(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
|
|
|
- Vanessa Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT AND SYSTEM THEREOF (75) Inventors: Young-sang Kim, Suwon-si (KR); Bong-geun Lee, Suwon-si (KR) Correspondence Address: SUGHRUE MION, PLLC 2100 PENNSYLVANIAAVENUE, N.W. SUTE 800 WASHINGTON, DC (US) (73) Assignee: SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. (21) Appl. No.: 11/185,840 (22) Filed: Jul. 21, 2005 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jul. 22, 2004 (KR) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H04L 12/26 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /252 (57) ABSTRACT A frame transmission method performed by a transmitting end in a Video reproduction System having the transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a video signal. The transmitting end receives information about a State of a wireless environment from the receiving end, determines the frames to be trans mitted to the receiving end in consideration of the received information about the wireless environment State, and trans mits the determined frames to the receiving end. The receiv ing end measures the State of the wireless environment by judging whether an error exists in the received frames and transmits the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end. Accordingly, different frames can be transmitted according to the State of the wireless environ ment. S200 RECEIVE FRAMES S2O2 S204 MEASURE STATE OF WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT USING RECEIVED FRAMES TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT MEASURED STATE OF WIRELESS S2O6 ENVR ONMENT l
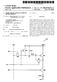
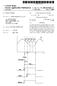
2 Patent Application Publication Feb. 16, 2006 Sheet 1 of 4 US 2006/ A1 FIG m o m m o o m - MPEG DECODER L. MPEG PENCODER WRELESS SWITCH HTRANSMISSION TUNER s MODULE r - 1 O O CONTROL UNIT O -- m o rr o om WRELESS RECEPTION 128 MODULE CONTROL UNIT L O a r r O
3 Patent Application Publication Feb. 16, 2006 Sheet 2 of 4 US 2006/ A1 FIG 2 S200 RECEIVE FRAMES S2O2 S2O4 MEASURE STATE OF WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT USING RECEIVED FRAMES TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT MEASURED STATE OF WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT S2O6 END )
4 Patent Application Publication Feb. 16, 2006 Sheet 3 of 4 US 2006/ A1 FIG 3 S300 RECEIVE INFORMATION ABOUT STATE OF WRELESS ENVIRONMENT S302 S304 GENERATE FRAMES S S310 STATE OF WIRELESSNY ENVIRONMENT 0092 s S306- ESESONN"f S314 S308 STATE OF WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT TRANSMIT GENERATED FRAMES TRANSMIT RECEIVED FRAME
5 Patent Application Publication Feb. 16, 2006 Sheet 4 of 4 FIG 4 US 2006/ A1 S400 S402 RECEIVE FRAMES - H MEASURE STATE OF WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT USING RECEIVED FRAMES S404 PRESENT STATE OF WRELESS ENVIRONMEN BETTER THAN PREVIOUS NS: OF WESS-1 NNIRONMEJ Ne REQUEST TRANSMISSION OF FRAMES HAVING A HIGHER LEVEL THAN THAT OF PREVIOUS FRAMES
6 US 2006/ A1 Feb. 16, 2006 FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT AND SYSTEM THEREOF 0001) This application claims benefit under 35 U.S.C. S 119 from Korean Patent Application No , filed on Jul. 22, 2004, the entire content of which is incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002) 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a video reproduc tion System for wirelessly transmitting transport Streams composed of frames. More particularly, the present inven tion relates to a frame transmission method in a wireless environment and a video reproduction System thereof that can transmit different transport Streams according to the State of the wireless environment Description of the Related Art 0005 IEEE a describes a scheme for a transmit ting-end's wireless transmission of transport Streams to a receiving end, and particularly, it describes a method of transmitting a GOP (group of pictures) that constitutes a Video signal. Generally, the GOP means a Set of an inter coded frame (I-frame), a predictive-coded frame (P-frame) and a bidirectionally predictive-coded frame (B-frame). Hereinafter, the I-frame, P-frame and B-frame will be explained in more detail AS described above, according to the MPEG stan dard for the compression coding of a digital Video signal, three types of frames, i.e., an I-frame, P-frame and B-frame, are considered. Particularly, the I-frame and B-frame have a high compression ratio by performing a motion-compensat ing prediction I-frame is coded without reference to other frames. The P-frame is coded with reference to the previous I-frame or P-frame. Since Successive frames of a digital Video signal have a high redundancy of color information, an effective compression coding of the digital Video signal can be achieved by performing the motion information estimation and motion compensation prediction between the previous I-frame or P-frame and the present P-frame and then coding predicted errors and motion information The B-frame has the highest compression ratio, and the prediction thereof is performed with reference to the following I-frame or P-frame in addition to the previous I-frame or P-frame. The B-frame uses the motion compen sation prediction in the same manner as the P-frame However, in coding the B-frame, two reference frames are used and a Superior prediction performance is Selected between the predictive performances obtained by the two reference frames, So that the B-frame has the highest compression ratio. Meanwhile, this B-frame is not used as the reference frame for other frames. I-picture and P-picture are called the reference frames Generally, a transmitting end of a video reproduc tion system transmits the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame to a receiving end thereof So that the receiving end can reproduce the corresponding video signal. The receiving end can receive all the frames transmitted from the transmitting end if the wireless environment is good. However, if the wireless environment is poor, the receiving end cannot normally receive the frames transmitted from the transmitting end. If the frames are not normally received, the receiving end cannot reproduce the Video signal. That is, a Scheme for normally reproducing a video Signal even if a signal inter ference or overload occurs due to a poor wireless environ ment is required. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been developed in order to Solve the above drawbacks and other problems associated with the conventional arrangement. An aspect of the present invention is to provide a Video reproduction System and method that can normally reproduce a Video signal even in a poor wireless environment Another aspect of the present invention is to pro vide a Video reproduction System and method that can adjust the amount of transmitted data according to the State of a wireless environment The foregoing and other objects and advantages are Substantially realized by providing a frame transmission method performed by a transmitting end in a Video repro duction System having the transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproduc ing a Video signal, according to the present invention, which comprises the Steps of receiving information about a State of a wireless environment from the receiving end, determining the frames to be transmitted to the receiving end in consid eration of the received information about the wireless envi ronment State, and transmitting the determined frames to the receiving end In another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a video reproduction method performed by a receiving end using received frames in a Video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting the frames and the receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a Video Signal, which comprises the Steps of receiving the frames from the transmitting end, measuring a State of a wireless environment by judging whether an error exists in the received frames and reproducing the Video signal using the received frames, and transmitting the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end In still another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a Video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a Video signal, which comprises a control unit for determining the frames to be transmitted to the receiving end in consideration of infor mation about a State of a wireless environment from the receiving end, an encoder for generating the frames to be transmitted in accordance with a control command from the control unit, and a wireless transmission module for wire lessly transmitting the generated frames In still another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a Video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a Video signal, which
7 US 2006/ A1 Feb. 16, 2006 comprises a wireless reception module for receiving the frames from the transmitting end, a wireless environment measurement unit for measuring a State of a wireless envi ronment by judging whether an error exists in the received frames, a decoder for reproducing the Video signal using the received frames, and a control unit for transmitting the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmit ting end. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above aspects and features of the present invention will be more apparent by describing certain embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a view illustrating the construction of transmitting/receiving ends in a Video reproduction System according to the present invention; FIG. 2 is a view illustrating the operation per formed by a receiving end in a video reproduction System according to the present invention; 0020 FIG. 3 is a view illustrating the operation per formed by a transmitting end in a Video reproduction System according to the present invention; and 0021 FIG. 4 is a view illustrating the operation per formed by a receiving end in a video reproduction System according to the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Certain embodiments of the present invention will be described in greater detail with reference to the accom panying drawings In the following description, same drawing refer ence numerals are used for the same elements even in different drawings. The matters defined in the description Such as in the detailed construction and elements are nothing but the ones provided to assist in a comprehensive under Standing of the invention. Thus, it is apparent that the present invention may be carried out without those defined matters. Also, well-known functions or constructions are not described in detail since they would obscure the invention in unnecessary detail The present invention proposes a scheme for trans mitting different transport Streams according to the State of a wireless environment. According to the present invention, in a good wireless environment, an I-frame, B-frame and P-frame are transmitted, while in a poor wireless environ ment, only the I-frame is transmitted. Additionally, either the B-frame or P-frame may be transmitted along with the I-frame according to the State of the wireless environment FIG. 1 is a view illustrating the construction of transmitting/receiving ends in a Video reproduction System according to the present invention Referring to FIG. 1, a transmitting end 100 includes a tuner 110, an MPEG decoder 112, an MPEG encoder 114, a Switch 116, a wireless transmission module 118 and a control unit 119. A receiving end 120 includes a wireless reception module 122, an MPEG decoder 124 and a control unit 126. Additionally, the Video preproduction System further includes a display unit 128 for reproducing and displaying a video signal received by the receiving end The transmitting/receiving ends of the video repro duction System may include other constituent elements in addition to the above-described constituent elements, but explanation will be made with respect to the above-de Scribed constituent elements only for convenience in expla nation The tuner 110, which is used in an input unit of a wireless receiving device, Selects and extracts a Specified radio wave (or an electric signal) by tuning the frequency of the specified radio wave (or electric Signal). In relation to the present invention, the tuner 110 can extract an analog signal or a digital signal If the extracted signal is the analog signal, the tuner 110 transfers the signal to the MPEG encoder 114, while if the extracted Signal is the digital signal, it transfers the Signal to the MPEG decoder 112 or the Switch 116 according to the channel environment. The MPEG decoder 112 performs a decoding process of the digital Signal transferred from the tuner 110. The MPEG decoder 112 outputs a CVBS (Com posite Video Banking Sync) signal through the decoding process. The CVBS signal is a kind of analog signal. 0030) The CVBS signal is transferred to the MPEG encoder 114. The MPEG encoder 114 performs an encoding process of the input analog signal. Also, the MPEG encoder 114 generates frames according to the wireless environment. That is, if the wireless environment is good, it generates an I-frame, B-frame and P-frame, while if the wireless envi ronment is poor, it generates an I-frame only. However, the frames generated by the MPEG encoder 114 may be changed according to a user's Setting. That is, the MPEG encoder 114 may generate the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame, and transfer only a part of the generated frames according to the wireless environment. If the wireless envi ronment is good, the MPEG encoder transfers the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame, while if the wireless environment is poor, it transfers only the I-frame. 0031) The MPEG encoder 114 transfers the generated frames to the Switch 116. The Switch 116 performs a Switching operation according to a control command. If the received signal is the analog signal, the Switch 116 outputs the frames transferred from the MPEG encoder 114. Spe cifically, if the received signal is the digital Signal and the channel environment is good, the Switch 116 outputs the frames transferred from the tuner 110. If the received signal is the digital Signal and the channel environment is poor, the Switch 116 outputs the frames transferred from the MPEG encoder 114. Although FIG. 1 illustrates that the Switch 116 receives the digital signal from the tuner 110 and the MPEG decoder 114, it may be set differently by a user. Specifically, in order to Simplify the construction of the transmitting end 100, if the extracted signal is the analog signal, the tuner 110 transfers the signal to the MPEG encoder 114, while if the extracted Signal is the digital Signal, it transfers the Signal to the MPEG decoder 112. In this case, the Switch 116 receives the frames only from the MPEG encoder The Switch 116 transfers the received frames to the wireless transmission module 118. The wireless transmis Sion module 118 processes the received frames according to
8 US 2006/ A1 Feb. 16, 2006 the control command, and then wirelessly transmits the processed frames. Since the operation of the wireless trans mission module 118 is not related to the present invention, the detailed explanation thereof will be omitted. The control unit 119 controls the elements that constitute the transmit ting end 100. Additionally, the control unit 119 determines the kind of frames to be generated by the MPEG encoder using information about the wireless environment being transferred from the receiving end Hereinafter, the construction of the receiving end 120 will be explained. The wireless reception module 122 processes the frames transferred from the wireless transmis Sion module 118 according to the control command. Since the operation of the wireless reception module 122 is not related to the present invention, the detailed explanation thereof will be omitted. However, the wireless reception module 122 performs an operation that is opposite to the operation of the wireless transmission module 118. The wireless reception module 122 transfers the processed frames to the MEPG decoder ) The MPEG decoder 124 decodes the frames trans ferred from the wireless reception module 122 to convert the frames into an RGB form. The MPEG decoder 124 transfers the analog signal converted into the RGB form to the display unit 128. The control unit 126 controls the constituent elements that constitute the receiving end ) In relation to the present invention, the control unit 126 measures the State of the wireless environment using the frames transferred from the wireless reception module 122. That is, the control unit 126 measures whether the wireless environment is good or poor using the transferred frames. Although FIG. 1 illustrates that the control unit 126 mea Sures the State of the wireless environment, it may be Set differently by the user. Specifically, a wireless environment measurement unit (not illustrated) measures the State of the wireless environment in which the frames are received according to the control command of the control unit 126. The wireless environment measurement unit transfers the measured State of the wireless environment to the control unit 126. A method of measuring the state of the wireless environment that is performed by the receiving end will be explained with reference to FIG. 2. The control unit 126 transmits information about the measured wireless environ ment to the transmitting end The display unit 128 reproduces and displays the Video Signal using the analog signal transferred from the MPEG decoder 124. In the event that the analog signal includes a Sound Signal, this Sound Signal is also reproduced using a Sound reproduction device FIG. 2 illustrates the operation performed by the receiving end according to the present invention. The opera tion of the receiving end will now be explained with reference to FIG At step S200, the receiving end receives at least one frame. AS described above, the receiving end may receive the I-frame, the I-frame and the B-frame, the I-frame and the P-frame, or the I-frame, and the B-frame and the P-frame. The receiving end reproduces the Video signal using the received frames as shown in FIG. 1, and measures the State of the wireless environment using the received frames as shown in FIG At step S202, the receiving end measures the state of the wireless environment using the received frames. That is, the receiving end measures the State of the wireless environment using whether any interference occurs among the received frames and whether any overload occurs in the wireless environment At step S204, the receiving end transmits the information about the measured State of the wireless envi ronment to the transmitting end. The receiving end can transmit the information about the wireless environment State in diverse methods First method is for the receiving end to transmit the information about the measured wireless environment State as it is. It is assumed that the State of the wireless environ ment that can be measured by the receiving end is classified into States a through h. The State a denotes the best wireless environment State, and the State h denotes the worst wireless environment State. If the wireless environment State mea Sured by the receiving end is the State a, the receiving end transmits the State a to the transmitting end. If the wireless environment State measured by the receiving end is the State d, the receiving end transmits the State d to the transmitting end. If the wireless environment state measured by the receiving end is the State h, the receiving end transmits the State h to the transmitting end Second method is for the receiving end to divide the measurable State of the wireless environment into at least two Sections. In relation to the present invention, the receiv ing end divides the measurable State of the wireless envi ronment into four Sections. That is, the receiving end divides the measurable State of the WireleSS environment into four Sections in consideration of the number of cases in which the transmitting end can transmit the frames. Hereinafter, an example of dividing the measurable State of the wireless environment into four Sections will be explained using Table 1 below. State of Wireless Environment TABLE 1. Information Corresponding to Frames Required to Be State of Wireless Environment Transmitted a, b A. I, B, P Frames c, d B I, B Frames e, f C I, P Frames g, h D IFrame As described in Table 1, by dividing the measur able State of the wireless environment into four Sections, the receiving end can transmit the State of the wireless environ ment using a Smaller number of bits. Specifically, three bits are required to transmit the State of the wireless environment in the event that the state of the wireless environment is divided into the states a to h, but only two bits are required in the event that the state of the wireless environment is divided into four sections. A to D. Hereinafter, for conve nience in explanation, the States a to h refer to first infor mation and the Sections. A to D refer to Second information. AS described above, by transmitting the Second information, the transmitting end can determine the frames to be trans mitted using the received Second information only. Accord ingly, by performing the above-described process, the load of the transmitting end can be reduced. In addition to the
9 US 2006/ A1 Feb. 16, 2006 above-described methods, the receiving end can transmit the State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end by diverse methods FIG. 3 illustrates the operation performed by the transmitting end in the video reproduction System according to the present invention. The operation of the transmitting end will now be explained with reference to FIG At step S300, the transmitting end receives the information about the wireless environment. As described above, the transmitting end receives the first information or the Second information At step S302, the transmitting end judges whether the received signal is the analog Signal. If the received signal is the analog signal as a result of judgment, the transmitting end proceeds to step S304, while if the received signal is the digital signal, the transmitting end proceeds to Step S At step S310, the transmitting end judges whether the state of the wireless environment received at step S300 is good. In relation to the present invention, it is assumed that the good wireless environment State corresponds to the States a and b or the Section A. If the wireless environment State is good as a result of judgment, the transmitting end proceeds to step S314, while if the wireless environment State is poor, the transmitting end proceeds to Step S At step S312, the transmitting end performs an MPEG decoding, and through this MPEG decoding, the digital Signal is converted into the analog Signal. If the conversion process is completed, the transmitting end pro ceeds to step S At step S304, the transmitting end performs an MPEG encoding. If the encoding is completed, the trans mitting end proceeds to step S306. At step S306, the transmitting end generates frames corresponding to the wireless environment State. The frames corresponding to the wireless environment state are shown in Table 1. If the wireless environment is good, the transmitting end generates the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame, and if the wireless environment is poor, it generates the I-frames only. If the frame generation is completed, the transmitting end pro ceeds to step S At step S308, the transmitting end transmits the generated frames to the receiving end. Although in order to wirelessly transmit the generated frames, a specified process should be performed, it is not related to the present inven tion, and the detailed explanation thereof will be omitted At step S314, the transmitting end transmits the received digital signal (i.e., frames) to the receiving end FIG. 4 is a view illustrating the operation per formed by the receiving end in the Video reproduction System according to the present invention At step S400, the receiving end receives at least one frame. The detailed operation performed at step S400 is equal to that performed at step S At step S402, the receiving end measures the state of the wireless environment using the received frames. That is, the receiving end measures the State of the wireless environment using whether any interference occurs among the received frames or whether any overload occurs in the wireless environment At step S404, the receiving end compares the wireless environment state measured at step S402 with the wireless environment State previously measured. In order to compare the wireless environment States, the receiving end may have a memory of a specified capacity. If the wireless environment State presently measured is good as a result of comparison, the receiving end proceeds to Step S406, while if the wireless environment State previously measured is good, the receiving end proceeds to Step S At step S406, the receiving end requests the trans mitting end to transmit frames that are higher than the previously received frames by one level. Referring to Table 1, it is assumed that the transmitting end has transmitted the I-frame and B-frame. If the receiving end requests the transmitting end to transmit the frames higher than the previously received frames by one level, the transmitting end transmits the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame At step S408, the receiving end requests the trans mitting end to transmit the frames lower than the previously received frames by one level. Referring to Table 1, it is assumed that the transmitting end has transmitted the I-frame and B-frame. If the receiving end requests the transmitting end to transmit the frames lower than the previously received frames by one level, the transmitting end transmits the I-frame and P-frame By performing the above-described process, the receiving end can reduce the amount of information being transmitted to the transmitting end. That is, the receiving end informs the transmitting end that the receiving end requests the frames of a higher level or a lower level only. Accord ingly, the information that is requested to the transmitting end can be expressed by one bit only As described above, according to the present invention, a Video signal can normally be reproduced even in a poor wireless environment by differently Setting trans port Streams being transmitted from a transmitting end to a receiving end in a Video reproduction System according to the state of a wireless environment. Additionally, by differ ently Setting the transmitted transport Streams according to the State of the wireless environment, data can be efficiently transmitted The foregoing embodiment and advantages are merely exemplary and are not to be construed as limiting the present invention. The present teaching can be readily applied to other types of apparatuses. Also, the description of the embodiments of the present invention is intended to be illustrative, and not to limit the Scope of the claims, and many alternatives, modifications, and variations will be apparent to those skilled in the art. What is claimed is: 1. A frame transmission method performed by a transmit ting end in a Video reproduction System having the trans mitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiv ing end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a Video signal, the method comprising: receiving information about a State of a wireless environ ment from the receiving end;
10 US 2006/ A1 Feb. 16, 2006 determining the frames to be transmitted to the receiving end in consideration of the received information about the State of the wireless environment; and transmitting the determined frames to the receiving end. 2. The frame transmission method of claim 1, wherein the frames that can be transmitted to the receiving end comprise an I-frame, a B-frame and a P-frame. 3. The frame transmission method of claim 2, wherein if the State of the wireless environment is good, all of the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame are transmitted. 4. The frame transmission method of claim 2, wherein if the State of the wireless environment is poor, only the I-frame is transmitted. 5. The frame transmission method of claim 1, wherein if the frames to be transmitted refer to an analog signal, the analog signal is converted into a digital Signal to be trans mitted. 6. A video reproduction method performed by a receiving end using received frames in a Video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting the frames and the receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a Video signal, the method comprising: receiving the frames from the transmitting end; measuring a State of a wireless environment by judging whether an error exists in the received frames and reproducing the Video signal using the received frames, and transmitting the measured State of the wireless environ ment to the transmitting end. 7. The video reproduction method of claim 6, wherein the transmitting the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end comprises: dividing a measurable State of the WireleSS environment into at least two Sections, and transmitting information about the at least two Sections corresponding to the measurable State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end. 8. The video reproduction method of claim 7, wherein a number of Sections is determined in consideration of the frames that can be transmitted by the transmitting end. 9. The video reproduction method of claim 6, wherein the transmitting the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end comprises: comparing a presently measured State of the wireless environment with a previously measured State of the wireless environment in a comparison; and transmitting information about a result of the comparison to the transmitting end. 10. A video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a video signal, the System comprising: a control unit configured to determine the frames to be transmitted to the receiving end in consideration of information about a State of a wireless environment from the receiving end; an encoder configured to generate the frames to be transmitted in accordance with a control command from the control unit; and a wireless transmission module configured to wirelessly transmit the generated frames. 11. The video reproduction system of claim 10, wherein the frames that can be transmitted to the receiving end are an I-frame, a B-frame and a P-frame. 12. The video reproduction system of claim 11, wherein if the State of the wireless environment is good, all of the I-frame, B-frame and P-frame are transmitted. 13. The video reproduction system of claim 11, wherein if the State of the wireless environment is poor, only the I-frame is transmitted. 14. The video reproduction system of claim 10, wherein if the frames to be transmitted refer to an analog signal, the control unit operates to convert the analog signal into a digital signal to transmit the digital Signal. 15. A video reproduction System having a transmitting end for wirelessly transmitting frames and a receiving end for receiving the frames transmitted from the transmitting end and reproducing a video signal, the System comprising: a wireless reception module configured to receive the frames from the transmitting end; a wireless environment measurement unit configured to measure a State of a wireless environment by judging whether an error exists in the received frames, a decoder configured to reproduce the Video signal using the received frames, and a control unit configured to transmit the measured State of the wireless environment to the transmitting end. 16. The video reproduction system of claim 15, wherein the control unit divides a measurable State of the wireless environment into at least two Sections and transmits infor mation about the at least two Sections corresponding to the measurable State of the wireless environment to the trans mitting end. 17. The video reproduction system of claim 15, wherein the control unit compares a presently measured State of the wireless environment with a previously measured State of the wireless environment in a comparison, and transmits information about a result of the comparison to the trans mitting end.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0080549 A1 YUAN et al. US 2016008.0549A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) MULT-SCREEN CONTROL METHOD AND DEVICE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
Appeal decision. Appeal No France. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2015-21648 France Appellant THOMSON LICENSING Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney INABA, Yoshiyuki Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney ONUKI, Toshifumi Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney EGUCHI,
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2015-21648 France Appellant THOMSON LICENSING Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney INABA, Yoshiyuki Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney ONUKI, Toshifumi Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney EGUCHI,
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent
 US0079623B2 (12) United States Patent Stone et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 11 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY OF MULTIPLE
US0079623B2 (12) United States Patent Stone et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 11 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY OF MULTIPLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070O8391 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0083910 A1 Haneef et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SEAMILESS Publication Classification
US 20070O8391 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0083910 A1 Haneef et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SEAMILESS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070011710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chiu (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) INTERACTIVE NEWS GATHERING AND Publication Classification MEDIA PRODUCTION
US 20070011710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chiu (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) INTERACTIVE NEWS GATHERING AND Publication Classification MEDIA PRODUCTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,786 B1
 USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Han et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006
 (19) United States US 2006O142968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0142968 A1 Han et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HOME CONTROL SYSTEM USING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 2006O142968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0142968 A1 Han et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HOME CONTROL SYSTEM USING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(10) Patent N0.: US 6,415,325 B1 Morrien (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002
 I I I (12) United States Patent US006415325B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,415,325 B1 Morrien (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) TRANSMISSION SYSTEM WITH IMPROVED 6,070,223 A * 5/2000 YoshiZaWa et a1......
I I I (12) United States Patent US006415325B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,415,325 B1 Morrien (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) TRANSMISSION SYSTEM WITH IMPROVED 6,070,223 A * 5/2000 YoshiZaWa et a1......
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9583250B2 (12) United States Patent Meyer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,583,250 B2 Feb. 28, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) MEMS TUNABLE INDUCTOR Applicant:
USOO9583250B2 (12) United States Patent Meyer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,583,250 B2 Feb. 28, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) MEMS TUNABLE INDUCTOR Applicant:
US 7,319,415 B2. Jan. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Gomila. (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 USOO73194B2 (12) United States Patent Gomila () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan., 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) CHROMA DEBLOCKING FILTER Inventor: Cristina Gomila,
USOO73194B2 (12) United States Patent Gomila () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan., 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) CHROMA DEBLOCKING FILTER Inventor: Cristina Gomila,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8891 632B1 (12) United States Patent Han et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Nov. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORENCODING VIDEO AND METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DECODINGVIDEO, BASED ON HERARCHICAL
USOO8891 632B1 (12) United States Patent Han et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Nov. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORENCODING VIDEO AND METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DECODINGVIDEO, BASED ON HERARCHICAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,316,390 B2. Zeidman (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 United States Patent USOO831 6390B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,316,390 B2 Zeidman (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR ADVERTISERS TO SPONSOR 6,097,383 A 8/2000 Gaughan et al.... 345,327
United States Patent USOO831 6390B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,316,390 B2 Zeidman (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) METHOD FOR ADVERTISERS TO SPONSOR 6,097,383 A 8/2000 Gaughan et al.... 345,327
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005
 (19) United States US 2005O28O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0280851A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) COLOR SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2005O28O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0280851A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2005 (54) COLOR SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,613,344 B2
 USOO761334.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,613,344 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2009 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR ENCODING (51) Int. Cl. AND DECODING AN MAGE USING G06K 9/36
USOO761334.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,613,344 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2009 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR ENCODING (51) Int. Cl. AND DECODING AN MAGE USING G06K 9/36
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O155728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0155728A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) CONTROL APPARATUS OPERATIVELY (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O155728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0155728A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) CONTROL APPARATUS OPERATIVELY (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7916217B2 (12) United States Patent Ono (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Kenichiro Ono, Kanagawa (JP) (73) (*) (21) (22) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo
USOO7916217B2 (12) United States Patent Ono (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Kenichiro Ono, Kanagawa (JP) (73) (*) (21) (22) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014
 (19) United States US 2014O108943A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0108943 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR BROWSING INTERNET OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O108943A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0108943 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR BROWSING INTERNET OF (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 7,872,186 B1. Jan. 18, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent Tatman (54) (76) Kenosha, WI (US) (*)
 US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,020,022 B2. Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited
 United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O1294.08A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0129408A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2005O1294.08A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0129408A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
(19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,043,203 B2. Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2011
 US0080432O3B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,043,203 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2011 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FORTINNITUS (58) Field of Classification Search... 600/25,
US0080432O3B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,043,203 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2011 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FORTINNITUS (58) Field of Classification Search... 600/25,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
(10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001
 (12) United States Patent US006301556B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001 (54) REDUCING SPARSENESS IN CODED (58) Field of Search..... 764/201, 219, SPEECH
(12) United States Patent US006301556B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001 (54) REDUCING SPARSENESS IN CODED (58) Field of Search..... 764/201, 219, SPEECH
