(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2012
|
|
|
- Anne Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
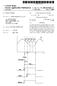
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2012 (54) ANIMATED SCREEN OBJECT FOR 5,537,528 7/1996 Takahashi et al. ANNOTATION AND SELECTION OF VIDEO s: A 3. 3: R et t tal w anews, 111 et al. SEQUENCES 5,767,835 A 6/1998 Obbink et al. 5,828,370, 1998 Moeller et al. (75) Inventors: Michael W. Wallace, Vancouver, WA 5,880,729 A 3, 1999 G. et al. (US); Troy Steven Acott, Beaverton, OR 5,940,076 A 8, 1999 Sommers et al. (US); Larry Alan Westerman, Portland, 6,005,562 A * 12/1999 Shiga et al ,721 OR (US); Carl Johnson, Portland, OR 6,133,920 A /2000 decarmo et al. US (US) OTHER PUBLICATIONS (73) Assignee: Ensequence, Inc., Portland, OR (US) Li, Francis C. et al., Browsing Digital Video'. CHI 2000 Apr. 1-6, (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 2000: patent is extended or adjusted under 35 Hanjalic, et al., Automation of Systems Enabling Search on Stored U.S.C. 4(b) by 3218 days Video Data, Proceedings of the Spie, Spie, Bellingham, VA, US, Feb. M YW- y ys. 13, 1997, pp , vol. 3022, XP ISSN: X. (21) Appl. No.: /066,144 * cited by examiner (22) Filed: Jan. 31, Prior Publication D Primary Examiner Namitha Pillai (65) rior Publication Data (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Marger Johnson & US 20O2/O 5535 A1 Aug. 8, 2002 McCollom, P.C. Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional application No. 60/266,012, filed on Feb. (57) ABSTRACT 2, A simple display of items from a list, which changes in (51) Int. Cl synchrony with the corresponding video display, and permits Goof M48 ( ) simple navigation under user control. The display includes 16. three control objects positioned below a video frame window (52) U.S. Cl.... 7/721; 7/720; 7/722; 72E. on a display screen. A middle displayed object is located in a (58) Field of Classification Search 345/720 focus position and corresponds to the video segment cur 345/723, : 725 rently being played in the video window. When play of the See application file for complete search history. segment is complete, the object located to the right of the focus position moves and displaces the middle displayed (56) References Cited object, most recently displayed within the focus position, to indicate a forward progression within the viewed video U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Sequence. 5,461,711 A /1995 Wang et al. 5,5,486 A 5, 1996 Amro et al. 5,521,841. A * 5/1996 Arman et al / Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets VIDEO SEGMENTS set EXTENDED --5 EXTENDED 42 BATTLE 11c 1 HAPPY ENDING (skip N Sb SAD I ABATTLE/I- ENDING - mur- a-- or b BATTLE 5a
2 U.S. Patent May 8, 2012 Sheet 1 of 2 r VIDEO SEGMENTS 1 C ABATTLE)- (IE), ar 1 1. BATTLE 5a BATTLE (DEFAULT) SAD ENDING HAPPY ENDING (DEFAULT) EXTENDED HAPPY ENDING 2a -> 3a -> 4a -> 5a, 2bs - 4b ---- sb 1-2c - SL3b2-4c is - 5c N VIDEO SEGMENT it INSEQUENCE FIG. 3
3 U.S. Patent May 8, 2012 Sheet 2 of 2 FIG. 4 FIG. 5 FIG. 6
4 1. ANIMATED SCREEN OBJECT FOR ANNOTATION AND SELECTION OF VIDEO SEQUENCES CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims the benefit from U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 60/266,012 filed Feb. 2, 2001 whose contents are incorporated herein for all purposes. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to computer graphics pro cessing, and more specifically to the annotation and manipu lation of video objects by means of a graphical user interface object comprising multiple buttons. 2. Description of the Prior Art Graphical user interfaces exist which provide elaborate and flexible manipulation of objects and actions on computer screens. Such interfaces have been developed to accommo date the power and performance available in contemporary processor chips, and to permit the incorporation of direct manipulation interface hardware such as computer mice, trackballs, joysticks and the like. One common function required in computer systems is the viewing and selection of items from a list. The prior art contains a number of examples of user interface Schemes which work well within the conventional computer environ ment for this task. The most comprehensive of these from the perspective of the current disclosure is U.S. Pat. No. 5, , which is assigned to Microsoft and is titled System for Displaying a List on a Display Screen. The 708 patent discloses the display, on a screen, of a list of user-selectable items, at least three in number, where the items on the edge of the screen are only partially displayed. The user can make a selection from one of the items on the screen, or scroll the list to move additional items on or off the screen. The combina tion of these actions results in a selection, which results in Some action by the underlying user interface Software. The patent literature contains other examples of movable or animated button selections. For example, U.S. Pat. No. 5,5,486 which is assigned to IBM and is titled Method, Apparatus and Memory for Directing a Computer System to Display a Multi-Axis Rotatable, Polyhedral-Shape Panel Container Having Front Panels for Displaying Objects' describes the graphical presentation of an apparently three dimensional container, the faces of which represent informa tion or choices to the user. U.S. Pat. No. 5,940,076, which is assigned to Motorola and is titled Graphical User Interface for an Electronic Device and Method Therefor describes a circular display of choices or features. The need for a complex and highly featured user interface has moved beyond the computer environment, however. Digi tal technology is moving into the field of home entertainment. The new digital television standard is encouraging the inte gration of computer technology into home entertainment appliances. One example of this convergence is the digital set top box, which functions to receive digital signals from cable or satellite broadcast Sources, and to demodulate, decom press, and convert these signals into analog signals viewable on conventional television sets. The new generation of these boxes will incorporate disk drives, making them more like computers in their ability to store and reproduce digital con tent. Similarly, computers are being used as home entertain ment vehicles, incorporating DVD drives and VCR-like func tionality. Consumer television systems present more of a challenge for the user interface designer, since the television or the set top box typically has a lower level of computer performance, and a paucity of direct manipulation options. The typical TV remote control utilizes only a rocker Switch input mechanism or opposing button Switches for controlling Volume or select ing channels, rather than the more flexible mouse or track ball interface. Another aspect of digital technology that is entering the home entertainment market is the provision of enhanced or interactive television content. Viewers are no longer limited to simply viewing a program, nor to the simple VCR-like choices of fast forward, rewind, pause and continue. The new interactive television paradigm promises to provide the user with a richer, more flexible and engaging experience, through the incorporation of selective navigation through a multiplic ity of linear and non-linear paths displaying segments of Video, still images, and other types of entertainment and information content. The selection of paths through video will no longer follow the passive start-and-watch model, but will permit or require active choices by the viewer. However, the typical expected user of interactive television cannot be expected to learn and master a complex interface paradigm. Therefore, the interaction control must be simple, self-ex planatory, intuitive, and direct. Furthermore, the interface must provide a means of assisting the user in understanding the significance of the content being viewed, a means of labeling the various choices available to the user, assistance in remembering the path taken through the content, and a mechanism for visually depicting linear time flow and allow ing the opportunity to alter the speed and direction of that flow. None of the existing interface methods combines the anno tated display of multiple relevant choices for time-varying content, with a simple means of navigating the time series. Accordingly, the need remains for an improved system for user navigation through video content and the like. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The current invention combines a simple display of items from a list, which changes in Synchrony with the correspond ing video display, and permits simple navigation under user control. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of video segments to be displayed graphed against a timeline. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of video segments physically arrayed on a storage device. FIG. 3 is a schematic flow diagram showing the several branching pathways obtained by selection of various video segments using the teachings of the invention. FIG. 4 is a layout for video display implemented according to a preferred embodiment of the invention. FIG. 5 is the button configuration of FIG. 4 during a tran sition sequence. FIG. 6 is a screen view with multiple future choices imple mented according to an alternate embodiment of the inven tion. DETAILED DESCRIPTION The current invention is adapted for use with video display systems, such as those known in the art, that include various
5 3 Video segments that are arranged to play in Some linear (or non-linear) progression to form a video sequence. An example of such a known video display system is a DVD, or digital video disc, in which a user may selectively skip to a desired segment of the video movie using the graphic user interface, programmed in Software on the disc and operable on the DVD player to allow user navigation between the segments. The segments are delineated by the producer of the DVD, where each segment may include one or more scenes. A typical DVD movie may have as many as forty designated segments that the user may select and play. The current invention is also operable on other video sys tems such as hard-drive based systems (such as those found on some modem set-top boxes) and video-on-demand sys tems where the video content is continuously being down loaded over a network for play in response to user interaction with the network. FIG. 1 illustrates the organization of a video sequence at 20, comprised of a plurality of video segments on timeline 22, here labeled from segments 1 through 11. In a typical video sequence, say of a movie, playback over the video system occurs in a linear fashion by playing video segment 1 (which corresponds to the first scene of the movie) to completion and then immediately playing video segment 2 and so forth until the end of the movie is reached after completion of video segment 11. While playback of the video sequences 1-11 in order typi cally occurs by default and without further interaction by the user with the video display system, it may be desirable to provide a video sequence having many possible branches and/or endings. In FIG. 1, for example, video segment 5 has three different possibilities 5a, 5b, and 5c. Segment 5a may be, for instance, a video segment showing a great battle in the middle of the movie video sequence 20. Segment 5b may be, for instance, a null video segment of virtually no time that essentially skips the battle scene and instead bridges segment 4 with segment 6. This may be useful if, for instance, one of the viewers is a young child who is sensitive to violence. Finally, segment 5c may show an extended and unedited version of video segment 5a that may have initially been cut from the movie released in the theaters. FIG. 1 also shows segment 11 with three possible endings 11a, 11b, and 11c to the video sequence 20. As will be appreciated below, only one of these endings will be selected by user interaction with the video display system using the selection and annotation scheme disclosed in the present invention and discussed in more detail further below. FIG. 2 illustrates the physical arrangement of data for the Video segments on a storage medium Such as a digital video disc (DVD) or hard disk drive. As it is desired for the read head of the storage medium to traverse the least distance, Video segments are typically arranged sequentially in the expected order in which they are to be played. In the present example, the video sequence (movie) formed by the default organization of the video segments that is, without further user interaction as described further below results in seg ment 5a (the battle scene) being played immediately after segment 4 and before segment 6. Similarly, the default ending 11a to the video sequence is stored immediately after the data for segment since the expectation is that a viewer of the video segment would chose to view the default ending. The other endings, segments 11b and 11c, are stored after default ending segment 11a. FIG. 3 illustrates the arrangement of video segments into one of a plurality of possible video sequences, where the sequence shown is produced by combining a total of five Video segments. The sequence branching follows a series of predefined rules that regulate the flow of the sequence from beginning to end. For instance, in the example shown, all possible video sequences begin with a display of video seg ment 1. From there, the sequence has three possible branch paths: to segment 2a along the double-lined arrow, to segment 2b along dashed arrow, and to segment 2c along single-lined arrow. The simplified user interface for selecting 2a, 2b, or 2c is explained further below. If segment 2a is selected (or if 2a is the default segment absent further user interaction), then segment 2a is displayed on the video display system such as an attached television or computer monitor and the like and the sequence proceeds to segments 3a, 4a and then 5a before ending. Note that the rules associated with selection of seg ment 2a require that no further branching exists once the path designated by the double-lined arrows is chosen. If segment 2b is selected, as by using the user interface of the present invention, then play proceeds to 2b and thence to segment 3b. If segment 2c is selected, then play proceeds to 2c and thence to segment 3b. The rules for selection of segment 2b or 2c disallow segment 3a from appearing in the rightmost position on the display screen as a possible branching option. At 3b, the user of the video display system is again given a choice of branching paths. The system is programmed to default to one of the paths in the absence of further user interaction with the video display system. In one example, a user who proceeded down the viewing path denoted by the dashed line would default to segment 4b after viewing segment 3b because, for instance, scenes within video segment 4b may better correlate with scenes shown in earlier-viewed segment 2b. A user who pro ceeded down the viewing path denoted by the single-lined arrow would default to segment 4c for similar reasons. It is also possible that both paths could default to the same seg ment (e.g. segment 4b). Finally, segment 4c branches into three different paths segment 5c, segment 5d, and segment 5e with one of the segments being set to default and the remaining ones selected under control of user input. The current invention is intended for the annotation and interactive display of video segments. Typically such seg ments are viewed as they are played, and the annotated labels are displayed in sequence, in Synchrony with the video dis play. However, the invention may also be used in a mode where the video is not being played (having been paused, for example, or prior to initiating playback). In this case, the displayed images will correspond to still images taken from the video segments corresponding to the annotations. To display the contents of a list of annotations, the current invention uses at most three buttons or button-sets (referred to herein as control objects ) displayed on a video display screen 24 as shown in FIG. 4. The video screen has displayed thereon a video segment within a video frame 26 and, in a preferred embodiment, a plurality of control objects 28, 30 located in non-overlapping relation to the video frame 26 in which the video segment is displayed. The center object 28 is located within a centrally located focus position 32, desig nated by dashed line, which represents the current focus of the list and corresponds to the video selected by the user and/or displayed on the screen. Several aspects of this diagram are remarkable. First, at most three buttons or button sets are displayed on the screen, each of them shown in its entirety. Only in special cases. Such as that in FIG. 4, are less than three buttons shown: For the first segment of video, the previous (left) button is not shown. Similarly, for the last segment of video, the next (right) button is not shown. In the rare case that the video contains only one segment, only one button would be shown.
6 5 Second, the center button, which represents the video cur rently showing, or last shown prior to pause, is highlighted to indicate its selection. The selected button is always displayed in the center position. If the user chooses, in the display shown in FIG. 5, to select either the previous (in this case, segment 1) or next selection (here, segment 3), and does so by means of selection arrows or a rocker Switch on a typical remote control, the focus shifts to the corresponding button, and the button itself moves to the center position. This move ment may be accomplished by animating the movement, using a multiplicity of intermediate positions, or by simply repainting the labels of the buttons, replacing the label of the center button with the label from the selected button, and updating the corresponding labels for the previous and next buttons. FIG. 5 shows how a transition state may appear following the selection of the next button when the button movement is animated. The selection and annotation method practiced according to a preferred embodiment of the invention dis plays a first control object 28, associated with a displayed first Video segment 1 of the video sequence, on the display Screen 24 in the focus position 32 simultaneous with the display of the first video segment 1 on the display screen within the video frame 26. A second control object 30, associated with a second video segment, is displayed on the display Screen 24 adjacent to the focus position. Here, since the video segment 2 associated with second control object 30 would normally be shown within a video sequence at a later time than the video segment 1 associated with first control object 28, the second object 30 is shown to the right of object 28. It is understood that the invention is not limited to the arrangement of the objects and that any arrangement of objects can be imple mented so long as the arrangement is temporally consistent. For instance, English language speakers read from left-to-left and therefore it is more appropriate to have the flow of time in the same direction. Speakers of Hebrew (right-to-left) and of Japanese (up-to-down) may necessitate a different organiza tion to make it more intuitive to the natural directional flow of the language. During a transition between video segments, the second control object 30 moves to the focus position 32 (centered and directly below video frame 26), and the first control object 28 moves out of the focus position toward the left in the direction of arrow 33, in substantial synchronicity with a transition between the display of the first video segment 1 and the second video segment 2 on the display Screen 24. Movement is denoted by the repeating dashed portions to the right of each object. Following the transition, the right button (control object 34) appears with the label appropriate for associated Video segment 3. The first, second, and third objects (28, 30, and 34, respec tively) correspond to current, future and past segments respectfully within the default video sequence. It is signifi cant to note that the forward transition (that is, to segments later in time) can be done automatically as the video sequence is played. These transitions, as well as backward transitions, may also be made under user control. Transitions can occur when video is paused, that is, when a still image is displayed. The focus position 32 is interposed between the now moved first control button 28 and the third control button34. Once video segment 2 has completed play, the following sequence of events occur: associated control object 30 is moved to the left out of the focus position 32, leftmost first object 28 is moved off the display screen 24, third control object 34 moves into the focus position, and a fourth object (not shown in FIG. 5) is simultaneously moved into the posi tion previously vacated by the third control object 24. The object movement occurs in Substantial synchronicity with the start of the next video segment 3 and the end object position results in the focus position being interposed between the control object 30 and the fourth (not shown) control object. The control objects are signified by annotations, such as still images and/or descriptive text, corresponding to the con tent of the video segments associated with the control objects. The object buttons may be labeled in a variety of ways, including images, icons, animations, keywords, game clues, trivia answers. Such labels need not specifically define or describe the corresponding video segment, but will be related to it in Some way. FIG. 1 includes examples of Such annota tions, where the object associated with segment 5a is anno tated Battle, 5b as Skip Battle', 5c as Extended Battle', 11a as Happy Ending, 11b as "Sad Ending, and 11c as Extended Happy Ending. Turning next to FIG. 6, shown is the video display 24 (television, computer monitor, cell phone, etc.) having dis played thereon control objects 36, 38 and 40 associated with video segments 9, and 11 respectively. Control object 40 includes a plurality of subobjects (40a, 40b, and 40c) corre sponding to video segments 11a, 11b and 11c, each of which provide a selectable branching pathway from the previous video segment, designated by control object 38. Objects 40a, 40b and 40c correspond to video segments of alternate end ings to the video sequence/movie. In the absence of input from a user of the video display system and at the end of video segment, a preset one of the three Subobjects (e.g. object 40b) moves to the focus position 32 and the corresponding Video segment to that object (segment 11b) plays within the video frame 26. User selection of one subobjects (or of another of the objects) occurs by Scrolling among the plurality of control objects based on input from a user of the video display sys tem, as by using the rocker Switch on a remote control. The designated object is selected as by depressing an enter or Some similar function key on the remote control and the selection of one of the control objects (or subobjects) is accepted by the video display system. The selected object is then moved to the focus position and the associated video segment is played within the video frame window 26. Scroll ing is accomplished using visual cues such as a focus frame 42, shown highlighting a particular control object 11c in FIG. 1, which is moveable between the plurality of objects to provide a visual indication of user control of the selected control object. The selection process may also be accomplished by means of a screen object, such as a pointer or indicator, which is manipulated by any standard user interface pointer device like a mouse or trackball; by means of designated keys, such as the '4' and 6 keys on a telephone touchpad; or directly by means of a touch-sensitive display screen. As shown in FIG. 6, the number of subobject buttons may be increased, with two or more buttons on each side of the center (focus) button. Navigation would then be a two-dimen sional process, with various options available for past (left) and/or future (right) movement. As described above, segment 11b would be the segment displayed if no user intervention occurred, while segments 11a and 11c would be optional choices available to the user. In this scenario, multiple branching paths through the video segments would be pos sible. Navigation in Such an interface might require a joystick or other control capable of selecting from multiple directions, rather than a simple right arrow or rocker Switch control, or could be accomplished with the use of rapid multiple button presses, or combinations of simultaneous button presses, or
7 7 alternative keys such as the 3 and 9 keys on a touch pad, Page Up/Page Down, or others. The buttons might be animated with an indication of the progression of time within the particular segment named by the button. This may take the form of a line or bar with a mark or coloration change that moves along or across the graphic to mark the relative position within the segment. Buttons may provide additional functionality, including pop-up menus for additional information or selections. Having described and illustrated the principles of the invention in a preferred embodiment thereof, it should be apparent that the invention can be modified in arrangement and detail without departing from such principles. We claim all modifications and variation coming within the spirit and Scope of the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. In connection with a video display system capable of displaying a sequence of video segments, a method for dis playing a plurality of control objects associated with said Video segments on a display Screen comprising the steps of displaying a first control object, associated with the dis played first video segment, on the display screen in a focus position simultaneous with the display of a first Video segment on the display screen; displaying a second control object, associated with a sec ond video segment, adjacent to the focus position; and moving the second control object to the focus position, and the first control object out of the focus position, in sub stantial synchronicity with a transition between the dis play of the first video segment and the second video segment on the display Screen. 2. The method of claim 1, further comprising the step of displaying a third control object adjacent to the focus posi tion, whereby the focus position is interposed between the second control object and the third control object. 3. The method of claim 1, further comprising the steps of: Scrolling among the plurality of control objects based on input from a user of the video display system; accepting the selection of one of the plurality of control objects based on input from a user of the video display system; and displaying a video segment associated with the selected control object. 4. The method of claim 1, further comprising displaying a focus frame within said focus position, said focus frame operative to Supply a visual indication of user control of the first control object and moving said focus frame under user control to the second control object. 5. The method of claim 1, said first and second control objects including displayed therein visual annotation corre sponding to the content of the video segments associated with said control objects. 6. The method of claim 2 wherein the first, second, and third objects correspond to current, future, and past segments respectively within a default video sequence. 7. The method of claim 6, further comprising the step of simultaneously moving the third object off of the display screen, and a fourth object onto the display Screen simulta neous with the movement of the first object out of the focus position and the second object into the focus position so that the end position results in the focus position being interposed between the first control object and the fourth control object. 8. The method of claim 1, further comprising the step of displaying at the second control object a plurality of Subob jects, each corresponding to a respective video segment, to provide a selectable branching pathway from the video seg ment associated with the first control object The method of claim8, further comprising the step of, in the absence of input from a user of the video display system, moving the preselected one of the second control Subobjects to the focus position, and the first control object out of the focus position, at the end of the display of the first video Segment.. A system, comprising a video display system, for dis playing a plurality of control objects simultaneous with asso ciated video segments on a display screen, comprising: a first control object displayed in a focus position on said display Screen simultaneous with an associated first video segment; a second control object, associated with a second video segment, displayed adjacent to said focus position on said display Screen, wherein the second control object is moveable into the focus position, and the first control object out of the focus position, in Substantial synchronicity with a tran sition between the display of the first video segment and the second video segment on the display sermon. 11. The system of claim, further comprising a third control object, associated with a third video segment, dis played adjacent to said focus position on said display screen, whereby the focus position is interposed between the second control object and the third control object. 12. The system of claim 11, wherein the plurality of control objects can be scrolled based on input from a user of the video display system and wherein one of the plurality of objects can be selected based on input from a user of the video control system to thereby cause the selected object to move to the focus position on the display Screen in Substantial synchro nicity with a start of the display of the video segment associ ated with the selected object. 13. The system of claim 12, further comprising a focus frame moveable between the plurality of objects based on input from the user of the video display system. 14. The system of claim, said first and second control objects including displayed therein visual annotation corre sponding to the content of the video segments associated with said control objects.. The system of claim 12 wherein the first, second, and third objects correspond to current, future, and past segments respectively within the video sequence. 16. The system of claim, further comprising a plurality of subobjects located in place of the second object, each corresponding to a respective video segment, to provide a selectable branching pathway from the video segment asso ciated with the first control object. 17. The system of claim 16, wherein in the absence of input from a user of the video display system, moving the prese lected one of the second control subobjects to the focus posi tion, and the first control object out of the focus position, at the end of the display of the first video segment. 18. The system of claim, further comprising a video frame in which the video segments are displayed where said Video frame is spaced from said focus position. 19. A computer-readable medium on which is stored a program for displaying a plurality of control objects on a display Screen in connection with a video display system, the program comprising instructions which, when executed by the computer, perform the steps of: displaying a first control object, associated with the dis played first video segment, on the display screen in a focus position simultaneous with the display of a first video segment on the display screen; displaying a second control object, associated with a sec ond video segment, adjacent to the focus position; and
8 moving the second control object to the focus position, and the first control object out of the focus position, in sub stantial synchronicity with a transition between the dis play of the first video segment and the second video segment on the display Screen. 20. The medium of claim 19, further comprising: displaying a third control object, associated with a third Video segment, adjacent to the focus position so that the focus position is interposed between the second and third control objects; and moving the third object off of the display screen, and a fourth object onto the display screen simultaneous with the movement of the first object out of the focus position and the second object into the focus position so that the end position results in the focus position being inter posed between the first control object and the fourth control object. 21. The medium of claim 20, further comprising displaying a video segment associated with the control object located in the focus position within a video frame on the display screen, wherein the video frame is non-overlapped with the focus position. 22. The medium of claim 20, further comprising displaying at the second control object a plurality of Subobjects, each corresponding to a respective video segment, to provide a selectable branching pathway from the video segment asso ciated with the first control object. 23. The medium of claim 22, further comprising the step of, in the absence of input from a user of the video display system, moving the preselected one of the second control subobjects to the focus position, and the first control object out of the focus position, at the end of the display of the first Video segment.
9 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 8, B2 Page 1 of 1 APPLICATIONNO. : / DATED : May 8, 2012 INVENTOR(S) : Michael W. Wallace et al. It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: In the Specification Column 3, Line 14 should read: on Some modern Set-top boxes) and Video-on-demand SyS In the Claims Column 8, Line 20 should read: the second video segment on the display screen. Signed and Sealed this First Day of October, 2013 Teresa Stanek Rea Deputy Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
File Edit View Layout Arrange Effects Bitmaps Text Tools Window Help
 USOO6825859B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,825,859 B1 Severenuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2004 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROCESSING 5,564,004 A 10/1996 Grossman et al. CONTENT
USOO6825859B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,825,859 B1 Severenuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2004 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROCESSING 5,564,004 A 10/1996 Grossman et al. CONTENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9709605B2 (12) United States Patent Alley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul.18, 2017 (54) SCROLLING MEASUREMENT DISPLAY TICKER FOR TEST AND MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENTS (71) Applicant: Tektronix,
USOO9709605B2 (12) United States Patent Alley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul.18, 2017 (54) SCROLLING MEASUREMENT DISPLAY TICKER FOR TEST AND MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENTS (71) Applicant: Tektronix,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sims USOO6734916B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,734,916 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) VIDEO FIELD ARTIFACT REMOVAL (76) Inventor: Karl Sims, 8 Clinton St., Cambridge, MA
(12) United States Patent Sims USOO6734916B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,734,916 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) VIDEO FIELD ARTIFACT REMOVAL (76) Inventor: Karl Sims, 8 Clinton St., Cambridge, MA
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O124606A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/012.4606A1 LM et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
III. USOO A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998
 III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,448,987 B1
 USOO644.8987B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Easty et al. () Date of Patent: *Sep. 10, 2002 (54) GRAPHIC USER INTERFACE FOR A 5,898,4 A * 4/1999 Nagahara et al.... 3/2 DIGITAL CONTENT DELIVERY
USOO644.8987B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Easty et al. () Date of Patent: *Sep. 10, 2002 (54) GRAPHIC USER INTERFACE FOR A 5,898,4 A * 4/1999 Nagahara et al.... 3/2 DIGITAL CONTENT DELIVERY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2
 US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006004.8184A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0048184A1 Poslinski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USE IN DISPLAYING MULTIMEDIA
(19) United States US 2006004.8184A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0048184A1 Poslinski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USE IN DISPLAYING MULTIMEDIA
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,623,589 Needham et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 1997
 USOO5623589A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Needham et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 1997 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,524,193 6/1996 Covington et al.... 395/154. NCREMENTALLY BROWSNG
USOO5623589A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Needham et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 1997 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,524,193 6/1996 Covington et al.... 395/154. NCREMENTALLY BROWSNG
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl. M M 110 / <E
 (19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0245680A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0245680 A1 TSUKADA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) TELEVISION OPERATION METHOD (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B1
 USOO9658462B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,658.462 B1 Duffy (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR (58) Field of Classification Search MANUFACTURING AREAR PROJECTION
USOO9658462B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,658.462 B1 Duffy (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR (58) Field of Classification Search MANUFACTURING AREAR PROJECTION
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040148636A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0148636A1 Weinstein et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMBINING TELEVISION BROADCAST AND PERSONALIZED/INTERACTIVE
(19) United States US 20040148636A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0148636A1 Weinstein et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMBINING TELEVISION BROADCAST AND PERSONALIZED/INTERACTIVE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,228,372 B2
 US008228372B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Griffin (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2012 (54) DIGITAL VIDEO EDITING SYSTEM (58) Field of Classification Search... 348/1401, 348/515, 47, 14.12,
US008228372B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Griffin (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2012 (54) DIGITAL VIDEO EDITING SYSTEM (58) Field of Classification Search... 348/1401, 348/515, 47, 14.12,
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,786 B1
 USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
USOO6462786B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Glen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BLENDING 5,874.967 2/1999 West et al.... 34.5/113 IMAGE INPUT LAYERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
(19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD. LG ELECTRONICS, INC. Petitioner. ATI TECHNOLOGIES ULC Patent Owner
 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD LG ELECTRONICS, INC. Petitioner v. ATI TECHNOLOGIES ULC Patent Owner Case: IPR2015-00322 Patent 6,784,879 PETITION FOR
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD LG ELECTRONICS, INC. Petitioner v. ATI TECHNOLOGIES ULC Patent Owner Case: IPR2015-00322 Patent 6,784,879 PETITION FOR
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,717,620 B1
 USOO671762OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chow et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,579,052 A 11/1996 Artieri... 348/416 DECOMPRESSING COMPRESSED DATA 5,623,423
USOO671762OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chow et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,579,052 A 11/1996 Artieri... 348/416 DECOMPRESSING COMPRESSED DATA 5,623,423
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(12) United States Patent
 US0088059B2 (12) United States Patent Esumi et al. (54) REPRODUCING DEVICE, CONTROL METHOD, AND RECORDING MEDIUM (71) Applicants: Kenji Esumi, Tokyo (JP); Kiyoyasu Maruyama, Tokyo (JP) (72) Inventors:
US0088059B2 (12) United States Patent Esumi et al. (54) REPRODUCING DEVICE, CONTROL METHOD, AND RECORDING MEDIUM (71) Applicants: Kenji Esumi, Tokyo (JP); Kiyoyasu Maruyama, Tokyo (JP) (72) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al.
 United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / A1
 THAI MAMMA WA MAI MULT DE LA MORT BA US 20180013978A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / 0013978 A1 DUAN et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Jan. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) VIDEO SIGNAL
THAI MAMMA WA MAI MULT DE LA MORT BA US 20180013978A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / 0013978 A1 DUAN et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Jan. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) VIDEO SIGNAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 20030002689A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0002689 A1 Folio (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUPPLEMENTALAUDIO CONTENT SYSTEM WITH WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FOR A CINEMA
(19) United States US 20030002689A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0002689 A1 Folio (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUPPLEMENTALAUDIO CONTENT SYSTEM WITH WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FOR A CINEMA
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO972O865 (10) Patent No.: US 9,720,865 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 1, 2017 (54) BUS SHARING SCHEME USPC... 327/333: 326/41, 47 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent USOO972O865 (10) Patent No.: US 9,720,865 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 1, 2017 (54) BUS SHARING SCHEME USPC... 327/333: 326/41, 47 See application file for complete
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,969,021 B1. Nibarger (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005
 United States Patent US006969021B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Nibarger (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005 (54) VARIABLE CURVATURE IN TAPE GUIDE 4,607,806 A * 8/1986 Yealy..... 242/236.2 ROLLERS 5,992,827 A
United States Patent US006969021B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Nibarger (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005 (54) VARIABLE CURVATURE IN TAPE GUIDE 4,607,806 A * 8/1986 Yealy..... 242/236.2 ROLLERS 5,992,827 A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060095317A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0095317 A1 BrOWn et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORMONITORING (22) Filed: Nov.
US 20060095317A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0095317 A1 BrOWn et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORMONITORING (22) Filed: Nov.
IIIHIIIHIIIHHHHII. United States Patent (19) 5,107,744. Bradley. Apr. 28, Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets
 United States Patent (19) Bradley 54 MUSIC RULE 76 Inventor: Barry C. Bradley, 7748 Gloria, Van uys, Calif. 91406 (21) Appl. o.: 540,440 (22) Filed: Jun. 14, 1990 51) Int. Cl... G09B 15/08 52) U.S. C....
United States Patent (19) Bradley 54 MUSIC RULE 76 Inventor: Barry C. Bradley, 7748 Gloria, Van uys, Calif. 91406 (21) Appl. o.: 540,440 (22) Filed: Jun. 14, 1990 51) Int. Cl... G09B 15/08 52) U.S. C....
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al.
 (12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
