VivoSense. User Manual Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) Analysis Module. VivoSense, Inc. Newport Beach, CA, USA Tel. (858) , Fax.
|
|
|
- Garry Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VivoSense User Manual Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) Analysis VivoSense Version 3.1 VivoSense, Inc. Newport Beach, CA, USA Tel. (858) , Fax. (248) Web:
2 Cautions and disclaimer VivoSense software is not a medical diagnostic tool. It is for research and investigational purposes only and is not intended to be, or to replace, medical advice or review by a physician. Copyright Notice Copyright 2017 VivoSense. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 16
3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction Galvanic Skin Response Analysis for VivoSense System Requirements GSR Background Anatomical and Physiological Basis Background Artifact Marking for GSR Editing GSR Markings GSR Waveform Interpolation Excluding Regions of GSR Data as Artifact Artifact Thresholds Artifact Editing Layouts GSR Data Processing Waveform Channels Marker Channels Measures Channels GSR Layouts Page 3 of 16
4 1. Introduction 1.1. Galvanic Skin Response Analysis for VivoSense This manual describes the Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) analysis module for VivoSense. This module may be used to analyze and visualize several GSR metrics. The manual includes a background to the analysis of GSR, a description of the artifact editing capabilities included in the module and a description of the various indices and methods of calculation and visualization. The module is delivered with several layouts that facilitate the use of the GSR analysis. The module also allows for the export of GSR parameters in a variety of possible configurations. Familiarity with the core VivoSense module is a prerequisite for use with the GSR analysis module. VivoSense GSR allows a user to visualize GSR metrics of sympathetic nervous system activation, synchronized with relevant data channels from other sensors to provide a contextual significance to any research study. Further automated and graphical artifact management capabilities allow for precise and accurate calculations of sympathetic system responses in a variety of application domains System Requirements This module is an add-on analysis module to VivoSense and requires VivoSense Core with a sensor import module that supports a Galvanic Skin Resistance (GSR) sensor. This is also sometimes referred to as an Electro-dermal Activation (EDA) sensor. Page 4 of 16
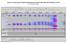
5 2. GSR Background 2.1. Anatomical and Physiological Basis The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the portion of the nervous system operating below the level of consciousness. It acts as a control system for the body's visceral functions, including perspiration, heart rate, respiration rate, movement of the gastrointestinal tract, salivation and many other vital activities. As the ANS is not directly under conscious control, it is affected by mental and emotional states. The ANS consists of two main branches: The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The SNS is best known as the fight or flight system, although it has many additional roles. While most organs of the body are innervated by both the SNS and the PNS, the skin is mainly innervated by the SNS, making it an ideal place to measure sympathetic arousal. The skin is an organ with many vital and dynamic functions and thus the skin constantly receives signals from control centers in the brain. It was noted many years ago that we can essentially listen in to these signals as their arrival at the skin results in measurable electrical changes. This is called electrodermal activity. The primary function of endocrine sweat glands in the human body is thermoregulation. However, the sweat glands located on the hands and soles of the feet are particularly more responsive to emotional stimuli than to thermal stimuli. Thus emotion evoked sweating is most evident at these sites due to the high gland density. As stated, human sweat glands have predominantly SNS innervation and as the degree of SNS activation increases, more sweat glands become activated, resulting in a more conductive path through the relatively resistant skin epidermis. Thus measurement of the skin resistance offers us a non-invasive window into psychologically induced changes in the sympathetic nervous system Background Changes in mental or emotional state leads to SNS changes, which in turn results in changes to the skin resistance. The goal of GSR analysis is thus to work in reverse and investigate a subjects affective state by making inferences from the measured skin resistance waveform. A GSR sensor creates a very small current across the surface of the skin and measures the voltage across the applied electrodes. From this it is possible to generate a resistance waveform that is sensitive to the subtle electrical changes arising from the activity of the sweat glands. The output of the GSR sensor is the skin s conductance represented in units called microsiemens (µs). A typical GSR waveform is displayed in Figure 1. Page 5 of 16
6 Figure 1. GSR waveform with response peaks identified in red. The GSR waveform is characterized by two important components: A fast component called phasic and a slow component called tonic. Both tonic and phasic components contain information associated with specific psychophysiological aspects of brain states. The tonic component is the baseline level of skin conductance in the absence of any particular environmental event and it varies over time in individuals depending on psychological state and autonomic regulation. The tonic component changes very slowly and represents the background of the signal called the skin conductance level (SCL). The phasic component is associated with fast changes (peaks) that occur in response to a single stimulus and is a called a (specific) skin conductance response (SCR). In contrast to a specific SCR, non-specific fluctuations also frequently occur spontaneously without any external stimulus. The most widely used measure of SNS activity or psychophysiological activation is the frequency (rate per minute) of these non-specific SCRs. VivoSense GSR analysis module may be used to accurately identify and quantify non-specific SCR s and SCL s. Responses to specific stimulus may be visualized in VivoSense software, but no specific analyses are available for these types of responses. The analysis of SCRs requires accurate identification and marking of response peaks. Page 6 of 16
7 3. Artifact Marking for GSR GSR waveform data channels markings will often contain artifact. There are several possible sources of artifact that may arise. Artifact will contaminate the raw measured signal which may in turn result in erroneous measurement of tonic of phasic responses. The most commonly encountered GSR artifact is motion artifact. Other forms of artifact include electrode movement with respect to the skin interface (disrupting electrochemical equilibrium); signal saturation; spike transients or jumps and signal drift. Some forms of artifact may be eliminated through the use of advanced filtering techniques and design considerations such as shielded cables. Despite this however, artifact may still occur when recording GSR waveforms. Errors in the location of the SCR peaks will result in errors in the calculation of the non-specific SCR event rate. Therefore, to ensure accurate results, it is critical to manage artifact appropriately prior to performing any GSR analyses. VivoSense provides several mechanisms for the management of artifact and the appropriate selection will depend on the nature of the artifact. These different mechanisms and their recommended usage are described below. The module includes a GSR Artifact Editing layout in the s > GSR Analysis folder Editing GSR Markings VivoSense calculates non-specific fluctuation (NSF) peaks from a GSR waveform. If the sensors were poorly applied, the subject moves a lot, or the waveform is noisy, these markings may be erroneously calculated. The GSR analysis module provides a mechanism to edit the location of NSF peak markings. NSF peak marking editing must be performed from the NSF peak channel. This channel is located in GSR > Markers. It is recommended that the SCR (EDA) waveform channel be used to visually locate erroneous markings and to correctly place new markings. This channel may be present on the same chart. Manually editing NSF peak markings is recommended for portions of the data where the NSF peak detection algorithm may have failed, and the correct markings are clearly visible via visual inspection. This may occur in the presence of noise. This is the most accurate form of artifact management prior to GSR analysis and should be performed if possible. Deleting NSF Peak Markings To delete a NSF peak marking, the cursor must be located on a chart that includes a plot of the NSF peak marking. It is recommended to use the appropriate GSR Artifact Editing layout, which will identify deleted NSF u press the D Hotkey. This will delete the NSF peak marking closest to the cursor. VivoSense will search for an NSF peak marking within a range of 2 seconds around the cursor. By default, a NSF peak must be marked within a range of 2 seconds centered on the cursor for the menu item to appear. This distance is editable in the NSF peak channel s Search Duration property. In addition, an annotation will be added to the annotation bar designating the deleted NSF peak marking. The annotation will be centered on the NSF peak with default duration of 1 second, and all NSF peak markings within the range of this annotation will be deleted. The default duration may be modified with the NSF peak channel s Annotation Duration property. To undo this operation, right click the mouse as close as possible to the deleted NSF peak marking and select Artifact Management>Edit NSF peak>undo Delete, or by pressing the D Hotkey again. Page 7 of 16
8 Inserting NSF Peak Markings To insert a NSF peak marking, the cursor must be located on a chart that includes a plot of the NSF peak marking. It is recommended to use the appropriate GSR Artifact Editing layout, which will identify inserted NSF peak markings without the blue outline. Position the cursor as close to the location where the NSF peak marking should be, right click the mouse and select Artifact Management>Edit NSF peak>insert, or press the I Hotkey. A NSF peak marking will be inserted at the nearest peak within 50ms of the time at the cursor. In addition, an annotation will be added to the annotation bar designating the inserted NSF peak marking. To undo this operation, right click the mouse as close as possible to the deleted NSF peak marking and select Artifact Management>Edit NSF peak>undo Insert, or press the I Hotkey. NSF peak insertion uses the same Search Duration and Annotation Duration properties as NSF peak insertion. Un-doing NSF Peak Editing Editing an NSF peak marking does not alter the original NSF peak channel, but rather modifies it in the areas denoted by annotations. To undo multiple edits select a range on the NSF peak channel including the edits to delete and select Artifact Management>Edit NSF peak>undo Insert Annotations, or Artifact Management>Edit NSF peak>undo Delete Annotations, or press the U Hotkey to undo all NSF peak editing within the selected range. Alternatively you may use the Annotation Manager to navigate, sort, select and delete the annotations directly which will return those areas to the original NSF peak channel. Moving and Sizing NSF Peak Edits Sometimes it is desirable to have even more control over where the NSF peak edit is placed. This can be done by moving the Insert or Delete annotation by dragging and releasing the annotation itself on the annotation bar. The annotation duration can be changed in the Annotation Properties window in Duration. The result of the change will visible as you move or size the annotation. Delete edits may delete multiple markings. Insert edits will always insert a single marking at the maximum value within the annotation range. Delete edits always override insert edits. Figure 2. NSF peak editing with one insertion and one deletion. Page 8 of 16
9 3.2. GSR Waveform Interpolation If the GSR signal is too noisy to accurately determine the correct peak markings it may be possible to interpolate over regions to smooth the signal. This may be more efficient than editing individual peaks. Performing GSR Waveform Interpolation GSR waveform interpolation must be performed on any chart containing a plot of the raw GSR channel. This will be located in the data explorer under Raw > GSR > Waveforms. Using the time range and minimum and maximum values selected, the interpolation algorithm will adjust the raw waveform shape. This will be smoothed out in the filtered waveform. Select the region and acceptable range (select the left hand corner, left-click and drag the mouse to the right hand corner and release). Select Artifact Management > Interpolate > Interpolate over region OR Select the region and acceptable range and press the N Hotkey. This will automatically apply an interpolation to GSR values that fall between the selected rectangle. Interpolated areas will be marked by an annotation that appears only on charts containing the Raw GSR waveform channel. See Figure 3 and Figure 4 for a visual demonstration of the interpolation process. Figure 3. Raw GSR waveform before interpolation. Figure 4. Interpolated Raw GSR waveform smoothing out noise in a section to make marking of peaks easier. Page 9 of 16
10 Removing Interpolations Removing Interpolations using the Annotation Manager Interpolations may be removed by deleting the annotation associated with the interpolation in the annotation manager. Note that it is possible to select and delete a group of interpolations. Removing Interpolations using the Context Menu It is possible to right click on a raw GSR waveform interpolation annotation and select Artifact Management > Interpolate > Remove interpolation from the context menu. This will remove the annotation and undo the interpolation, reverting to the original state prior to application of the interpolation. Alternatively, place the crosshair cursor over an interpolation annotation and press the U Hotkey. It is also possible to select a range of data containing at least one interpolation using a rectangle and upon releasing the mouse select Artifact Management > Interpolate > Remove interpolations. This will undo all interpolations in the range Excluding Regions of GSR Data as Artifact If large sections of data are contaminated by significant noise with poor NSF peak identification, these artifacts will significantly bias GSR analyses and must be managed appropriately. Interpolating over large regions will cause unwanted bias and it may not be possible to visually correct NSF peak markings. In this instance, it will be necessary to exclude these regions from any further calculations. Performing Artifact Exclusion To exclude a region as artifact, select a range with the mouse on any chart containing the raw GSR waveform. Upon releasing the mouse a context menu will appear. Select Artifact Management > Exclude > Exclude as artifact to add an annotation and exclude this region from all calculations. Alternatively, you may select the range and press the X Hotkey. Figure 5. A region of GSR waveform data is excluded. Page 10 of 16
11 Removing Artifact Exclusions Removing Artifact Exclusions using the Annotation Manager Exclusions may be removed by deleting the annotation associated with the exclusion in the annotation manager. Please note that it is possible to select and delete a group of exclusions. Removing Artifact Exclusions using the Context Menu It is possible to right click on an artifact exclusion annotation and select Artifact Management > Exclude > Remove exclusion from the context menu. This will remove the annotation and undo the exclusion, reverting to the original state prior to application of the exclusion. Alternatively, place the crosshair cursor over an interpolation annotation and press the U Hotkey. It is also possible to select a range of data containing at least one exclusion using a rectangle and upon releasing the mouse select Artifact Management > Exclude > Remove exclusions. In this way it is possible to undo all exclusions in the range Artifact Thresholds Artifact marking is a complicated and time-intensive process that for now requires human intervention to achieve the best results. In some cases, the signal quality is very poor and either saturates or is below physiologically normal ranges. In these cases, one can set thresholds for automated exclusions to assist with artifact markings. Setting Artifact Thresholds The SCR (EDA) channel is the channel that is used for NSF peak detection. The properties for this channel contains a set of thresholds that can assist with artifact management. See Figure 6. The Threshold Lower Limit indicates the lowest acceptable range that is physiologically appropriate. The default for this is 0.2 µs. Anything below this threshold this will be set to the value in the Lower Value field. NaN (not a number) is used in VivoSense to display a blank and thus exclude or remove the data. Similarly the Threshold Upper Limit is used to set a maximum range useful for efficiently excluding sensor saturations. The defaults are an arbitrary very large number such that this would not have any noticeable effect. Page 11 of 16
12 Figure 6. Properties for the SCR (EDA) channel Artifact Editing Layouts Artifact editing layouts are included in the module to help streamline the artifact management process. VivoSense contains a single basic artifact editing layout. To begin using a layout, open a file with GSR data and then select the GSR Artifact Editing layout from the folder in the Layout Manager. Two charts will be placed on the screen the first shows the desired SCR (EDA) plot and its associated NSF peak markings. The second chart displays the NSF event rate, along with the Trend NSF even rate. See Figure 7. One special plot that shows the original state of the data has been added to the first chart. As edits are made to the NSF peak, the user will be able to visualize exactly what changes have been made and how these affect the data. In the first chart, the original NSF peak markings made by the NSF peak picker are shown as a blue square with a surrounding red box. User inserted markings will just show the blue square and user deleted NSF peaks will just show the red outline. Page 12 of 16
13 Figure 7. GSR Artifact Editing Layout Page 13 of 16
14 4. GSR Data Processing 4.1. Waveform Channels GSR This is a scaled version of the raw GSR waveform channel with units in µs. The raw waveform may be inverted as required depending on the sensor used. SCL This is a filtered version of the GSR waveform. A low pass filter is used to smooth out rapid transients to leave only the slowly changing (tonic) level of the skin conductance. The default filter cut-off frequency is Hz or 18s. This may be changed in the filter settings in the SCL channel properties. SCR This is a filtered version of the GSR waveform. A high pass filter is used to remove the slowly changing portion of the signal to leave only the rapid transients (phasic response). The default filter cut-off frequency is Hz or 18s. This may be changed in the filter settings in the SCL channel properties. SCR (EDA) This is a filtered version of the GSR waveform. A low pass filter is used to smooth out very rapid noisy transients or low amplitude responses. This leaves a smoothed waveform that still displays peaks and nonspecific fluctuations. This waveform is then used to perform the NSF peak detection. The default filter cut-off frequency is 0.2Hz or 5s. This may be changed in the filter settings in the SCL channel properties 4.2. Marker Channels NSF peak These markings note the peaks of detected non-specific skin conductance responses. The channel has several properties that may be changed to modify the detection algorithm. These properties are: Blockout duration: After the occurrence of a peak, it is less likely that another true response peak occurs until the response has settled. This setting determines the minimum time between responses and the default is 6s. Minimum Threshold: This is an important setting which determines the minimum amplitude of a response. The default is 0.05 µs. Increasing this may help in the presence of a noisy signal or if the user only wants to search for responses exceeding a minimum amplitude. Rise time: This setting determines maximum time from the start of a response to the peak. In other words this is the allowable time the signal has to rise over the minimum threshold. Responses are typically sharp and do not rise very slowly. The default is 3s. Page 14 of 16
15 4.3. Measures Channels NSF event rate The NSF event rate is the number of non-specific responses per minute. This is a measure of SNS activity or psychophysiological activation. Page 15 of 16
16 5. GSR Layouts VivoSense includes a GSR Artifact Editing layout in the s > folder. This may be used to assist with visualization and editing of detected NSF peaks, as well as the associated event rate together with a trend of this event rate. Page 16 of 16
Heart Rate Variability Preparing Data for Analysis Using AcqKnowledge
 APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com 01.06.2016 Application Note 233 Heart Rate Variability Preparing Data for Analysis
APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com 01.06.2016 Application Note 233 Heart Rate Variability Preparing Data for Analysis
Pre-Processing of ERP Data. Peter J. Molfese, Ph.D. Yale University
 Pre-Processing of ERP Data Peter J. Molfese, Ph.D. Yale University Before Statistical Analyses, Pre-Process the ERP data Planning Analyses Waveform Tools Types of Tools Filter Segmentation Visual Review
Pre-Processing of ERP Data Peter J. Molfese, Ph.D. Yale University Before Statistical Analyses, Pre-Process the ERP data Planning Analyses Waveform Tools Types of Tools Filter Segmentation Visual Review
Lesson 14 BIOFEEDBACK Relaxation and Arousal
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 14 BIOFEEDBACK Relaxation and Arousal Manual Revision 3.7.3 090308 EDA/GSR Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Indiana University School
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 14 BIOFEEDBACK Relaxation and Arousal Manual Revision 3.7.3 090308 EDA/GSR Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Indiana University School
Common Spatial Patterns 2 class BCI V Copyright 2012 g.tec medical engineering GmbH
 g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Common Spatial Patterns 2 class
g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Common Spatial Patterns 2 class
Common Spatial Patterns 3 class BCI V Copyright 2012 g.tec medical engineering GmbH
 g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Common Spatial Patterns 3 class
g.tec medical engineering GmbH Sierningstrasse 14, A-4521 Schiedlberg Austria - Europe Tel.: (43)-7251-22240-0 Fax: (43)-7251-22240-39 office@gtec.at, http://www.gtec.at Common Spatial Patterns 3 class
Getting Started. Connect green audio output of SpikerBox/SpikerShield using green cable to your headphones input on iphone/ipad.
 Getting Started First thing you should do is to connect your iphone or ipad to SpikerBox with a green smartphone cable. Green cable comes with designators on each end of the cable ( Smartphone and SpikerBox
Getting Started First thing you should do is to connect your iphone or ipad to SpikerBox with a green smartphone cable. Green cable comes with designators on each end of the cable ( Smartphone and SpikerBox
DATA! NOW WHAT? Preparing your ERP data for analysis
 DATA! NOW WHAT? Preparing your ERP data for analysis Dennis L. Molfese, Ph.D. Caitlin M. Hudac, B.A. Developmental Brain Lab University of Nebraska-Lincoln 1 Agenda Pre-processing Preparing for analysis
DATA! NOW WHAT? Preparing your ERP data for analysis Dennis L. Molfese, Ph.D. Caitlin M. Hudac, B.A. Developmental Brain Lab University of Nebraska-Lincoln 1 Agenda Pre-processing Preparing for analysis
Getting started with Spike Recorder on PC/Mac/Linux
 Getting started with Spike Recorder on PC/Mac/Linux You can connect your SpikerBox to your computer using either the blue laptop cable, or the green smartphone cable. How do I connect SpikerBox to computer
Getting started with Spike Recorder on PC/Mac/Linux You can connect your SpikerBox to your computer using either the blue laptop cable, or the green smartphone cable. How do I connect SpikerBox to computer
Lab experience 1: Introduction to LabView
 Lab experience 1: Introduction to LabView LabView is software for the real-time acquisition, processing and visualization of measured data. A LabView program is called a Virtual Instrument (VI) because
Lab experience 1: Introduction to LabView LabView is software for the real-time acquisition, processing and visualization of measured data. A LabView program is called a Virtual Instrument (VI) because
Exercise 1: Muscles in Face used for Smiling and Frowning Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles of the face that work to smile or frown.
 Experiment HP-9: Facial Electromyograms (EMG) and Emotion Exercise 1: Muscles in Face used for Smiling and Frowning Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles of the face that work to smile or frown. Procedure
Experiment HP-9: Facial Electromyograms (EMG) and Emotion Exercise 1: Muscles in Face used for Smiling and Frowning Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles of the face that work to smile or frown. Procedure
A low noise multi electrode array system for in vitro electrophysiology. Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE SU-MED640
 A low noise multi electrode array system for in vitro electrophysiology Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE SU-MED640 Information in this document is subject to change without notice.no part of this document
A low noise multi electrode array system for in vitro electrophysiology Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE SU-MED640 Information in this document is subject to change without notice.no part of this document
Analyzing and Saving a Signal
 Analyzing and Saving a Signal Approximate Time You can complete this exercise in approximately 45 minutes. Background LabVIEW includes a set of Express VIs that help you analyze signals. This chapter teaches
Analyzing and Saving a Signal Approximate Time You can complete this exercise in approximately 45 minutes. Background LabVIEW includes a set of Express VIs that help you analyze signals. This chapter teaches
The Measurement Tools and What They Do
 2 The Measurement Tools The Measurement Tools and What They Do JITTERWIZARD The JitterWizard is a unique capability of the JitterPro package that performs the requisite scope setup chores while simplifying
2 The Measurement Tools The Measurement Tools and What They Do JITTERWIZARD The JitterWizard is a unique capability of the JitterPro package that performs the requisite scope setup chores while simplifying
BitWise (V2.1 and later) includes features for determining AP240 settings and measuring the Single Ion Area.
 BitWise. Instructions for New Features in ToF-AMS DAQ V2.1 Prepared by Joel Kimmel University of Colorado at Boulder & Aerodyne Research Inc. Last Revised 15-Jun-07 BitWise (V2.1 and later) includes features
BitWise. Instructions for New Features in ToF-AMS DAQ V2.1 Prepared by Joel Kimmel University of Colorado at Boulder & Aerodyne Research Inc. Last Revised 15-Jun-07 BitWise (V2.1 and later) includes features
The BAT WAVE ANALYZER project
 The BAT WAVE ANALYZER project Conditions of Use The Bat Wave Analyzer program is free for personal use and can be redistributed provided it is not changed in any way, and no fee is requested. The Bat Wave
The BAT WAVE ANALYZER project Conditions of Use The Bat Wave Analyzer program is free for personal use and can be redistributed provided it is not changed in any way, and no fee is requested. The Bat Wave
Thought Technology Ltd Belgrave Avenue, Montreal, QC H4A 2L8 Canada
 Thought Technology Ltd. 2180 Belgrave Avenue, Montreal, QC H4A 2L8 Canada Tel: (800) 361-3651 ٠ (514) 489-8251 Fax: (514) 489-8255 E-mail: _Hmail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage: _Hhttp://www.thoughttechnology.com
Thought Technology Ltd. 2180 Belgrave Avenue, Montreal, QC H4A 2L8 Canada Tel: (800) 361-3651 ٠ (514) 489-8251 Fax: (514) 489-8255 E-mail: _Hmail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage: _Hhttp://www.thoughttechnology.com
PRODUCT SHEET TRANSDUCER MODULE GSR100C
 TRANSDUCER MODULE GSR100C The GSR100C electrodermal activity amplifier module is a single-channel, high-gain, differential amplifier designed to measure skin conductance via the constant voltage technique.
TRANSDUCER MODULE GSR100C The GSR100C electrodermal activity amplifier module is a single-channel, high-gain, differential amplifier designed to measure skin conductance via the constant voltage technique.
D-Lab & D-Lab Control Plan. Measure. Analyse. User Manual
 D-Lab & D-Lab Control Plan. Measure. Analyse User Manual Valid for D-Lab Versions 2.0 and 2.1 September 2011 Contents Contents 1 Initial Steps... 6 1.1 Scope of Supply... 6 1.1.1 Optional Upgrades... 6
D-Lab & D-Lab Control Plan. Measure. Analyse User Manual Valid for D-Lab Versions 2.0 and 2.1 September 2011 Contents Contents 1 Initial Steps... 6 1.1 Scope of Supply... 6 1.1.1 Optional Upgrades... 6
A Matlab toolbox for. Characterisation Of Recorded Underwater Sound (CHORUS) USER S GUIDE
 Centre for Marine Science and Technology A Matlab toolbox for Characterisation Of Recorded Underwater Sound (CHORUS) USER S GUIDE Version 5.0b Prepared for: Centre for Marine Science and Technology Prepared
Centre for Marine Science and Technology A Matlab toolbox for Characterisation Of Recorded Underwater Sound (CHORUS) USER S GUIDE Version 5.0b Prepared for: Centre for Marine Science and Technology Prepared
Cisco Spectrum Expert Software Overview
 CHAPTER 5 If your computer has an 802.11 interface, it should be enabled in order to detect Wi-Fi devices. If you are connected to an AP or ad-hoc network through the 802.11 interface, you will occasionally
CHAPTER 5 If your computer has an 802.11 interface, it should be enabled in order to detect Wi-Fi devices. If you are connected to an AP or ad-hoc network through the 802.11 interface, you will occasionally
PulseCounter Neutron & Gamma Spectrometry Software Manual
 PulseCounter Neutron & Gamma Spectrometry Software Manual MAXIMUS ENERGY CORPORATION Written by Dr. Max I. Fomitchev-Zamilov Web: maximus.energy TABLE OF CONTENTS 0. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. DEFAULT SCREEN
PulseCounter Neutron & Gamma Spectrometry Software Manual MAXIMUS ENERGY CORPORATION Written by Dr. Max I. Fomitchev-Zamilov Web: maximus.energy TABLE OF CONTENTS 0. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. DEFAULT SCREEN
SedLine Sedation Monitor
 SedLine Sedation Monitor Quick Reference Guide Not intended to replace the Operator s Manual. See the SedLine Sedation Monitor Operator s Manual for complete instructions, including warnings, indications
SedLine Sedation Monitor Quick Reference Guide Not intended to replace the Operator s Manual. See the SedLine Sedation Monitor Operator s Manual for complete instructions, including warnings, indications
Using different reference quantities in ArtemiS SUITE
 06/17 in ArtemiS SUITE ArtemiS SUITE allows you to perform sound analyses versus a number of different reference quantities. Many analyses are calculated and displayed versus time, such as Level vs. Time,
06/17 in ArtemiS SUITE ArtemiS SUITE allows you to perform sound analyses versus a number of different reference quantities. Many analyses are calculated and displayed versus time, such as Level vs. Time,
Spectrum Analyser Basics
 Hands-On Learning Spectrum Analyser Basics Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited Email: phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca June 28, 2014 Introduction Figure 1: GUI Startup Screen In a previous exercise,
Hands-On Learning Spectrum Analyser Basics Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited Email: phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca June 28, 2014 Introduction Figure 1: GUI Startup Screen In a previous exercise,
NOTICE. The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
 NOTICE The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Toontrack Music AB makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the
NOTICE The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Toontrack Music AB makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the
Pre-processing of revolution speed data in ArtemiS SUITE 1
 03/18 in ArtemiS SUITE 1 Introduction 1 TTL logic 2 Sources of error in pulse data acquisition 3 Processing of trigger signals 5 Revolution speed acquisition with complex pulse patterns 7 Introduction
03/18 in ArtemiS SUITE 1 Introduction 1 TTL logic 2 Sources of error in pulse data acquisition 3 Processing of trigger signals 5 Revolution speed acquisition with complex pulse patterns 7 Introduction
Contents. Welcome to LCAST. System Requirements. Compatibility. Installation and Authorization. Loudness Metering. True-Peak Metering
 LCAST User Manual Contents Welcome to LCAST System Requirements Compatibility Installation and Authorization Loudness Metering True-Peak Metering LCAST User Interface Your First Loudness Measurement Presets
LCAST User Manual Contents Welcome to LCAST System Requirements Compatibility Installation and Authorization Loudness Metering True-Peak Metering LCAST User Interface Your First Loudness Measurement Presets
#PS168 - Analysis of Intraventricular Pressure Wave Data (LVP Analysis)
 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #PS168 - Analysis of Intraventricular Pressure Wave Data (LVP Analysis) The Biopac
BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #PS168 - Analysis of Intraventricular Pressure Wave Data (LVP Analysis) The Biopac
MAutoPitch. Presets button. Left arrow button. Right arrow button. Randomize button. Save button. Panic button. Settings button
 MAutoPitch Presets button Presets button shows a window with all available presets. A preset can be loaded from the preset window by double-clicking on it, using the arrow buttons or by using a combination
MAutoPitch Presets button Presets button shows a window with all available presets. A preset can be loaded from the preset window by double-clicking on it, using the arrow buttons or by using a combination
Supplemental Material for Gamma-band Synchronization in the Macaque Hippocampus and Memory Formation
 Supplemental Material for Gamma-band Synchronization in the Macaque Hippocampus and Memory Formation Michael J. Jutras, Pascal Fries, Elizabeth A. Buffalo * *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Supplemental Material for Gamma-band Synchronization in the Macaque Hippocampus and Memory Formation Michael J. Jutras, Pascal Fries, Elizabeth A. Buffalo * *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
PowerMonic. FAQs [2/12]
![PowerMonic. FAQs [2/12] PowerMonic. FAQs [2/12]](/thumbs/86/94869864.jpg) PowerMonic FAQs [2/12] Table of Contents FAQ 1. Why do I need to connect Phase A?... 2 FAQ 2. What is the purpose of the internal battery in a PowerMonic?... 2 FAQ 3. What power does a PowerMonic draw
PowerMonic FAQs [2/12] Table of Contents FAQ 1. Why do I need to connect Phase A?... 2 FAQ 2. What is the purpose of the internal battery in a PowerMonic?... 2 FAQ 3. What power does a PowerMonic draw
NOTICE: This document is for use only at UNSW. No copies can be made of this document without the permission of the authors.
 Brüel & Kjær Pulse Primer University of New South Wales School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering September 2005 Prepared by Michael Skeen and Geoff Lucas NOTICE: This document is for use only
Brüel & Kjær Pulse Primer University of New South Wales School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering September 2005 Prepared by Michael Skeen and Geoff Lucas NOTICE: This document is for use only
Ultra 4K Tool Box. Version Release Note
 Ultra 4K Tool Box Version 2.1.43.0 Release Note This document summarises the enhancements introduced in Version 2.1 of the software for the Omnitek Ultra 4K Tool Box and related products. It also details
Ultra 4K Tool Box Version 2.1.43.0 Release Note This document summarises the enhancements introduced in Version 2.1 of the software for the Omnitek Ultra 4K Tool Box and related products. It also details
USB Mini Spectrum Analyzer User s Guide TSA5G35
 USB Mini Spectrum Analyzer User s Guide TSA5G35 Triarchy Technologies, Corp. Page 1 of 21 USB Mini Spectrum Analyzer User s Guide Copyright Notice Copyright 2011 Triarchy Technologies, Corp. All rights
USB Mini Spectrum Analyzer User s Guide TSA5G35 Triarchy Technologies, Corp. Page 1 of 21 USB Mini Spectrum Analyzer User s Guide Copyright Notice Copyright 2011 Triarchy Technologies, Corp. All rights
PRELIMINARY INFORMATION. Professional Signal Generation and Monitoring Options for RIFEforLIFE Research Equipment
 Integrated Component Options Professional Signal Generation and Monitoring Options for RIFEforLIFE Research Equipment PRELIMINARY INFORMATION SquareGENpro is the latest and most versatile of the frequency
Integrated Component Options Professional Signal Generation and Monitoring Options for RIFEforLIFE Research Equipment PRELIMINARY INFORMATION SquareGENpro is the latest and most versatile of the frequency
Data Acquisition Using LabVIEW
 Experiment-0 Data Acquisition Using LabVIEW Introduction The objectives of this experiment are to become acquainted with using computer-conrolled instrumentation for data acquisition. LabVIEW, a program
Experiment-0 Data Acquisition Using LabVIEW Introduction The objectives of this experiment are to become acquainted with using computer-conrolled instrumentation for data acquisition. LabVIEW, a program
The Syscal family of resistivity meters. Designed for the surveys you do.
 The Syscal family of resistivity meters. Designed for the surveys you do. Resistivity meters may conveniently be broken down into several categories according to their capabilities and applications. The
The Syscal family of resistivity meters. Designed for the surveys you do. Resistivity meters may conveniently be broken down into several categories according to their capabilities and applications. The
Defining and Labeling Circuits and Electrical Phasing in PLS-CADD
 610 N. Whitney Way, Suite 160 Madison, WI 53705 Phone: 608.238.2171 Fax: 608.238.9241 Email:info@powline.com URL: http://www.powline.com Defining and Labeling Circuits and Electrical Phasing in PLS-CADD
610 N. Whitney Way, Suite 160 Madison, WI 53705 Phone: 608.238.2171 Fax: 608.238.9241 Email:info@powline.com URL: http://www.powline.com Defining and Labeling Circuits and Electrical Phasing in PLS-CADD
ME EN 363 ELEMENTARY INSTRUMENTATION Lab: Basic Lab Instruments and Data Acquisition
 ME EN 363 ELEMENTARY INSTRUMENTATION Lab: Basic Lab Instruments and Data Acquisition INTRODUCTION Many sensors produce continuous voltage signals. In this lab, you will learn about some common methods
ME EN 363 ELEMENTARY INSTRUMENTATION Lab: Basic Lab Instruments and Data Acquisition INTRODUCTION Many sensors produce continuous voltage signals. In this lab, you will learn about some common methods
Analysis. mapans MAP ANalysis Single; map viewer, opens and modifies a map file saved by iman.
 Analysis Analysis routines (run on LINUX): iman IMage ANalysis; makes maps out of raw data files saved be the acquisition program (ContImage), can make movies, pictures of green, compresses and decompresses
Analysis Analysis routines (run on LINUX): iman IMage ANalysis; makes maps out of raw data files saved be the acquisition program (ContImage), can make movies, pictures of green, compresses and decompresses
BioGraph Infiniti Physiology Suite
 Thought Technology Ltd. 2180 Belgrave Avenue, Montreal, QC H4A 2L8 Canada Tel: (800) 361-3651 ٠ (514) 489-8251 Fax: (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage: http://www.thoughttechnology.com
Thought Technology Ltd. 2180 Belgrave Avenue, Montreal, QC H4A 2L8 Canada Tel: (800) 361-3651 ٠ (514) 489-8251 Fax: (514) 489-8255 E-mail: mail@thoughttechnology.com Webpage: http://www.thoughttechnology.com
The most sensitive microelectrode array system for in vitro extracellular electrophysiology. Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE MED-A64MD1/MED-A64HE1
 The most sensitive microelectrode array system for in vitro extracellular electrophysiology Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE MED-A64MD1/MED-A64HE1 Information in this document is subject to change without
The most sensitive microelectrode array system for in vitro extracellular electrophysiology Mobius Tutorial AMPLIFIER TYPE MED-A64MD1/MED-A64HE1 Information in this document is subject to change without
SpikePac User s Guide
 SpikePac User s Guide Updated: 7/22/2014 SpikePac User's Guide Copyright 2008-2014 Tucker-Davis Technologies, Inc. (TDT). All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in
SpikePac User s Guide Updated: 7/22/2014 SpikePac User's Guide Copyright 2008-2014 Tucker-Davis Technologies, Inc. (TDT). All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in
The EEGer 4.3 Tutorial
 The EEGer 4.3 Tutorial How to Conduct A Neurofeedback Session 1 Introduction 3 1.1 How To Use This Tutorial............................................................................ 3 1.2 What You Should
The EEGer 4.3 Tutorial How to Conduct A Neurofeedback Session 1 Introduction 3 1.1 How To Use This Tutorial............................................................................ 3 1.2 What You Should
Topic: Instructional David G. Thomas December 23, 2015
 Procedure to Setup a 3ɸ Linear Motor This is a guide to configure a 3ɸ linear motor using either analog or digital encoder feedback with an Elmo Gold Line drive. Topic: Instructional David G. Thomas December
Procedure to Setup a 3ɸ Linear Motor This is a guide to configure a 3ɸ linear motor using either analog or digital encoder feedback with an Elmo Gold Line drive. Topic: Instructional David G. Thomas December
Linrad On-Screen Controls K1JT
 Linrad On-Screen Controls K1JT Main (Startup) Menu A = Weak signal CW B = Normal CW C = Meteor scatter CW D = SSB E = FM F = AM G = QRSS CW H = TX test I = Soundcard test mode J = Analog hardware tune
Linrad On-Screen Controls K1JT Main (Startup) Menu A = Weak signal CW B = Normal CW C = Meteor scatter CW D = SSB E = FM F = AM G = QRSS CW H = TX test I = Soundcard test mode J = Analog hardware tune
HBI Database. Version 2 (User Manual)
 HBI Database Version 2 (User Manual) St-Petersburg, Russia 2007 2 1. INTRODUCTION...3 2. RECORDING CONDITIONS...6 2.1. EYE OPENED AND EYE CLOSED CONDITION....6 2.2. VISUAL CONTINUOUS PERFORMANCE TASK...6
HBI Database Version 2 (User Manual) St-Petersburg, Russia 2007 2 1. INTRODUCTION...3 2. RECORDING CONDITIONS...6 2.1. EYE OPENED AND EYE CLOSED CONDITION....6 2.2. VISUAL CONTINUOUS PERFORMANCE TASK...6
ISCEV SINGLE CHANNEL ERG PROTOCOL DESIGN
 ISCEV SINGLE CHANNEL ERG PROTOCOL DESIGN This spreadsheet has been created to help design a protocol before actually entering the parameters into the Espion software. It details all the protocol parameters
ISCEV SINGLE CHANNEL ERG PROTOCOL DESIGN This spreadsheet has been created to help design a protocol before actually entering the parameters into the Espion software. It details all the protocol parameters
Please feel free to download the Demo application software from analogarts.com to help you follow this seminar.
 Hello, welcome to Analog Arts spectrum analyzer tutorial. Please feel free to download the Demo application software from analogarts.com to help you follow this seminar. For this presentation, we use a
Hello, welcome to Analog Arts spectrum analyzer tutorial. Please feel free to download the Demo application software from analogarts.com to help you follow this seminar. For this presentation, we use a
Multiwell-MEA-System
 NEW 1152 Electrodes Multiwell-MEA-System High throughput electrophysiology 24- and 96-well plates with up to 1152 electrodes Up to 50 khz sampling rate Integrated stimulator Different well plate variants
NEW 1152 Electrodes Multiwell-MEA-System High throughput electrophysiology 24- and 96-well plates with up to 1152 electrodes Up to 50 khz sampling rate Integrated stimulator Different well plate variants
Full Disclosure Monitoring
 Full Disclosure Monitoring Power Quality Application Note Full Disclosure monitoring is the ability to measure all aspects of power quality, on every voltage cycle, and record them in appropriate detail
Full Disclosure Monitoring Power Quality Application Note Full Disclosure monitoring is the ability to measure all aspects of power quality, on every voltage cycle, and record them in appropriate detail
Analysis of AP/axon classes and PSP on the basis of AP amplitude
 Analysis of AP/axon classes and PSP on the basis of AP amplitude In this analysis manual, we aim to measure and analyze AP amplitudes recorded with a suction electrode and synaptic potentials recorded
Analysis of AP/axon classes and PSP on the basis of AP amplitude In this analysis manual, we aim to measure and analyze AP amplitudes recorded with a suction electrode and synaptic potentials recorded
Experiment PP-1: Electroencephalogram (EEG) Activity
 Experiment PP-1: Electroencephalogram (EEG) Activity Exercise 1: Common EEG Artifacts Aim: To learn how to record an EEG and to become familiar with identifying EEG artifacts, especially those related
Experiment PP-1: Electroencephalogram (EEG) Activity Exercise 1: Common EEG Artifacts Aim: To learn how to record an EEG and to become familiar with identifying EEG artifacts, especially those related
STB Front Panel User s Guide
 S ET-TOP BOX FRONT PANEL USER S GUIDE 1. Introduction The Set-Top Box (STB) Front Panel has the following demonstration capabilities: Pressing 1 of the 8 capacitive sensing pads lights up that pad s corresponding
S ET-TOP BOX FRONT PANEL USER S GUIDE 1. Introduction The Set-Top Box (STB) Front Panel has the following demonstration capabilities: Pressing 1 of the 8 capacitive sensing pads lights up that pad s corresponding
Working with a Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope EE 310: ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN I
 Working with a Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope EE 310: ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN I Prepared by: Kyle Botteon Questions? kyle.botteon@psu.edu 2 Background Information Recall that oscilloscopes (scopes)
Working with a Tektronix TDS 3012B Oscilloscope EE 310: ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN I Prepared by: Kyle Botteon Questions? kyle.botteon@psu.edu 2 Background Information Recall that oscilloscopes (scopes)
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-13: Crayfish Motor Nerve
 Experiment AN-13: Crayfish Motor Nerve Background The purpose of this experiment is to record the extracellular action potentials of crayfish motor axons. These spontaneously generated action potentials
Experiment AN-13: Crayfish Motor Nerve Background The purpose of this experiment is to record the extracellular action potentials of crayfish motor axons. These spontaneously generated action potentials
Contents DIVISION OF LIBRARY SERVICES. EndNote X7 Mac User Manual Part 2
 DIVISION OF LIBRARY SERVICES EndNote X7 Mac User Manual Part 2 Contents Using EndNote with Word (Cite While You Write)... 2 Inserting Citations into the Text... 2 Removing Citations Very Important!...
DIVISION OF LIBRARY SERVICES EndNote X7 Mac User Manual Part 2 Contents Using EndNote with Word (Cite While You Write)... 2 Inserting Citations into the Text... 2 Removing Citations Very Important!...
Word Tutorial 2: Editing and Formatting a Document
 Word Tutorial 2: Editing and Formatting a Document Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Create bulleted and numbered lists Move text within a document Find and replace text Check spelling and grammar Format
Word Tutorial 2: Editing and Formatting a Document Microsoft Office 2010 Objectives Create bulleted and numbered lists Move text within a document Find and replace text Check spelling and grammar Format
Virtual instruments and introduction to LabView
 Introduction Virtual instruments and introduction to LabView (BME-MIT, updated: 26/08/2014 Tamás Krébesz krebesz@mit.bme.hu) The purpose of the measurement is to present and apply the concept of virtual
Introduction Virtual instruments and introduction to LabView (BME-MIT, updated: 26/08/2014 Tamás Krébesz krebesz@mit.bme.hu) The purpose of the measurement is to present and apply the concept of virtual
Introduction To LabVIEW and the DSP Board
 EE-289, DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LAB November 2005 Introduction To LabVIEW and the DSP Board 1 Overview The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with the DSP development system by looking at sampling,
EE-289, DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LAB November 2005 Introduction To LabVIEW and the DSP Board 1 Overview The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with the DSP development system by looking at sampling,
LA xlimit. Manual. by tb-software (C) tb-software 2015 Page 1 of 6
 LA xlimit Manual by tb-software 2015 (C) tb-software 2015 Page 1 of 6 1 Introduction Welcome to LA xlimit, a look ahead, wideband linked-stereo limiter including ISP (inter sample peak) detection and oversampling.
LA xlimit Manual by tb-software 2015 (C) tb-software 2015 Page 1 of 6 1 Introduction Welcome to LA xlimit, a look ahead, wideband linked-stereo limiter including ISP (inter sample peak) detection and oversampling.
Scout 2.0 Software. Introductory Training
 Scout 2.0 Software Introductory Training Welcome! In this training we will cover: How to analyze scwest chip images in Scout Opening images Detecting peaks Eliminating noise peaks Labeling your peaks of
Scout 2.0 Software Introductory Training Welcome! In this training we will cover: How to analyze scwest chip images in Scout Opening images Detecting peaks Eliminating noise peaks Labeling your peaks of
SIDRA INTERSECTION 8.0 UPDATE HISTORY
 Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd PO Box 1075G, Greythorn, Vic 3104 AUSTRALIA ABN 79 088 889 687 For all technical support, sales support and general enquiries: support.sidrasolutions.com SIDRA INTERSECTION
Akcelik & Associates Pty Ltd PO Box 1075G, Greythorn, Vic 3104 AUSTRALIA ABN 79 088 889 687 For all technical support, sales support and general enquiries: support.sidrasolutions.com SIDRA INTERSECTION
SEM- EDS Instruction Manual
 SEM- EDS Instruction Manual Double-click on the Spirit icon ( ) on the desktop to start the software program. I. X-ray Functions Access the basic X-ray acquisition, display and analysis functions through
SEM- EDS Instruction Manual Double-click on the Spirit icon ( ) on the desktop to start the software program. I. X-ray Functions Access the basic X-ray acquisition, display and analysis functions through
Artifact rejection and running ICA
 Artifact rejection and running ICA Task 1 Reject noisy data Task 2 Run ICA Task 3 Plot components Task 4 Remove components (i.e. back-projection) Exercise... Artifact rejection and running ICA Task 1 Reject
Artifact rejection and running ICA Task 1 Reject noisy data Task 2 Run ICA Task 3 Plot components Task 4 Remove components (i.e. back-projection) Exercise... Artifact rejection and running ICA Task 1 Reject
Exercise #1: Create and Revise a Smart Group
 EndNote X7 Advanced: Hands-On for CDPH Sheldon Margen Public Health Library, UC Berkeley Exercise #1: Create and Revise a Smart Group Objective: Learn how to create and revise Smart Groups to automate
EndNote X7 Advanced: Hands-On for CDPH Sheldon Margen Public Health Library, UC Berkeley Exercise #1: Create and Revise a Smart Group Objective: Learn how to create and revise Smart Groups to automate
PYROPTIX TM IMAGE PROCESSING SOFTWARE
 Innovative Technologies for Maximum Efficiency PYROPTIX TM IMAGE PROCESSING SOFTWARE V1.0 SOFTWARE GUIDE 2017 Enertechnix Inc. PyrOptix Image Processing Software v1.0 Section Index 1. Software Overview...
Innovative Technologies for Maximum Efficiency PYROPTIX TM IMAGE PROCESSING SOFTWARE V1.0 SOFTWARE GUIDE 2017 Enertechnix Inc. PyrOptix Image Processing Software v1.0 Section Index 1. Software Overview...
Tutorial 3 Normalize step-cycles, average waveform amplitude and the Layout program
 Tutorial 3 Normalize step-cycles, average waveform amplitude and the Layout program Step cycles are defined usually by choosing a recorded ENG waveform that shows long lasting, continuos, consistently
Tutorial 3 Normalize step-cycles, average waveform amplitude and the Layout program Step cycles are defined usually by choosing a recorded ENG waveform that shows long lasting, continuos, consistently
Transmitter Interface Program
 Transmitter Interface Program Operational Manual Version 3.0.4 1 Overview The transmitter interface software allows you to adjust configuration settings of your Max solid state transmitters. The following
Transmitter Interface Program Operational Manual Version 3.0.4 1 Overview The transmitter interface software allows you to adjust configuration settings of your Max solid state transmitters. The following
Matching Components (minidsp_a) Description. 4x Decimation (Stereo) 4x Decimation (Mono) MonoDec4xIn. 2x Decimation (Stereo) 2x Decimation (Mono)
 Interpolator Overview The first component of any process flow is the Framework. After that the user may determine that interpolation and/or decimation filters are required in their design. The following
Interpolator Overview The first component of any process flow is the Framework. After that the user may determine that interpolation and/or decimation filters are required in their design. The following
Eventide Inc. One Alsan Way Little Ferry, NJ
 Copyright 2015, Eventide Inc. P/N: 141257, Rev 2 Eventide is a registered trademark of Eventide Inc. AAX and Pro Tools are trademarks of Avid Technology. Names and logos are used with permission. Audio
Copyright 2015, Eventide Inc. P/N: 141257, Rev 2 Eventide is a registered trademark of Eventide Inc. AAX and Pro Tools are trademarks of Avid Technology. Names and logos are used with permission. Audio
Application Note AN-708 Vibration Measurements with the Vibration Synchronization Module
 Application Note AN-708 Vibration Measurements with the Vibration Synchronization Module Introduction The vibration module allows complete analysis of cyclical events using low-speed cameras. This is accomplished
Application Note AN-708 Vibration Measurements with the Vibration Synchronization Module Introduction The vibration module allows complete analysis of cyclical events using low-speed cameras. This is accomplished
Getting Started with the LabVIEW Sound and Vibration Toolkit
 1 Getting Started with the LabVIEW Sound and Vibration Toolkit This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of the sound and vibration analysis capabilities in the industry-leading software tool
1 Getting Started with the LabVIEW Sound and Vibration Toolkit This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of the sound and vibration analysis capabilities in the industry-leading software tool
HST Neural Coding and Perception of Sound. Spring Cochlear Nucleus Unit Classification from Spike Trains. M.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.723: Neural Coding and Perception of Sound Instructor: Bertrand Delgutte HST.723 - Neural Coding and Perception of Sound Spring 2004 Cochlear
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.723: Neural Coding and Perception of Sound Instructor: Bertrand Delgutte HST.723 - Neural Coding and Perception of Sound Spring 2004 Cochlear
NanoGiant Oscilloscope/Function-Generator Program. Getting Started
 Getting Started Page 1 of 17 NanoGiant Oscilloscope/Function-Generator Program Getting Started This NanoGiant Oscilloscope program gives you a small impression of the capabilities of the NanoGiant multi-purpose
Getting Started Page 1 of 17 NanoGiant Oscilloscope/Function-Generator Program Getting Started This NanoGiant Oscilloscope program gives you a small impression of the capabilities of the NanoGiant multi-purpose
User s Manual. Log Scale (/LG) GX10/GX20/GP10/GP20/GM10 IM 04L51B01-06EN. 3rd Edition
 User s Manual Model GX10/GX20/GP10/GP20/GM10 Log Scale (/LG) 3rd Edition Introduction Thank you for purchasing the SMARTDAC+ Series GX10/GX20/GP10/GP20/GM10 (hereafter referred to as the recorder, GX,
User s Manual Model GX10/GX20/GP10/GP20/GM10 Log Scale (/LG) 3rd Edition Introduction Thank you for purchasing the SMARTDAC+ Series GX10/GX20/GP10/GP20/GM10 (hereafter referred to as the recorder, GX,
MindMouse. This project is written in C++ and uses the following Libraries: LibSvm, kissfft, BOOST File System, and Emotiv Research Edition SDK.
 Andrew Robbins MindMouse Project Description: MindMouse is an application that interfaces the user s mind with the computer s mouse functionality. The hardware that is required for MindMouse is the Emotiv
Andrew Robbins MindMouse Project Description: MindMouse is an application that interfaces the user s mind with the computer s mouse functionality. The hardware that is required for MindMouse is the Emotiv
Appendix D. UW DigiScope User s Manual. Willis J. Tompkins and Annie Foong
 Appendix D UW DigiScope User s Manual Willis J. Tompkins and Annie Foong UW DigiScope is a program that gives the user a range of basic functions typical of a digital oscilloscope. Included are such features
Appendix D UW DigiScope User s Manual Willis J. Tompkins and Annie Foong UW DigiScope is a program that gives the user a range of basic functions typical of a digital oscilloscope. Included are such features
... read The Art of Tap Tuning by Roger H. Siminoff (Hal Leonard Publishing).
 ... PO Box 2992 Atascadero, CA 93423 USA siminoff@siminoff.net www.siminoff.net 805.365.7111 Instruction Manual and Set-up Strobosoft v2.0 for tap tuning Rev: 11/25 /13 Pt# n/a StroboSoft is a software
... PO Box 2992 Atascadero, CA 93423 USA siminoff@siminoff.net www.siminoff.net 805.365.7111 Instruction Manual and Set-up Strobosoft v2.0 for tap tuning Rev: 11/25 /13 Pt# n/a StroboSoft is a software
EndNote X6 Workshop Michigan State University Libraries
 EndNote X6 Workshop Michigan State University Libraries http://libguides.lib.msu.edu/endnote/ endnote@mail.lib.msu.edu Contents What is EndNote?... 2 Building an EndNote Library... 2 Starting EndNote...
EndNote X6 Workshop Michigan State University Libraries http://libguides.lib.msu.edu/endnote/ endnote@mail.lib.msu.edu Contents What is EndNote?... 2 Building an EndNote Library... 2 Starting EndNote...
System Requirements SA0314 Spectrum analyzer:
 System Requirements SA0314 Spectrum analyzer: System requirements Windows XP, 7, Vista or 8: 1 GHz or faster 32-bit or 64-bit processor 1 GB RAM 10 MB hard disk space \ 1. Getting Started Insert DVD into
System Requirements SA0314 Spectrum analyzer: System requirements Windows XP, 7, Vista or 8: 1 GHz or faster 32-bit or 64-bit processor 1 GB RAM 10 MB hard disk space \ 1. Getting Started Insert DVD into
Laser Beam Analyser Laser Diagnos c System. If you can measure it, you can control it!
 Laser Beam Analyser Laser Diagnos c System If you can measure it, you can control it! Introduc on to Laser Beam Analysis In industrial -, medical - and laboratory applications using CO 2 and YAG lasers,
Laser Beam Analyser Laser Diagnos c System If you can measure it, you can control it! Introduc on to Laser Beam Analysis In industrial -, medical - and laboratory applications using CO 2 and YAG lasers,
Performing a Sound Level Measurement
 APPENDIX 9 Performing a Sound Level Measurement Due to the many features of the System 824 and the variety of measurements it is capable of performing, there is a great deal of instructive material in
APPENDIX 9 Performing a Sound Level Measurement Due to the many features of the System 824 and the variety of measurements it is capable of performing, there is a great deal of instructive material in
Analyze Frequency Response (Bode Plots) with R&S Oscilloscopes Application Note
 Analyze Frequency Response (Bode Plots) with R&S Oscilloscopes Application Note Products: R&S RTO2002 R&S RTO2004 R&S RTO2012 R&S RTO2014 R&S RTO2022 R&S RTO2024 R&S RTO2044 R&S RTO2064 This application
Analyze Frequency Response (Bode Plots) with R&S Oscilloscopes Application Note Products: R&S RTO2002 R&S RTO2004 R&S RTO2012 R&S RTO2014 R&S RTO2022 R&S RTO2024 R&S RTO2044 R&S RTO2064 This application
Quick reference guide
 Quick reference guide Manufactured by: Esaote Europe B.V. Philipsweg 1 6227 AJ Maastricht The Netherlands Tel. +31 (43) 382 4600 Fax +31 (43) 382 4601 Internet: www.esaote.com Email: international.sales@esaote.com
Quick reference guide Manufactured by: Esaote Europe B.V. Philipsweg 1 6227 AJ Maastricht The Netherlands Tel. +31 (43) 382 4600 Fax +31 (43) 382 4601 Internet: www.esaote.com Email: international.sales@esaote.com
MIE 402: WORKSHOP ON DATA ACQUISITION AND SIGNAL PROCESSING Spring 2003
 MIE 402: WORKSHOP ON DATA ACQUISITION AND SIGNAL PROCESSING Spring 2003 OBJECTIVE To become familiar with state-of-the-art digital data acquisition hardware and software. To explore common data acquisition
MIE 402: WORKSHOP ON DATA ACQUISITION AND SIGNAL PROCESSING Spring 2003 OBJECTIVE To become familiar with state-of-the-art digital data acquisition hardware and software. To explore common data acquisition
Background. About automation subtracks
 16 Background Cubase provides very comprehensive automation features. Virtually every mixer and effect parameter can be automated. There are two main methods you can use to automate parameter settings:
16 Background Cubase provides very comprehensive automation features. Virtually every mixer and effect parameter can be automated. There are two main methods you can use to automate parameter settings:
COMPARED IMPROVEMENT BY TIME, SPACE AND FREQUENCY DATA PROCESSING OF THE PERFORMANCES OF IR CAMERAS. APPLICATION TO ELECTROMAGNETISM
 COMPARED IMPROVEMENT BY TIME, SPACE AND FREQUENCY DATA PROCESSING OF THE PERFORMANCES OF IR CAMERAS. APPLICATION TO ELECTROMAGNETISM P. Levesque 1, P.Brémond 2, J.-L. Lasserre 3, A. Paupert 2, D. L. Balageas
COMPARED IMPROVEMENT BY TIME, SPACE AND FREQUENCY DATA PROCESSING OF THE PERFORMANCES OF IR CAMERAS. APPLICATION TO ELECTROMAGNETISM P. Levesque 1, P.Brémond 2, J.-L. Lasserre 3, A. Paupert 2, D. L. Balageas
Torsional vibration analysis in ArtemiS SUITE 1
 02/18 in ArtemiS SUITE 1 Introduction 1 Revolution speed information as a separate analog channel 1 Revolution speed information as a digital pulse channel 2 Proceeding and general notes 3 Application
02/18 in ArtemiS SUITE 1 Introduction 1 Revolution speed information as a separate analog channel 1 Revolution speed information as a digital pulse channel 2 Proceeding and general notes 3 Application
Guide to Analysing Full Spectrum/Frequency Division Bat Calls with Audacity (v.2.0.5) by Thomas Foxley
 Guide to Analysing Full Spectrum/Frequency Division Bat Calls with Audacity (v.2.0.5) by Thomas Foxley Contents Getting Started Setting Up the Sound File Noise Removal Finding All the Bat Calls Call Analysis
Guide to Analysing Full Spectrum/Frequency Division Bat Calls with Audacity (v.2.0.5) by Thomas Foxley Contents Getting Started Setting Up the Sound File Noise Removal Finding All the Bat Calls Call Analysis
Field Test 2. Installation and operation manual OPDAQ Installation and operation manual
 Field Test 2 Installation and operation manual OPDAQ 17.08.25 Installation and operation manual January 2016 How to get copies of OpDAQ technical publications: 53, St-Germain Ouest Rimouski, Québec Canada
Field Test 2 Installation and operation manual OPDAQ 17.08.25 Installation and operation manual January 2016 How to get copies of OpDAQ technical publications: 53, St-Germain Ouest Rimouski, Québec Canada
A New "Duration-Adapted TR" Waveform Capture Method Eliminates Severe Limitations
 31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.3.B.4 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17567 A New "Duration-Adapted TR" Waveform Capture Method Eliminates
31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.3.B.4 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17567 A New "Duration-Adapted TR" Waveform Capture Method Eliminates
Lab 1 Introduction to the Software Development Environment and Signal Sampling
 ECEn 487 Digital Signal Processing Laboratory Lab 1 Introduction to the Software Development Environment and Signal Sampling Due Dates This is a three week lab. All TA check off must be completed before
ECEn 487 Digital Signal Processing Laboratory Lab 1 Introduction to the Software Development Environment and Signal Sampling Due Dates This is a three week lab. All TA check off must be completed before
CAEN Tools for Discovery
 Viareggio March 28, 2011 Introduction: what is the SiPM? The Silicon PhotoMultiplier (SiPM) consists of a high density (up to ~10 3 /mm 2 ) matrix of diodes connected in parallel on a common Si substrate.
Viareggio March 28, 2011 Introduction: what is the SiPM? The Silicon PhotoMultiplier (SiPM) consists of a high density (up to ~10 3 /mm 2 ) matrix of diodes connected in parallel on a common Si substrate.
G4500. Portable Power Quality Analyser. Energy Efficiency through power quality
 G4500 Portable Power Quality Analyser Energy Efficiency through power quality The BlackBox portable series power quality analyser takes power quality monitoring to a whole new level by using the revolutionary
G4500 Portable Power Quality Analyser Energy Efficiency through power quality The BlackBox portable series power quality analyser takes power quality monitoring to a whole new level by using the revolutionary
Why We Measure Loudness
 Menu Why We Measure Loudness Measuring loudness is key to keeping an audience tuned to your channel. Image: digital.eca.ed.ac.uk It is all very well being able to quantify the volume of a signal, however,
Menu Why We Measure Loudness Measuring loudness is key to keeping an audience tuned to your channel. Image: digital.eca.ed.ac.uk It is all very well being able to quantify the volume of a signal, however,
RG NDT INTERNATIONAL INC
 RG NDT INTERNATIONAL INC User Manual 165 Oates Road Houston, Texas 77013 Phone: 713-673-5928 Fax: 713-673-5957 GENERAL OVERVIEW Features two (2) inline inspection stations for the detection of: 1. Transverse
RG NDT INTERNATIONAL INC User Manual 165 Oates Road Houston, Texas 77013 Phone: 713-673-5928 Fax: 713-673-5957 GENERAL OVERVIEW Features two (2) inline inspection stations for the detection of: 1. Transverse
EDL8 Race Dash Manual Engine Management Systems
 Engine Management Systems EDL8 Race Dash Manual Engine Management Systems Page 1 EDL8 Race Dash Page 2 EMS Computers Pty Ltd Unit 9 / 171 Power St Glendenning NSW, 2761 Australia Phone.: +612 9675 1414
Engine Management Systems EDL8 Race Dash Manual Engine Management Systems Page 1 EDL8 Race Dash Page 2 EMS Computers Pty Ltd Unit 9 / 171 Power St Glendenning NSW, 2761 Australia Phone.: +612 9675 1414
Oscilloscope Guide Tektronix TDS3034B & TDS3052B
 Tektronix TDS3034B & TDS3052B Version 2008-Jan-1 Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Portland State University Copyright 2008 Portland State University 1 Basic Information This guide provides basic
Tektronix TDS3034B & TDS3052B Version 2008-Jan-1 Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Portland State University Copyright 2008 Portland State University 1 Basic Information This guide provides basic
TASTEPROBE Type DTP-1. Pre-amplifier for recording from contact chemosensilla INSTRUCTIONS
 TASTEPROBE Type DTP-1 Pre-amplifier for recording from contact chemosensilla INSTRUCTIONS SYNTECH 2002 Hilversum, The Netherlands Reproduction of text and/or drawings is permitted for personal use. The
TASTEPROBE Type DTP-1 Pre-amplifier for recording from contact chemosensilla INSTRUCTIONS SYNTECH 2002 Hilversum, The Netherlands Reproduction of text and/or drawings is permitted for personal use. The
