(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
|
|
|
- Solomon Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 Folio (43) Pub. Date: (54) SUPPLEMENTALAUDIO CONTENT SYSTEM WITH WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FOR A CINEMA AND RELATED METHODS (75) Inventor: Richard J. Folio, Melbourne, FL (US) Correspondence Address: ALLEN, DYER, DOPPELT, MILBRATH & GILCHRIST PA CITRUS CENTER 255 SOUTHORANGE AVENUE P.O. BOX 3791 ORLANDO, FL (US) (73) Assignee: Harris Corporation, Melbourne, FL (21) Appl. No.: 09/896,894 (22) Filed: Jun. 29, 2001 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl.... H04B 3700 (52) U.S. Cl /77; 381/2 (57) ABSTRACT A Supplemental audio content System is for providing Supplemental audio content to movie patrons during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex including a plurality of individual cin emas. The System may include a player for playing Supple mental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack, and a wireless transmitter con nected to the Supplemental audio content player. An ear phone may be worn by the movie patron, and the earphone may be connected to a wireless receiver to cooperate with the wireless transmitter to deliver Supplemental audio con tent to the at least one movie patron. The wireless transmitter and wireless receiver preferably have operating character istics to avoid interference with respective Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex a e WRELESS TRANSMITTER SATELLITE MCROWAVE-> (P-to-P) INTERNET
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 5 US 2003/ A1
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 5 US 2003/ A1 23a G.) 54a CINEMA "A" G.) 35a ; SOUNDTRACK 36a T B582, SSAHAMPLIFIERS S 1. 30a -37a -S \ 50a 42a WIRELESS O IE11 trsmir Q \, 4 -? SATELLITE-TA-1, -21a MCROWAVE-> O a is (P-to-P) INTERNET 21d a - - m war wah wa m or a m - r my w - um my kit - w CINEMA "D" 23d G.) 34d : PROJ : s -37d ; G.) 35C 36d / ; SOUNDTRACK s ERSESSSFHAMPLIFIERS 2 30dy S. 42d 40d 1/ WRELESS d IE14, TRANSMITTER ge 4-7
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 5 US 2003/ A1 LE []?O HOCH LÀ NOI (HELIVWHO-JEQ) C1ECIVOT
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 5 US 2003/ A1 71 a 72a
6 Patent Application Publication Sheet 5 of 5 US 2003/ A1 WIRELESS TRANSMITTER WIRELESS RECEIVER DIGITAL 44 DIGITAL 81 MODULATOR a DEMODULATOR 3. (RADIO FREQ. P (RADIO FREQ. OR INFRARED) OR INFRARED) FIG. 5 : WIRELESS -42a : WIRELESS -80a TRANSMITTER RECEIVER SPREARSPECTRUMaa SPREARSECRUM a MODULATOR Y'a DEMODULATOR Yra (DIRECT SEQ. OR (DIRECT SEQ. OR FREQ. HOPPING) : FREQ. HOPPING). FIG. 6 : WIRELESS -42a" WIRELESS -80a" TRANSMITTER RECEIVER - Z - SEABLE 44a SBLE 81a. CHANNEL -44a CHANNEL -81a RADIO FREQ. RADIO FREO. MODULATOR I. DEMODULATOR
7 SUPPLEMENTALAUDIO CONTENT SYSTEM WITH WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FOR A CINEMA AND RELATED METHODS FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to entertainment sys tems and methods, and more particularly, to Supplemental audio content Systems and methods for cinemas of a cine plex. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002 Motion pictures are commonly shown in cine plexes which include up to twenty or more individual cinemas. Each cinema includes a movie patron Seating area, a projection Screen and a projector for displaying the motion picture on the Screen. Sound Systems are also highly devel oped, and multi-channel Soundtracks are typically played along with the motion picture. The Soundtrack information in the past has been provided typically from analog tracks adjacent the motion picture frames of the film. A number of cinemas Still use these analog Soundtracks, however, equip ment to provide higher quality digital Soundtracks has also been developed and is in use. 0003) For example, U.S. Pat. No. 6,072,760 to Shirasu, discloses the Sony Digital Dynamic Sound technology wherein an S track is provided to the left of the left perforations and a P track is provided to the right of the right perforations of the motion picture. The Sound information is thus digitally encoded as a pattern of rectangular dots or pits 22.5 microns by 24 microns U.S. Pat. No. 6,211,940 B1 discloses motion pic ture film wherein digital Sound information is Stored in the Space between a line or perforations on the Same side of the film as the analog audio Soundtrack. Since the information may be lost due to wear or mechanical damage, the System may Select the analog track if the digital information is corrupted Along these lines, U.S. Pat. No. 5, to Beard et al. discloses a digital Sound System for motion picture films wherein a digital time code is provided on the film. The digital time code is read during playing of the film, and, together with Zero crossing data from the power line, is used to Synchronize a digital Soundtrack Stored on an compact disk or digital audio tape. Accordingly, the film can be played back in theaters using either the analog or digital Sound tracks U.S. Pat. No. 5,055,939 to Karamon et al. discloses another approach to compatibility for analog and digital formats. More particularly, the patent discloses an approach that does not require Synchronizing tracks, codes, markers or time codes or other extrinsic data to be recorded on the film. Instead the standard audio itself, from the film, provides the information that controls the timing of the higher quality auxiliary Sound Source Although many approaches to supplemental audio are directed toward providing a higher quality Soundtrack, the Karamon et al. patent, for example, also discloses that alternate languages can be Synchronized to the higher qual ity auxiliary Sound Source. These translations would be available for Selection for listening by a cinema audience or by Segments of the audience sitting in preselected Seating areas having listening devices assigned to respective lan guages Another category of supplemental audio content is offered under the Theatre Vision program created by the founding president of RP International, a non-profit organi zation fighting retinitis pigmentosa (RP), and other blinding, degenerative eye diseases. Theatre Vision makes films acces Sible to the Visually challenged by incorporating a special soundtrack for feature films that runs concurrently with the dialogue of the picture. This track provides a descriptive narration of what is being shown on the Screen, So that those without Sight can Still experience the medium of motion pictures. Over the next few years, plans call for these special narrative tracts to be heard via headsets in theaters all over the United States As motion picture technology continues to progress, there are plans for distribution and presentation of motion picture entertainment entirely in digital format, that, is, without the current film with frames, etc. Unfortunately, a typical motion picture may require terabytes of digital data. Moreover, digital projectors are very costly and Still may require further technical development to be more compatible with existing film-based projectors. Accordingly, migration to an all-digital format may be many years away. An all digital approach may readily accommodate Supple mental audio content which can be stored along with the picture data and main Soundtrack data. In the meantime, however, Supplemental audio content distribution and pre Sentation in cinemas is Severely hampered and complicated by requiring compatibility with existing motion picture film equipment and formats. Moreover, delivery of the Supple mental audio content to only Selected movie patrons within a cinema may also be difficult, especially where adding wiring throughout the cinema may be cost prohibitive. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In view of the foregoing background, it is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a System and method for efficiently and economically providing Supple mental audio content to movie patrons in cinemas using motion picture film This and other objects, features and advantages in accordance with the present invention are provided by a Supplemental audio content System for providing Supple mental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas. In particular, the Supplemental audio content Sys tem may comprise a Supplemental audio content player for playing Supplemental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack, and a wireless transmitter connected to the player At least one earphone may be provided to be worn by the at least one movie patron, and the System may also include at least one wireless receiver connected to the at least one earphone and cooperating with the wireless trans mitter to deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron. Moreover, the wireless transmitter and wireless receiver may preferably have operating character istics to avoid interference with respective Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex.
8 Accordingly, the Supplemental audio content System may be readily used in many modern cineplexes without requiring extensive rewiring and without having undesired interfer ence between adjacent cinemas within the cineplex The Supplemental audio content may comprise spoken words devoid of music and sound effects. For example, the Supplemental audio content may comprise alternate language audio content, or may comprise descrip tive narrative audio content, Such as to aid the Sight impaired The wireless transmitter may use digital modula tion, that is, include a digital modulator, and the at least one wireless receiver may also use digital demodulation, that is, include a digital demodulator. For example, in one particu larly advantageous class of embodiments, the wireless trans mitter may use spread spectrum modulation, and the at least one wireless receiver may use spread Spectrum demodula tion. The Spread spectrum modulation/demodulation may be either direct Sequence or frequency hopping, for example In another class of embodiments, the wireless transmitter and the at least one wireless receiver may use at least one Selectable channel. For example, the at least one Selectable channel may comprise at least one Selectable radio frequency channel. Accordingly, interference may be readily avoided between adjacent cinemas in the cineplex by proper Selection of the frequency channels of the Supple mental audio content Systems in adjacent cinemas In some embodiments, the wireless transmitter may comprise a radio frequency RF transmitter, and the at least one wireless receiver may include at least one RF receiver. The RF transmitter and at least one RF receiver may also preferably operate in an unlicensed RF band in Some embodiments. For example, the unlicensed band may be in a range of about to GHZ, although other bands are also possible In other embodiments, the wireless transmitter may comprise an infrared transmitter, and the at least one wire less receiver may comprise at least one infrared receiver. The infrared signals will not penetrate the walls of the cinema So that interference with adjacent Systems is readily avoided The at least one wireless receiver may comprise a respective wireless receiver for each earphone. In other words, the earphone and wireless receiver may define a movie patron unit to be used by the movie patron. In addition, the movie patron unit may include an earphone level control connected to the earphone to permit the patron to Select an appropriate listening level The at least one earphone may comprise at least one open field earphone. Accordingly, the movie patron can hear the music, Sound effects, dialogue, etc. of the movie Soundtrack along with the Supplemental audio content. The Supplemental audio content player may comprise a Storage device for Storing the Supplemental audio content, and a processor for reading the Supplemental audio content from the Storage device during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack A method aspect of the invention is for delivering Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas. The method may include providing at least one movie patron unit comprising an earphone and a wireless receiver connected thereto, and wirelessly trans mitting the Supplemental audio content from a wireless transmitter to the at least one movie patron unit to thereby deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron. Moreover, the wireless transmitter and wireless receiver may have operating characteristics to avoid inter ference with respective Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0021 FIG. 1 is a schematic plan view of a cineplex illustratively including four cinemas, each cinema including the Supplemental audio content System in accordance with the present invention FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the Supplemental audio content System and related equipment as shown in FIG. 1 for two cinemas FIG. 3 is a more detailed schematic diagram of a portion of the Supplemental audio system as shown in FIG FIG. 4 is a perspective view of an embodiment of a movie patron unit of the Supplemental audio System as shown in FIG FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a wireless trans mitter and receiver as may be used in the Supplemental audio system of FIG FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of another wireless transmitter and receiver as may be used in the Supplemental audio system of FIG FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of yet another wireless transmitter and receiver as may be used in the supplemental audio system of FIG. 2. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS The present invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which preferred embodiments of the invention are shown. This invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodi ments Set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are pro Vided So that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. Like numbers refer to like elements throughout, and prime and multiple prime notation are used to indicate Similar elements in alternate embodiments Referring initially to FIG. 1, the Supplemental audio content System in accordance with the present inven tion may be used in a cineplex 20 including a plurality of individual cinemas 21a-21d. Indeed, in the illustrated embodiment of the cineplex 20, each of the cinemas 21a-21d includes a respective Supplemental audio content System 30a-30d. Each of the supplemental audio content systems 30a-30d is connected to a respective movie film projector 23a-23d. In other embodiments, not all of the cinemas 21a-21d need be So equipped as will be appreciated by those
9 skilled in the art. The number of cinemas 21 in a cineplex 20 may vary, with twenty or more cinemas not uncommon Each of the cinemas 21a-21d includes a respective room 22a-22d with a screen 24a-24d at the forward wall thereof to display the projected movie image. The rooms 22a-22d illustratively include doors 26a-26d which open into a common hallway. Stairs 33a-33d lead alongside the illustrated Seating areas 32a-32d as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. Of course, other room and Seating configurations are possible and contemplated by the present invention ) A number of the movie patrons may be interested in Some form of Supplemental audio content, Such as the descriptive narrative audio to aid the Sight-impaired, and/or alternative language audio. Accordingly, the hexagons in FIG. 1 are used to schematically indicate those movie patrons using the Supplemental audio content System, Such as by using the movie patron unit 50 as will be described in greater detail below Referring now additionally to FIG. 2, further details of the respective Supplemental audio content Systems and other related equipment for two of the cinemas 21a, 21d are now described. Each cinema 21a, 21d includes a pro jector 23a, 23d for playing a respective motion picture film 34a, 34d Each projector 23a, 23b may of the type that uses DOLBYOR processing to produce a bitstream of identifica tion data during playing. In particular, the identification information may include at least one of a reel identification, a frame identification, and a frame portion identification. For example, the reel may be identified with a number, Such as reel 6, and the frame and frame portion may be identified with a continuous running number count or film block number. In View of the typical number of frames, and Since each frame may be divided into four portions, the block number may range from 0 to about 260,000, depending on the length of the motion picture Digital data packets may be encoded in twodimen sional blocks, with four blocks for each picture frame, for example, on the film. Since twenty-four frames are com monly shown per Second, 96 data packets are output per Second. Each data packet may include 32 bytes of identifi cation information. Further details regarding the two-dimen Sional encoding and reading are disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 6,211,940, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. Of course, those of skill in the art will appreciate that other data formats are also contemplated by the invention The respective digitally encoded soundtrack infor mation may be processed by the Soundtrack processors 35a, 35d. The soundtrack processors 35a, 35d, in turn are con nected to respective amplifiers 36a, 36d which drive the sets of speakers 37a, 37d in the cinemas 21a, 21d. These components are conventional and need no further discussion herein. 0036). In the illustrated embodiment, a Supplemental audio content player in the form of a personal computer 40a, 40d is provided in each cinema 21a, 21d, such as in the projection room, for example, and as part of the Supplemen tal audio content system 30a, 30d. As will be described in greater detail below, the personal computers 40a, 40d may be used in Some embodiments to provide the Signal pro cessing to Synchronize playing of the respective Supplemen tal audio content with the playing of the motion picture film 34a, 34d The personal computers 40a, 40d are also illustra tively connected to a common Server 41. The common Server 41 may be used to receive the Supplemental audio content via the Internet in Some embodiments. This content pushed via the Internet may be stored on the server 41 for later playing, or may be preprocessed and Stored as described in greater detail below The supplemental audio content can also be received via Satellite distribution (point-to-multipoint) or via a point-to-point communications link, eg. microwave link, as also Schematically illustrated. Of course, in other embodi ments, the Server 41 may acquire the Supplemental audio content as data Stored on digital disks, digital tapes, or other Similar physically transported media The server 41 is illustratively connected to each of the projection room personal computers 40a, 40d, Such as via a wired or wireless local area network (LAN) as will be readily appreciated by those skilled in the art. AS will also be appreciated by those skilled in the art, the Server 41 may not be needed in other embodiments One important aspect is that the Supplemental audio content Signals during playing can be distributed or delivered to movie patrons in the cinema via a wireless communications link. More particularly, as Schematically shown in FIG. 2, each personal computer 40a, 40d may be connected to a respective wireless transmitter 42a, 42d. The wireless transmitters 42a, 42d then communicate with cor responding wireless receivers in the respective movie patron units 50a, 50d as will also be described in greater detail below. The wireless link may be infrared or radio frequency (RF) as also described in greater detail below. These approaches may be employed to reduce the likelihood of interference between adjacent cinemas 21a-21d in the cine plex Referring now additionally to FIG. 3, various processing Steps and portions of a Supplemental audio content system 30a are now described. For clarity of expla nation, only a single system 30a will be described in detail, and those of skill in the art will recognize that the other Systems in the cineplex 20 may the same or Similar The system 30a includes a clock 50a connected to the time tagger 51a. The clock 50a may be the clock or the personal computer 4.0a or derived therefrom, as Such pro vides an accurate wall clock'source for further processing. The time tagger 51a deformats the identification data pack ets output from the projector 23a. The time tagger 51a also time tags or associates with the data, a time based upon the clock 50a. In other words, the time tagger 51a cooperates with the clock 50a for generating time tagged identification data based upon the identification data from the motion picture film 34a during playing thereof The time tagger 51a is illustratively connected to a Synchronizer 52a for Synchronizing playing of the Supple mental audio content with playing of the motion picture film 34a and associated Soundtrack and based upon the time tagged identification data. More particularly, the Synchro nizer 52a may play the Supplemental audio content at a play
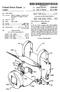
10 rate based upon the time tagged identification data to Syn chronize with playing of the motion picture film. In addition, the Synchronizer 52a may also skip ahead or wait while playing the Supplemental audio content based upon the time tagged identification data to Synchronize with playing of the motion picture film. Skipping ahead, for example, may be desired where splices have been made to the motion picture film and a number of frames have been deleted, as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. 0044) To perform these functions, the synchronizer 52a may include a time base generator 54.a for generating a time base signal based upon the time tagged identification data, and an output stage 55a for playing the Supplemental audio content at a rate based upon the time base Signal from the time base generator 54a. To improve Synchronization, the illustrated Synchronizer 52a also further comprises a time base correction controller 56a for adjusting the time base generator 54a based upon the time tagged identification data. In other words, the time base correction controller 56a may provide feedback control to follow the rate of playing of the motion picture film 34a which can vary. The playing rate may be varied slightly without causing undesired changes in pitch of Supplemental audio content as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art Turning now to the bottom portion of FIG. 3, preprocessing Steps as may enhance Synchronization are now described. Such preprocessing may be performed by the preprocessor 60a. The preprocessor 60a may be imple mented in the server 41 (FIG. 2) or in the personal computer 40a, or the functions may be shared, as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. The preprocessing may also be performed by the originating Source prior to delivery to the cineplex 20 in other embodiments. 0046) The illustrated preprocessor 60a is for preprocess ing the Supplemental audio content to identify quiet portions between adjacent live portions. Since the Supplement audio content is preferably spoken words, e.g. dialogue or descrip tive narration, there are typically pauses between words, or between phrases or Sentences. These pauses, for example, define quiet portions which can be extended or reduced in order to aid Synchronization during playing. As an example, a quiet portion may be identified as occurring between reel X, and between block numbers Y and Y--75. Of course, quiet portions can be considerably longer or shorter as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art Once identified during preprocessing and associ ated with the identification information that is also used on the motion picture film or which can be correlated therewith, these quiet portions can be extended or reduced by the illustrated sample formatter 57a. Of course, by reduced is also meant to include the complete reduction or elimination of a quiet portion, and extended is meant to cover the creation of a quiet portion. To reduce noise which may otherwise be generated, the sample formatter 57a may hold a prior Sample during extension of a quiet portion as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art The preprocessor 60a illustratively includes a first memory 61 a for Storing the downloaded Supplemental audio content. The Supplemental audio content is upsampled in the illustrated upsampler 62a to match the desired play Sample rate. The Supplemental audio content is then processed to determine quiet portions and their locations in the illustrated quiet portion processor and tagger 63a. This quiet portion processor and tagger 63a can be provided by the micropro cessor of the portable computer 4.0a of the projection area, or the common server 41 as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. This preprocessed Supplemental audio content may then be stored in the second memory 64a for use during playing. This Second memory 64a may typically be the hard drive of the portable computer 40a associated with the projection room. Of course, the preprocessed Supplement audio content can also be Stored in the first memory along with the downloaded content, or in place of the downloaded content Turning now to FIG.4, a movie patron unit 50a for the Supplemental audio content System 30a is now described. The movie patron unit 50a delivers the Supple mental audio content to the movie patron. The illustrated movie patron unit 50a includes an earphone 70a connected to a headband 71a to be worn on the head of the movie patron. In other embodiments, a pair of earphones may be provided. Also, the headband 71a may not be needed in other embodiments where the earphone 70a is otherwise attachable adjacent the movie patron's ear. The earphone 70a may be an open field earphone that allows the patron to hear the music, Sound effects, main dialogue, etc. from the main Soundtrack, while also hearing the Supplemental audio content from the earphone The earphone 70a is connected to an associated device 73a via a cable 72a. The device 73a may include a housing 74a containing associated electronics, Such as an amplifier 79a and may also carry level setting Switches 75a on a portion of the housing. A battery, not shown, may also be carried by the housing 74a. Where the Supplemental audio content is an alternate language, Selector Switches 76a may be used to allow the movie patron to Select the desired alternate language. In other embodiments, the device 73a may be constructed or arranged together with the earphone 70a, Such as part of a headset, for a more compact arrange ment In some other embodiments, such as for construc tion of a new cinema, wiring may be run to each movie Seating position, So that the movie patron unit 50a may be a simple headset which plugs into a Suitable jack at the Seating position. It should be recognized by those skilled in the art, however, that retrofitting Such extensive wiring to an existing cinema may be cost prohibitive. Accordingly, another aspect of the Supplemental audio content System 30a is that a wireless communications link may be used instead of wired links to each movie Seat position. Thus, the device 73a may include a wireless receiver 80a carried within the housing 74a as will be described in greater detail below. Moreover, Since motion pictures are typically now shown in cineplexes 20 including multiple cinemas 21a-21d, it is also highly desirable that interference be Suppressed between adjacent Systems using wireless communications links Referring now additionally to FIGS. 5-7, various embodiments of wireless transmitters and receivers for implementing wireless communications links are now described. In particular as shown in FIG. 5, to reduce interference, the wireless transmitter 42a may include a digital modulator 44a. Correspondingly, the wireless receiver 80a may include a digital demodulator 81a. For example, the digital modulator and demodulator may oper ate over radio frequency bands or in the infrared band.
11 0.053 Infrared operation offers the advantage that infra red radiation will not pass through the walls of the cinema, therefore interference with adjacent cinemas is prevented. However, delivering the infrared signals within the cinema requires that there be no Substantial blockage between the transmitter and each receiver RF operation offers the advantage over infrared of being less Susceptible to blockage of a direct path between the transmitter and the receivers; however, RF operation may be more Susceptible to interference. The digital modu lation may offer advantages in avoiding interference, espe cially, for example, where spread Spectrum modulation is used, as illustratively shown in FIG. 6. More particularly, the wireless transmitter 42a" may include a spread spectrum modulator 44a' and the wireless receiver 80a' may include a Spread Spectrum demodulator 81a'. The Spread spectrum may be either direct Sequence or frequency hopping as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. As will also be appreciated by those skilled in the art, multiple Such spread Spectrum communications links can be operated adjacent one another, as in adjacent cinemas 21a-21d, without caus ing undesirable mutual interference The RF spread spectrum wireless transmitter 42a' and wireless receiver 80a' may also preferably operate in an unlicensed band, Such as the to GHz ISM band. The wireless link may be the same as or similar to those used for wireless LANs (WLANs) operating in accordance with the standard as will be appreciated by those skilled in the art. As will also be understood by those skilled in the art, other unlicensed bands are also available. Operation in an unlicensed band offers the advantage of not requiring application for and approval of government operating licenses for the cineplex Turning now to FIG. 7, another embodiment of wireless communications link is explained. In this embodi ment, the wireless transmitter 42a" includes a Selectable channel RF modulator 44a". Correspondingly, the wireless receiver 80a" includes a selectable channel RF demodulator 81a" that is set to the same channel as the transmitter. Accordingly, operation at different frequencies, or at differ ent polarizations or other codings, for example, can be used to provide multiple channels within the cineplex 20 that are less likely to interfere with one another. Of course, those of skill in the art will appreciate other equivalent wireless communications Schemes that provide reduced interference, but provide the advantages of wireless communications One method aspect in accordance with the inven tion is for providing Supplemental audio content during playing of a motion picture film including identification data thereon. The method preferably comprises generating time tagged identification databased upon a clock and the iden tification data from the motion picture film during playing thereof, and Synchronizing playing of the Supplemental audio content with playing of the motion picture film and based upon the time tagged identification data. Synchroniz ing may comprise playing the Supplemental audio content at a play rate based upon the time tagged identification data to Synchronize with playing of the motion picture film. In addition, Synchronizing may skip ahead or wait while play ing the Supplemental audio content based upon the time tagged identification data to Synchronize with playing of the motion picture film Another method aspect of the invention is for delivering Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associ ated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex 20 comprising a plurality of individual cinemas 21a-21d. The method may include providing at least one movie patron unit 50a com prising an earphone 70a and a wireless receiver 80a con nected thereto, and wirelessly transmitting the Supplemental audio content from a wireless transmitter to the at least one movie patron unit 50a to thereby deliver supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron. Moreover, the wireless transmitter and wireless receiver 42a, 80a (FIG. 5); 42, 80a' (FIG. 6); and 42a", 80a" (FIG. 7) may have operating characteristics to avoid interference with respec tive Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex 20 (FIG. 1) In addition, other features relating to supplemental audio content Systems are disclosed in copending patent application filed concurrently here with and assigned to the assignee of the present invention and entitled SUPPLE MENTALAUDIO CONTENT SYSTEM FOR A CINEMA AND RELATED METHODS, attorney work docket number 51220, the entire disclosure of which is incorporated herein in its entirety by reference. Therefore, it is to be understood that the invention is not to be limited to the specific embodiments disclosed, and that modifications and embodi ments are intended to be included within the scope of the appended claims. That which is claimed is: 1. A Supplemental audio content System for providing Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas, the Supplemental audio content System comprising: a Supplemental audio content player for playing Supple mental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack; a wireless transmitter connected to Said Supplemental audio content player; at least one earphone to be worn by the at least one movie patron; and at least one wireless receiver connected to Said at least one earphone and cooperating with Said wireless transmit ter to deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron; Said wireless transmitter and wireless receiver having operating characteristics to avoid interference with respective Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex. 2. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises spoken words devoid of music and Sound effects. 3. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises alternate language audio content. 4. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises descriptive narrative audio content. 5. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises a digital
12 modulator, and wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises a digital demodulator. 6. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises a spread Spectrum modulator, and wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises a spread spectrum demodulator. 7. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 6 wherein Said spread Spectrum modulator uses direct Sequence spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said Spread spectrum demodulator uses direct Sequence spread Spectrum demodulation. 8. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 6 wherein Said spread spectrum modulation uses frequency hopping spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said spread Spectrum demodulator uses frequency hopping spread spectrum demodulation. 9. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said wireless transmitter and Said at least one wireless receiver use at least one Selectable channel. 10. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 9 wherein the at least one Selectable channel com prises at least one Selectable radio frequency channel. 11. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises a radio frequency (RF) transmitter; and wherein said at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one RF receiver. 12. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 11 wherein said RF transmitter and at least one RF receiver operate in an unlicensed RF band. 13. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 11 wherein Said RF transmitter and Said at least one RF receiver operate in a range of about to Ghz. 14. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises an infrared transmitter; and wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one infrared receiver. 15. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises a respective wireless receiver for each at least one earphone. 16. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 further comprising at least one earphone level control connected to Said at least one earphone. 17. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said at least one earphone comprises at least one open field earphone. 18. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 1 wherein Said Supplemental audio content player comprises: a storage device for Storing the Supplemental audio con tent; and a processor for reading the Supplemental audio content from Said Storage device during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack. 19. A Supplemental audio content System for providing Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas, the Supplemental audio content System comprising: a Supplemental audio content player for playing Supple mental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack; a wireless transmitter connected to Said Supplemental audio content player; and at least one movie patron unit comprising an earphone and a wireless receiver connected thereto and cooperating with Said wireless transmitter to deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron; Said wireless transmitter and wireless receiver comprising a digital modulator and a digital demodulator respec tively to avoid interference with respective Supplemen tal audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex. 20. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises spoken words devoid of music and Sound effects. 21. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises alternate language audio content. 22. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises descriptive narrative audio content. 23. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said digital modulator uses direct Sequence Spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said digital demodulator uses direct Sequence spread spectrum demodu lation. 24. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said digital modulator uses frequency hopping Spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said digital demodulator uses frequency hopping spread spec trum demodulation. 25. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said wireless transmitter and Said at least one wireless receiver use at least one Selectable channel. 26. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 25 wherein the at least one Selectable channel com prises at least one Selectable radio frequency channel. 27. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises a radio frequency (RF) transmitter; and wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one RF receiver. 28. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises an infrared transmitter; and wherein Said at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one infrared receiver. 29. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said movie patron unit further comprises an earphone level control connected to Said earphone. 30. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said earphone comprises an open field earphone. 31. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 19 wherein Said Supplemental audio content player comprises: a storage device for Storing the Supplemental audio con tent; and a processor for reading the Supplemental audio content from Said Storage device during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack. 32. A Supplemental audio content System for providing Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated
13 Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas, the Supplemental audio content System comprising: a Supplemental audio content player for playing Supple mental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack; a wireless transmitter connected to Said Supplemental audio content player; at least one earphone to be worn by the at least one movie patron; and at least one wireless receiver connected to Said at least one earphone and cooperating with Said wireless transmit ter to deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron; Said wireless transmitter and wireless receiver comprising a spread Spectrum modulator and a spread Spectrum demodulator respectively. 33. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises spoken words devoid of music and Sound effects. 34. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises alternate language audio content. 35. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises descriptive narrative audio content. 36. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein said spread spectrum modulator uses direct Sequence Spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said spread spectrum demodulator uses direct Sequence Spread spectrum demodulation. 37. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein Said spread spectrum modulator uses frequency hopping spread spectrum modulation; and wherein Said spread Spectrum demodulator uses frequency hopping spread spectrum demodulation. 38. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein Said wireless transmitter comprises a radio frequency (RF) transmitter; and wherein said at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one RF receiver. 39. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 38 wherein said RF transmitter and at least one RF receiver operate in an unlicensed RF band. 40. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 38 wherein said RF transmitter and said at least one RF receiver operate in a range of about to Ghz. 41. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 further comprising at least one earphone level control connected to Said at least one earphone. 42. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein Said at least one earphone comprises at least one open field earphone. 43. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 32 wherein Said Supplemental audio content player comprises: a storage device for Storing the Supplemental audio con tent; and a processor for reading the Supplemental audio content from Said Storage device during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack. 44. A Supplemental audio content System for providing Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas, the Supplemental audio content System comprising: a Supplemental audio content player for playing Supple mental audio content during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack; an infrared transmitter connected to Said Supplemental audio content player; at least one earphone to be worn by the at least one movie patron; and at least one infrared receiver connected to Said at least one earphone and cooperating with Said wireless transmit ter to deliver Supplemental audio content to the at least one movie patron. 45. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises spoken words devoid of music and Sound effects. 46. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises alternate language audio content. 47. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 wherein the Supplemental audio content comprises descriptive narrative audio content. 48. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 further comprising at least one earphone level control connected to Said at least one earphone. 49. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 wherein Said at least one earphone comprises at least one open field earphone. 50. A Supplemental audio content System according to claim 44 wherein Said Supplemental audio content player comprises: a storage device for Storing the Supplemental audio con tent; and a processor for reading the Supplemental audio content from Said Storage device during playing of the motion picture and associated Soundtrack. 51. A method for delivering Supplemental audio content to at least one movie patron during playing of a motion picture film and associated Soundtrack in a cinema of cineplex comprising a plurality of individual cinemas, the method comprising: providing at least one movie patron unit comprising an earphone and a wireless receiver connected thereto, and wirelessly transmitting the Supplemental audio content from a wireless transmitter to the at least one movie patron unit to thereby deliver Supplemental audio con tent to the at least one movie patron; the wireless transmitter and wireless receiver having operating characteristics to avoid interference with respective Supplemental audio content Systems for other cinemas of the cineplex. 52. A method according to claim 51 wherein the Supple mental audio content comprises spoken words devoid of music and Sound effects.
14 53. A method according to claim 51 wherein the supple mental audio content comprises alternate language audio COntent. 54. A method according to claim 51 wherein the supple mental audio content comprises descriptive narrative audio COntent. 55. A method according to claim 51 wherein the wireless transmitter uses digital modulation; and wherein the at least one wireless receiver uses digital demodulation. 56. A method according to claim 51 wherein the wireless transmitter uses spread spectrum modulation; and wherein the at least one wireless receiver uses spread spectrum demodulation. 57. A method according to claim 56 wherein the spread Spectrum modulation comprises direct Sequence spread Spectrum modulation; and wherein the Spread spectrum demodulation comprises direct Sequence spread spectrum demodulation. 58. A method according to claim 56 wherein the spread Spectrum modulation comprises frequency hopping spread Spectrum modulation; and wherein the Spread spectrum demodulation comprises frequency hopping spread Spec trum demodulation. 59. A method according to claim 51 wherein the wireless transmitter and the at least one wireless receiver use at least one Selectable channel. 60. A method according to claim 59 wherein the at least one Selectable channel comprises at least one Selectable radio frequency channel. 61. A method according to claim 51 wherein the wireless transmitter comprises a radio frequency RF transmitter; and wherein the at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one RF receiver. 62. A method according to claim 51 wherein the wireless transmitter comprises an infrared transmitter; and wherein the at least one wireless receiver comprises at least one infrared receiver. 63. A method according to claim 51 wherein the movie patron unit further comprises an earphone level control connected to the earphone. 64. A method according to claim 51 wherein the earphone comprises an open field earphone.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(19) United States US 2012O114336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0114336A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 10, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) NETWORK DGITAL SIGNAGE SOLUTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(19) United States US 20100057781A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Stohr (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 (54) MEDIA IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.... 707/104.1: 709/203; 707/E17.032;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
2) }25 2 O TUNE IF. CHANNEL, TS i AUDIO
 US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
US 20050160453A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2005/0160453 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) APPARATUS TO CHANGE A CHANNEL (52) US. Cl...... 725/39; 725/38; 725/120;
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
US 2008O1891. 14A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0189114A1 FAIL et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR ASSISTING (22) Filed: Mar.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 20130260844A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0260844 A1 Rucki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SERIES-CONNECTED COUPLERS FOR Publication Classification ACTIVE
US 20130260844A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0260844 A1 Rucki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SERIES-CONNECTED COUPLERS FOR Publication Classification ACTIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
III. USOO A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998
 III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 18527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0118527 A1 Wachob et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2017 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING H04N 7/2 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 201701 18527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0118527 A1 Wachob et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2017 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING H04N 7/2 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, Ireland /1958 Fed. Rep. of Germany...
 IIIHIIIHIIIHIII USOO5326297A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 (54) LIFE JACKET 4,241,459 12/1980 Quayle... 2102 O 5,029,293 7/1991 Fontanille...
IIIHIIIHIIIHIII USOO5326297A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 (54) LIFE JACKET 4,241,459 12/1980 Quayle... 2102 O 5,029,293 7/1991 Fontanille...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070O8391 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0083910 A1 Haneef et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SEAMILESS Publication Classification
US 20070O8391 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0083910 A1 Haneef et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SEAMILESS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O140615A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0140615 A1 Kerrisk et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS, DEVICES AND METHODS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2016O140615A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0140615 A1 Kerrisk et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS, DEVICES AND METHODS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
(19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A 7001Ö
 Serial Number 09/678.881 Filing Date 4 October 2000 Inventor Robert C. Higgins NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
Serial Number 09/678.881 Filing Date 4 October 2000 Inventor Robert C. Higgins NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004815 A1 Schultz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MASKING Related U.S.
(19) United States US 2011 0004815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004815 A1 Schultz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MASKING Related U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,717,620 B1
 USOO671762OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chow et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,579,052 A 11/1996 Artieri... 348/416 DECOMPRESSING COMPRESSED DATA 5,623,423
USOO671762OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chow et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,579,052 A 11/1996 Artieri... 348/416 DECOMPRESSING COMPRESSED DATA 5,623,423
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003OO3O269A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030269 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE RECEIPT DIARY WITH (52) U.S. Cl.... 283/63.1 ADHESIVE STRIP
US 2003OO3O269A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030269 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE RECEIPT DIARY WITH (52) U.S. Cl.... 283/63.1 ADHESIVE STRIP
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) United States Patent Imai et al. USOO6507611B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 14, 2003 (54) TRANSMITTING APPARATUS AND METHOD, RECEIVING APPARATUS AND METHOD, AND PROVIDING MEDIUM (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2
 US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
USOO9609033B2 (12) United States Patent Hong et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 28, 2017 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SHARING PRESENTATION DATA AND ANNOTATION (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS
(12) United States Patent
 US0079623B2 (12) United States Patent Stone et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 11 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY OF MULTIPLE
US0079623B2 (12) United States Patent Stone et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 11 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY OF MULTIPLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0347114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0347114A1 YOON (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR H04L 29/06 (2006.01) CONTROLLING
(19) United States US 2015.0347114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0347114A1 YOON (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR H04L 29/06 (2006.01) CONTROLLING
CAUTION: RoAD. work 7 MILEs. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0303458 A1 Schuler, JR. US 20120303458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) GPS CONTROLLED ADVERTISING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0303458 A1 Schuler, JR. US 20120303458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 29, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) GPS CONTROLLED ADVERTISING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl. M M 110 / <E
 (19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
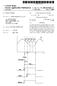 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001
 (12) United States Patent US006301556B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001 (54) REDUCING SPARSENESS IN CODED (58) Field of Search..... 764/201, 219, SPEECH
(12) United States Patent US006301556B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,301,556 B1 Hagen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 9, 2001 (54) REDUCING SPARSENESS IN CODED (58) Field of Search..... 764/201, 219, SPEECH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
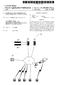 US 20070011710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chiu (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) INTERACTIVE NEWS GATHERING AND Publication Classification MEDIA PRODUCTION
US 20070011710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chiu (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) INTERACTIVE NEWS GATHERING AND Publication Classification MEDIA PRODUCTION
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,058,377 B1. Mitsdarffer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006
 United States Patent US007058377B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Mitsdarffer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) DUAL CHANNEL DOWNCONVERTER FOR 5,508,605 A 4/1996 Lo et al.... 324f76.42 PULSED RADIO
United States Patent US007058377B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Mitsdarffer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) DUAL CHANNEL DOWNCONVERTER FOR 5,508,605 A 4/1996 Lo et al.... 324f76.42 PULSED RADIO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
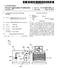 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2012
 USOO8176425B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2012 (54) ANIMATED SCREEN OBJECT FOR 5,537,528 7/1996 Takahashi et al. ANNOTATION AND SELECTION OF VIDEO
USOO8176425B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2012 (54) ANIMATED SCREEN OBJECT FOR 5,537,528 7/1996 Takahashi et al. ANNOTATION AND SELECTION OF VIDEO
United States Patent 19 11) 4,450,560 Conner
 United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,149,941 B2
 USOO8149941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2012 (54) DTV TELEVISION (56) References Cited TRANSMITTER/RECEIVER AND METHOD OF PROCESSING DATANDTV U.S.
USOO8149941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2012 (54) DTV TELEVISION (56) References Cited TRANSMITTER/RECEIVER AND METHOD OF PROCESSING DATANDTV U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9064484B1 (12) United States Patent Jääskeläinen et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) METHOD OF PROVIDING FEEDBACK ON PERFORMANCE
USOO9064484B1 (12) United States Patent Jääskeläinen et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) METHOD OF PROVIDING FEEDBACK ON PERFORMANCE
Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993
 United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5258937A Patent Number: 5,258,937 Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993 54 ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75 inventor: Fletcher
United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5258937A Patent Number: 5,258,937 Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993 54 ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75 inventor: Fletcher
METHOD, COMPUTER PROGRAM AND APPARATUS FOR DETERMINING MOTION INFORMATION FIELD OF THE INVENTION
 1 METHOD, COMPUTER PROGRAM AND APPARATUS FOR DETERMINING MOTION INFORMATION FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to motion 5tracking. More particularly, the present invention relates to
1 METHOD, COMPUTER PROGRAM AND APPARATUS FOR DETERMINING MOTION INFORMATION FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to motion 5tracking. More particularly, the present invention relates to
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand
 United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
105-HOO-104. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 20, KUMAR et al.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/011010.6 A1 KUMAR et al. US 201701 1 0 1 06A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) CALIBRATION AND STABILIZATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/011010.6 A1 KUMAR et al. US 201701 1 0 1 06A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) CALIBRATION AND STABILIZATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1
 USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
