 16 Segments to a 7-Segment Digit f e a/a1 g1 d/d2 b c dp 11
12 Table 4. Character and Annunciator Register Address Map in 48/1 Mode REGISTER ADDRESS HEX D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 CODE Digit 0 character x20 Digit 1 character x21 Digit 2 character x22 UP TO Digit 45 character x4D Digit 46 character x4E Digit 47 character x4F Digit 0 annunciators x50 Digit 1 annunciators x51 Digit 2 annunciators x52 UP TO Digit 45 annunciators x7D Digit 46 annunciators x7E Digit 47 annunciators x7F Table 5. Character Register Address Map in 96/2 Mode REGISTER ADDRESS HEX D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 CODE Digit 0 character, 1st row x20 Digit 1 character, 1st row x21 Digit 2 character, 1st row x22 UP TO 0 Digit 45 character, 1st row x4D Digit 46 character, 1st row x4E Digit 47 character, 1st row x4F Digit 0 character, 2nd row x50 Digit 1 character, 2nd row x51 Digit 2 character, 2nd row x52 UP TO 0 Digit 45 character, 2nd row x7D Digit 46 character, 2nd row x7E Digit 47 character, 2nd row x7F The character map follows the Arial font for 96 characters in the x through x range. The first 32 characters map the 24 user-definable positions (RAM00 to RAM23), plus eight extra common characters in ROM. User-Defined Fonts The 24 user-definable characters are represented by 48 entries of 7-bit data, two entries per character, and are stored in the s internal RAM. 12
13 Table 6. Character Registers Format MODE Writing character data to use font map data with DP segment unlit Writing character data to use font map data with DP segment lit ADDRESS 0x20 to 0x4F (48/1 mode) 0x20 to 0x7F (96/2 mode) 0x20 to 0x4F (48/1 mode) 0x20 to 0x7F (96/2 mode) D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 0 Bits D6 to D0 select font characters 0 to The user-definable characters are preloaded on powerup with 24 fonts. These fonts are intended to be useful for 7-segment displays, and include the hexadecimal set for the first 16 characters, plus eight other useful segment combinations. Table 12 shows how the 14-segment and 16-segment fonts map to 7-segment displays. The 48 user-definable font data entries are written and read through a single register, address 0x05. An autoincrementing font address pointer in the indirectly accesses the font data. The font address pointer can be written, setting one of 48 addresses between 0x00 and 0x2F, but cannot be read back. The font data is written to and read from the indirectly, using this font address pointer. Unused font locations can be used as general-purpose scratch RAM, bearing in mind that the font registers are only 7 bits wide, not 8. Table 9 shows how to use the single user-defined font register 0x05 to set the font address pointer, write font data, and read font data. A read action always returns font data from the font address pointer position. A write action sets the 7-bit font address pointer if the MSB is set, or writes 7-bit font data to the font address pointer position if the MSB is clear. The font address pointer autoincrements after a valid access to the user-definable font data. Autoincrementing allows the 48-font data entries to be written and read back very quickly because the font pointer address needs to be set only once. After the last data location 0x2F has been written, further font data entries are ignored until the font address pointer is reset. If the font address pointer is set to an out-of-range address by writing data in the 0xB0 to 0xFF range, then address 0x00 is set instead (Table 10). Table 11 shows the user-definable font pointer addresses. Table 12 shows bit/segment mapping for user-defined fonts when applied to 7-, 14-, or 16-segment digits. Table 13 illustrates how to set the font address pointer to a value within the acceptable range. D7 is set (1) to denote that the user is writing the font address pointer. If the user attempts to set the font address to one of the out-of-range addresses by writing data in range 0xB0 to 0xFF, then address 0x00 is set instead. The font address pointer autoincrements from address (the last user font location) to point to address 0x00 (the first user font location). Thus, the font address pointer autoincrements indefinitely through font RAM. Cursor Register The cursor register controls the behavior of the cursor segments (Table 14). The controls 48 cursors in 48/1 mode, and 96 cursors in 96/2 mode. The cursor register selects one digit s cursor to be lit either continuously or blinking. All the other digits cursors are off. The 7 least significant bits (LSBs) of the cursor register identify the cursor position. The MSB is clear for the cursor to be on continuously, and set for the cursor to be lit only during the first half of each blink period. The valid cursor position address range is contiguous: 0 to 47 (0x00 to 0x2F) for the first row, and 48 to 95 (0x30 to 0x5F) for the 2nd row. If the cursor register is programmed with an out-of-range value of 96 to 127 (0x60 to 0x7F), then all cursors are off. Annunciator Registers The annunciator registers are organized in bytes, with each segment of each grid being represented by 2 bits. Thus, the four annunciators segments allowed for each grid are represented by exactly 1 byte (Table 15). Annunciators are only available in 48/1 mode. The annunciator address map is shown in Table 4. Configuration Register The configuration register is used to enter and exit shutdown, lock the key VFD configuration settings, select the blink rate, globally clear the digit and annunciator data, reset the blink timing, and select between 48/1 and 96/2 display modes (Table 16). 13
14 Table Segment Display Font Map MSB LSB x000 x001 x010 x011 x100 x101 x110 x111 RAM00 RAM01 RAM10 RAM11 Table Segment Display Font Map MSB LSB x000 x001 x010 x011 x100 x101 x110 x111 RAM00 RAM01 RAM10 RAM RAM02 RAM RAM02 RAM RAM03 RAM RAM03 RAM RAM04 RAM RAM04 RAM RAM05 RAM RAM05 RAM RAM06 RAM RAM06 RAM RAM07 RAM RAM07 RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM0A 1010 RAM0A 1011 RAM0B 1011 RAM0B 1100 RAM0C 1100 RAM0C 1101 RAM0D 1101 RAM0D 1110 RAM0E 1110 RAM0E 1111 RAM0F 1111 RAM0F 14
15 Table 9. Memory Mapping of User-Defined Font Register 0x05 ADDRESS REGISTER DATA READ OR WRITE 0x05 0x00 0x7F Read FUNCTION Read 7-bit user-definable font data entry from current font address. MSB of the register data is clear. Font address pointer is incremented after the read. 0x05 0x00 0x7F Write Write 7-bit user-definable font data entry to current font address. Font address pointer is incremented after the write. 0x05 0x80 0xFF Write Write font address pointer with the register data. Table 10. Font Pointer Address Behavior FONT POINTER ADDRESS ACTION 0x80 to 0xAE Valid range to set the font address pointer. Pointer autoincrements after a font data read or write, while pointer address remains in this range. 0xAF Last valid address. Further font data is ignored after a font data read or write to this pointer address. 0xB0 to 0xFF Invalid range to set the font address pointer. Pointer is set to 0x80. Table 11. User-Definable Font Pointer Addresses FONT POWER-UP POWER-UP REGISTER CHARACTER DEFAULT (BIN) CHARACTER ADDRESS DATA D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 RAM00 byte segment 0 0x05 0x RAM00 byte x05 0x RAM01 byte segment 1 0x05 0x RAM01 byte x05 0x RAM02 byte segment 2 0x05 0x RAM02 byte x05 0x RAM03 byte segment 3 0x05 0x RAM03 byte x05 0x RAM04 byte segment 4 0x05 0x RAM04 byte x05 0x RAM05 byte segment 5 0x05 0x8A RAM05 byte x05 0x8B RAM06 byte segment 6 0x05 0x8C RAM06 byte x05 0x8D RAM07 byte segment 7 0x05 0x8E RAM07 byte x05 0x8F RAM08 byte segment 8 0x05 0x RAM08 byte x05 0x RAM09 byte segment 9 0x05 0x RAM09 byte x05 0x RAM10 byte segment A 0x05 0x
16 Table 11. User-Definable Font Pointer Addresses (continued) FONT CHARACTER POWER-UP DEFAULT (BIN) POWER-UP CHARACTER ADDRESS REGISTER DATA D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 RAM10 byte x05 0x RAM11 byte segment B 0x05 0x RAM11 byte x05 0x RAM12 byte segment C 0x05 0x RAM12 byte x05 0x RAM13 byte segment D 0x05 0x9A RAM13 byte x05 0x9B RAM14 byte segment E 0x05 0x9C RAM14 byte x05 0x9D RAM15 byte segment F 0x05 0x9E RAM15 byte x05 0x9F RAM16 byte segment c 0x05 0xA RAM16 byte x05 0xA RAM17 byte segment n 0x05 0xA RAM17 byte x05 0xA RAM18 byte segment N 0x05 0xA RAM18 byte x05 0xA RAM19 byte segment o 0x05 0xA RAM19 byte x05 0xA RAM20 byte segment r 0x05 0xA RAM20 byte x05 0xA RAM21 byte segment t 0x05 0xAA RAM21 byte x05 0xAB RAM22 byte segment u 0x05 0xAC RAM22 byte x05 0xAD RAM23 byte segment y 0x05 0xAE RAM23 byte x05 0xAF Shutdown Mode (S Data Bit D0) Format The S bit in the configuration register selects shutdown or normal operation (Table 17). The display driver can be programmed while in shutdown mode, and shutdown mode is overridden when in display test mode. For normal operation, set S bit to 1. When the is in shutdown mode, the multiplex oscillator is halted at the end of the current 100µs multiplex period (OSC = 4MHz), and the VFBLANK output is used to disable the VFD tube driver. Data in the digit and other control registers remain unaltered. If the PUMP output is configured as a square-wave clock, then the PUMP output is forced low for the duration of shutdown, and the square-wave clock restored when the comes out of shutdown. If the PHASE1 output or PHASE2 output is configured as a filament driver, then that output is forced low for the duration of shutdown and the filament drive waveforms restored when the comes out of shutdown. When the comes out of shutdown, the external VFD tube driver is presumed to contain invalid data. The VFBLANK output is used to disable the VFD tube driver for the first multiplex cycle after exiting shutdown, clearing any invalid data. The next multiplex cycle uses newly sent valid data. 16
17 Table 12. User-Definable Character Mapping BIT/SEGMENT MAPPING FOR USER-DEFINABLE FONTS WHEN APPLIED TO 7-SEGMENT DIGITS FONT BYTE BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0 RAMxx byte 0 7-seg a 7-seg b 7-seg c 7-seg d 7-seg e 7-seg f 7-seg g RAMxx byte 1 No action No action No action No action No action No action No action BIT/SEGMENT MAPPING FOR USER-DEFINABLE FONTS WHEN APPLIED TO 14-SEGMENT DIGITS FONT BYTE BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0 RAMxx byte 0 7-seg a 7-seg b 7-seg c 7-seg d 7-seg e 7-seg f 7-seg g1 RAMxx byte 1 14-seg g2 14-seg h 14-seg i 14-seg j 14-seg k 14-seg l 14-seg m BIT/SEGMENT MAPPING FOR USER-DEFINABLE FONTS WHEN APPLIED TO 16-SEGMENT DIGITS FONT BYTE BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0 RAMxx byte 0 7-seg a1 7-seg b 7-seg c 7-seg d2 7-seg e 7-seg f 7-seg g1 RAMxx byte 1 14-seg g2 14-seg h 14-seg i 14-seg j 14-seg k 14-seg l 14-seg m Table 13. Setting a Font Character to RAM MODE ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Set font address to minimum (zero) with data 128 or 0x80. (Note that this address is set as power-up default.) Set font address to maximum (47 or 0x2F) with data 175 or 0xAF. 0x x Set font address out of range (48 or 0x30) with data 176 or 0xB0 results in font address pointer being set to zero. 0x UP TO 0x05 UP TO Set font address out of range (127 or 0x7F) with data 255 or 0xFF results in font address pointer being set to zero. 0x Read font address. 0x05 0 Font address; has value 0x00 to 0xAF Table 14. Cursor Register Format MODE ADDRESS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Cursor register. 0x0F BLINK CURSOR POSITION 1st row digit 0 s cursor is lit continuously. 0x0F st row digit 0 s cursor is lit only for the first half of each blink period. 0x0F UP TO 0x0F UP TO 2nd row digit 47 s cursor is lit continuously. 0x0F nd row digit 47 s cursor is lit only for the first half of each blink period. 0x0F No cursor is lit. 0x0F X 1 1 X X X X X 17
18 Table 15. Annunciator Registers Format ANNUNCIATOR BYTE BIT ALLOCATIONS D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ANNUNCIATOR A4 ANNUNCIATOR A3 ANNUNCIATOR A2 ANNUNCIATOR A1 Annunciator A1 is off. X X X X X X 0 0 Annunciator A1 is lit only for the first half of each blink period. Annunciator A1 is lit only for the second half of each blink period. X X X X X X 0 1 X X X X X X 1 0 Annunciator A1 is lit continuously. X X X X X X 1 1 Annunciator A2 is off. X X X X 0 0 X X Annunciator A2 is lit only for the first half of each blink period. Annunciator A2 is lit only for the second half of each blink period. X X X X 0 1 X X X X X X 1 0 X X Annunciator A2 is lit continuously. X X X X 1 1 X X Annunciator A3 is off. X X 0 0 X X X X Annunciator A3 is lit only for the first half of each blink period. Annunciator A3 is lit only for the second half of each blink period. X X 0 1 X X X X X X 1 0 X X X X Annunciator A3 is lit continuously. X X 1 1 X X X X Annunciator A4 is off. 0 0 X X X X X X Annunciator A4 is lit only for the first half of each blink period. Annunciator A4 is lit only for the second half of each blink period. 0 1 X X X X X X 1 0 X X X X X X Annunciator A4 is lit continuously. 1 1 X X X X X X Table 16. Configuration Register Format MODE Configuration register D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 P M R T F B L S Table 17. Shutdown Control (S Data Bit D0) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Shutdown P M R T F B L 0 Normal operation P M R T F B L 1 Configuration Lock (L Data Bit D1) Format The configuration lock register is a safety feature to reduce the risk of the VFD configuration settings being inadvertently changed due to spurious writes if software fails. When set, the shift-limit register (0x0E), grids register (0x03), and output map data (0x06) can be read but cannot be written. The output map data pointer itself may be written in order to allow the output map data to be read back (Table 18). Blink Rate Selection (B Data Bit D2) Format The B bit in the configuration register selects the blink rate of the cursor and annunciator segments. This is the speed that the segments blink on and off when blinking is selected for these segments. The frequency of the multiplex clock OSC and the setting of the B bit (Table 19) determine the blink rate. 18
19 Table 18. Configuration Lock (L Data Bit D1) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Unlocked P M R T F B 0 S Locked P M R T F B 1 S Font Selection (F Data Bit D3) Format The F bit (Table 20) selects the internal font map between 14-segment and 16-segment displays. If a 7- segment display is used, the F bit can be either set or cleared. Global Blink Timing Synchronization (T Data Bit D4) Format Setting the T bit in multiple s at the same time (or in quick succession) synchronizes the blink timing across all the devices (Table 21). The display multiplexing sequence is also reset, which can give rise to a one-time display flicker when the register is written. Global Clear Digit Data (R Data Bit D5) Format When the R bit (Table 22) is set, the segment and annunciator data are cleared. Display Mode (M Data Bit D6) Format The M bit (Table 23) selects the display modes (Table 1). The display modes trade maximum allowable number of digits (mode 96/2) against the availability of annunciator segments (mode 48/1). Blink Phase Readback (P Data Bit D7) Format When the configuration register is read, the P bit reflects the blink phase at that time (Table 24). Serial Interface Serial Addressing The operates as a slave that sends and receives data through an I 2 C-compatible 2-wire interface. The interface uses a serial data line (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL) to achieve bidirectional communication between master(s) and slave(s). A master (typically a microcontroller) initiates all data transfers to and from the, and generates the SCL clock that synchronizes the data transfer (Figure 8). The SDA line operates as both an input and an open-drain output. A pullup resistor, typically 4.7kΩ, is required on the SDA. The SCL line operates only as an input. A pullup resistor, typically 4.7kΩ, is required on SCL if there are multiple masters on the 2-wire interface, or if the master in a single-master system has an open-drain SCL output. Each transmission consists of a START condition (Figure 9) sent by a master, followed by the 7-bit slave address plus R/W bit (Figure 10), a register address byte, 1 or more data bytes, and finally a STOP condition (Figure 9). Start and Stop Conditions Both SCL and SDA remain high when the interface is not busy. A master signals the beginning of a transmission with a START (S) condition by transitioning SDA from high to low while SCL is high. When the master has finished communicating with the slave, it issues a STOP (P) condition by transitioning the SDA from low to high while SCL is high. The bus is then free for another transmission (Figure 9). Bit Transfer One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The data on the SDA line must remain stable while SCL is high (Figure 11). Acknowledge The acknowledge bit is a clocked 9th bit that the recipient uses to handshake receipt of each byte of data (Figure 12). Thus, each byte transferred effectively requires 9 bits. The master generates the 9th clock pulse, and the recipient pulls down SDA during the acknowledge clock pulse, such that the SDA line is stable low during the high period of the clock pulse. When the master is transmitting to the, the generates the acknowledge bit because the is the recipient. When the is transmitting to the master, the master generates the acknowledge bit because the master is the recipient. In this case, the master acknowledges all bytes received from the MAX6853 except for the last byte required, after which the master issues a STOP condition to signify end of transmission. Slave Address The has a 7-bit-long slave address (Figure 10). The eighth bit following the 7-bit slave address is the R/W bit. Set it low for a write command, high for a read command. The first 5 bits (MSBs) of the slave address are always Slave address bits A1 and A0 correspond to the state of the address input pin AD0. This input may be connected to GND, V+, SDA, or SCL. The has four possible slave addresses and therefore a maximum of four devices may share the same interface. 19
20 Table 19. Blink Rate Selection (B Data Bit D2) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Slow blinking (cursor and annunciators blink on for 1s, off for 1s, for OSC = 4MHz) P M R T F 0 L S Fast blinking (cursor and annunciators blink on for 0.5s, off for 0.5s, for OSC = 4MHz) P M R T F 1 L S Table 20. Font Selection (F Data Bit D3) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 14- and 7-segment fonts P M R T 0 B L S 16- and 7-segment fonts P M R T 1 B L S Table 21. Global Blink Timing Synchronization (T Data Bit D4) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Blink timing counters are unaffected. P M R 0 F B L S Blink timing counters are cleared at the end of the present multiplex cycle. P M R 1 F B L S Table 22. Global Clear Digit Data (R Data Bit D5) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Segment and annunciator data are unaffected. P M 0 T F B L S Segment and annunciator data (address range 0x20 to 0x7F) are cleared during the I 2 C acknowledge. P M 1 T F B L S Table 23. Display Mode (M Data Bit D6) Format MODE DISPLAY TYPE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 48/1 Up to 48 digits, 1 digit per grid P 0 R T F B L S 96/2 Up to 96 digits, 2 digits per grid P 1 R T F B L S Table 24. Blink Phase Readback (P Data Bit D7) Format MODE D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 P1 blink phase 0 M R T F B L S P0 blink phase 1 M R T F B L S 20
21 SDA SCL t HD, STA t LOW t HD, STA t SU, STO t HD, DAT t SU, DAT t SU, STA t HIGH t BUF t R t F START CONDITION REPEATED START CONDITION STOP CONDITION START CONDITION Figure 8. 2-Wire Serial Interface Timing Details SDA SCL S P START CONDITION STOP CONDITION Figure 9. Start and Stop Conditions SDA A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W ACK SCL START MSB LSB Figure 10. Slave Address START CONDITION SCL CLOCK PULSE FOR ACKNOWLEDGMENT SDA SDA BY TRANSMITTER SCL DATA LINE STABLE, DATA VALID CHANGE OF DATA ALLOWED SDA BY RECEIVER S Figure 11. Bit Transfer Figure 12. Acknowledge 21
22 Message Format for Writing A write to the comprises the transmission of the s slave address with the R/W bit set to zero, followed by at least 1 byte of information. The first byte of information is the command byte, which determines which register of the is to be written by the next byte, if received. If a STOP condition is detected after the command byte is received, then the takes no further action (Figure 13) beyond storing the command byte. Any bytes received after the command byte are data bytes. The first data byte goes into the internal register of the selected by the command byte (Figure 14). If multiple data bytes are transmitted before a STOP condition is detected, these bytes are generally stored in subsequent internal registers because the command byte address generally autoincrements (Table 26) (Figure 15). Message Format for Reading The is read using the s internally stored command byte as address pointer, the same way the stored command byte is used as address pointer for a write. The pointer generally autoincrements after each data byte is read using the same rules as for a write (Table 26). Thus, a read is initiated by first configuring the s command byte by performing a write (Figure 13). The master can now read n consecutive bytes from the, with the first data byte being read from the register addressed by the initialized command byte (Figure 15). When performing read-after-write verification, reset the command byte s address because the stored byte address generally is autoincremented after the write (Table 26). Operation with Multiple Masters If the is operated on a 2-wire interface with multiple masters, a master reading the should use a repeated start between the write, which sets the s address pointer, and the read(s) that takes the data from the location(s). This is because it is possible for master 2 to take over the bus after master 1 has set up the s address pointer but before master 1 has read the data. If master 2 subsequently changes the s address pointer, then master 1 s delayed read may be from an unexpected location. Command Address Autoincrementing Address autoincrementing allows the to be configured with the shortest number of transmissions by minimizing the number of times the command byte needs to be sent. The command address stored in the generally increments after each data byte is written or read (Table 26). Table 25. Address Map PIN CONNECTION DEVICE ADDRESS AD0 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 GND V SDA SCL Table 26. Command Address Autoincrement Rules BYTE ADDRESS RANGE x to x X , x X x to x x AUTOINCREMENT BEHAVIOR Command byte address autoincrements after byte read or written. Command byte address remains at x or x after byte read or written, but the font address pointer (x ) or output map address pointer (x ) autoincrements. Factory reserved; do not write to this register. Command byte address autoincrements after byte read or written. Command byte address remains at x after byte read or written. 22
23 BYTE IS STORED ON RECEIPT OF STOP CONDITION D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 ACKNOWLEDGE FROM S SLAVE ADDRESS 0 A BYTE A R/W ACKNOWLEDGE FROM Figure 13. Command Byte Received P ACKNOWLEDGE FROM ACKNOWLEDGE FROM HOW CONTROL BYTE AND DATA BYTE MAP INTO 's REGISTERS D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ACKNOWLEDGE FROM S SLAVE ADDRESS 0 A BYTE A DATA BYTE A P R/W 1 BYTE AUTOINCREMENT MEMORY WORD ADDRESS Figure 14. Command and Single Data Byte Received ACKNOWLEDGE FROM ACKNOWLEDGE FROM HOW CONTROL BYTE AND DATA BYTE MAP INTO 's REGISTERS D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ACKNOWLEDGE FROM S SLAVE ADDRESS 0 A BYTE A DATA BYTE A P R/W n BYTE AUTOINCREMENT MEMORY WORD ADDRESS Figure 15. n Data Bytes Received VFD Driver Serial Interface The VFD driver interface on the is a serial interface using three output pins, VFLOAD, VFCLK, and VFDOUT (Figure 16) to drive industry-standard, shiftregister, high-voltage grid/anode VFD tube drivers (Figures 4 and 6). The speed of VFCLK is 1MHz when OSC is 4MHz. The maximum speed of VFCLK is 2MHz when OSC is 8MHz. This interface is used to transfer display data from the to the VFD tube driver. The serial interface bit stream output is programmable up to 84 bits, which are labeled DD0 DD83. The functions of the three interface pins are as follows: VFCLK is the serial clock output, which shifts data on its falling edge from the s 84-bit output shift register to VFLOAD. VFDOUT is the serial data output. The data changes on VFCLK s falling edge, and is stable when it is sampled by the display driver on the rising edge of VFCLK. VFLOAD is the latch-load output. VFLOAD is high to transfer data from the display tube driver s shift register to the display driver s output latch (transparent mode), and low to retain that data in the display driver s output latch. A fourth output pin, VFBLANK, provides gating control of the tube driver. VFBLANK can be configured to be either high or low using the VFBLANK polarity register (Table 29) to enable the VFD tube driver. In the default condition, VFBLANK is high to disable the VFD tube driver, which is expected to force its driver outputs low to blank the display without altering the contents of its output latches. In the default condition, VFBLANK is low to 23
24 enable its VFD tube driver outputs to follow the state of the VFD tube driver s output latches. The VFBLANK output is used for PWM intensity control and to disable the VFD tube driver in shutdown. Multiplex Architecture The multiplex engine transmits grid and anode control data to the external VFD driver using the VFCLK, VFD- OUT, and VFLOAD. The number of data bits M transmitted is set by the user in the shift-limit register (Table 31). Figure 17 is the VFD multiplex timing diagram. The essential rules for multiplex action are as follows: The external VFD driver s data latch contains the data for the current grid being displayed. The VFBLANK input is controlled to provide the PWM intensity control. The VFCLK and VFDOUT outputs are used to fill the external VFD driver s shift register with the multiplex data for the next grid, during the multiplex timeslot for the current grid. The VFLOAD output loads the new grid-anode data pattern at the start of its multiplex cycle. Grids Register The grids register sets how many grids are multiplexed from 1 to 48 (Table 27). When the grids register is written, the external VFD tube driver is presumed to contain invalid data. The VFBLANK output is used to disable the VFD tube driver for the first multiplex cycle after exiting shutdown, clearing any invalid data. The next multiplex cycle uses newly sent, valid data. If the grids register is written with an out-of-range value of 0x30 to 0xFF, then the value 0x2F is stored instead. VFLOAD t VCL t VCH t VCP t VCSH t VCSW VFCLK t VDS VFDOUT DD0 DD1 M-1 M (M IS VALUE IN SHIFT-LIMIT REGISTER) Figure 16. VFD Interface Timing Diagram ONE COMPLETE MULTIPLEX CYCLE AROUND N GRIDS (OSC = 4MHz) START OF NEXT CYCLE 100µs TIMESLOT GRID 0 100µs TIMESLOT GRID 1 100µs TIMESLOT GRID N-4 100µs TIMESLOT GRID N-3 100µs TIMESLOT GRID N-2 100µs TIMESLOT GRID N-1 100µs TIMESLOT GRID 0 500ns 500ns 500ns 500ns GRID 0's 100µs MULTIPLEX TIMESLOT VFCLK VFDOUT DD0 DD1 DD2 DD3 DD4 DD5 DD6 DD7 DD8 DD9 DD10 M-4 M-3 M-2 M-1 M (M IS VALUE IN SHIFT-LIMIT REGISTER) GRID 1's DATA, SENT DURING GRID 0's TIMESLOT VFLOAD Figure 17. VFD Multiplex Timing Diagram 24
V6118 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
M66004SP/FP M66004SP/FP MITSUBISHI DIGITAL ASSP ASSP 16-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT VFD CONTROLLER 16-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT VFD CONTROLLER
 ASSP M664SP/FP M664SP/FP 6-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER 6-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER DESCRIPTION The M664 is a 6-digit 5 7-segment vacuum fluorescent display (FD) controller using the silicon gate
ASSP M664SP/FP M664SP/FP 6-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER 6-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER DESCRIPTION The M664 is a 6-digit 5 7-segment vacuum fluorescent display (FD) controller using the silicon gate
HT9B92 RAM Mapping 36 4 LCD Driver
 RAM Mapping 36 4 LCD Driver Feature Logic Operating Voltage: 2.4V~5.5V Integrated oscillator circuitry Bias: 1/2 or 1/3; Duty: 1/4 Internal LCD bias generation with voltage-follower buffers External pin
RAM Mapping 36 4 LCD Driver Feature Logic Operating Voltage: 2.4V~5.5V Integrated oscillator circuitry Bias: 1/2 or 1/3; Duty: 1/4 Internal LCD bias generation with voltage-follower buffers External pin
Serially Interfaced, 8-Digit LED Display Drivers
 MA729-SMD DRIVER LED MATRI General Description The MA729/MA722 are compact, serial input/output common-cathode display drivers that interface microprocessors (µps) to 7-segment numeric LED displays of
MA729-SMD DRIVER LED MATRI General Description The MA729/MA722 are compact, serial input/output common-cathode display drivers that interface microprocessors (µps) to 7-segment numeric LED displays of
SDA 3302 Family. GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses
 GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
GHz PLL with I 2 C Bus and Four Chip Addresses Preliminary Data Features 1-chip system for MPU control (I 2 C bus) 4 programmable chip addresses Short pull-in time for quick channel switch-over and optimized
7 Segment LED CB-035. ElectroSet. Module. Overview The CB-035 device is an, 8-digit 7-segment display. Features. Basic Parameters
 of rev.. 7 Segment LED Module CB-35 Overview The CB-35 device is an, 8-digit 7-segment display. Each segment can be individually addressed and updated separately using a 2 wire I²C interface. Only one
of rev.. 7 Segment LED Module CB-35 Overview The CB-35 device is an, 8-digit 7-segment display. Each segment can be individually addressed and updated separately using a 2 wire I²C interface. Only one
SMPTE-259M/DVB-ASI Scrambler/Controller
 SMPTE-259M/DVB-ASI Scrambler/Controller Features Fully compatible with SMPTE-259M Fully compatible with DVB-ASI Operates from a single +5V supply 44-pin PLCC package Encodes both 8- and 10-bit parallel
SMPTE-259M/DVB-ASI Scrambler/Controller Features Fully compatible with SMPTE-259M Fully compatible with DVB-ASI Operates from a single +5V supply 44-pin PLCC package Encodes both 8- and 10-bit parallel
Nuvoton Touch Key Series NT086D Datasheet
 DATASHEET Touch Key Series Nuvoton Touch Key Series Datasheet The information described in this document is the exclusive intellectual property of Nuvoton Technology Corporation and shall not be reproduced
DATASHEET Touch Key Series Nuvoton Touch Key Series Datasheet The information described in this document is the exclusive intellectual property of Nuvoton Technology Corporation and shall not be reproduced
Component Analog TV Sync Separator
 19-4103; Rev 1; 12/08 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Component Analog TV Sync Separator General Description The video sync separator extracts sync timing information from standard-definition (SDTV), extendeddefinition
19-4103; Rev 1; 12/08 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Component Analog TV Sync Separator General Description The video sync separator extracts sync timing information from standard-definition (SDTV), extendeddefinition
EM6126 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver. Features. Typical Applications
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA EM616 Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver Features Slim IC for COG, COF and COB technologies I C & Serial bus interface Internal display
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA EM616 Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver Features Slim IC for COG, COF and COB technologies I C & Serial bus interface Internal display
HCF4054B 4 SEGMENT LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVER WITH STROBED LATCH FUNCTION
 4 SEGMENT LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVER WITH STROBED LATCH FUNCTION QUIESCENT CURRENT SPECIF. UP TO 20V OPERATION OF LIQUID CRYSTALS WITH CMOS CIRCUITS PROVIDES ULTRA LOW POWER DISPLAYS EQUIVALENT AC OUTPUT
4 SEGMENT LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVER WITH STROBED LATCH FUNCTION QUIESCENT CURRENT SPECIF. UP TO 20V OPERATION OF LIQUID CRYSTALS WITH CMOS CIRCUITS PROVIDES ULTRA LOW POWER DISPLAYS EQUIVALENT AC OUTPUT
MAX11503 BUFFER. Σ +6dB BUFFER GND *REMOVE AND SHORT FOR DC-COUPLED OPERATION
 19-4031; Rev 0; 2/08 General Description The is a low-power video amplifier with a Y/C summer and chroma mute. The device accepts an S-video or Y/C input and sums the luma (Y) and chroma (C) signals into
19-4031; Rev 0; 2/08 General Description The is a low-power video amplifier with a Y/C summer and chroma mute. The device accepts an S-video or Y/C input and sums the luma (Y) and chroma (C) signals into
PCA8534A. 1. General description. 2. Features and benefits. Automotive LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 3 25 July 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
Rev. 3 25 July 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
VFD Driver/Controller IC
 DESCRIPTION is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/4 to 1/11 duty factor. Eleven segment output lines, 6 grid output lines, 5 segment/grid output drive lines, one display memory,
DESCRIPTION is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/4 to 1/11 duty factor. Eleven segment output lines, 6 grid output lines, 5 segment/grid output drive lines, one display memory,
Quadruple, 2:1, Mux Amplifiers for Standard-Definition and VGA Signals
 9-4457; Rev ; 2/9 Quadruple, 2:, Mux Amplifiers for General Description The MAX954/MAX9542 are quadruple-channel, 2: video mux amplifiers with input sync tip clamps. These devices select between two video
9-4457; Rev ; 2/9 Quadruple, 2:, Mux Amplifiers for General Description The MAX954/MAX9542 are quadruple-channel, 2: video mux amplifiers with input sync tip clamps. These devices select between two video
LM16X21A Dot Matrix LCD Unit
 LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
 Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
TEA6425 VIDEO CELLULAR MATRIX
 IDEO CELLULAR MATRIX 6 ideo Inputs - 8 ideo Outputs Internal Selectable YC Adders MHz Bandwidth @ -db Selectable 0./6.dB Gain FOR EACH Output High Impedance Switch for each Output (- state operation) Programmable
IDEO CELLULAR MATRIX 6 ideo Inputs - 8 ideo Outputs Internal Selectable YC Adders MHz Bandwidth @ -db Selectable 0./6.dB Gain FOR EACH Output High Impedance Switch for each Output (- state operation) Programmable
ams AG austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information:
 austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
RST RST WATCHDOG TIMER N.C.
 19-3899; Rev 1; 11/05 Microprocessor Monitor General Description The microprocessor (µp) supervisory circuit provides µp housekeeping and power-supply supervision functions while consuming only 1/10th
19-3899; Rev 1; 11/05 Microprocessor Monitor General Description The microprocessor (µp) supervisory circuit provides µp housekeeping and power-supply supervision functions while consuming only 1/10th
FEATURES DESCRIPTION APPLICATION BLOCK DIAGRAM. PT6311 VFD Driver/Controller IC
 VFD Driver/Controller IC DESCRIPTION PT6311 is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/8 to 1/16 duty factor housed in 52-pin plastic LQFP Package. Twelve segment output lines, 8 grid
VFD Driver/Controller IC DESCRIPTION PT6311 is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/8 to 1/16 duty factor housed in 52-pin plastic LQFP Package. Twelve segment output lines, 8 grid
Special circuit for LED drive control TM1638
 I. Introduction TM1638 is an IC dedicated to LED (light emitting diode display) drive control and equipped with a keypad scan interface. It integrates MCU digital interface, data latch, LED drive, and
I. Introduction TM1638 is an IC dedicated to LED (light emitting diode display) drive control and equipped with a keypad scan interface. It integrates MCU digital interface, data latch, LED drive, and
S6B CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver with Selectable Slew Rate TOP VIEW +3.3V. 10nF IN+ IN- MAX3812 SD/HD GND RSET +3.
 19-3571; Rev ; 2/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver General Description The is a multirate SMPTE cable driver designed to operate at data rates up to 1.485Gbps, driving one or
19-3571; Rev ; 2/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Multirate SMPTE SD/HD Cable Driver General Description The is a multirate SMPTE cable driver designed to operate at data rates up to 1.485Gbps, driving one or
AS Digit LED Display Driver
 4-Digit LED Display Driver 1 General Description The AS1108 is a compact display driver for 7-segment numeric displays of up to 4 digits. The device can be programmed via SPI, QSPI, and Microwire as well
4-Digit LED Display Driver 1 General Description The AS1108 is a compact display driver for 7-segment numeric displays of up to 4 digits. The device can be programmed via SPI, QSPI, and Microwire as well
MAX7461 Loss-of-Sync Alarm
 General Description The single-channel loss-of-sync alarm () provides composite video sync detection in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM standard-definition television (SDTV) systems. The s advanced detection circuitry
General Description The single-channel loss-of-sync alarm () provides composite video sync detection in NTSC, PAL, and SECAM standard-definition television (SDTV) systems. The s advanced detection circuitry
DM Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits to drive
7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits to drive
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
PCF8534A. 1. General description. 2. Features and benefits. Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 6 25 July 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
Rev. 6 25 July 2011 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
1 Watt, MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.40 x 0.387
 MN-3-52-X-S4 1 Watt, 3 52 MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.4 x.387 Typical Applications Military Radios Military Radar SATCOM Test and Measurement Equipment Industrial and Medical
MN-3-52-X-S4 1 Watt, 3 52 MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.4 x.387 Typical Applications Military Radios Military Radar SATCOM Test and Measurement Equipment Industrial and Medical
ICM Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver. Features. Related Literature FN Data Sheet February 15, 2007
 ICM2 Data Sheet February 5, 200 FN359.2 -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the circuitry
ICM2 Data Sheet February 5, 200 FN359.2 -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the circuitry
Datasheet. AS1106, AS Digit LED Display Drivers. 2 Key Features. 1 General Description. 3 Applications AS1106/ AS1107
 Datasheet 8-Digit LED Display Drivers 1 General Description The AS1106 and the AS1107 are compact display drivers for 7- segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The devices can be programmed via SPI,
Datasheet 8-Digit LED Display Drivers 1 General Description The AS1106 and the AS1107 are compact display drivers for 7- segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The devices can be programmed via SPI,
ams AG austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information:
 austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
FEATURES APPLICATIONS BLOCK DIAGRAM. PT6311 VFD Driver/Controller IC
 VFD Driver/Controller IC DESCRIPTION PT6311 is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/8 to 1/16 duty factor housed in 52-pin plastic QFP Package. Twelve segment output lines, 8 grid
VFD Driver/Controller IC DESCRIPTION PT6311 is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/8 to 1/16 duty factor housed in 52-pin plastic QFP Package. Twelve segment output lines, 8 grid
LED Driver IC IK2108A TECHNICAL DATA. Description
 TECHNICAL DATA LED Driver IC IK2108A Description The IK2108A are anode-grid LED display drives 5.0V~18.0V with output size 8 digits x 14 segments to 12 digits x 10 segments and addition key scan function.
TECHNICAL DATA LED Driver IC IK2108A Description The IK2108A are anode-grid LED display drives 5.0V~18.0V with output size 8 digits x 14 segments to 12 digits x 10 segments and addition key scan function.
PCA General description. 2. Features and benefits. Automotive 80 4 LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 5 12 November 2018 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive
Rev. 5 12 November 2018 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive
深圳市天微电子有限公司 LED DRIVER
 LED DRIVER TM1628 DESCRIPTION TM1628 is an LED Controller driven on a 1/7 to 1/8 duty factor. Eleven segment output lines, six grid output lines, 1 segment/grid output lines, one display memory, control
LED DRIVER TM1628 DESCRIPTION TM1628 is an LED Controller driven on a 1/7 to 1/8 duty factor. Eleven segment output lines, six grid output lines, 1 segment/grid output lines, one display memory, control
uresearch GRAVITECH.US GRAVITECH GROUP Copyright 2007 MicroResearch GRAVITECH GROUP
 GRAVITECH.US uresearch GRAVITECH GROUP Description The I2C-7SEG board is a 5-pin CMOS device that provides 4-digit of 7-segment display using I 2 C bus. There are no external components required. Only
GRAVITECH.US uresearch GRAVITECH GROUP Description The I2C-7SEG board is a 5-pin CMOS device that provides 4-digit of 7-segment display using I 2 C bus. There are no external components required. Only
Low-Cost, 900MHz, Low-Noise Amplifier and Downconverter Mixer
 19-193; Rev 1; 1/ EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Low-Cost, 9MHz, Low-Noise Amplifier General Description The s low-noise amplifier (LNA) and downconverter mixer comprise the major blocks of an RF front-end receiver.
19-193; Rev 1; 1/ EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE Low-Cost, 9MHz, Low-Noise Amplifier General Description The s low-noise amplifier (LNA) and downconverter mixer comprise the major blocks of an RF front-end receiver.
DM Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
ICM7218A COMMON ANODE ICM7218C COMMON ANODE ICM7218B COMMON CATHODE ICM7218D COMMON CATHODE ID0-ID7 ID4-ID7 MODE WRITE ID0-ID3 INPUT
 DATASHEET ICM2 -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver FN359 Rev 4.00 May, 206 The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the circuitry
DATASHEET ICM2 -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver FN359 Rev 4.00 May, 206 The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the circuitry
AS1106, AS Digit LED Display Drivers
 8-Digit LED Display Drivers Data Sheet 1 General Description The AS1106 and the AS1107 are compact display drivers for 7-segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The devices can be programmed via SPI,
8-Digit LED Display Drivers Data Sheet 1 General Description The AS1106 and the AS1107 are compact display drivers for 7-segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The devices can be programmed via SPI,
PCA General description. 2. Features and benefits. Automotive LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 3 4 July 2014 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive signals
Rev. 3 4 July 2014 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive signals
high performance needs great design.
 high performance needs great design. AS1105 Serially interfaced 4-digit LED driver datasheet Please be patient while we update our brand image as austriamicrosystems and TAOS are now ams. www.ams.com Serially
high performance needs great design. AS1105 Serially interfaced 4-digit LED driver datasheet Please be patient while we update our brand image as austriamicrosystems and TAOS are now ams. www.ams.com Serially
ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 11 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2302. Data Sheet (Ver. 1.20)
 ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 11 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2302 Data Sheet (Ver. 1.20) Version 1.20 Published by FAE Team 2008 ABOV Semiconductor Co., Ltd. All right reserved Additional information
ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 11 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2302 Data Sheet (Ver. 1.20) Version 1.20 Published by FAE Team 2008 ABOV Semiconductor Co., Ltd. All right reserved Additional information
AS1100 Serially Interfaced, 8-Digit LED Driver. +5V k 18 ISET VDD DIFG0-DIG3 AS DIN LOAD CLK GND SEG A-G SEP DP GND
 Datasheet AS1100 Serially Interfaced, 8-Digit LED Driver 1 General Description The AS1100 is an LED driver for 7 segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The AS1100 can be programmed via a conventional
Datasheet AS1100 Serially Interfaced, 8-Digit LED Driver 1 General Description The AS1100 is an LED driver for 7 segment numeric displays of up to 8 digits. The AS1100 can be programmed via a conventional
SC75823E/W. Silan Semiconductors 1/3 DUTY GENERAL-PURPOSE LCD DRIVER HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS CO.,LTD DESCRIPTION FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION
 1/3 DUTY GENERAL-PURPOSE LCD DRIVER DESCRIPTION The is a general-purpose LCD driver that can be used for frequency display in microprocessor-controlled radio receives and in other display applications.
1/3 DUTY GENERAL-PURPOSE LCD DRIVER DESCRIPTION The is a general-purpose LCD driver that can be used for frequency display in microprocessor-controlled radio receives and in other display applications.
Data Sheet. Electronic displays
 Data Pack F Issued November 0 029629 Data Sheet Electronic displays Three types of display are available; each has differences as far as the display appearance, operation and electrical characteristics
Data Pack F Issued November 0 029629 Data Sheet Electronic displays Three types of display are available; each has differences as far as the display appearance, operation and electrical characteristics
ams AG austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information:
 austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
austriamicrosystems AG is now The technical content of this austriamicrosystems datasheet is still valid. Contact information: Headquarters: Tobelbaderstrasse 30 8141 Unterpremstaetten, Austria Tel: +43
4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter
 19-2948; Rev 1; 1/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video
19-2948; Rev 1; 1/5 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 4-Channel Video Reconstruction Filter General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video
VFD Driver/Controller IC
 查询 供应商 Tel : 886-2-29162151 DESCRIPTION is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/4 to 1/12 duty factor. Sixteen segment output lines, 4 grid output lines, 8 segment/grid output drive
查询 供应商 Tel : 886-2-29162151 DESCRIPTION is a Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) Controller driven on a 1/4 to 1/12 duty factor. Sixteen segment output lines, 4 grid output lines, 8 segment/grid output drive
ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 10 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2102. Data Sheet (Ver. 1.21)
 ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 10 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2102 Data Sheet (Ver. 1.21) Version 1.21 Published by FAE Team 2008 ABOV Semiconductor Co., Ltd. All right reserved Additional information
ABOV SEMICONDUCTOR 10 SEGMENT X 7 GRID LED DRIVER WITH KEYSCAN MC2102 Data Sheet (Ver. 1.21) Version 1.21 Published by FAE Team 2008 ABOV Semiconductor Co., Ltd. All right reserved Additional information
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
 General Description The MAX6701 microprocessor (µp) supervisory circuits reduce the complexity and components required to monitor power-supply functions in µp systems. These devices significantly improve
General Description The MAX6701 microprocessor (µp) supervisory circuits reduce the complexity and components required to monitor power-supply functions in µp systems. These devices significantly improve
Vorne Industries. 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual Industrial Drive Itasca, IL (630) Telefax (630)
 Vorne Industries 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60141849 (60) 875600 elefax (60) 875609 Page 2 2000B Series Buffered Display 2000B Series Buffered Display Release
Vorne Industries 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60141849 (60) 875600 elefax (60) 875609 Page 2 2000B Series Buffered Display 2000B Series Buffered Display Release
HCC4054B/55B/56B HCF4054B/55B/56B
 HCC454B/55B/56B HCF454B/55B/56B LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIERS 454B 4-SEGMENT DISPLAY DRIER - STROBED LATCH FUNCTION 455B BCD TO 7-SEGMENT DECODER/DRIER, WITH DIS- PLAY-FREQUENCY OUTPUT 456B BCD TO 7-SEGMENT
HCC454B/55B/56B HCF454B/55B/56B LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIERS 454B 4-SEGMENT DISPLAY DRIER - STROBED LATCH FUNCTION 455B BCD TO 7-SEGMENT DECODER/DRIER, WITH DIS- PLAY-FREQUENCY OUTPUT 456B BCD TO 7-SEGMENT
Data Sheet March Features. ICM7218AIJI -40 to Ld CERDIP F28.6 Common Anode. ICM7218BIJI -40 to Ld CERDIP F28.
 TM ICM2 Data Sheet March 200 File Number 359. -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the
TM ICM2 Data Sheet March 200 File Number 359. -Digit LED Microprocessor-Compatible Multiplexed Display Decoder Driver The ICM2 series of universal LED driver systems provide, in a single package, all the
SmartSwitch TM. Wide View LCD 36 x 24 Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS PART NUMBER & DESCRIPTION
 Wide View LCD 36 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced LED Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD Variety
Wide View LCD 36 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced LED Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD Variety
IS31FL CHANNEL LED DRIVER WITH PROGRAMMABLE PATTERN SEQUENCING. August 2017
 3-CHANNEL LED DRIVER WITH PROGRAMMABLE PATTERN SEQUENCING August 2017 GENERAL DESCRIPTION IS31FL3194 is a 3-channel LED driver which features two-dimensional auto breathing mode. It has Pattern and Current
3-CHANNEL LED DRIVER WITH PROGRAMMABLE PATTERN SEQUENCING August 2017 GENERAL DESCRIPTION IS31FL3194 is a 3-channel LED driver which features two-dimensional auto breathing mode. It has Pattern and Current
DATA SHEET. PCF8576C Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Product specification Supersedes data of 2001 Oct 02
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Universal LCD driver for low multiple rates Supersedes data of 2001 Oct 02 2004 Nov 22 Universal LCD driver for low multiple rates CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Universal LCD driver for low multiple rates Supersedes data of 2001 Oct 02 2004 Nov 22 Universal LCD driver for low multiple rates CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PCA General description. 2. Features and benefits. 40 x 4 automotive LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 6 7 April 2015 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive signals
Rev. 6 7 April 2015 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive signals
Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations.
 Wide View Compact LCD 6 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations. Compact body size: 19.0mm (.78 ) x 18.0mm (.709
Wide View Compact LCD 6 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations. Compact body size: 19.0mm (.78 ) x 18.0mm (.709
Part Number Terminals LCD Mode LED Color. * Simultaneous RGB illumination achieves infinite colors. Forward Current I F 20mA Power Dissipation P d mw
 Wide View 36 x Display DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced Illumination: Programmable to display graphics, alphanumeric characters and animated sequences. Standard SMARTDISPLAY TM can be
Wide View 36 x Display DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced Illumination: Programmable to display graphics, alphanumeric characters and animated sequences. Standard SMARTDISPLAY TM can be
NS8050U MICROWIRE PLUSTM Interface
 NS8050U MICROWIRE PLUSTM Interface National Semiconductor Application Note 358 Rao Gobburu James Murashige April 1984 FIGURE 1 Microwire Mode Functional Configuration TRI-STATE is a registered trademark
NS8050U MICROWIRE PLUSTM Interface National Semiconductor Application Note 358 Rao Gobburu James Murashige April 1984 FIGURE 1 Microwire Mode Functional Configuration TRI-STATE is a registered trademark
LED7706/7/8. LED drivers for backlighting and lighting applications.
 LED7706/7/8 LED drivers for backlighting and lighting applications www.st.com/led Content Advanced power management to drive LEDs...3 LED7706/7: six rows of up to 10 white LEDs, with adjustable maximum
LED7706/7/8 LED drivers for backlighting and lighting applications www.st.com/led Content Advanced power management to drive LEDs...3 LED7706/7: six rows of up to 10 white LEDs, with adjustable maximum
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd16315 1/4- to 1/12-DUTY FIP TM (VFD) CONTROLLER/DRIVER DESCRIPTION The µpd16315 is a FIP (Fluorescent Indicator Panel, or Vacuum Fluorescent Display) controller/driver
DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd16315 1/4- to 1/12-DUTY FIP TM (VFD) CONTROLLER/DRIVER DESCRIPTION The µpd16315 is a FIP (Fluorescent Indicator Panel, or Vacuum Fluorescent Display) controller/driver
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945
 Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
NT Output LCD Segment/Common Driver NT7701. Features. General Description. Pin Configuration 1 V1.0
 160 Output LCD Segment/Common Driver Features (Segment mode)! Shift Clock frequency : 14 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 5V ± 10%) 8 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 2.5V - 4.5V)! Adopts a data bus system! 4-bit/8-bit parallel input
160 Output LCD Segment/Common Driver Features (Segment mode)! Shift Clock frequency : 14 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 5V ± 10%) 8 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 2.5V - 4.5V)! Adopts a data bus system! 4-bit/8-bit parallel input
Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s)
 OCTAL BUS TRANSCEIVER/REGISTER WITH 3 STATE OUTPUTS HIGH SPEED: f MAX = 60 MHz (TYP.) at V CC = 4.5V LOW POWER DISSIPATION: I CC = 4µA(MAX.) at T A =25 C COMPATIBLE WITH TTL OUTPUTS : V IH = 2V (MIN.)
OCTAL BUS TRANSCEIVER/REGISTER WITH 3 STATE OUTPUTS HIGH SPEED: f MAX = 60 MHz (TYP.) at V CC = 4.5V LOW POWER DISSIPATION: I CC = 4µA(MAX.) at T A =25 C COMPATIBLE WITH TTL OUTPUTS : V IH = 2V (MIN.)
HCF4027B DUAL J-K MASTER SLAVE FLIP-FLOP
 DUAL J-K MASTER SLAVE FLIP-FLOP SET RESET CAPABILITY STATIC FLIP-FLOP OPERATION - RETAINS STATE INDEFINETELY WITH CLOCK LEVEL EITHER HIGH OR LOW MEDIUM-SPEED OPERATION - 16MHz (Typ. clock toggle rate at
DUAL J-K MASTER SLAVE FLIP-FLOP SET RESET CAPABILITY STATIC FLIP-FLOP OPERATION - RETAINS STATE INDEFINETELY WITH CLOCK LEVEL EITHER HIGH OR LOW MEDIUM-SPEED OPERATION - 16MHz (Typ. clock toggle rate at
Complete 10-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9943
 a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
Features TEMP. RANGE ( C) ICM7245AIM44Z ICM7245 AIM44Z -25 C to +85 C 44 Ld MQFP Q44.10x10
 DATASHEET 8-Character, 16-Segment, Microprocessor Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver FN8587 Rev 0.00 The is an 8-character, alphanumeric display driver and controller which provides all the circuitry
DATASHEET 8-Character, 16-Segment, Microprocessor Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver FN8587 Rev 0.00 The is an 8-character, alphanumeric display driver and controller which provides all the circuitry
MT8814AP. ISO-CMOS 8 x 12 Analog Switch Array. Features. -40 to 85 C. Description. Applications
 MT884 8 x 2 Analog Switch Array Features Internal control latches and address decoder Short set-up and hold times Wide operating voltage: 4.5 to 3.2 2pp analog signal capability R ON 65Ω max. @ DD =2,
MT884 8 x 2 Analog Switch Array Features Internal control latches and address decoder Short set-up and hold times Wide operating voltage: 4.5 to 3.2 2pp analog signal capability R ON 65Ω max. @ DD =2,
OBSOLETE. CMOS 80 MHz Monolithic (18) Color Palette RAM-DACs ADV478/ADV471
 a FEATURES Personal System/2* Compatible 80 MHz Pipelined Operation Triple 8-Bit (6-Bit) D/A Converters 256 24(18) Color Palette RAM 15 24(18) Overlay Registers RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Outputs Sync on
a FEATURES Personal System/2* Compatible 80 MHz Pipelined Operation Triple 8-Bit (6-Bit) D/A Converters 256 24(18) Color Palette RAM 15 24(18) Overlay Registers RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Outputs Sync on
ICM Digit µp Compatible LED Display Decoder Driver. Features. Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 SEMICODUCTOR ICM22 December 993 Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 200ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal, Code B and o Decode Modes Individual
SEMICODUCTOR ICM22 December 993 Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 200ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal, Code B and o Decode Modes Individual
4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video
 19-2951; Rev 2; 2/7 4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video applications
19-2951; Rev 2; 2/7 4-Channel Video Filter for RGB and CVBS Video General Description The 4-channel, buffered video reconstruction filter is ideal for anti-aliasing and DAC-smoothing video applications
DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port
 DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port General Description The DP8212 DP8212M is an 8-bit input output port contained in a standard 24-pin dual-in-line package The device which is fabricated using Schottky
DP8212 DP8212M 8-Bit Input Output Port General Description The DP8212 DP8212M is an 8-bit input output port contained in a standard 24-pin dual-in-line package The device which is fabricated using Schottky
HT162X HT1620 HT1621 HT1622 HT16220 HT1623 HT1625 HT1626 COM
 Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ HT1620 RAM Mapping 324 LCD Controller for I/O MCU Features Logic operating voltage: 2.4V~3.3V LCD voltage: 3.6V~4.9V
Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ HT1620 RAM Mapping 324 LCD Controller for I/O MCU Features Logic operating voltage: 2.4V~3.3V LCD voltage: 3.6V~4.9V
AS LED Driver with Detailed Error Detection
 64 LED Driver with Detailed Error Detection 1 General Description The AS1116 is a compact LED driver for 64 single LEDs or 8 digits of 7-segments. The devices can be programmed via an SPI compatible 3-wire
64 LED Driver with Detailed Error Detection 1 General Description The AS1116 is a compact LED driver for 64 single LEDs or 8 digits of 7-segments. The devices can be programmed via an SPI compatible 3-wire
PCF8576C. 1. General description. 2. Features and benefits. Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 13 16 December 2013 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive
Rev. 13 16 December 2013 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiplex rates. It generates the drive
PCF8576D. 1. General description. 2. Features. Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 7 18 December 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) with low multiple rates. It generates
Rev. 7 18 December 2008 Product data sheet 1. General description 2. Features The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) with low multiple rates. It generates
Complete 10-Bit/12-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9943/AD9944
 a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit (AD9943), 12-Bit (AD9944), 25 MSPS
a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit (AD9943), 12-Bit (AD9944), 25 MSPS
DM Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
 DM9368 7-Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder Driver Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs General Description The DM9368 is a 7-segment decoder driver incorporating input latches and constant current output circuits
Description. ICM7228AIPI Sequential Common Anode -40 to Ld PDIP E28.6. ICM7228BIPI Sequential Common Cathode -40 to Ld PDIP E28.
 ICM22 August 99 -Digit, Microprocessor- Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 200ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal,
ICM22 August 99 -Digit, Microprocessor- Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 200ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal,
HCF40193B PRESETTABLE UP/DOWN COUNTERS (DUAL CLOCK WITH RESET) BINARY TYPE
 PRESETTABLE UP/DOWN COUNTERS (DUAL CLOCK WITH RESET) BINARY TYPE INDIVIDUAL CLOCK LINES FOR COUNTING UP OR COUNTING DOWN SYNCHRONOUS HIGH-SPEED CARRY AND BORROW PROPAGATION DELAYS FOR CASCADING ASYNCHRONOUS
PRESETTABLE UP/DOWN COUNTERS (DUAL CLOCK WITH RESET) BINARY TYPE INDIVIDUAL CLOCK LINES FOR COUNTING UP OR COUNTING DOWN SYNCHRONOUS HIGH-SPEED CARRY AND BORROW PROPAGATION DELAYS FOR CASCADING ASYNCHRONOUS
OBSOLETE FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM 256-COLOR/GAMMA PALETTE RAM. RED 256 x 10. GREEN 256 x 10 CONTROL REGISTERS PIXEL MASK REGISTER TEST REGISTERS MODE
 a FEATURES 22 MHz, 24-Bit (3-Bit Gamma Corrected) True Color Triple -Bit Gamma Correcting D/A Converters Triple 256 (256 3) Color Palette RAM On-Chip Clock Control Circuit Palette Priority Select Registers
a FEATURES 22 MHz, 24-Bit (3-Bit Gamma Corrected) True Color Triple -Bit Gamma Correcting D/A Converters Triple 256 (256 3) Color Palette RAM On-Chip Clock Control Circuit Palette Priority Select Registers
Specification of Vacuum Fluorescent Display NORITAKE ITRON CORPORATION Sheet 1/19 DS25402
 Specification of Vacuum Fluorescent Display NORITAKE ITRON CORPORATION Sheet 1/19 DS25402 Item No. Rev. Spec. No. Date(M-D-Y) 0 P-R Aug-16-07 DS2045G 1 P-R1 Dec-10-07 2 P-R2 Dec-19-07 3 T-R Dec-26-07 4
Specification of Vacuum Fluorescent Display NORITAKE ITRON CORPORATION Sheet 1/19 DS25402 Item No. Rev. Spec. No. Date(M-D-Y) 0 P-R Aug-16-07 DS2045G 1 P-R1 Dec-10-07 2 P-R2 Dec-19-07 3 T-R Dec-26-07 4
SignalTap Plus System Analyzer
 SignalTap Plus System Analyzer June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Simultaneous internal programmable logic device (PLD) and external (board-level) logic analysis 32-channel external logic analyzer 166
SignalTap Plus System Analyzer June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Simultaneous internal programmable logic device (PLD) and external (board-level) logic analysis 32-channel external logic analyzer 166
A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER
 A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER Item Type text; Proceedings Authors CONN, RAYMOND; BREEDLOVE, PHILLIP Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A MISSILE INSTRUMENTATION ENCODER Item Type text; Proceedings Authors CONN, RAYMOND; BREEDLOVE, PHILLIP Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
ICM7228AIPI Sequential Common Anode -40 to Ld PDIP E28.6. ICM7228BIPI Sequential Common Cathode -40 to Ld PDIP E28.6
 ICM22 May 22 -Digit, Microprocessor- Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 2ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal,
ICM22 May 22 -Digit, Microprocessor- Compatible, LED Display Decoder Driver Features Improved 2nd Source to Maxim ICM2 Fast Write Access Time of 2ns Multiple Microprocessor Compatible Versions Hexadecimal,
DATA SHEET. PCF8566 Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates INTEGRATED CIRCUITS May 04
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Universal LCD driver for low multiple Supersedes data of 1997 Apr 02 File under Integrated Circuits, IC12 1998 May 04 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3 ORDERING
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET Universal LCD driver for low multiple Supersedes data of 1997 Apr 02 File under Integrated Circuits, IC12 1998 May 04 CONTENTS 1 FEATURES 2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3 ORDERING
Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits
 Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits Chapter 9 Objectives Selected areas covered in this chapter: Analyzing/using decoders & encoders in circuits. Advantages and disadvantages of LEDs and LCDs. Observation/analysis
Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits Chapter 9 Objectives Selected areas covered in this chapter: Analyzing/using decoders & encoders in circuits. Advantages and disadvantages of LEDs and LCDs. Observation/analysis
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945
 Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
Complete 12-Bit 40 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9945 FEATURES 40 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking
Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of
 Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of applications such as home appliances, medical, automotive,
Hello and welcome to this training module for the STM32L4 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) controller. This controller can be used in a wide range of applications such as home appliances, medical, automotive,
PCF General description. 2. Features and benefits. Universal LCD driver for low multiplex rates
 Rev. 7 21 July 2015 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
Rev. 7 21 July 2015 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a peripheral device which interfaces to almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) 1 with low multiple rates. It generates the drive signals
MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers
 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin molded package.
Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin molded package.
DS2176 T1 Receive Buffer
 T1 Receive Buffer www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Synchronizes loop timed and system timed T1 data streams Two frame buffer depth; slips occur on frame boundaries Output indicates when slip occurs Buffer may
T1 Receive Buffer www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Synchronizes loop timed and system timed T1 data streams Two frame buffer depth; slips occur on frame boundaries Output indicates when slip occurs Buffer may
3 V/5 V, 450 μa 16-Bit, Sigma-Delta ADC AD7715
 3 V/5 V, 450 μa 16-Bit, Sigma-Delta ADC AD7715 FEATURES Charge-balancing ADC 16-bits no missing codes 0.0015% nonlinearity Programmable gain front end Gains of 1, 2, 32 and 128 Differential input capability
3 V/5 V, 450 μa 16-Bit, Sigma-Delta ADC AD7715 FEATURES Charge-balancing ADC 16-bits no missing codes 0.0015% nonlinearity Programmable gain front end Gains of 1, 2, 32 and 128 Differential input capability
Vorne Industries. 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual Industrial Drive Itasca, IL (630) Telefax (630)
 Vorne Industries 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60143-1849 (630) 875-3600 Telefax (630) 875-3609 . 3 Chapter 1 Introduction... 1.1 Accessing Wiring Connections
Vorne Industries 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60143-1849 (630) 875-3600 Telefax (630) 875-3609 . 3 Chapter 1 Introduction... 1.1 Accessing Wiring Connections
MBI5050 Application Note
 MBI5050 Application Note Foreword In contrast to the conventional LED driver which uses an external PWM signal, MBI5050 uses the embedded PWM signal to control grayscale output and LED current, which makes
MBI5050 Application Note Foreword In contrast to the conventional LED driver which uses an external PWM signal, MBI5050 uses the embedded PWM signal to control grayscale output and LED current, which makes
SmartSwitch. Wide View LCD 36 x 24 Pushbuttons & Display DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS PART NUMBERS & DESCRIPTIONS
 Wide View LCD 36 x 24 Pushbuttons & Display DISTINCTIV CHARACTRISTICS Standard with nhanced LD Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD
Wide View LCD 36 x 24 Pushbuttons & Display DISTINCTIV CHARACTRISTICS Standard with nhanced LD Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD
