Empirical Evaluation of Animated Agents In a Multi-Modal E-Retail Application
|
|
|
- Katherine Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
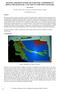
1 From: AAAI Technical Report FS Compilation copyright 2000, AAAI ( All rights reserved. Empirical Evaluation of Animated Agents In a Multi-Modal E-Retail Application Helen McBreen, Mervyn Jack Centre for Communication Interface Research, The University of Edinburgh, 80 South Bridge, EH1 1HN, Scotland, UK Helen.McBreen@ccir.ed.ac.uk, Mervyn.Jack@ccir.ed.ac.uk Abstract This paper presents the results of an empirical evaluation of the effectiveness and user acceptability of a selection of animated agents in a multi-modal electronic retail application. Male and female versions of six animated agent technologies were repeatedly evaluated in the role of an interactive conversational sales assistant. The experiment involved participants eavesdropping on spoken dialogues between a customer and each of the animated assistants. Participants then completed usability questionnaires and took part in a debriefing interview designed to elicit information relating to the agents voice, aspects of personality, appearance, facial expressions and gestures. Introduction This paper presents the results of an experiment aimed at assessing usability attributes of twelve personified agents in the context of a multi-modal electronic retail application by having participants eavesdrop in turn on brief dialogues between a customer (represented by a disembodied voice) and each of the twelve agents. The retail application (Figure 1) was created in the style of MUeSLI (Wyard and Churcher 1999). The main window was a 3D view of a living room complete with furniture. Immediately above was a row of fabric and wallpaper samples that could be selected in order to decorate the walls, sofa, chairs and curtains. The dialogues were designed to illustrate the customer conversing with the agent to select colours and patterns in order to decorate the room. The twelve agents differed in terms of their gender and visual appearance. Male and female versions of six different agent types (T) were created and are described in more detail here: T1: Disembodied voice. T2: 2D graphically animated head, appearing to the left of the 3D room. This agent had lip movement synchronised to the speech output. The agent blinked and smiled occasionally at appropriate times during the course of the conversation with the customer. T3: 3D graphically animated head, appearing to the left of the 3D room. This agent had synchronised lip movement, blinking, and because it nodded and turning slightly its 3D appearance was evident. T4: 2D graphically animated full-bodied agent using the heads of T2, appearing outside the 3D room. T5: 3D graphically animated full-bodied agent using the heads of T3, appearing outside the 3D room. T6: 3D graphically animated full-bodied agent identical to T5, appearing inside the 3D room. Copyright 2000, American Association for Artificial Intelligence ( All rights reserved. Figure 1: The E-Retail Application Interface with Animated Agent
2 male agents, and one female voice was used as the voice of all the female agents. An example of the dialogue between the customer and the assistant is presented in Figure 3. Figure 2: Female and Male Embodied Agents (used for T4, T5 and T6) All the agents that appeared on the screen (T2-T6) were provided with facial expression based on four categories defined by Cassell (Cassell et al. 1998). The 2D and 3D animated heads directed gaze toward the customer at all times as the dialogue turns were short. Head nods were used to add emphasis although this was more evident in the 3D head and embodied agents and eyebrow raising was also included at appropriate pitch accents. Further nonverbal facial feedback displays were included for all the agents allowing the agents to look toward the customer during pauses and when asking questions. The agents also looked toward the customers at the end of a turn. The 2D and 3D heads and 2D embodied agents maintained mutual gaze with the customer. However the 3D embodied agents were more mobile, they turned to look at the changes being made in the 3D room, but always returned to look at the customer at the end of the utterance. Gesturing was included in the design of the 2D and 3D embodied agents. Specifically, propositional and spontaneous gestures including iconic, metamorphic and deictic gestures were used (Cassell et al. 1998). Experimental Procedure The experiment used a repeated measures, balanced order design in which 36 participants, balanced for gender, eavesdropped on a short dialogue between a customer and each of the agents in turn (McBreen et al. 2000). Following each dialogue participants completed a 7 point (agree-disagree continuum). Likert format usability questionnaires with a maximum of 22 items, were taken as the dependent variables for the purposes of analysis (Likert 1932). The independent variables were agent gender and type. A post experiment interview was also conducted to obtained detailed qualitative data on users responses to the agents. Twelve similar but not identical dialogue scripts were created. One male voice was used as the voice for all the Hello Hi, can I see a selection of curtain materials please? Would you like to choose one of these fabrics or see some more? Show me the Camellia Stripe Do you like it? Not really, change it to Wesley Dual. OK Show me some matching sofa fabrics please. Certainly, here you are Show me some more Figure 3: Section of the Dialogue Results The attitude questionnaire addressed five main issues regarding the agent: voice, personality, appearance, facial expressions and gesturing. Agents Voice The female voice was significantly (F = 7.37, df = 1.0, p < 0.01) preferred to the male voice (mean female = 5.28, mean male = 4.84). Qualitative comments indicated that both voices were clear. However there were comments which suggested that the female voice was more friendly and natural. The male was perceived to be slightly monotonous. There was a greater preference by female participants for the female agents (F = 8.645, df = 1.0, p < 0.01). The male participants however liked the male and female voices equally. T-Tests indicated that the male voice of T4 and T6 (p < 0.01) were significantly less preferred to their female counterparts, suggesting that the male embodied characters may be less popular. The voice of the male agents were perceived to be significantly less natural than the female (F = 13.53, df = 1.0, p < 0.01), with the female participants preferring the female voice. Statistical results showed that the female voice was less annoying than the male voice, (F = 10.96, df = 1.0, p < 0.05). The questionnaires also showed significant differences between agent types with respect to the naturalness of the voices: an indication that the voice of the agent may effect participants attitudes towards the appearance of the agent. The voice of T5 was the least annoying, in fact T-Tests confirmed that the voices of T5 were significantly preferred to T3 and T4.
3 Agents Personality Politeness: Participants felt that all agents were polite, but the quantitative results showed some significant agent type differences, (F = 5.17, df = 5.0, p < 0.01). T5 was significantly more polite that T2, T3 and T4, but it had similar mean scores to T1 and T6. The disembodied voices and the 3D embodied characters were thought to be more polite. This suggests that gesturing may play an important role in participants perceptions of politeness. An interaction between participant gender and agent gender, (F = 9.15, df = 1.0, p < 0.01), showed that female participants thought that female agents were more polite than male agents, and male participants thought that male agents were more polite than female agents. Friendliness: There were significant differences between agent types for perception of friendliness, (F = 3.15, df = 50, p < 0.05), and also an interaction between agent type and agent gender, (F = 2.74, df = 5.0, p < 0.05). Mean scores show that in general T5 and T6 were deemed to be most friendly. In fact, T-Tests showed that T5 and T6 were significantly more friendly than T2 and T3, all at p < 0.01, yet another indication that gesturing plays an important role in participants perceptions of characteristics such as friendliness for embodied agents. Competence: Female agents were perceived to be more competent than male agents. Because participants did not like the male voice as much as the female overall, they may have associated this with his competence (mean female = 5.657, mean male = 5.52). This was specifically the situation for T1, T4, T5 and T6, and significantly the case for T4. With respect to the talking heads (2D or 3D), participants thought the male and female agents were equally competent, but for the fully embodied agents participants felt that the female was more competent. Forcefulness: T5 was significantly less forceful than all other technologies (p < 0.01), and T4 was significantly more forceful than all other technologies, (p < 0.01). Many participants said that agents who made suggestions were more helpful. Although the dialogue scripts were slightly different, the scripts of T4 did make specific suggestions about fabrics (e.g., "Would you like to try Stella Dual instead"). It seems feasible, based on the analysis of the qualitative feedback that participants could have felt that the assistant was indeed too forceful. The scripts for the other technologies did not make such specific selections, instead they asked if the customer would like to "try another", without saying the specific name of a fabric. Agents Appearance (T2-T6 only) The appearances of the female agents were preferred to the male agents, (F = 22.0, df = 1.0, p < 0.01). More specifically, gender differences occurred significantly for agent types T4, T5 and T6 (fully-embodied agents), where the female appearance was significantly preferred to the male, all p < Upon analysis of the qualitative interview data, many participants thought that the male embodied agents used hand gestures that dominated the interface. Mean Attitude Scores T2 Agent Technology Figure 4: Attitude to Agent Appearance The female agents were thought to be significantly more helpful (mean female = 4.617, mean male = 4.294). The mean score for T5 suggests that it was the most helpful of all agents. Female agents were perceived to be more suitable for the Home Furnishings application than the male agents. A combination of poor attitude responses to the male voice and the exaggerated gestures of the male embodied agents were the probable cause of this gender bias. Female participants thought the female agents were more suitable for the application than the male agents. Male participants thought the male and female agents were equally suitable. T-Tests showed that the female embodied characters (T4, T5, T6) were more suitable than the male embodied characters, (p < 0.01). Figure 4 shows these findings graphically. Facial Expressions (T2-T6 only) T 3 T4 Significantly the lip movements of T5 and T6 were less distracting than T2, T3 and T4, (F = 3.996, df = 4.0, p < 0.01). In the interviews, many participants said that that the lip movements were distracting because they looked dubbed and that the lip movements of the talking heads were more noticeable but they looked artificial. It also became apparent that the female agent was rendered as if wearing lipstick, her lips were more noticeable and obvious. Significant results for agent type differences (F = 3.692, df = 4.0, p < 0.05), showed that the facial expressions of T3 and T5 appeared to be the most life-like. T-Tests showed that the facial expressions of T3 were significantly more life-like than T2, T4 and T6, (p < 0.01). Even though the face of T5 was smaller, making it more difficult for participants to evaluate, it still had a mean score that was similar to that of T3, a talking head, where the facial expressions could be clearly seen. T2 had the most distracting lip movement, significantly less so than the embodied characters, p < T5 T6 A gen t G ender F em ale M ale
4 Participants thought that the female T2 had the most noticeable smile; her lip colour seemed to attract attention. In fact, again showing that the facial expressions of T2 were noticeable, it was found that they were unhelpful in comparison to other agent types, namely T3 and T5, p < It may be concluded from this that less obvious and more natural expressions could promote a sense of helpfulness in animated agents. It was found that the facial expressions of the agents were friendly, and that none were less friendly than others. T5 had the highest mean score (5.07). Gestures (T4-T6 only) Participants preferred the female gestures to the male gestures (mean female = 3.898, mean male = 3.694) and also thought they were less exaggerated than the male gestures. The gesturing of T4 was less exaggerated than T5 and T6, p < T4 only had pointing gestures, and no spontaneous gestures. It seems that deictic gestures may be more useful in e-retail interfaces. Many participants felt that the males gestures were exaggerated which may explain why participants did not like the male appearance. The results did show that for T4 and T6, this gender divide was significant, p < 0.01, but for T5 both male and female agents had similar mean scores. There were significant results for technology when asked if the gestures made the assistants appear life-like, with T5 being more life-like than T6, and significantly more so than T4, p < The gestures contributed to the perceived friendliness of the agents. The agents with more gestures (T5 and T6) were significantly more friendly. Qualitatively it was found that participants wanted the agents to be friendly, a feature that can be promoted by the use of gestures. However, the point at which gesturing becomes annoying and undermines the perception of friendliness remains to be investigated. As regards gesturing effecting the helpfulness of the assistants, analysis showed that T5 was most helpful. Besides the fact that male T6 was poorly accepted because of his large gestures, T5 and T6 were still rated strongly and were thought to be more helpful the T4. T5 was significantly more helpful than T4, p < Discussion Half of the participant population preferred the female agents. This fact is related to participants dislike of the male voice and the poor perception of the embodied male agents exaggerated gestures. What is of particular interest is the fact that on many occasions the female participants significantly preferred the female agents, suggesting that female participants may prefer to interact with agents of their own gender. This bias was not apparent for male participants. In previous experiments (McBreen et al. 2000) where different voices were used, the preference was for the male voice, with results suggesting that fluent conversational voices with intonation should be used. Such voices were therefore used in this simulation. The female voice was acceptable and was more friendly, however the male voice seemed to be monotonous. A finding that clearly emerged from this experiment was that it is important to select the voices of the agents carefully, as possible cross-modal effects may occur: if the voice is not favoured it could effect user perceptions of the visual display of the agents. In general there was a preference for the female agents over male agents as regards personality. The embodied characters were thought to be more friendly, helpful and even polite. This raises interesting research questions about the perception of embodied agents personality and the movement of their bodies. The dialogue between the customer and the assistant was by design, sophisticated and included system initiative. The agent was assumed to be capable of making intelligent suggestions to assist the user in decorating the room. It can be seen from the results that competence and forcefulness are in some respect reflected in the speech output from the agent. It is for this reason that it is important to design dialogues where the agent can make suggestions, without being too forceful. Forcefulness can be off-putting for the participant, and in an interactive situation such an agent could undermine the participant s perception of its ability as an assistant. In general, participants did think that the agents enhanced the service. Despite the poor acceptability of the male embodied agents, it was obvious from the results that participants had a preference to interact with embodied agents as opposed to talking heads. The inclusion of a full body (with non-verbal behaviour associated with such) can indeed enhance the interaction between the user and the agent. However, one third of this participant sample did not like to see the animated agent in the interface, for this reason interactive systems should cater for this by perhaps allowing users to turn off the visual display as required. However, if the non-verbal behaviour can be developed enough to provide essential information to the user, the user may prefer to look at the agent more. In some cases, participants felt that the 3D embodied agent distracted them from the task. The experiment also investigated the relative desirability of an embodied 3D agent appearing inside the 3D world. For this type of shopping application, especially given that participants were asked to eavesdrop on the dialogues between the customer and the user, the results are not conclusive about whether or not it would be more desirable for 3D agents to appear outside, rather than inside the 3D world. Half of the participants stated a preference to see the agent inside the 3D environment, saying that the agent in the room was more complete, natural and they added to the realism. Those who preferred to see the agent outside the 3D world commented that for this application having the agent inside the world distracted their attention from the task and they could not see what was happening in the 3D environment. This was especially a problem for the male
5 agent (T6) as this agent was larger than its female counterpart and also had a more extreme range of gestures. Conclusion A number of hypotheses were made before running this experiment. It was predicted that there would be a dichotomy in the participant group about the use of animated agents in e-retail applications. Encouragingly, two thirds of the user group did prefer to see an animated character in the interface, as opposed to just hearing a disembodied voice. It was hypothesised that 3D talking heads would be preferred to 2D talking heads. This was indeed the case, because the facial expressions are more natural and users do have a desire to interact with more natural looking characters. It was also shown that facial expressions promote helpfulness and friendliness. Further, the facial expressions of a 3D talking head are more lifelike than a 2D talking head. It was also hypothesised that 3D embodied agents would be preferred to 2D embodied agents. This was indeed found to be the case. Although 2D deictic gestures are helpful, the integration of other non-verbal behaviour in a 3D embodiment can promote the acceptability of that agent. It was also hypothesised that 3D embodied agents in a 3D world would be more acceptable than 3D embodied agents outside a 3D world. For reasons outlined in the discussion, this in fact turned out not to be the case. This research has provided the agents community with new facts about various aspects of the inclusion of animated agents in e-retail environments and several issues have been raised. Future work will aim to develop acceptable agents that will appear in a selection of interactive e-retail environments to investigate further non-verbal behaviour of such e-retail assistants and also their use in various retail applications. The following summaries the main issues that evolved from this experiment to assist with the development of an acceptable agent to appear in interactive interfaces: If using a human voice, consider and choose it carefully. The voice should be fluent, conversational with intonation. Ensure the dimensions of the character are in proportional with the dimensions of the 3D environment in which it appears. When using animated humanoid talking heads or embodied agents, 3D agents are more appealing to the user than 2D agents. Carefully select appropriate gestures and facial expressions, too much could undermine the user s perception of the agent. When designing interactive agents, it may be appropriate for the user to personalise the agent with whom they are going to interact. Acknowledgements The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support for this research from BT under its Strategic University Research Initiative, and the helpful planning of the experiment made by the research staff at BT Adastral Park. The work has benefited greatly from helpful discussions with colleagues at the Centre for Communication Interface Research, in particular Dr. John Foster. References Andre, E., and Rist, T Personalising the User Interface: Projects on Life-like Characters at DFKI. In Proceedings of Workshop on Conversational Characters, , Tahoe City, California. Cassell, J.; Bickmore, T.; Billinghurst, M.; Campbell, L.; Chang, K.; Vilhjalmsson, H.; and Yan, H An Architecture for Embodied Conversational Characters. In Proceedings of Workshop on Conversational Characters,21-30, Tahoe City, California. Cassell, J Embodied Conversational Agents. MIT Press. King, J., and Ohya, J., The Representation of Agents: Anthropomorphism, Agency and Intelligence. In Proceedings of CHI. Lester, J., and Stone, B., Increasing Believability in Animated Pedagogical Agents. In Proceedings of Agents Conference, Marina del Rey, CA USA. Likert, R., Some Applications of Behavioural Research. Paris Press. McBreen, H.; Shade, P.; Jack, M.; Wyard, P.; Experimental Assessment of the Effectiveness of Synthetic Personae for Multi-Modal E-Retail Applications. In Proceedings of Autonomous Agents 2000, 39-45, Barcelona, Spain. McBreen, H., and Jack, M., Animated Conversational Agents in E-Commerce Enterprises. In Proceedings of Third International Workshop on Human- Computer Conversation, , Bellagio, Italy. Rust, J., and Golomok, S., The Science of Modern Psychological Assessment. Thorisson, K., Communicative Humanoids: Model of Psychosocial Dialogue Skills. Ph.D. Thesis MIT Media Laboratory. Wyard, P., and Churcher, G., The MUeSLI Multimodal 3D Retail System. In Proceedings of ESCA Workshop on Interactive Dialogue Systems.
MAKING INTERACTIVE GUIDES MORE ATTRACTIVE
 MAKING INTERACTIVE GUIDES MORE ATTRACTIVE Anton Nijholt Department of Computer Science University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands anijholt@cs.utwente.nl Abstract We investigate the different roads
MAKING INTERACTIVE GUIDES MORE ATTRACTIVE Anton Nijholt Department of Computer Science University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands anijholt@cs.utwente.nl Abstract We investigate the different roads
BBC Trust Review of the BBC s Speech Radio Services
 BBC Trust Review of the BBC s Speech Radio Services Research Report February 2015 March 2015 A report by ICM on behalf of the BBC Trust Creston House, 10 Great Pulteney Street, London W1F 9NB enquiries@icmunlimited.com
BBC Trust Review of the BBC s Speech Radio Services Research Report February 2015 March 2015 A report by ICM on behalf of the BBC Trust Creston House, 10 Great Pulteney Street, London W1F 9NB enquiries@icmunlimited.com
Louis-Philippe Morency Institute for Creative Technologies University of Southern California Fiji Way, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA
 Parasocial Consensus Sampling: Combining Multiple Perspectives to Learn Virtual Human Behavior Lixing Huang Institute for Creative Technologies University of Southern California 13274 Fiji Way, Marina
Parasocial Consensus Sampling: Combining Multiple Perspectives to Learn Virtual Human Behavior Lixing Huang Institute for Creative Technologies University of Southern California 13274 Fiji Way, Marina
The Effects of Web Site Aesthetics and Shopping Task on Consumer Online Purchasing Behavior
 The Effects of Web Site Aesthetics and Shopping Task on Consumer Online Purchasing Behavior Cai, Shun The Logistics Institute - Asia Pacific E3A, Level 3, 7 Engineering Drive 1, Singapore 117574 tlics@nus.edu.sg
The Effects of Web Site Aesthetics and Shopping Task on Consumer Online Purchasing Behavior Cai, Shun The Logistics Institute - Asia Pacific E3A, Level 3, 7 Engineering Drive 1, Singapore 117574 tlics@nus.edu.sg
Sound in the Interface to a Mobile Computer
 Sound in the Interface to a Mobile Computer Stephen A. Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12 8RZ, UK. Tel: +44 (0)141 330 4966
Sound in the Interface to a Mobile Computer Stephen A. Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group, Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12 8RZ, UK. Tel: +44 (0)141 330 4966
Expressive Multimodal Conversational Acts for SAIBA agents
 Expressive Multimodal Conversational Acts for SAIBA agents Jeremy Riviere 1, Carole Adam 1, Sylvie Pesty 1, Catherine Pelachaud 2, Nadine Guiraud 3, Dominique Longin 3, and Emiliano Lorini 3 1 Grenoble
Expressive Multimodal Conversational Acts for SAIBA agents Jeremy Riviere 1, Carole Adam 1, Sylvie Pesty 1, Catherine Pelachaud 2, Nadine Guiraud 3, Dominique Longin 3, and Emiliano Lorini 3 1 Grenoble
Imitating the Human Form: Four Kinds of Anthropomorphic Form Carl DiSalvo 1 Francine Gemperle 2 Jodi Forlizzi 1, 3
 Imitating the Human Form: Four Kinds of Anthropomorphic Form Carl DiSalvo 1 Francine Gemperle 2 Jodi Forlizzi 1, 3 School of Design 1, Institute for Complex Engineered Systems 2, Human-Computer Interaction
Imitating the Human Form: Four Kinds of Anthropomorphic Form Carl DiSalvo 1 Francine Gemperle 2 Jodi Forlizzi 1, 3 School of Design 1, Institute for Complex Engineered Systems 2, Human-Computer Interaction
Development of extemporaneous performance by synthetic actors in the rehearsal process
 Development of extemporaneous performance by synthetic actors in the rehearsal process Tony Meyer and Chris Messom IIMS, Massey University, Auckland, New Zealand T.A.Meyer@massey.ac.nz Abstract. Autonomous
Development of extemporaneous performance by synthetic actors in the rehearsal process Tony Meyer and Chris Messom IIMS, Massey University, Auckland, New Zealand T.A.Meyer@massey.ac.nz Abstract. Autonomous
CHILDREN S CONCEPTUALISATION OF MUSIC
 R. Kopiez, A. C. Lehmann, I. Wolther & C. Wolf (Eds.) Proceedings of the 5th Triennial ESCOM Conference CHILDREN S CONCEPTUALISATION OF MUSIC Tânia Lisboa Centre for the Study of Music Performance, Royal
R. Kopiez, A. C. Lehmann, I. Wolther & C. Wolf (Eds.) Proceedings of the 5th Triennial ESCOM Conference CHILDREN S CONCEPTUALISATION OF MUSIC Tânia Lisboa Centre for the Study of Music Performance, Royal
Vuzik: Music Visualization and Creation on an Interactive Surface
 Vuzik: Music Visualization and Creation on an Interactive Surface Aura Pon aapon@ucalgary.ca Junko Ichino Graduate School of Information Systems University of Electrocommunications Tokyo, Japan ichino@is.uec.ac.jp
Vuzik: Music Visualization and Creation on an Interactive Surface Aura Pon aapon@ucalgary.ca Junko Ichino Graduate School of Information Systems University of Electrocommunications Tokyo, Japan ichino@is.uec.ac.jp
Chapter Two: Long-Term Memory for Timbre
 25 Chapter Two: Long-Term Memory for Timbre Task In a test of long-term memory, listeners are asked to label timbres and indicate whether or not each timbre was heard in a previous phase of the experiment
25 Chapter Two: Long-Term Memory for Timbre Task In a test of long-term memory, listeners are asked to label timbres and indicate whether or not each timbre was heard in a previous phase of the experiment
DEMOGRAPHIC DIFFERENCES IN WORKPLACE GOSSIPING BEHAVIOUR IN ORGANIZATIONS - AN EMPIRICAL STUDY ON EMPLOYEES IN SMES
 DEMOGRAPHIC DIFFERENCES IN WORKPLACE GOSSIPING BEHAVIOUR IN ORGANIZATIONS - AN EMPIRICAL STUDY ON EMPLOYEES IN SMES Dr.Vijayalakshmi Kanteti, Professor & Principal, St Xaviers P.G.College, Gopanpally,
DEMOGRAPHIC DIFFERENCES IN WORKPLACE GOSSIPING BEHAVIOUR IN ORGANIZATIONS - AN EMPIRICAL STUDY ON EMPLOYEES IN SMES Dr.Vijayalakshmi Kanteti, Professor & Principal, St Xaviers P.G.College, Gopanpally,
Brief Report. Development of a Measure of Humour Appreciation. Maria P. Y. Chik 1 Department of Education Studies Hong Kong Baptist University
 DEVELOPMENT OF A MEASURE OF HUMOUR APPRECIATION CHIK ET AL 26 Australian Journal of Educational & Developmental Psychology Vol. 5, 2005, pp 26-31 Brief Report Development of a Measure of Humour Appreciation
DEVELOPMENT OF A MEASURE OF HUMOUR APPRECIATION CHIK ET AL 26 Australian Journal of Educational & Developmental Psychology Vol. 5, 2005, pp 26-31 Brief Report Development of a Measure of Humour Appreciation
Spatial Formations. Installation Art between Image and Stage.
 Spatial Formations. Installation Art between Image and Stage. An English Summary Anne Ring Petersen Although much has been written about the origins and diversity of installation art as well as its individual
Spatial Formations. Installation Art between Image and Stage. An English Summary Anne Ring Petersen Although much has been written about the origins and diversity of installation art as well as its individual
THE SONIC ENHANCEMENT OF GRAPHICAL BUTTONS
 THE SONIC ENHANCEMENT OF GRAPHICAL BUTTONS Stephen A. Brewster 1, Peter C. Wright, Alan J. Dix 3 and Alistair D. N. Edwards 1 VTT Information Technology, Department of Computer Science, 3 School of Computing
THE SONIC ENHANCEMENT OF GRAPHICAL BUTTONS Stephen A. Brewster 1, Peter C. Wright, Alan J. Dix 3 and Alistair D. N. Edwards 1 VTT Information Technology, Department of Computer Science, 3 School of Computing
How about laughter? Perceived naturalness of two laughing humanoid robots
 How about laughter? Perceived naturalness of two laughing humanoid robots Christian Becker-Asano Takayuki Kanda Carlos Ishi Hiroshi Ishiguro Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International
How about laughter? Perceived naturalness of two laughing humanoid robots Christian Becker-Asano Takayuki Kanda Carlos Ishi Hiroshi Ishiguro Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International
BBC Television Services Review
 BBC Television Services Review Quantitative audience research assessing BBC One, BBC Two and BBC Four s delivery of the BBC s Public Purposes Prepared for: November 2010 Prepared by: Trevor Vagg and Sara
BBC Television Services Review Quantitative audience research assessing BBC One, BBC Two and BBC Four s delivery of the BBC s Public Purposes Prepared for: November 2010 Prepared by: Trevor Vagg and Sara
Making Progress With Sounds - The Design & Evaluation Of An Audio Progress Bar
 Making Progress With Sounds - The Design & Evaluation Of An Audio Progress Bar Murray Crease & Stephen Brewster Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK. Tel.: (+44) 141 339
Making Progress With Sounds - The Design & Evaluation Of An Audio Progress Bar Murray Crease & Stephen Brewster Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK. Tel.: (+44) 141 339
Approaching Aesthetics on User Interface and Interaction Design
 Approaching Aesthetics on User Interface and Interaction Design Chen Wang* Kochi University of Technology Kochi, Japan i@wangchen0413.cn Sayan Sarcar University of Tsukuba, Japan sayans@slis.tsukuba.ac.jp
Approaching Aesthetics on User Interface and Interaction Design Chen Wang* Kochi University of Technology Kochi, Japan i@wangchen0413.cn Sayan Sarcar University of Tsukuba, Japan sayans@slis.tsukuba.ac.jp
Running head: FACIAL SYMMETRY AND PHYSICAL ATTRACTIVENESS 1
 Running head: FACIAL SYMMETRY AND PHYSICAL ATTRACTIVENESS 1 Effects of Facial Symmetry on Physical Attractiveness Ayelet Linden California State University, Northridge FACIAL SYMMETRY AND PHYSICAL ATTRACTIVENESS
Running head: FACIAL SYMMETRY AND PHYSICAL ATTRACTIVENESS 1 Effects of Facial Symmetry on Physical Attractiveness Ayelet Linden California State University, Northridge FACIAL SYMMETRY AND PHYSICAL ATTRACTIVENESS
Supplemental results from a Garden To Café scannable taste test survey for snack fruit administered in classrooms at PSABX on 12/14/2017
 Supplemental results from a Garden To Café scannable taste test survey for snack fruit administered in classrooms at PSABX on 12/14/2017 Robert Abrams, Ph.D. 2/14/2018 Table Contents Executive Summary...
Supplemental results from a Garden To Café scannable taste test survey for snack fruit administered in classrooms at PSABX on 12/14/2017 Robert Abrams, Ph.D. 2/14/2018 Table Contents Executive Summary...
The psychological impact of Laughter Yoga: Findings from a one- month Laughter Yoga program with a Melbourne Business
 The psychological impact of Laughter Yoga: Findings from a one- month Laughter Yoga program with a Melbourne Business Dr Melissa Weinberg, Deakin University Merv Neal, CEO Laughter Yoga Australia Research
The psychological impact of Laughter Yoga: Findings from a one- month Laughter Yoga program with a Melbourne Business Dr Melissa Weinberg, Deakin University Merv Neal, CEO Laughter Yoga Australia Research
LAUGHTER IN SOCIAL ROBOTICS WITH HUMANOIDS AND ANDROIDS
 LAUGHTER IN SOCIAL ROBOTICS WITH HUMANOIDS AND ANDROIDS Christian Becker-Asano Intelligent Robotics and Communication Labs, ATR, Kyoto, Japan OVERVIEW About research at ATR s IRC labs in Kyoto, Japan Motivation
LAUGHTER IN SOCIAL ROBOTICS WITH HUMANOIDS AND ANDROIDS Christian Becker-Asano Intelligent Robotics and Communication Labs, ATR, Kyoto, Japan OVERVIEW About research at ATR s IRC labs in Kyoto, Japan Motivation
Multimodal databases at KTH
 Multimodal databases at David House, Jens Edlund & Jonas Beskow Clarin Workshop The QSMT database (2002): Facial & Articulatory motion Clarin Workshop Purpose Obtain coherent data for modelling and animation
Multimodal databases at David House, Jens Edlund & Jonas Beskow Clarin Workshop The QSMT database (2002): Facial & Articulatory motion Clarin Workshop Purpose Obtain coherent data for modelling and animation
Why Publish in Journals? How to write a technical paper. How about Theses and Reports? Where Should I Publish? General Considerations: Tone and Style
 How to write a technical paper Mohamed A. El-Sharkawi Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington http://cialab.org Why Publish in Journals? Research is complete only when the results
How to write a technical paper Mohamed A. El-Sharkawi Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington http://cialab.org Why Publish in Journals? Research is complete only when the results
Usability testing of an Electronic Programme Guide and Interactive TV applications
 Usability testing of an Electronic Programme Guide and Interactive TV applications Pedro Concejero, Santiago Gil, Rocío Ramos, José Antonio Collado, Miguel Ángel Castellanos Human Factors Group. Telefónica
Usability testing of an Electronic Programme Guide and Interactive TV applications Pedro Concejero, Santiago Gil, Rocío Ramos, José Antonio Collado, Miguel Ángel Castellanos Human Factors Group. Telefónica
BBC Red Button: Service Review
 BBC Red Button: Service Review Quantitative audience research assessing the BBC Red Button service s delivery of the BBC s Public Purposes Prepared for: October 2010 Prepared by: Trevor Vagg, Kantar Media
BBC Red Button: Service Review Quantitative audience research assessing the BBC Red Button service s delivery of the BBC s Public Purposes Prepared for: October 2010 Prepared by: Trevor Vagg, Kantar Media
Environment Expression: Expressing Emotions through Cameras, Lights and Music
 Environment Expression: Expressing Emotions through Cameras, Lights and Music Celso de Melo, Ana Paiva IST-Technical University of Lisbon and INESC-ID Avenida Prof. Cavaco Silva Taguspark 2780-990 Porto
Environment Expression: Expressing Emotions through Cameras, Lights and Music Celso de Melo, Ana Paiva IST-Technical University of Lisbon and INESC-ID Avenida Prof. Cavaco Silva Taguspark 2780-990 Porto
Social Interaction based Musical Environment
 SIME Social Interaction based Musical Environment Yuichiro Kinoshita Changsong Shen Jocelyn Smith Human Communication Human Communication Sensory Perception and Technologies Laboratory Technologies Laboratory
SIME Social Interaction based Musical Environment Yuichiro Kinoshita Changsong Shen Jocelyn Smith Human Communication Human Communication Sensory Perception and Technologies Laboratory Technologies Laboratory
CANADIAN AUDIENCE REPORT. Full report
 CANADIAN AUDIENCE REPORT Full report November 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES OVERALL KEY FINDINGS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY KEY FINDINGS: VIEWING HABITS KEY FINDINGS: ENGAGEMENT TOWARDS
CANADIAN AUDIENCE REPORT Full report November 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES OVERALL KEY FINDINGS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY KEY FINDINGS: VIEWING HABITS KEY FINDINGS: ENGAGEMENT TOWARDS
Multidimensional analysis of interdependence in a string quartet
 International Symposium on Performance Science The Author 2013 ISBN tbc All rights reserved Multidimensional analysis of interdependence in a string quartet Panos Papiotis 1, Marco Marchini 1, and Esteban
International Symposium on Performance Science The Author 2013 ISBN tbc All rights reserved Multidimensional analysis of interdependence in a string quartet Panos Papiotis 1, Marco Marchini 1, and Esteban
Quantify. The Subjective. PQM: A New Quantitative Tool for Evaluating Display Design Options
 PQM: A New Quantitative Tool for Evaluating Display Design Options Software, Electronics, and Mechanical Systems Laboratory 3M Optical Systems Division Jennifer F. Schumacher, John Van Derlofske, Brian
PQM: A New Quantitative Tool for Evaluating Display Design Options Software, Electronics, and Mechanical Systems Laboratory 3M Optical Systems Division Jennifer F. Schumacher, John Van Derlofske, Brian
D PSB Audience Impact. PSB Report 2011 Information pack June 2012
 D PSB Audience Impact PSB Report 2011 Information pack June 2012 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 11 Nations and regions news 25 Individual PSB channel summaries 33 Overall satisfaction
D PSB Audience Impact PSB Report 2011 Information pack June 2012 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 11 Nations and regions news 25 Individual PSB channel summaries 33 Overall satisfaction
BBC 6 Music: Service Review
 BBC 6 Music: Service Review Prepared for: BBC Trust Research assessing BBC 6 Music s delivery of the BBC s public purposes Prepared by: Laura Chandler and Trevor Vagg BMRB Media Telephone: 020 8433 4379
BBC 6 Music: Service Review Prepared for: BBC Trust Research assessing BBC 6 Music s delivery of the BBC s public purposes Prepared by: Laura Chandler and Trevor Vagg BMRB Media Telephone: 020 8433 4379
The Effects of Study Condition Preference on Memory and Free Recall LIANA, MARISSA, JESSI AND BROOKE
 The Effects of Study Condition Preference on Memory and Free Recall LIANA, MARISSA, JESSI AND BROOKE Introduction -Salamè & Baddeley 1988 Presented nine digits on a computer screen for 750 milliseconds
The Effects of Study Condition Preference on Memory and Free Recall LIANA, MARISSA, JESSI AND BROOKE Introduction -Salamè & Baddeley 1988 Presented nine digits on a computer screen for 750 milliseconds
Smile and Laughter in Human-Machine Interaction: a study of engagement
 Smile and ter in Human-Machine Interaction: a study of engagement Mariette Soury 1,2, Laurence Devillers 1,3 1 LIMSI-CNRS, BP133, 91403 Orsay cedex, France 2 University Paris 11, 91400 Orsay, France 3
Smile and ter in Human-Machine Interaction: a study of engagement Mariette Soury 1,2, Laurence Devillers 1,3 1 LIMSI-CNRS, BP133, 91403 Orsay cedex, France 2 University Paris 11, 91400 Orsay, France 3
Humor and Embodied Conversational Agents
 Humor and Embodied Conversational Agents Anton Nijholt Center for Telematics and Information Technology TKI-Parlevink Research Group University of Twente, PO Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands Abstract
Humor and Embodied Conversational Agents Anton Nijholt Center for Telematics and Information Technology TKI-Parlevink Research Group University of Twente, PO Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands Abstract
Glasgow eprints Service
 Brewster, S.A. and Wright, P.C. and Edwards, A.D.N. (1993) An evaluation of earcons for use in auditory human-computer interfaces. In, Ashlund, S., Eds. Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
Brewster, S.A. and Wright, P.C. and Edwards, A.D.N. (1993) An evaluation of earcons for use in auditory human-computer interfaces. In, Ashlund, S., Eds. Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
Consumer Assessment of Baked Breads made with StarchLite. Results Summary Tragon Corporation
 Consumer Assessment of Baked Breads made with StarchLite Results Summary Tragon Corporation Research Objectives for on Bread Kanak Udani contacted Tragon on behalf of Pharmachem Laboratories who have developed
Consumer Assessment of Baked Breads made with StarchLite Results Summary Tragon Corporation Research Objectives for on Bread Kanak Udani contacted Tragon on behalf of Pharmachem Laboratories who have developed
Purpose Remit Survey Autumn 2016
 Purpose Remit Survey 2016 UK Report A report by ICM on behalf of the BBC Trust Creston House, 10 Great Pulteney Street, London W1F 9NB enquiries@icmunlimited.com www.icmunlimited.com +44 020 7845 8300
Purpose Remit Survey 2016 UK Report A report by ICM on behalf of the BBC Trust Creston House, 10 Great Pulteney Street, London W1F 9NB enquiries@icmunlimited.com www.icmunlimited.com +44 020 7845 8300
Code : is a set of practices familiar to users of the medium
 Lecture (05) CODES Code Code : is a set of practices familiar to users of the medium operating within a broad cultural framework. When studying cultural practices, semioticians treat as signs any objects
Lecture (05) CODES Code Code : is a set of practices familiar to users of the medium operating within a broad cultural framework. When studying cultural practices, semioticians treat as signs any objects
Non-Reducibility with Knowledge wh: Experimental Investigations
 Non-Reducibility with Knowledge wh: Experimental Investigations 1 Knowing wh and Knowing that Obvious starting picture: (1) implies (2). (2) iff (3). (1) John knows that he can buy an Italian newspaper
Non-Reducibility with Knowledge wh: Experimental Investigations 1 Knowing wh and Knowing that Obvious starting picture: (1) implies (2). (2) iff (3). (1) John knows that he can buy an Italian newspaper
2012, the Author. This is the final version of a paper published in Participations: Journal of Audience and Reception Studios.
 2012, the Author. This is the final version of a paper published in Participations: Journal of Audience and Reception Studios. Reproduced in accordance with the publisher s self- archiving policy. Redfern,
2012, the Author. This is the final version of a paper published in Participations: Journal of Audience and Reception Studios. Reproduced in accordance with the publisher s self- archiving policy. Redfern,
THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND
 THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND 1999 LIBRARY CUSTOMER SURVEY THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND LIBRARY Survey October 1999 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 BACKGROUND... 1 1.2 OBJECTIVES... 2 1.3 THE SURVEY PROCESS...
THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND 1999 LIBRARY CUSTOMER SURVEY THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND LIBRARY Survey October 1999 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 BACKGROUND... 1 1.2 OBJECTIVES... 2 1.3 THE SURVEY PROCESS...
Outcome EN4-1A A student: responds to and composes texts for understanding, interpretation, critical analysis, imaginative expression and pleasure
 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- Building capacity with new syallabuses Teaching visual literacy and multimodal texts English syllabus continuum Stages 3 to 5 Outcome
------------------------------------------------------------------------- Building capacity with new syallabuses Teaching visual literacy and multimodal texts English syllabus continuum Stages 3 to 5 Outcome
SURVEYS FOR REFLECTIVE PRACTICE
 SURVEYS FOR REFLECTIVE PRACTICE These surveys are designed to help teachers collect feedback from students about their use of the forty-one elements of effective teaching. The high school student survey
SURVEYS FOR REFLECTIVE PRACTICE These surveys are designed to help teachers collect feedback from students about their use of the forty-one elements of effective teaching. The high school student survey
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA PSYCHOLOGY 1 Psychology PSY 120 Introduction to Psychology 3 cr A survey of the basic theories, concepts, principles, and research findings in the field of Psychology. Core
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA PSYCHOLOGY 1 Psychology PSY 120 Introduction to Psychology 3 cr A survey of the basic theories, concepts, principles, and research findings in the field of Psychology. Core
PREPARATION (0-30 POINTS PER SONG) (Visual Plan)
 PREPARATION (0-30 POINTS PER SONG) (Visual Plan) The showmanship judge considers all facets of the performance that should have been planned in advance, to determine how effectively the performer has prepared
PREPARATION (0-30 POINTS PER SONG) (Visual Plan) The showmanship judge considers all facets of the performance that should have been planned in advance, to determine how effectively the performer has prepared
The semiotics of multimodal argumentation. Paul van den Hoven, Utrecht University, Xiamen University
 The semiotics of multimodal argumentation Paul van den Hoven, Utrecht University, Xiamen University Multimodal argumentative discourse exists! Rhetorical discourse is discourse that attempts to influence
The semiotics of multimodal argumentation Paul van den Hoven, Utrecht University, Xiamen University Multimodal argumentative discourse exists! Rhetorical discourse is discourse that attempts to influence
This full text version, available on TeesRep, is the post-print (final version prior to publication) of:
 This full text version, available on TeesRep, is the post-print (final version prior to publication) of: Charles, F. et. al. (2007) 'Affective interactive narrative in the CALLAS Project', 4th international
This full text version, available on TeesRep, is the post-print (final version prior to publication) of: Charles, F. et. al. (2007) 'Affective interactive narrative in the CALLAS Project', 4th international
Anthropomorphism. the rationalization of animal or system behavior through superposing aspects of the human observer.
 Wizard of Oz Anthropomorphism the rationalization of animal or system behavior through superposing aspects of the human observer. Having a naturalistic embodiment is often cited as necessary for meaningful
Wizard of Oz Anthropomorphism the rationalization of animal or system behavior through superposing aspects of the human observer. Having a naturalistic embodiment is often cited as necessary for meaningful
ESP: Expression Synthesis Project
 ESP: Expression Synthesis Project 1. Research Team Project Leader: Other Faculty: Graduate Students: Undergraduate Students: Prof. Elaine Chew, Industrial and Systems Engineering Prof. Alexandre R.J. François,
ESP: Expression Synthesis Project 1. Research Team Project Leader: Other Faculty: Graduate Students: Undergraduate Students: Prof. Elaine Chew, Industrial and Systems Engineering Prof. Alexandre R.J. François,
Differentiated Approaches to Aural Acuity Development: A Case of a Secondary School in Kiambu County, Kenya
 Differentiated Approaches to Aural Acuity Development: A Case of a Secondary School in Kiambu County, Kenya Muya Francis Kihoro Mount Kenya University, Nairobi, Kenya. E-mail: kihoromuya@hotmail.com DOI:
Differentiated Approaches to Aural Acuity Development: A Case of a Secondary School in Kiambu County, Kenya Muya Francis Kihoro Mount Kenya University, Nairobi, Kenya. E-mail: kihoromuya@hotmail.com DOI:
WRoCAH White Rose NETWORK Expressive nonverbal communication in ensemble performance
 Applications are invited for three fully-funded doctoral research studentships in a new Research Network funded by the White Rose College of the Arts & Humanities. WRoCAH White Rose NETWORK Expressive
Applications are invited for three fully-funded doctoral research studentships in a new Research Network funded by the White Rose College of the Arts & Humanities. WRoCAH White Rose NETWORK Expressive
Department of MBA, School of Communication and Management Studies, Nalukettu, Kerala, India
 Original Article International Multidisciplinary Research Journal 2015, 5: 16-22 http://scienceflora.org/journals/index.php/imrj/ doi: 10.19071/imrj.2015.v5.3174 Viewership analysis of news channels with
Original Article International Multidisciplinary Research Journal 2015, 5: 16-22 http://scienceflora.org/journals/index.php/imrj/ doi: 10.19071/imrj.2015.v5.3174 Viewership analysis of news channels with
Mind Formative Evaluation. Limelight. Joyce Ma and Karen Chang. February 2007
 Mind Formative Evaluation Limelight Joyce Ma and Karen Chang February 2007 Keywords: 1 Mind Formative Evaluation
Mind Formative Evaluation Limelight Joyce Ma and Karen Chang February 2007 Keywords: 1 Mind Formative Evaluation
Choral Sight-Singing Practices: Revisiting a Web-Based Survey
 Demorest (2004) International Journal of Research in Choral Singing 2(1). Sight-singing Practices 3 Choral Sight-Singing Practices: Revisiting a Web-Based Survey Steven M. Demorest School of Music, University
Demorest (2004) International Journal of Research in Choral Singing 2(1). Sight-singing Practices 3 Choral Sight-Singing Practices: Revisiting a Web-Based Survey Steven M. Demorest School of Music, University
1: University Department with high profile material but protective of its relationship with speakers
 Appendix 4: Use Cases 1: University Department with high profile material but protective of its relationship with speakers 2: Podcast material published in a journal 3: Podcasts created from video and
Appendix 4: Use Cases 1: University Department with high profile material but protective of its relationship with speakers 2: Podcast material published in a journal 3: Podcasts created from video and
An ecological approach to multimodal subjective music similarity perception
 An ecological approach to multimodal subjective music similarity perception Stephan Baumann German Research Center for AI, Germany www.dfki.uni-kl.de/~baumann John Halloran Interact Lab, Department of
An ecological approach to multimodal subjective music similarity perception Stephan Baumann German Research Center for AI, Germany www.dfki.uni-kl.de/~baumann John Halloran Interact Lab, Department of
Devices I have known and loved
 66 l Print this article Devices I have known and loved Joel Chadabe Albany, New York, USA joel@emf.org Do performing devices match performance requirements? Whenever we work with an electronic music system,
66 l Print this article Devices I have known and loved Joel Chadabe Albany, New York, USA joel@emf.org Do performing devices match performance requirements? Whenever we work with an electronic music system,
Formalizing Irony with Doxastic Logic
 Formalizing Irony with Doxastic Logic WANG ZHONGQUAN National University of Singapore April 22, 2015 1 Introduction Verbal irony is a fundamental rhetoric device in human communication. It is often characterized
Formalizing Irony with Doxastic Logic WANG ZHONGQUAN National University of Singapore April 22, 2015 1 Introduction Verbal irony is a fundamental rhetoric device in human communication. It is often characterized
Musical Futures: A case study investigation. Final report from. Institute of Education University of London. for the. Paul Hamlyn Foundation
 Musical Futures: A case study investigation Final report from Institute of Education University of London for the Paul Hamlyn Foundation October 2011 Professor Susan Hallam Dr Andrea Creech Dr Hilary McQueen
Musical Futures: A case study investigation Final report from Institute of Education University of London for the Paul Hamlyn Foundation October 2011 Professor Susan Hallam Dr Andrea Creech Dr Hilary McQueen
Interacting with a Virtual Conductor
 Interacting with a Virtual Conductor Pieter Bos, Dennis Reidsma, Zsófia Ruttkay, Anton Nijholt HMI, Dept. of CS, University of Twente, PO Box 217, 7500AE Enschede, The Netherlands anijholt@ewi.utwente.nl
Interacting with a Virtual Conductor Pieter Bos, Dennis Reidsma, Zsófia Ruttkay, Anton Nijholt HMI, Dept. of CS, University of Twente, PO Box 217, 7500AE Enschede, The Netherlands anijholt@ewi.utwente.nl
Study Abroad Programme
 MODULE SPECIFICATION UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES KEY FACTS Module name Module code School Department or equivalent Music Business MU2109 School of Arts and Social Sciences Music UK credits 15 ECTS 7.5 Level
MODULE SPECIFICATION UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES KEY FACTS Module name Module code School Department or equivalent Music Business MU2109 School of Arts and Social Sciences Music UK credits 15 ECTS 7.5 Level
Application of a Musical-based Interaction System to the Waseda Flutist Robot WF-4RIV: Development Results and Performance Experiments
 The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 24-27, 2012 Application of a Musical-based Interaction System to the Waseda Flutist Robot
The Fourth IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics Roma, Italy. June 24-27, 2012 Application of a Musical-based Interaction System to the Waseda Flutist Robot
Measurement of Motion and Emotion during Musical Performance
 Measurement of Motion and Emotion during Musical Performance R. Benjamin Knapp, PhD b.knapp@qub.ac.uk Javier Jaimovich jjaimovich01@qub.ac.uk Niall Coghlan ncoghlan02@qub.ac.uk Abstract This paper describes
Measurement of Motion and Emotion during Musical Performance R. Benjamin Knapp, PhD b.knapp@qub.ac.uk Javier Jaimovich jjaimovich01@qub.ac.uk Niall Coghlan ncoghlan02@qub.ac.uk Abstract This paper describes
Don t Judge a Book by its Cover: A Discrete Choice Model of Cultural Experience Good Consumption
 Don t Judge a Book by its Cover: A Discrete Choice Model of Cultural Experience Good Consumption Paul Crosby Department of Economics Macquarie University North American Workshop on Cultural Economics November
Don t Judge a Book by its Cover: A Discrete Choice Model of Cultural Experience Good Consumption Paul Crosby Department of Economics Macquarie University North American Workshop on Cultural Economics November
B - PSB Audience Impact. PSB Report 2013 Information pack August 2013
 B - PSB Audience Impact PSB Report 2013 Information pack August 2013 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 11 Nations and regions news 27 Individual PSB channel summaries 35 Overall satisfaction
B - PSB Audience Impact PSB Report 2013 Information pack August 2013 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 11 Nations and regions news 27 Individual PSB channel summaries 35 Overall satisfaction
Klee or Kid? The subjective experience of drawings from children and Paul Klee Pronk, T.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Klee or Kid? The subjective experience of drawings from children and Paul Klee Pronk, T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Pronk, T. (Author).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Klee or Kid? The subjective experience of drawings from children and Paul Klee Pronk, T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Pronk, T. (Author).
Improving music composition through peer feedback: experiment and preliminary results
 Improving music composition through peer feedback: experiment and preliminary results Daniel Martín and Benjamin Frantz and François Pachet Sony CSL Paris {daniel.martin,pachet}@csl.sony.fr Abstract To
Improving music composition through peer feedback: experiment and preliminary results Daniel Martín and Benjamin Frantz and François Pachet Sony CSL Paris {daniel.martin,pachet}@csl.sony.fr Abstract To
Believability factor in Malayalam Reality Shows: A Study among the Television Viewers of Kerala
 International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 7722, ISSN (Print): 2319 7714 Volume 6 Issue 5 May. 2017 PP.10-14 Believability factor in Malayalam Reality Shows: A
International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 7722, ISSN (Print): 2319 7714 Volume 6 Issue 5 May. 2017 PP.10-14 Believability factor in Malayalam Reality Shows: A
coach The students or teacher can give advice, instruct or model ways of responding while the activity takes place. Sometimes called side coaching.
 Drama Glossary atmosphere In television, much of the atmosphere of the programme is created in post-production through editing and the inclusion of music. In theatre, the actor hears and sees all the elements
Drama Glossary atmosphere In television, much of the atmosphere of the programme is created in post-production through editing and the inclusion of music. In theatre, the actor hears and sees all the elements
Agreed key principles, observation questions and Ofsted grade descriptors for formal learning
 Barnsley Music Education Hub Quality Assurance Framework Agreed key principles, observation questions and Ofsted grade descriptors for formal learning Formal Learning opportunities includes: KS1 Musicianship
Barnsley Music Education Hub Quality Assurance Framework Agreed key principles, observation questions and Ofsted grade descriptors for formal learning Formal Learning opportunities includes: KS1 Musicianship
Music in Practice SAS 2015
 Sample unit of work Contemporary music The sample unit of work provides teaching strategies and learning experiences that facilitate students demonstration of the dimensions and objectives of Music in
Sample unit of work Contemporary music The sample unit of work provides teaching strategies and learning experiences that facilitate students demonstration of the dimensions and objectives of Music in
Introduction. The report is broken down into four main sections:
 Introduction This survey was carried out as part of OAPEN-UK, a Jisc and AHRC-funded project looking at open access monograph publishing. Over five years, OAPEN-UK is exploring how monographs are currently
Introduction This survey was carried out as part of OAPEN-UK, a Jisc and AHRC-funded project looking at open access monograph publishing. Over five years, OAPEN-UK is exploring how monographs are currently
Computer Coordination With Popular Music: A New Research Agenda 1
 Computer Coordination With Popular Music: A New Research Agenda 1 Roger B. Dannenberg roger.dannenberg@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~rbd School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh,
Computer Coordination With Popular Music: A New Research Agenda 1 Roger B. Dannenberg roger.dannenberg@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~rbd School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh,
Meaning Machines CS 672 Deictic Representations (3) Matthew Stone THE VILLAGE
 Meaning Machines CS 672 Deictic Representations (3) Matthew Stone THE VILLAGE Department of Computer Science Center for Cognitive Science Rutgers University Agenda Pylyshyn on visual indices Iris Implementing
Meaning Machines CS 672 Deictic Representations (3) Matthew Stone THE VILLAGE Department of Computer Science Center for Cognitive Science Rutgers University Agenda Pylyshyn on visual indices Iris Implementing
Embodied Agents: A New Impetus to Humor Research
 Embodied Agents: A New Impetus to Humor Research Anton Nijholt University of Twente Department of Computer Science PO Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands anijholt@cs.utwente.nl Abstract In this paper
Embodied Agents: A New Impetus to Humor Research Anton Nijholt University of Twente Department of Computer Science PO Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands anijholt@cs.utwente.nl Abstract In this paper
Laura Gallop. INNERVATE Leading Undergraduate Work in English, Volume 6 ( ), pp
 According to Jiří Veltruský, All that is on stage is a sign. Using appropriate semiotic terms and critical support, discuss this assertion, making reference to elements of performance you have been involved
According to Jiří Veltruský, All that is on stage is a sign. Using appropriate semiotic terms and critical support, discuss this assertion, making reference to elements of performance you have been involved
BBC WORLD SERVICE JOB SPECIFICATION
 BBC WORLD SERVICE JOB SPECIFICATION Job Title: Department: Base: Grade: Video Editor, BBC Bengali Service BBC World Service South Asia region Dhaka, Bangladesh Local terms & conditions Flexible working
BBC WORLD SERVICE JOB SPECIFICATION Job Title: Department: Base: Grade: Video Editor, BBC Bengali Service BBC World Service South Asia region Dhaka, Bangladesh Local terms & conditions Flexible working
Information about Visiting The Customs House
 Information about Visiting The Customs House This document may be useful for new visitors to The Customs House including groups and people with access needs who are planning a visit. Throughout this document
Information about Visiting The Customs House This document may be useful for new visitors to The Customs House including groups and people with access needs who are planning a visit. Throughout this document
Master thesis. The effects of L2, L1 dubbing and L1 subtitling on the effectiveness of persuasive fictional narratives.
 Master thesis The effects of L2, L1 dubbing and L1 subtitling on the effectiveness of persuasive fictional narratives. Author: Edu Goossens Student number: 4611551 Student email: e.goossens@student.ru.nl
Master thesis The effects of L2, L1 dubbing and L1 subtitling on the effectiveness of persuasive fictional narratives. Author: Edu Goossens Student number: 4611551 Student email: e.goossens@student.ru.nl
Scope and Sequence for NorthStar Listening & Speaking Intermediate
 Unit 1 Unit 2 Critique magazine and Identify chronology Highlighting Imperatives television ads words Identify salient features of an ad Propose advertising campaigns according to market information Support
Unit 1 Unit 2 Critique magazine and Identify chronology Highlighting Imperatives television ads words Identify salient features of an ad Propose advertising campaigns according to market information Support
The Aesthetic Experience and the Sense of Presence in an Artistic Virtual Environment
 The Aesthetic Experience and the Sense of Presence in an Artistic Virtual Environment Dr. Brian Betz, Kent State University, Stark Campus Dr. Dena Eber, Bowling Green State University Gregory Little, Bowling
The Aesthetic Experience and the Sense of Presence in an Artistic Virtual Environment Dr. Brian Betz, Kent State University, Stark Campus Dr. Dena Eber, Bowling Green State University Gregory Little, Bowling
How to write a RILM thesis Guidelines
 How to write a RILM thesis Guidelines Version 3.0 October 25, 2017 0 Purpose... 1 1 Planning... 1 1.1 When to start... 1 2 The topic... 1 2.1 What? The topic... 1 2.2 Why? Reasons to select a topic...
How to write a RILM thesis Guidelines Version 3.0 October 25, 2017 0 Purpose... 1 1 Planning... 1 1.1 When to start... 1 2 The topic... 1 2.1 What? The topic... 1 2.2 Why? Reasons to select a topic...
Media Examination Revision 2018
 Media Examination Revision 2018 Pre Release Material issued Monday 7 th May 2018 Examination Date: Monday 4 th June (pm) 1 ½ hours (20 mins per question) 4 Questions each worth 15 marks You MUST be able
Media Examination Revision 2018 Pre Release Material issued Monday 7 th May 2018 Examination Date: Monday 4 th June (pm) 1 ½ hours (20 mins per question) 4 Questions each worth 15 marks You MUST be able
Musically Expressive Doll in Face-to-face Communication
 Musically Expressive Doll in Face-to-face Communication Tomoko Yonezawa, *1 and Kenji Mase, *2 ATR Media Integration & Communications Research Laboratories ATR Media Information Science Laboratories yonezawa.tomoko@lab.ntt.co.jp,
Musically Expressive Doll in Face-to-face Communication Tomoko Yonezawa, *1 and Kenji Mase, *2 ATR Media Integration & Communications Research Laboratories ATR Media Information Science Laboratories yonezawa.tomoko@lab.ntt.co.jp,
Stage Terminology. As you take your place onstage, you will discover that the theatre. The Performance Space
 Stage Terminology 4 LESSON OBJECTIVES Identify the different parts of the performance space. Identify the proscenium stage acting areas. Follow basic stage directions using the acting areas. S tage Terms
Stage Terminology 4 LESSON OBJECTIVES Identify the different parts of the performance space. Identify the proscenium stage acting areas. Follow basic stage directions using the acting areas. S tage Terms
Inducing change in user s perspective with the arrangement of body orientation of embodied agents
 Inducing change in user s perspective with the arrangement of body orientation of embodied agents Satoshi V. Suzuki and Hideaki Takeda Abstract We set out to reveal that arrangement of embodied agents
Inducing change in user s perspective with the arrangement of body orientation of embodied agents Satoshi V. Suzuki and Hideaki Takeda Abstract We set out to reveal that arrangement of embodied agents
Signia Rated Superior to Competing Products for Music Sound Quality
 Signia Rated Superior to Competing Products for Music Sound Quality White Paper Matthias Froehlich, PhD Veronika Littmann, PhD Jonathan Vaisberg, PhD Candidate Paula Folkeard, AuD Vijay Parsa, PhD Susan
Signia Rated Superior to Competing Products for Music Sound Quality White Paper Matthias Froehlich, PhD Veronika Littmann, PhD Jonathan Vaisberg, PhD Candidate Paula Folkeard, AuD Vijay Parsa, PhD Susan
Humor: Prosody Analysis and Automatic Recognition for F * R * I * E * N * D * S *
 Humor: Prosody Analysis and Automatic Recognition for F * R * I * E * N * D * S * Amruta Purandare and Diane Litman Intelligent Systems Program University of Pittsburgh amruta,litman @cs.pitt.edu Abstract
Humor: Prosody Analysis and Automatic Recognition for F * R * I * E * N * D * S * Amruta Purandare and Diane Litman Intelligent Systems Program University of Pittsburgh amruta,litman @cs.pitt.edu Abstract
PSB Annual Report 2015 PSB Audience Opinion Annex. Published July 2015
 PSB Annual Report 2015 PSB Audience Opinion Annex Published July 2015 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 5 Overall satisfaction with PSB 19 Nations and regions news 29 Children s PSB
PSB Annual Report 2015 PSB Audience Opinion Annex Published July 2015 Contents Page Background 2 Overview of PSB television 5 Overall satisfaction with PSB 19 Nations and regions news 29 Children s PSB
THEATRE AND DANCE (TRDA)
 THEATRE AND DANCE (TRDA) Explanation of Course Numbers Courses in the 1000s are primarily introductory undergraduate courses Those in the 2000s to 4000s are upper-division undergraduate courses that can
THEATRE AND DANCE (TRDA) Explanation of Course Numbers Courses in the 1000s are primarily introductory undergraduate courses Those in the 2000s to 4000s are upper-division undergraduate courses that can
Engaging Virtual Pedagogical Agents (VPAs)
 Engaging Virtual Pedagogical Agents (VPAs) Agneta Gulz Div. of Cognitive Science (LUCS) Lund University agneta.gulz@lucs.lu.se Magnus Haake Dept. of Design Sciences, LTH Lund University magnus.haake@design.lth.se
Engaging Virtual Pedagogical Agents (VPAs) Agneta Gulz Div. of Cognitive Science (LUCS) Lund University agneta.gulz@lucs.lu.se Magnus Haake Dept. of Design Sciences, LTH Lund University magnus.haake@design.lth.se
Speech Recognition and Signal Processing for Broadcast News Transcription
 2.2.1 Speech Recognition and Signal Processing for Broadcast News Transcription Continued research and development of a broadcast news speech transcription system has been promoted. Universities and researchers
2.2.1 Speech Recognition and Signal Processing for Broadcast News Transcription Continued research and development of a broadcast news speech transcription system has been promoted. Universities and researchers
Real-time composition of image and sound in the (re)habilitation of children with special needs: a case study of a child with cerebral palsy
 Real-time composition of image and sound in the (re)habilitation of children with special needs: a case study of a child with cerebral palsy Abstract Maria Azeredo University of Porto, School of Psychology
Real-time composition of image and sound in the (re)habilitation of children with special needs: a case study of a child with cerebral palsy Abstract Maria Azeredo University of Porto, School of Psychology
Gender Empowerment: Opportunities and Challenges
 R.S Mundle Dharampeth Arts and Commerce College Multidisciplinary National Conference on 25 January 2019 Gender Empowerment: Opportunities and Challenges Research Papers and Posters are invited on the
R.S Mundle Dharampeth Arts and Commerce College Multidisciplinary National Conference on 25 January 2019 Gender Empowerment: Opportunities and Challenges Research Papers and Posters are invited on the
To Link this Article: Vol. 7, No.1, January 2018, Pg. 1-11
 Identifying the Importance of Types of Music Information among Music Students Norliya Ahmad Kassim, Kasmarini Baharuddin, Nurul Hidayah Ishak, Nor Zaina Zaharah Mohamad Ariff, Siti Zahrah Buyong To Link
Identifying the Importance of Types of Music Information among Music Students Norliya Ahmad Kassim, Kasmarini Baharuddin, Nurul Hidayah Ishak, Nor Zaina Zaharah Mohamad Ariff, Siti Zahrah Buyong To Link
What Can Experimental Philosophy Do? David Chalmers
 What Can Experimental Philosophy Do? David Chalmers Cast of Characters X-Phi: Experimental Philosophy E-Phi: Empirical Philosophy A-Phi: Armchair Philosophy Challenges to Experimental Philosophy Empirical
What Can Experimental Philosophy Do? David Chalmers Cast of Characters X-Phi: Experimental Philosophy E-Phi: Empirical Philosophy A-Phi: Armchair Philosophy Challenges to Experimental Philosophy Empirical
Music Years 7 10 Life Skills unit: Australian music
 Music Years 7 10 Life Skills unit: Australian music Unit title: Australian music Description: In this unit students explore a wide variety of traditional and contemporary Australian music through experiences
Music Years 7 10 Life Skills unit: Australian music Unit title: Australian music Description: In this unit students explore a wide variety of traditional and contemporary Australian music through experiences
