Introduction to Fiber Optic Cable Technology Jerry Bednarczyk, PE Course Content
|
|
|
- Gloria Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Fiber Optic Cable Technology Jerry Bednarczyk, PE Course Content Page 1 of 10
2 GENERAL A fiber optic cable system is very similar to a copper wire system in that it is used to transmit data from one location to another. The primary difference between the two is that the fiber optic cable system uses light pulses to transmit data instead of electrical impulses. At one end of the cable, a transmitter receives electric signals, translates the information into coded light pulses and channels the resultant light pulses into the fiber optic cable. Light emitting diodes or injection laser diodes are typically used to generate the light pulses. The light pulses are transmitted through the fiber optic cable. Because of the characteristics of the fiber optic cable, the majority of the light pulses are reflected into and along the fiber core with very little loss of light through the cable. Like the losses experienced in copper wires, the light signals do lose strength through the dispersion of light within the cable. An optical detector (receiver) at the opposite end of the cable then converts the light pulse signals back to the original digital electrical signals. PIN diodes or avalanche photodiodes (APD) are typically used as detectors. Depending upon the length of the fiber cable run, repeater stations may be inserted to boost the strength of the light signals. Unlike copper wires, which have limited capacity, the fiber optic cable is capable of transmitting billions of digital bits per second or the equivalent of thousands of telephone calls simultaneously. Other benefits of fiber optic cable include tremendously higher rates of transmission, lower losses in signal strength, increased resistance to electromagnetic interference. While initial installation costs are generally higher, maintenance costs are lower. BASIC FIBER OPTIC CABLE CONSTRUCTION A fiber optic cable is essentially constructed in two concentric layers of hair-like silica glass fibers forming the core and the cladding. The core is the center of the cable and is where the light is transmitted. Around the core is the cladding. The cladding forms the outer optical layer of the fiber. The index of refraction of the core is always higher then the index of the cladding so that the light can be trapped in the core and guided along the fiber. The coating or buffer is the outermost layer of the fiber cable and provides protection from physical damage and moisture. JACKET FIBER CORE COATING CLADDING STRENGTH MEMBERS (ARAMID FIBERS) TYPICAL FIBER OPTIC CABLE Page 2 of 10
3 To provide protection and strength, the fiber optic cable is encased in a tough outer covering, called the jacket. Additional strength members, typically aramid type fibers (i.e. Kevlar by Dupont) and occasionally an overall armor shielding are also added. These components provide the physical strength to allow the cable to be installed in buildings, outdoors, underground and underwater. The cable itself can have as few as one fiber to hundreds of fibers. FIBER OPTIC CABLE TYPES Multimode Fiber Cable: The multimode fiber optic cable has a larger core that is typically manufactured to 62.5 microns but can range from 50 to 100 microns in diameter. The 62.5 microns dimension is used with light sources at wavelengths of 850nm (bandwidth of 160 MHz) and 1300nm (bandwidth of 500 MHz) which are the wavelengths that produce the lowest losses in the cable. The less popular 50 micron cable is also used with light sources at wavelengths of 850 and 1300nm, however the bandwidth associated with each wavelength is 500 MHz. Since the total bandwidth is greater than the 62.5 micron cable, the 50 micron cable is gaining in popularity. Because of the larger core diameter, the light pulses travelling down the cable will not all travel in a direct route. Some of the light rays, or modes, that make up the pulse will travel in a more direct route, while others will be reflected off the cladding causing the pulses to bounce back and forth as the light travels down the core. The result is an output signal that is attenuated and undergoes a time dispersion compared to the original pulse. The attenuation decreases and the dispersion increases with the length of the cable. For these reasons, multimode fiber cable is typically used for installations involving shorter distances and lower speed networks, such as a small LAN system or in certain medical applications. CLADDING CORE Typical Multimode Cable (Dimensions are in microns) INPUT SIGNAL OUTPUT SIGNAL MULTIMODE FIBER CABLE Page 3 of 10
4 Graded Index Multimode Fiber Cable: The graded index mutimode fiber cable is constructed with a core with a lower refractive index near the cladding as compared to the center of the core. This causes the light rays, or modes, that are on a more direct route down the center of the core to travel slower relative to those that are near the cladding. Also, instead of bouncing off the cladding at sharper angles, the light tends to curve in a helical pattern due to the graded refractive index. The result is an output signal that is less dispersed and undergoes less attenuation compared to the standard multimode cable. While the cost of this type cable is higher, the quality of the output signal is greatly increased making it the preferred choice for on premise data and communications installations. CLADDING CORE Typical Graded Index Multimode Cable (Dimensions are in microns) INPUT SIGNAL OUTPUT SIGNAL GRADED INDEX MULTIMODE FIBER CABLE Single Mode Fiber Cable: Single mode fiber optic cable is constructed of a single glass fiber core approximately 8.5 microns in diameter. The cladding surrounding the core is several times thicker than the core. As the name indicates, only one mode will propogate along the single mode cable either at a wavelength of 1300 nm or 1550 nm in a bandwidth in the gigahertz range. Operating at the higher wavelengths greatly reduces the attenuation of the signal. Because of the huge bandwidth, the capacity of a single mode fiber cable is tremendous. Due to the small diameter core, virtually all of the light travels in a direct route along the fiber with extremely minimal amounts of light bouncing off the cladding, as happens with the multimode cable. Very little light is lost through the cladding, resulting in very low attenuation rates and minimal dispersions. Page 4 of 10
5 Single mode fiber cable is used when the lengths of the cable runs are large. Experimental installations have demonstrated that signals can be transmitted over 1,000 miles. The telephone and cable television industries install hundreds of thousands of miles of single mode cable yearly. Although it is somewhat more expensive than multimode cable, college campuses and large industrial facilities have found that the benefits of the single mode cable are well worth the added installation costs. CLADDING CORE Typical Single Mode Cable (Dimensions are in microns) INPUT SIGNAL OUTPUT SIGNAL SINGLE MODE FIBER CABLE Plastic Fiber: The cables discussed above are manufactured with extremely high quality silica glass fibers. Fiber optic cable is also manufactured using plastic core and cladding. The cable is huge, sometimes approaching 1 mm in diameter, compared to the dimensions of glass fiber cable. Plastic fiber optic cable operates at longer wavelengths, using visible light with very low bandwidths. Because of the large cable and longer wavelengths, there are considerable losses to the signal. These cables are generally used in applications requiring lengths of only a few feet. It is used in some automotive applications and in some high-end audio applications. Costs of the cable are relatively low and installation of plastic cable is fairly simple. CABLE DESIGNS There are two basic cable designs for fiber optic cables, loose tube (or loose buffered tube) and tight buffered types. The cables are designed to protect the fibers and to minimize the stresses on the fiber optic bundles. The properties of the cables are impacted by the stresses that are imposed on the cables. Any stress to the cable that cause density deviations to the fibers, will alter the propagation characteristics of the cable. If the damage is significant, the cable will be rendered useless and will have to Page 5 of 10
6 be abandoned or replaced. Loose tube cable is generally used for outside plant installations (that is, longer cable runs). Tight buffered type cable is primarily used inside buildings. Cable Designs Loose Tube Cable: In a loose tube cable, the fiber cable is housed in a soft plastic tube, generally gel filled, to provide protection from moisture. The fiber in the tube is longer than the tube itself allowing the fiber to coil while under compression and to straighten when under tension. The tubes/fiber are joined with other color-coded tubes/fiber around a central strength member. They are surrounded by other protective materials and are finally enclosed in an overall polyethylene jacketing material. The outer jackets may also be encased in some form of armor jacketing and an additional overall plastic sheath. The construction of the overall cable provides protection to the fibers both during installation and while in service. The strength members are used to assist in pulling and/or supporting the cable structure. Loose tube cables are generally preferred for longer distance installations where high fiber quantities, lower attenuation and the ability to handle wider temperature ranges are desired. Splices and terminations of loose tube cables can be difficult and messy due to the gel used to protect the fiber cables. Also, if the tubes are damaged while installing the cable, the protective gel could leak and allow water to penetrate to the fiber making it unusable. CABLE (NORMAL) GEL FILLED (TYPICAL) CABLE TUBE CABLE (COMPRESSED) CABLE TUBE CABLE (TENSION) PROTECTIVE FILL CABLE FIBER STRENGTH MEMBER CABLE TUBE ARAMID FIBERS OVERALL JACKET LOOSE TUBE CABLE Page 6 of 10
7 Cable Designs Tight Buffered Cable: In a tight buffered constructed cable, a soft polymer layer is fabricated in direct contact with the fiber cable. This layer provides the fiber cable with protection from external strains. The cable assembly can then be encased with amarid fibers and an overall cable jacket. Tight buffered cables are better suited to on-site, or intra-building installations. The design of the tight buffered cable is more flexible than the loose tube cable. This makes it easier to install particularly in areas with tight bending radii. Also, the fiber itself is easier to access and there is no gel layer. This makes this type of cable easier to splice and terminate. ARAMID FIBER OVERALL JACKET POLYMER LAYER TIGHT BUFFERED CABLE CONNECTORS AND SPLICES In a fiber optic cable system, it is extremely important to minimize the losses in the light rays being transmitted on the cable. Two locations that can cause significant increases in cable losses occur at Connectors and in Splices. The electrical signal into the transmitter and exiting the receiver are generally sent along copper conductors. After the signals are converted to digital light rays and before they leave the transmitter and enter the fiber optic cable (or enter the receiver at the end of the run), they must pass through a Connector. The connector is a mechanical device that is attached to the fiber optic cable and can be easily attached to, or detached from, the transmitter or receiver. A Splice is used when two fiber optic cables need to be permanently joined to one another. For example, splices are required when the total length of the cable run exceeds the length that could be reasonably manufactured or shipped. They are also installed in order to bypass natural obstructions in the cable route, or at building entrances. Page 7 of 10
8 Connectors Where the fiber cable transitions from the transmitter or to the receiver in a circuit is where significant losses can occur. The type of connector used and the quality of the installation can have a large impact on the quality of the signal. In the years since fiber optics became a commercially viable technology, the quality of available connectors has improved dramatically. Some of the most widely-used types are described below. TYPICAL ST CONNECTOR (ST is a registered trademark of AT&T) One of the most popular type of connectors on the market, especially for multimode operation, is the ST type. The ST connector is a bayonet type with a ferrule made of either ceramic, plastic or metal. The connection is keyed and spring loaded to help assure that the cable is properly seated. The installation of the ST connector is relatively simple and is generally made up on the project site. TYPICAL FC CONNECTOR For years, the FC/PC connector has proven to be an extremely popular single mode connector. The connection is notched and screws together providing a very secure and accurate connection that minimizes system losses. TYPICAL SC CONNECTOR Another type of single mode connector that is rapidly taking the place of the FC/PC type, is the SC connector. The SC is a push-pull type mechanism with a locking tab to hold the connection in place. It also provides a very accurate connection. This connection s low cost, ease of installation and durability, are making it the connector of choice for single mode installations. Page 8 of 10
9 Splices While connectors are considered as temporary connections, splices provide a permanent connection between two fibers. Splices are used when cable runs are very long, when cable are accidentally cut or when splitting a multi-conductor fiber cable into several smaller multi-conductor cables. There are two types of splices, fusion and mechanical. A fusion splice is made by welding, or fusing, two fibers together. A mechanical splice is comprised of some form of clamping mechanism to hold the fibers in place with the actual fibers being joined by a glue or gel compound to facilitate the signal transfer. With either type of splice, the fibers must be precisely lined up in order to minimize the losses across the splice junction. Fusion splice PERMANENT CONNECTION With a fusion splice, the fiber cables to be joined are arranged so the ends of the cables are touching. The connection point is then heated past the cables melting point with an electric arc until the cables are fused. Mechanical splice SLEEVE OR CLAMP A mechanical splice is considered a temporary connection. The cable is cleaved, polished, and joined together with a clamp or crimp mechanism often in combination with an epoxy or gel. Connector and splice losses: Earlier, we discussed the losses in signal strength that occur in the transmission along a fiber optic cable that depend on the type of cable used, the length of the run and the quality of the signal. Losses can also occur at every connector or splice. If a connector or splice is installed perfectly and the fiber cores are identical, the losses will be minimized. Page 9 of 10
10 Common problems that can cause losses in connectors and splices are gaps at the point of connection, improper cleaning and finishing of the cables, Numerical Aperture (NA) mismatches, improper alignment or mismatches in cable core diameters at splice points. End Gap: A gap at a splice or termination will allow the light signal to disperse out of the core and be lost. The air gap will also cause losses due to the light reflecting off the end of the adjoining cable. NA Mismatch: The Numerical Aperture (NA) of the cable is one measure of the performance characteristics of a fiber optic cable. Splicing cables with differing NA values will cause losses in the signal. A multimode fiber cable will transmit light efficiently only when the angle of incidence of the light is within a specific number of degrees of the axis of the fiber. The numerical aperture of a cable is the angle the cable can accept light. The value is dependent on the construction characteristics of the cable. Improper Alignment: A misalignment of a cable splice will cause losses in the signals being transmitted along the cable. SUMMARY Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables can be used to transmit large volumes of data along a single cable. Electrical signals are converted into light pulses which are then transmitted along the fiber cable. Due to the advances made in fiber cable technology, thousands of signals can be transmitted over hundreds of miles simultaneously with minimal losses in signal strength. Multimode cables, while generally lower in cost, have higher losses in signal strength as compared to single mode cables. Single mode cables are usually used in installations that are very long and require low losses. Page 10 of 10
Selection of a cable depends on functions such as The material Singlemode or multimode Step or graded index Wave length of the transmitter
 Fibre Optic Communications The greatest advantage of fibre cable is that it is completely insensitive to electrical and magnetic disturbances. It is therefore ideal for harsh industrial environments. It
Fibre Optic Communications The greatest advantage of fibre cable is that it is completely insensitive to electrical and magnetic disturbances. It is therefore ideal for harsh industrial environments. It
Introduction to Fibre Optics
 Introduction to Fibre Optics White paper White Paper Introduction to Fibre Optics v1.0 EN 1 Introduction In today s networks, it is almost impossible to find a network professional who has never been in
Introduction to Fibre Optics White paper White Paper Introduction to Fibre Optics v1.0 EN 1 Introduction In today s networks, it is almost impossible to find a network professional who has never been in
Fiber Optics Redefined
 Fiber Optics Redefined Questions and Answers on the basics of fiber optic installation TECHLOGIX NETWORX Questions & Answers Questions and Answers Q: What are the two main types of fiber? A: The two main
Fiber Optics Redefined Questions and Answers on the basics of fiber optic installation TECHLOGIX NETWORX Questions & Answers Questions and Answers Q: What are the two main types of fiber? A: The two main
Public Works Division Lighting District Fiber Optic Specifications April 2009
 Public Works Division Lighting District Fiber Optic Specifications April 2009 7000 Florida Street Punta Gorda, Florida 33950 Tele: 941.575.3600 Fax : 941.637.9265 www.charlottecountyfl.com/publicworks
Public Works Division Lighting District Fiber Optic Specifications April 2009 7000 Florida Street Punta Gorda, Florida 33950 Tele: 941.575.3600 Fax : 941.637.9265 www.charlottecountyfl.com/publicworks
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6191 Fiber Optic Cable
 2004 Specifications CSJ 0014-02-014, etc SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6191 Fiber Optic Cable 1. Description. Furnish, install, splice, field terminate, and test the fiber optic cables. 2. Materials. A. General
2004 Specifications CSJ 0014-02-014, etc SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6191 Fiber Optic Cable 1. Description. Furnish, install, splice, field terminate, and test the fiber optic cables. 2. Materials. A. General
We will look first at the cable, and then the transceivers (which act as both transmitter and receiver on each end of the fiber cable).
 Nuclear Sensors & Process Instrumentation Fiber Cable Basics Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light
Nuclear Sensors & Process Instrumentation Fiber Cable Basics Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 2284 Fiber Optic Cable (Self-Supporting)
 2004 Specifications CSJ 0086-14-046 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 2284 Fiber Optic Cable (Self-Supporting) 1. Description. Furnish, install, splice, field terminate, and test the fiber optic cables. 2. Materials.
2004 Specifications CSJ 0086-14-046 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 2284 Fiber Optic Cable (Self-Supporting) 1. Description. Furnish, install, splice, field terminate, and test the fiber optic cables. 2. Materials.
Installation of Optical Fiber
 Application Notes Installation of Optical Fiber Author Mr. Prasanna Pardesi This procedure describes general information for installation of optical fiber cable pulled or blown in HDPE ducts. Keywords
Application Notes Installation of Optical Fiber Author Mr. Prasanna Pardesi This procedure describes general information for installation of optical fiber cable pulled or blown in HDPE ducts. Keywords
SECTION 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Contents Introduction LC, SC and ST Series...4-2 Markets and Applications...4-2 International Standard Documents Compliance...4-2 LC Series Features and Benefits...4-3 LC Standard... 4-4 to 4-5 LC for
Contents Introduction LC, SC and ST Series...4-2 Markets and Applications...4-2 International Standard Documents Compliance...4-2 LC Series Features and Benefits...4-3 LC Standard... 4-4 to 4-5 LC for
Lensed Fibers & Tapered Ends Description:
 Lensed Fibers & Tapered Ends Description: LaseOptics Corporation ( LaseOptics ) has been producing next generation optical lensed fibers. LaseOptics Lensed Optical Fibers technology is proprietary integrated
Lensed Fibers & Tapered Ends Description: LaseOptics Corporation ( LaseOptics ) has been producing next generation optical lensed fibers. LaseOptics Lensed Optical Fibers technology is proprietary integrated
Chapter 5 Fiber Optics
 Optical Fibers Chapter 5 Fiber Optics As fiber optic cables fall in price, they are being used more and more for communications. In a nutshell, electrical signals are converted into a light beam (possibly
Optical Fibers Chapter 5 Fiber Optics As fiber optic cables fall in price, they are being used more and more for communications. In a nutshell, electrical signals are converted into a light beam (possibly
Triax TechInfo. Installing and pulling Fibre Optic cables
 Installation methods for both wire cables and Fibre Optical cables are similar. Fibre cable can be pulled with much greater force than copper wire if you pull it correctly. Just remember these rules: 1)
Installation methods for both wire cables and Fibre Optical cables are similar. Fibre cable can be pulled with much greater force than copper wire if you pull it correctly. Just remember these rules: 1)
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6559 Telecommunication Cable
 2004 Specifications CSJ 0015-09-147, etc. SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6559 Telecommunication Cable 1. Description. This specification governs the materials, installation, termination, splicing, testing, training,
2004 Specifications CSJ 0015-09-147, etc. SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6559 Telecommunication Cable 1. Description. This specification governs the materials, installation, termination, splicing, testing, training,
Cable Jacket - The outermost layer of the fiber cable. Application: Types Single mode Multi mode. Simplex or Duplex available
 Fiber Optic Products FIBER OPTIC PRODUCTS FIBER OPTIC PATCH CORD CABLE The Construction of a Fiber-Optic Cable Cable Jacket - The outermost layer of the fiber cable. Strengthening fibers - The strengthening
Fiber Optic Products FIBER OPTIC PRODUCTS FIBER OPTIC PATCH CORD CABLE The Construction of a Fiber-Optic Cable Cable Jacket - The outermost layer of the fiber cable. Strengthening fibers - The strengthening
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 8540 Telecommunication Cable
 2004 Specifications CSJ 0914-00-307 & CSJ 0914-25-003 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 8540 Telecommunication Cable 1. Description. This specification governs the materials, installation, termination, splicing, testing,
2004 Specifications CSJ 0914-00-307 & CSJ 0914-25-003 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 8540 Telecommunication Cable 1. Description. This specification governs the materials, installation, termination, splicing, testing,
Gel-sealed in-line fiber optic closure
 SCIL-C Gel donut INSTALLATION INSTRUCTION TC-1363-1-IP Rev A, Oct 2017 www.commscope.com Gel-sealed in-line fiber optic closure Contents 1 General 2 Sizing and product kit information 3 Installation conditions
SCIL-C Gel donut INSTALLATION INSTRUCTION TC-1363-1-IP Rev A, Oct 2017 www.commscope.com Gel-sealed in-line fiber optic closure Contents 1 General 2 Sizing and product kit information 3 Installation conditions
FOSC-600 C and D I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N
 FOSC-600 C and D I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N In-line and butt version Cold applied re-usable fiber optic closure Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Product description 1.2 Capacity 2 General
FOSC-600 C and D I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N In-line and butt version Cold applied re-usable fiber optic closure Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Product description 1.2 Capacity 2 General
Broadband System - D
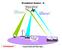 Broadband System - D Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
Broadband System - D Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
1995 Metric CSJ SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM 6031 SINGLE MODE FIBER OPTIC VIDEO TRANSMISSION EQUIPMENT
 1995 Metric CSJ 0508-01-258 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM 6031 SINGLE MODE FIBER OPTIC VIDEO TRANSMISSION EQUIPMENT 1.0 Description This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of color Single
1995 Metric CSJ 0508-01-258 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM 6031 SINGLE MODE FIBER OPTIC VIDEO TRANSMISSION EQUIPMENT 1.0 Description This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of color Single
1993 Specifications CSJ SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM Fiber Optic Cable System
 1993 Specifications CSJ 0008-12-071 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM 6540 Fiber Optic Cable System 1.0 Description. This item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of fiber optic cables in designated
1993 Specifications CSJ 0008-12-071 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION ITEM 6540 Fiber Optic Cable System 1.0 Description. This item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of fiber optic cables in designated
Delaware County Community College Project # Marple Campus Renovation - Phase % Construction Documents November 23, 2011
 SECTION 271323 - COMMUNICATIONS OPTICAL FIBER BACKBONE CABLING PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This section provides the specifications for the work related to the optical fiber system in the project.
SECTION 271323 - COMMUNICATIONS OPTICAL FIBER BACKBONE CABLING PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION A. This section provides the specifications for the work related to the optical fiber system in the project.
Product Catalogue. Fiber Optic Assemblies & Adapters. Table of Contents General Description... 2
 Product Catalogue Fiber Optic Assemblies & Adapters Table of Contents 1. General Description... 2 2. Connectors... 3 2.1 SC/UPC... 3 2.2 SC/APC... 3 2.3 FC/UPC... 3 2.4 FC/APC... 3 2.5 ST/UPC... 3 2.6
Product Catalogue Fiber Optic Assemblies & Adapters Table of Contents 1. General Description... 2 2. Connectors... 3 2.1 SC/UPC... 3 2.2 SC/APC... 3 2.3 FC/UPC... 3 2.4 FC/APC... 3 2.5 ST/UPC... 3 2.6
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6911 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment
 2004 Specifications CSJ 3256-02-079 & 3256-03-082 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6911 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment 1. Description. Furnish and install Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment
2004 Specifications CSJ 3256-02-079 & 3256-03-082 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6911 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment 1. Description. Furnish and install Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1987 Single Mode Fiber Optic Video Transmission Equipment
 1993 Specifications CSJ 0027-12-086, etc. SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1987 Single Mode Fiber Optic Video Transmission Equipment 1. Description. This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of color
1993 Specifications CSJ 0027-12-086, etc. SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1987 Single Mode Fiber Optic Video Transmission Equipment 1. Description. This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of color
UC FIBRE Optical Fibre Cable a fast, reliable and always available part of the Draka Datacom Solution. Be ready for the future: Draka Datacom Solution
 Be ready for the future: Draka Datacom Solution Modern networks face stiff demands. They must be fast and reliable, resist fire and not interfere with other equipment. Optical Fibre Cable a fast, reliable
Be ready for the future: Draka Datacom Solution Modern networks face stiff demands. They must be fast and reliable, resist fire and not interfere with other equipment. Optical Fibre Cable a fast, reliable
To select a fibre optic cable, you have to make choices of the fibre selection and the cable construction selection.
 Fibre Optic Cables & Connectors Guide Introduction Organising through cables and connectivity options can be an exasperating exercise. It's tough enough working through the categories and levels of copper
Fibre Optic Cables & Connectors Guide Introduction Organising through cables and connectivity options can be an exasperating exercise. It's tough enough working through the categories and levels of copper
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1291 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment
 1993 Specifications CSJ 0500-01-117 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1291 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment 1. Description. This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of Fiber Optic Video
1993 Specifications CSJ 0500-01-117 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 1291 Fiber Optic Video Data Transmission Equipment 1. Description. This Item shall govern for the furnishing and installation of Fiber Optic Video
Customer-Owned Outside Plant
 Customer Premises Products (Enterprise) 3 Customer-Owned Outside Plant Fiber Optic Splice Case 2178 Series and Accessories 372 Fiber Optic Dome Splice Closure FD Series 376 Fibrlok II Universal Optical
Customer Premises Products (Enterprise) 3 Customer-Owned Outside Plant Fiber Optic Splice Case 2178 Series and Accessories 372 Fiber Optic Dome Splice Closure FD Series 376 Fibrlok II Universal Optical
SJOF-BS604B. Fiber Optic Splice Closure User Manual Rev.1
 Fiber Optic Splice Closure 1. Introduction 1.1 General SAMJIN s SJOF-BS604B protects fiber optic splicing point in various installation conditions such as aerial, manholes, ducts, wall and direct buried
Fiber Optic Splice Closure 1. Introduction 1.1 General SAMJIN s SJOF-BS604B protects fiber optic splicing point in various installation conditions such as aerial, manholes, ducts, wall and direct buried
Specification for Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable (Non-Metallic, Dry Block, Figure-8) (G.652.D)
 2-3, Marunouchi 2-chome, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8322, Japan No. FB-KL4001C for Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable (Non-Metallic, Dry Block, Figure-8) (G.652.D) Aug 2014 1 1. General This specification describes
2-3, Marunouchi 2-chome, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8322, Japan No. FB-KL4001C for Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable (Non-Metallic, Dry Block, Figure-8) (G.652.D) Aug 2014 1 1. General This specification describes
SPECIFICATION FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE. Spec No : VSS-1007-BS403A-04A/SD. VSS-0107-BS403A-04A/SD R & D Center Manufacturing Division
 SPECIFICATION FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE Model Spec. No. Distribution Depts. VSOF-BS403A VSS-0107-BS403A-04A/SD R & D Center Manufacturing Division Sales Division Management Division Revision 10. 07 (Rev.4)
SPECIFICATION FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE Model Spec. No. Distribution Depts. VSOF-BS403A VSS-0107-BS403A-04A/SD R & D Center Manufacturing Division Sales Division Management Division Revision 10. 07 (Rev.4)
FiberLink 7142 Series
 MANUAL FiberLink 7142 Series 4 Channels of Composite Video and 8 Channels of Audio over one single mode or multimode fiber Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM FibeLink 7142 Series Contents
MANUAL FiberLink 7142 Series 4 Channels of Composite Video and 8 Channels of Audio over one single mode or multimode fiber Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM FibeLink 7142 Series Contents
OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE NETWORK 2004/1
 OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE NETWORK 2004/1 HELKAMA OPTICAL FIBRE CABLES Cabled optical fibre characteristics OS1 singlemode fibre SM ITU-T G.652 Mode field diameter 1310nm 9.3+/-0.5µm Mode field eccentricity 1.0
OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE NETWORK 2004/1 HELKAMA OPTICAL FIBRE CABLES Cabled optical fibre characteristics OS1 singlemode fibre SM ITU-T G.652 Mode field diameter 1310nm 9.3+/-0.5µm Mode field eccentricity 1.0
Bravo AV s Structured or Whole-House Wiring Approach
 Custom Audio & Video Systems: Design and Installation Bravo AV s Structured or Whole-House Wiring Approach THE QUALITY OF THE CABLE YOU USE IS CRITICALLY IMPORT TO THE PERFORMANCE OF YOUR SYSTEM Introduction
Custom Audio & Video Systems: Design and Installation Bravo AV s Structured or Whole-House Wiring Approach THE QUALITY OF THE CABLE YOU USE IS CRITICALLY IMPORT TO THE PERFORMANCE OF YOUR SYSTEM Introduction
Fibre Optic Cable & Connector Guide
 Fibre Optic Cable & Connector Guide White paper White Paper Fibre Optic Cable & Connector Guide v1.0 EN 1 Introduction Organising through cables and connectivity options can be an exasperating exercise.
Fibre Optic Cable & Connector Guide White paper White Paper Fibre Optic Cable & Connector Guide v1.0 EN 1 Introduction Organising through cables and connectivity options can be an exasperating exercise.
FIST-GCOG2-Dx6. Follow all local safety regulations related to optical fiber plant elements.
 FIST-GCOG2 I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N TC-986-IP Rev A, Mar 2017 www.commscope.com FIST-GCOG2-Dx6 Content 1 Introduction 2 General 2.1 Abbreviations 2.2 Kit contents 2.3 Tools 2.4 Accessories
FIST-GCOG2 I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N TC-986-IP Rev A, Mar 2017 www.commscope.com FIST-GCOG2-Dx6 Content 1 Introduction 2 General 2.1 Abbreviations 2.2 Kit contents 2.3 Tools 2.4 Accessories
Optical Distribution Box 300 Installation Guide. Version : R0.0
 Optical Distribution Box 300 Installation Guide Document No. : OD16-546-L-01 Version : R0.0 Date: 21-Mar-2018 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS When using fiber optic equipment, basic precautions should always be
Optical Distribution Box 300 Installation Guide Document No. : OD16-546-L-01 Version : R0.0 Date: 21-Mar-2018 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS When using fiber optic equipment, basic precautions should always be
Tech Breakfast: Fibre Optic Cabling
 Tech Breakfast: Fibre Optic Cabling An introduction phil.crawley@jigsaw24.com @IsItBroke on Twitter http://www.root6.com/author/phil Fibre optic cabling Applications within Film & TV Single mode vs. Multi
Tech Breakfast: Fibre Optic Cabling An introduction phil.crawley@jigsaw24.com @IsItBroke on Twitter http://www.root6.com/author/phil Fibre optic cabling Applications within Film & TV Single mode vs. Multi
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION (FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE) Model Spec. No. Distribution Depts. VSOF-BS403A SJP-0609-403A-01A/SD Quality Assurance Team Manufacturing Division Sales Division Management Division
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION (FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE) Model Spec. No. Distribution Depts. VSOF-BS403A SJP-0609-403A-01A/SD Quality Assurance Team Manufacturing Division Sales Division Management Division
How to Speak Fiber Geek Article 4: Single-Mode Optical Fiber Geometries
 Welcome back, Fiber Geeks! The first article in this series highlighted some bandwidth demand drivers and introductory standards information. Article 2 then focused on attenuation and Article 3 followed
Welcome back, Fiber Geeks! The first article in this series highlighted some bandwidth demand drivers and introductory standards information. Article 2 then focused on attenuation and Article 3 followed
Detailed Specifications & Technical Data
 For more information please call 1-800-Belden1 See Put-ups and Colors Related Documents: No.10 for Fiber Optic Cables.pdf Cable Characteristics: DESCRIPTION: 2 to 12 optical fibers, Central gel filling
For more information please call 1-800-Belden1 See Put-ups and Colors Related Documents: No.10 for Fiber Optic Cables.pdf Cable Characteristics: DESCRIPTION: 2 to 12 optical fibers, Central gel filling
RGB COMBINERS. 2.0 mm Narrow Key FC/PC or FC/APC Termination Excellent for Confocal. Ø900 µm Loose Hytrel Tube with the wavelength Laser Sources
 RGB COMBINERS Combine Three Input Colors into a Single Output Excellent for Confocal Microscopy, Fluoresence and Other Applications with Multiple Illumination Sources Unterminated, FC/PC, or FC/APC Outputs
RGB COMBINERS Combine Three Input Colors into a Single Output Excellent for Confocal Microscopy, Fluoresence and Other Applications with Multiple Illumination Sources Unterminated, FC/PC, or FC/APC Outputs
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
Cable Installation Tips
 Cable Installation Tips Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Cable Installation Tips Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Non-metallic Aerial Distribution Optical Cables for FTTH Networks
 Non-metallic Aerial Distribution Optical Cables for FTTH Networks Go Taki, 1 Akira Namazue, 1 and Ken Osato 1 One of the common practices to construct economical and efficient Fiber To The Home (FTTH)
Non-metallic Aerial Distribution Optical Cables for FTTH Networks Go Taki, 1 Akira Namazue, 1 and Ken Osato 1 One of the common practices to construct economical and efficient Fiber To The Home (FTTH)
Cable Installation Tips
 Cable Installation Tips Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Cable Installation Tips Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 944,105 Filing Date 30 September 1997 Inventor Gair D. Brown NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE
Serial Number 944,105 Filing Date 30 September 1997 Inventor Gair D. Brown NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE
HES HACILAR ELEKTRİK SANAYİ VE TİC.A.Ş.
 Technical Specification Revision/Date: 04/04.15 By N.KARAAĞAÇ Date : 27 February 2015 Cable Type HES Cable Product Number :, Outdoor F/O Cable :FOZZXXXSJSA41JYY (ZZ: fiber type G652=SD, G657 A1 = A1, G657
Technical Specification Revision/Date: 04/04.15 By N.KARAAĞAÇ Date : 27 February 2015 Cable Type HES Cable Product Number :, Outdoor F/O Cable :FOZZXXXSJSA41JYY (ZZ: fiber type G652=SD, G657 A1 = A1, G657
MiniXtend Cable with Binderless* FastAccess Technology Jacket and Buffer Tube Removal Procedures. 1. General. 2. Precautions
 MiniXtend Cable with Binderless* FastAccess Technology Jacket and Buffer Tube Removal Procedures 004-273-AEN, Issue 2 Table of Contents 1. General.... 1 2. Precautions.... 1 2.1 Cable Handling Precautions...
MiniXtend Cable with Binderless* FastAccess Technology Jacket and Buffer Tube Removal Procedures 004-273-AEN, Issue 2 Table of Contents 1. General.... 1 2. Precautions.... 1 2.1 Cable Handling Precautions...
MOST - Roadmap Physical Layer & Connectivity from 150Mbps to 5Gbps
 MOST - Roadmap Physical Layer & Connectivity from 150Mbps to 5Gbps 13th MOST(R) Interconnectivity Conference Asia on November 15, 2012 in Seoul, South Korea Andreas Engel Manager Advanced Infotainment
MOST - Roadmap Physical Layer & Connectivity from 150Mbps to 5Gbps 13th MOST(R) Interconnectivity Conference Asia on November 15, 2012 in Seoul, South Korea Andreas Engel Manager Advanced Infotainment
Micro duct Cable with HDPE Sheath for Installation by Blowing
 Optical Fiber Cable Technology Specification INTERNAL Optical Fiber Cable Specification Micro duct Cable with HDPE Sheath for Installation by Blowing GCYFY-12/24/36/48/72/96/144/288/432/576B1.3 V7.0 2018-3-20,CCopyright.
Optical Fiber Cable Technology Specification INTERNAL Optical Fiber Cable Specification Micro duct Cable with HDPE Sheath for Installation by Blowing GCYFY-12/24/36/48/72/96/144/288/432/576B1.3 V7.0 2018-3-20,CCopyright.
COMMON WORK RESULTS FOR INTEGRATED AUTOMATION DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION STANDARD
 PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
PART 1: GENERAL 1.01 Purpose: A. This standard is intended to provide useful information to the Professional Service Provider (PSP) to establish a basis of design. The responsibility of the engineer is
Crimp & Cleave Termination Instructions for SEL ST Connectors
 Your Optical Fiber Solutions Partner Crimp & Cleave Termination Instructions for SEL ST Connectors For Use With: ST Termination Kit (SEL, Part Number BT05402-01) 200 µm HCS Fiber-Optic Cable ST Crimp &
Your Optical Fiber Solutions Partner Crimp & Cleave Termination Instructions for SEL ST Connectors For Use With: ST Termination Kit (SEL, Part Number BT05402-01) 200 µm HCS Fiber-Optic Cable ST Crimp &
2178 Fiber Optic Splice Case and 2181 Cable Addition Kit
 2178 Fiber Optic Splice Case and 2181 Cable Addition Kit Instructions January 1994 Issue 1, 34-7029-6387-6 1 2 Contents: 1.0 General... 4 2.0 Specifications... 4 3.0 Kit Contents... 5 SECTION 1: 2178 Splice
2178 Fiber Optic Splice Case and 2181 Cable Addition Kit Instructions January 1994 Issue 1, 34-7029-6387-6 1 2 Contents: 1.0 General... 4 2.0 Specifications... 4 3.0 Kit Contents... 5 SECTION 1: 2178 Splice
UNIVERSITY of NORTH DAKOTA LOW VOLTAGE COMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS FOR CABLING, PATHWAYS, AND SPACE
 UNIVERSITY of NORTH DAKOTA LOW VOLTAGE COMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS FOR CABLING, PATHWAYS, AND SPACE Prepared in cooperation and approval from BICSI Building Industry Consulting Services International and
UNIVERSITY of NORTH DAKOTA LOW VOLTAGE COMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS FOR CABLING, PATHWAYS, AND SPACE Prepared in cooperation and approval from BICSI Building Industry Consulting Services International and
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
 ISSUED : OCT. 02, 2006 PAGE : 1 OF 9 REV. : 1 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR GST 2006-043A LOOSE TUBE DRY CORE CABLE SINGLE JACKET/SINGLE ARMOR (SJSA CABLE) Prepared By : Oh-Heoung Kwon Engineer Optical Technical
ISSUED : OCT. 02, 2006 PAGE : 1 OF 9 REV. : 1 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR GST 2006-043A LOOSE TUBE DRY CORE CABLE SINGLE JACKET/SINGLE ARMOR (SJSA CABLE) Prepared By : Oh-Heoung Kwon Engineer Optical Technical
LD Series High Performance Loose Tube Fiberoptic Cables
 Fiberoptic Cables Catalog LD Series High Performance Loose Tube Fiberoptic Cables APPLICATIONS Long-distance outside plant telephone, CATV as well as data communications Direct burial and installation
Fiberoptic Cables Catalog LD Series High Performance Loose Tube Fiberoptic Cables APPLICATIONS Long-distance outside plant telephone, CATV as well as data communications Direct burial and installation
STANDARD FOR MULTI-DWELLING UNIT (MDU) OPTICAL FIBER CABLE. Publication S First Edition - June 2012
 STANDARD FOR MULTI-DWELLING UNIT (MDU) OPTICAL FIBER CABLE Publication S-115-730 First Edition - June 2012 Published By Insulated Cable Engineers Association, Inc. Post Office Box 1568 Carrollton, Ga 30112,
STANDARD FOR MULTI-DWELLING UNIT (MDU) OPTICAL FIBER CABLE Publication S-115-730 First Edition - June 2012 Published By Insulated Cable Engineers Association, Inc. Post Office Box 1568 Carrollton, Ga 30112,
HCS - HES Cabling Systems
 HCS - HES Cabling Systems Installation Manual for HCS High-Capacity Fiber-Optic Rack-Mount Cabinets Be sure to read and completely understand this procedure before applying product. Be sure to select the
HCS - HES Cabling Systems Installation Manual for HCS High-Capacity Fiber-Optic Rack-Mount Cabinets Be sure to read and completely understand this procedure before applying product. Be sure to select the
FREEDM Loose Tube Interlocking Armored Cables
 features and benefits Flexible, interlocking armor design Gel-free waterblocking technology Color-coded tubes and fibers UV-resistant, flameretardant jacket UV-Resistant Flame-Retardant Outer Jacket InterlockingArmor
features and benefits Flexible, interlocking armor design Gel-free waterblocking technology Color-coded tubes and fibers UV-resistant, flameretardant jacket UV-Resistant Flame-Retardant Outer Jacket InterlockingArmor
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6735 Video Optical Transceiver
 2004 Specifications CSJ 0924-06-244 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6735 Video Optical Transceiver 1. Description. This Item governs the furnishing and installation of Video optical transceiver (VOTR) in field location(s)
2004 Specifications CSJ 0924-06-244 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6735 Video Optical Transceiver 1. Description. This Item governs the furnishing and installation of Video optical transceiver (VOTR) in field location(s)
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 86 2010 SCTE Recommended Optical Fiber Cable Types for Outside Plant Trunk and Distribution Applications NOTICE
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Interface Practices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 86 2010 SCTE Recommended Optical Fiber Cable Types for Outside Plant Trunk and Distribution Applications NOTICE
SPECIFICATION. Spec No : VSS-1402-CS603B
 SPECIFICATION Spec No : VSS-1402-CS603B 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. General This specification covers the design requirements and characteristics required of fiber optic splice closures to be used on fiber optic
SPECIFICATION Spec No : VSS-1402-CS603B 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. General This specification covers the design requirements and characteristics required of fiber optic splice closures to be used on fiber optic
NC-1000 INSTALLATION MANUAL NC-1000 FIBRE OPTIC CROSS-CONNECTION SYSTEM
 NC-1000 INSTALLATION MANUAL NC-1000 FIBRE OPTIC CROSS-CONNECTION SYSTEM Content 1. General 5 2. The products of NC-1000 system 6 3. Mounting of the frame 8 4. Earthing of the frame 8 NC-1000 FIBRE OPTIC
NC-1000 INSTALLATION MANUAL NC-1000 FIBRE OPTIC CROSS-CONNECTION SYSTEM Content 1. General 5 2. The products of NC-1000 system 6 3. Mounting of the frame 8 4. Earthing of the frame 8 NC-1000 FIBRE OPTIC
3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XSB/XSB-FR & 2178-XLB/XLB-FR 3M Cable Addition Kit 2181-XB/XB-FR
 3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XSB/XSB-FR & 2178-XLB/XLB-FR 3M Cable Addition Kit 2181-XB/XB-FR Instructions July 2010 78-8135-0094-5-K 3 1.0 General 1.1 3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XSB The
3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XSB/XSB-FR & 2178-XLB/XLB-FR 3M Cable Addition Kit 2181-XB/XB-FR Instructions July 2010 78-8135-0094-5-K 3 1.0 General 1.1 3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XSB The
SECTION 7 -- CROSS-CONNECT SYSTEMS
 DETAIL ENGINEERING REQUIREMENTS AT&T March, 2016 Section 7, ATT-TP-76400 Revised NA SECTION 7 -- CROSS-CONNECT SYSTEMS CONTENTS PAGE 1. GENERAL... 7-2 1.1. Introduction... 7-2 1.2. Cable Holes... 7-2 1.3.
DETAIL ENGINEERING REQUIREMENTS AT&T March, 2016 Section 7, ATT-TP-76400 Revised NA SECTION 7 -- CROSS-CONNECT SYSTEMS CONTENTS PAGE 1. GENERAL... 7-2 1.1. Introduction... 7-2 1.2. Cable Holes... 7-2 1.3.
3 Closure preparation 3.1 Work-stand 3.2. Opening FIST-GCOG2-Dx Preparing drop cable with micro-tubes
 FIST-GCOG2-Dx24 I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N FTTH closure for micro-tubes and micro-cables Content 1 Introduction 2 Kit content 3 Closure preparation 3.1 Work-stand 3.2. Opening FIST-GCOG2-Dx24
FIST-GCOG2-Dx24 I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N FTTH closure for micro-tubes and micro-cables Content 1 Introduction 2 Kit content 3 Closure preparation 3.1 Work-stand 3.2. Opening FIST-GCOG2-Dx24
K-LWLH1 2.0 m AA. K-LWLH m AA. K-LWLH m AA
 Glass Fiber Cable The fiber optic cables are used to connect the FM211, FM212, FS211, FS211/N and FS212 and FS212/N FASTBUS modules, enabling the connection of remote substations over large distances with
Glass Fiber Cable The fiber optic cables are used to connect the FM211, FM212, FS211, FS211/N and FS212 and FS212/N FASTBUS modules, enabling the connection of remote substations over large distances with
POLARIZED FIBER OPTIC SOURCE
 219 Westbrook Rd, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 Toll Free: 1-800-361-5415 Tel:(613) 831-0981 Fax:(613) 836-5089 E-mail: sales@ozoptics.com Features: High polarization extinction ratio (up to 40 db) Stable
219 Westbrook Rd, Ottawa, ON, Canada, K0A 1L0 Toll Free: 1-800-361-5415 Tel:(613) 831-0981 Fax:(613) 836-5089 E-mail: sales@ozoptics.com Features: High polarization extinction ratio (up to 40 db) Stable
SOLO ADSS Short-Span Cables, Fibers
 features and benefits Loose tube design Self-supporting Track-resistant jacket available Innovative waterblocking cable core SOLO ADSS Cable Drawing ZA-2615 Stable performance and compatibility with all
features and benefits Loose tube design Self-supporting Track-resistant jacket available Innovative waterblocking cable core SOLO ADSS Cable Drawing ZA-2615 Stable performance and compatibility with all
3M Distribution Box (DDB)
 3M Distribution Box (DDB) Merged Copper and Fiber Pole/Post Mount Enclosure Installation Instructions November 2015 78-0015-2736-1-A 2 November 2015 78-0015-2736-1-A Contents 1.0 General 2.0 Enclosure
3M Distribution Box (DDB) Merged Copper and Fiber Pole/Post Mount Enclosure Installation Instructions November 2015 78-0015-2736-1-A 2 November 2015 78-0015-2736-1-A Contents 1.0 General 2.0 Enclosure
APPLICATION NOTE. Practical Tips for Using Metalic Time Domain Reflectometers (The EZ Way) What is a Time Domain Reflectometer?
 a publication of R MEETING YOUR TESTING NEEDS TODAY AND TOMORROW Publication Number TTS3-0901 APPLICATION NOTE Practical Tips for Using Metalic Time Domain Reflectometers (The EZ Way) What is a Time Domain
a publication of R MEETING YOUR TESTING NEEDS TODAY AND TOMORROW Publication Number TTS3-0901 APPLICATION NOTE Practical Tips for Using Metalic Time Domain Reflectometers (The EZ Way) What is a Time Domain
OPTICAL FIBER CABLE, ALL DIELECTRIC SELF SUPPORTING CABLE
 SPEC NO. TEC-OPTIC-81101A(Rev.4)-2014.07 TECHNICAL PROPOSAL FOR OPTICAL FIBER CABLE, ALL DIELECTRIC SELF SUPPORTING CABLE ( Span length : Max. 100m ) APPROVED BY : J.Y. LEE / HEAD OF TEAM ENGINEERING TEAM
SPEC NO. TEC-OPTIC-81101A(Rev.4)-2014.07 TECHNICAL PROPOSAL FOR OPTICAL FIBER CABLE, ALL DIELECTRIC SELF SUPPORTING CABLE ( Span length : Max. 100m ) APPROVED BY : J.Y. LEE / HEAD OF TEAM ENGINEERING TEAM
National Wire and Cable and National Cable Molding Headquarters Los Angeles California
 National Wire and Cable and National Cable Molding Headquarters Los Angeles California CAPABILITIES Medical Business Machines Communications Equipment Computer Equipment Audio Systems General Instrumentation
National Wire and Cable and National Cable Molding Headquarters Los Angeles California CAPABILITIES Medical Business Machines Communications Equipment Computer Equipment Audio Systems General Instrumentation
1. General. 1. Scope. 2. Quality Assurance
 1. General 1. Scope 2. Quality Assurance This specification covers the construction and properties of 50/125 um Multimode (Graded-index, OM2), anti-rodent self-supporting (ARSS), single jacket, single
1. General 1. Scope 2. Quality Assurance This specification covers the construction and properties of 50/125 um Multimode (Graded-index, OM2), anti-rodent self-supporting (ARSS), single jacket, single
Special Specification 6242 Special Fiber Optic Cable
 Special Specification 6242 Special Fiber Optic Cable 1. DESCRIPTION 2. MATERIALS The contractor to install, splice, field terminate, test and document all fiber systems. A. General Requirements. Provide
Special Specification 6242 Special Fiber Optic Cable 1. DESCRIPTION 2. MATERIALS The contractor to install, splice, field terminate, test and document all fiber systems. A. General Requirements. Provide
Crimplok. Connectors. 3M Crimplok ST* Connector Multimode 1. 3M Crimplok SC Connector Single-mode 2
 3 Crimplok Connectors Quick, easy installation and superior performance To successfully design, install or operate today s fiber optic networks, you need components that offer speed and reliability from
3 Crimplok Connectors Quick, easy installation and superior performance To successfully design, install or operate today s fiber optic networks, you need components that offer speed and reliability from
Alternative Fiber Coupler Options
 980 NM, SINGLE MODE FUSED FIBER OPTIC COUPLERS / TAPS Narrowband and Wideband Couplers for 980 nm 50:50, 75:25, 90:10, or 99:1 Coupling Ratio Polarization Insensitive Combine or "Tap Off" Signals FC980-50B-APC
980 NM, SINGLE MODE FUSED FIBER OPTIC COUPLERS / TAPS Narrowband and Wideband Couplers for 980 nm 50:50, 75:25, 90:10, or 99:1 Coupling Ratio Polarization Insensitive Combine or "Tap Off" Signals FC980-50B-APC
FOSC 450 C6 and D6 Closures
 FOSC 450 C6 and D6 Closures I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N Fiber Optic Splice Closure 1. General Product Information The FOSC 450 C6 and D6 fiber optic splice closures use compressed gel
FOSC 450 C6 and D6 Closures I N S T A L L A T I O N I N S T R U C T I O N Fiber Optic Splice Closure 1. General Product Information The FOSC 450 C6 and D6 fiber optic splice closures use compressed gel
3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector
 Communication Markets Division 3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector For use with 1.6 to 3.0 mm Jacketed Cable 3M No Polish SC/APC Connector enables fast, on-site termination of 1.6 mm to 3.0 mm jacketed
Communication Markets Division 3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector For use with 1.6 to 3.0 mm Jacketed Cable 3M No Polish SC/APC Connector enables fast, on-site termination of 1.6 mm to 3.0 mm jacketed
2179-CD Series Fiber Optic Splice Closure. Installation Instructions
 2179-CD Series Fiber Optic Splice Closure Installation Instructions 1.0 Product Introduction The new 3M TM 2179-CD Series Fiber Optic Splice Closure can be used in buried, underground, aerial, and pedestal
2179-CD Series Fiber Optic Splice Closure Installation Instructions 1.0 Product Introduction The new 3M TM 2179-CD Series Fiber Optic Splice Closure can be used in buried, underground, aerial, and pedestal
FiberLink 3350 Series
 MANUAL FiberLink 3350 Series 3G/HD/SD-SDI Transmission over one single mode or multimode fiber Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM Contents Contents Welcome....3 Features....3 Package Contents....3
MANUAL FiberLink 3350 Series 3G/HD/SD-SDI Transmission over one single mode or multimode fiber Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM Contents Contents Welcome....3 Features....3 Package Contents....3
6 3 0 N M, S I N G L E M O D E F U S E D F I B E R O P T I C C OUPLERS / TA P S
 6 3 0 N M, S I N G L E M O D E F U S E D F I B E R O P T I C C OUPLERS / TA P S Narrowband and Wideband Couplers for 630 nm Available with 50:50, 75:25, 90:10, or 99:1 Terminated with 2.0 mm Narrow Key
6 3 0 N M, S I N G L E M O D E F U S E D F I B E R O P T I C C OUPLERS / TA P S Narrowband and Wideband Couplers for 630 nm Available with 50:50, 75:25, 90:10, or 99:1 Terminated with 2.0 mm Narrow Key
FIBER OPTIC CABLE CUT TO YOUR EXACT SPECS TO SAVE YOU TIME AND MONEY
 FIBER OPTIC CABLE CUT TO YOUR EXACT SPECS TO SAVE YOU TIME AND MONEY ADVANTAGES OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE Fiber optic cable is the preferred choice for backbone and horizontal applications. Black Box provides
FIBER OPTIC CABLE CUT TO YOUR EXACT SPECS TO SAVE YOU TIME AND MONEY ADVANTAGES OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE Fiber optic cable is the preferred choice for backbone and horizontal applications. Black Box provides
MT-RJ SECURE Product Expansion Now 10 Variants of the MT-RJ SECURE Products
 MT-RJ Product Expansion Now 0 Variants of the MT-RJ Products In response to several customers, the MT-RJ product line has been expanded with an additional six color/key versions. In addition to the original
MT-RJ Product Expansion Now 0 Variants of the MT-RJ Products In response to several customers, the MT-RJ product line has been expanded with an additional six color/key versions. In addition to the original
Optical. HDMI series NEW PRODUCTS 2019
 Optical HDMI series NEW PRODUCTS 2019 HDMI AT THE SPEED OF LIGHT HDMI 2.0 cables are great for transferring large amounts of data, therefore they are used in 4K@60Hz Ultra HD video applications like home
Optical HDMI series NEW PRODUCTS 2019 HDMI AT THE SPEED OF LIGHT HDMI 2.0 cables are great for transferring large amounts of data, therefore they are used in 4K@60Hz Ultra HD video applications like home
SPECIFICATION FOR FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE
 SP-CTN-CT3000M,CT3000ML-00 ISSUED : 2015/02/11 PAGE : 8 SPECIFICATION FOR FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE CT3000M/CT3000ML Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2 / 8 1. GENERAL This specification covers the standards
SP-CTN-CT3000M,CT3000ML-00 ISSUED : 2015/02/11 PAGE : 8 SPECIFICATION FOR FIBER OPTIC SPLICE CLOSURE CT3000M/CT3000ML Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2 / 8 1. GENERAL This specification covers the standards
e-enterable Fiber Optic Splice Closure (Re-Enterable Aerial Closure for Access Service)
 R e-enterable Fiber Optic Splice Closure (Re-Enterable Aerial Closure for Access Service) Optical Fiber Drop wire Closure Model FOC-CB1612-24DW. Available with optical fiber cable from 12 up to 24 fibers
R e-enterable Fiber Optic Splice Closure (Re-Enterable Aerial Closure for Access Service) Optical Fiber Drop wire Closure Model FOC-CB1612-24DW. Available with optical fiber cable from 12 up to 24 fibers
MOST. Getting the. BMW Assist. Climate. Settings
 feature BMW Assist Commun Getting the MOST Climate Any technological advance adds a level of complexity, and when it breaks we re the ones who are going to have to fix it. This includes the sophisticated
feature BMW Assist Commun Getting the MOST Climate Any technological advance adds a level of complexity, and when it breaks we re the ones who are going to have to fix it. This includes the sophisticated
Revision No. 4 Page No. Page 1 of 7
 Page No. Page 1 of 7 Single Mode Optical Fibre Cables With Loose Fibres in Stranded Tubes And Corrugated Steel tape Armouring For Duct Applications LITE KABEL SDN. BHD. reserves the right to make changes
Page No. Page 1 of 7 Single Mode Optical Fibre Cables With Loose Fibres in Stranded Tubes And Corrugated Steel tape Armouring For Duct Applications LITE KABEL SDN. BHD. reserves the right to make changes
3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector
 Communication Markets Division 3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector For use with 1.6 to 3.0 mm Jacketed Cable 3M No Polish SC/APC Connector enables fast, on-site termination of 1.6 mm to 3.0 mm jacketed
Communication Markets Division 3M No Polish Jacketed SC/APC Connector For use with 1.6 to 3.0 mm Jacketed Cable 3M No Polish SC/APC Connector enables fast, on-site termination of 1.6 mm to 3.0 mm jacketed
Fiber Optic Testing. The FOA Reference for Fiber Optics Fiber Optic Testing. Rev. 1/31/17 Page 1 of 12
 Fiber Optic Testing Testing is used to evaluate the performance of fiber optic components, cable plants and systems. As the components like fiber, connectors, splices, LED or laser sources, detectors and
Fiber Optic Testing Testing is used to evaluate the performance of fiber optic components, cable plants and systems. As the components like fiber, connectors, splices, LED or laser sources, detectors and
SPECIFICATION. Optical Fiber Cable
 SPECIFICATION Optical Fiber Cable (GYFS) Prepared by Zhang xin Approved by Yin peng xiang 1 1 Product description GYFS is gel-free, single-jacket, single-armored cable for direct burial and duct GYFS is
SPECIFICATION Optical Fiber Cable (GYFS) Prepared by Zhang xin Approved by Yin peng xiang 1 1 Product description GYFS is gel-free, single-jacket, single-armored cable for direct burial and duct GYFS is
Multi-Media Installation Guide
 Multi-Media Installation Guide Coaxial Page 2 Data Plug Page 7 Data Jack Page 10 Telephone Page 13 Splicing Page 15 Cable Types Cable Types Two basic types of cable are used in multimedia installations.
Multi-Media Installation Guide Coaxial Page 2 Data Plug Page 7 Data Jack Page 10 Telephone Page 13 Splicing Page 15 Cable Types Cable Types Two basic types of cable are used in multimedia installations.
FiberLink 3355 Series
 MANUAL Link 3355 Series 3G/HD/SD-SDI to DVI Optical Receiver Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM Contents Contents Welcome....3 Features....3 Package Contents....3 Technical Specifications
MANUAL Link 3355 Series 3G/HD/SD-SDI to DVI Optical Receiver Installation and Operations Manual WWW.ARTEL.COM Contents Contents Welcome....3 Features....3 Package Contents....3 Technical Specifications
Mid-Span Access of Loose-Tube Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable
 Application Notes Mid-Span Access of Loose-Tube Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable Author Prasanna Pardeshi and Sudipta Bhaumik Issued November 2013 Abstract In fiber optic network, it is sometime necessary to splice
Application Notes Mid-Span Access of Loose-Tube Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable Author Prasanna Pardeshi and Sudipta Bhaumik Issued November 2013 Abstract In fiber optic network, it is sometime necessary to splice
Loose Tube Cable Mid-Span Access for Splicing For Series 11D, 1GD, 12D, 1AD, 1DD, 1CD, 11, 1G, 12, 12L, 1A, 1D, 1C, 1NY, 13, 1H, HZD and HZA
 Loose Tube Cable Mid-Span Access for Splicing For Series 11D, 1GD, 12D, 1AD, 1DD, 1CD, 11, 1G, 12, 12L, 1A, 1D, 1C, 1NY, 13, 1H, HZD and HZA NOTE: These installation instructions have been written for
Loose Tube Cable Mid-Span Access for Splicing For Series 11D, 1GD, 12D, 1AD, 1DD, 1CD, 11, 1G, 12, 12L, 1A, 1D, 1C, 1NY, 13, 1H, HZD and HZA NOTE: These installation instructions have been written for
TENDER SUMMARY. Tender Title:
 TENDER SUMMARY Tender Title: Tender Ref: Closing Date: OPEN TENDER FOR THE SUPPLY OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE 384 CORE LOOSE TUBE ( FOC 384C ) FOR TELEKOM MALAYSIA BERHAD ( TM ) LPM/2018/T/02/FOC 384C 23 February
TENDER SUMMARY Tender Title: Tender Ref: Closing Date: OPEN TENDER FOR THE SUPPLY OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE 384 CORE LOOSE TUBE ( FOC 384C ) FOR TELEKOM MALAYSIA BERHAD ( TM ) LPM/2018/T/02/FOC 384C 23 February
HD4K18GB-FO-xx-MM. HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cables. Instruction Manual
 HD4K18GB-FO-xx-MM HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cables Instruction Manual 1 HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cable INTRODUCTION This Fiber Optic HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cable (AOC) allows you to transmit HDMI signals to a
HD4K18GB-FO-xx-MM HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cables Instruction Manual 1 HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cable INTRODUCTION This Fiber Optic HDMI 2.0 Active Optic Cable (AOC) allows you to transmit HDMI signals to a
3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XL & 2178-XL/FR
 3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XL & 2178-XL/FR 3M Cable Addition Kit 2181-XL and 2181-XL/FR Instructions September 2017 78-8130-5055-2-M 2 September 2017 78-8130-5055-2-M 1.0 Kit Contents 2.0 General...
3M Fiber Optic Splice Closure 2178-XL & 2178-XL/FR 3M Cable Addition Kit 2181-XL and 2181-XL/FR Instructions September 2017 78-8130-5055-2-M 2 September 2017 78-8130-5055-2-M 1.0 Kit Contents 2.0 General...
