(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Heather Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung, Miaoli Hsien (TW) (73) Assignee: Au Optronics Corporation, Hsinchu (TW) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. (21) Appl. No.: 10/065,631 (22) Filed: Nov. 5, 2002 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 16, 2002 (TW) A (51) Int. Cl.... G09G 3/30 (52) U.S. Cl /169.3; 34.5/92; 34.5/82 (58) Field of Search / ; 345/82 86, 55, 62, 65, 72, 75, 76, 92 (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 5,095,248 A 3/1992 Sato / ,509,692 B2 * 1/2003 Komiya / ,580,408 B1 6/2003 Bae et al /76 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner Wilson Lee (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Jiang Chyun IP Office (57) ABSTRACT Adriving circuit for a light emitting device is Suitable for use in an active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) display, which has a Scanning line to be input with a Scanning clock signal, So as to control the driving circuit. The driving circuit includes a driving circuit main part which includes a light emitting device driven by a driving transistor as well as a Scan line connection terminal and a data line connection terminal. The Scan line connection terminal receives a Scanning clock signal. A first transistor has a gate connected to this Scan line connection terminal, a Source. connected to the data line connection terminal, and a drain connected to a gate electrode of the driving transistor. A Second transistor has a gate electrode connected to the Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to a common Voltage, and a drain connected to an anode of the light emitting device. The common Voltage has a high Voltage level and a low Voltage level, alternating by a frequency, wherein the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is higher than a System low Voltage and the low voltage level is smaller than the system low voltage. When the first transistor and the Second transistor are Simulta neously activated by the Scanning clock signal, the data line can be input with an image digital data Voltage or a negative turning-off voltage. When the common Voltage is at the low voltage level, the turning-off voltage is input, So as to turn off the driving transistor and the light emitting device. 22 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets
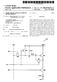
2 U.S. Patent Jan. 20, 2004 Sheet 1 of 3 US 6,680,580 B1 V doto V -? 100 WDD 106-/ Vref V v?. ED Vss FIG. 1 (PRIOR ART) Time FIG. 2 (PRIOR ART FIG. 3 Time
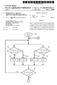
3 U.S. Patent Jan. 20, 2004 Sheet 2 of 3 US 6,680,580 B1 O Off O off : Different 1Groy Scales FIG. 5
4 U.S. Patent Jan. 20, 2004 Sheet 3 of 3 US 6,680,580 B1 Frome inverse Frome One Frome Two Of Of Of O... off off off off... Of Of O. Of... off off off off... O. Of Of Of. off off off Off... O. Of Of O... off off off off... FIG. 6A line inverse Frome One Frome Two Of O. Of O?... off off off off... off off off off... O. O. Of O... Of Oi Oi Of... Off Off Off off... off off off off... Of Of Of Of. FIG. 6B
5 1 DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims the priority benefit of Taiwan application serial no , filed on Sep. 16, BACKGROUND OF INVENTION 1. Field of Invention The present invention generally relates to a light emitting device display technique, and more particularly, to a driving technique of the active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED), so as to increase the driving voltage of the light emitting device as well as the Stability with regard to the time passed by. 2. Description of Related Art Accompanying the development of high technology, Video products, especially the digital Video or image devices, have become a popular product in our daily life. Within these digital Video or image devices, display devices are an important element for displaying the related infor mation. The users can read the information from the display further to control the device operation. In order to comply with modern life, the size of the video or image device is getting thinner and lighter. The conven tional Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) display occupies a large capacity and consumes more electricity. Therefore, comply ing with photoelectron and Semiconductor manufacturing technologies, the panel display device has been developed and has become a common used display product, like the LCD or the active matrix organic light emitting diode display. LCD technology has developed for Several years, So it is hard to have a breakthrough now. However, the active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) display technology, a newly developed technology, will be main Stream of the display device accompanying LCD in the future. The major feature of the AMOLED display is using TFT technique to drive the organic light emitting diode, and the driving IC is installed on the panel directly, so as to fulfill the requirement of being light/thin/short/small in Volume and reducing cost. The AMOLED display can be applied on the medium or Small size panel in cellular phone, PDA, digital camera and palm game player, portable DVD player and the automobile global positioning System, which can even be implemented in a large size panel like computer and plane TV in the future. The digital display is characterized by a display Screen composed of multiple pixels in a matrix arrangement man ner. In order to control individual pixels, a specific pixel is commonly Selected via a Scanning line and a data line, and an appropriate operating Voltage is also provided, So as to display the display information corresponding to this pixel. FIG. 1 schematically shows a sketch map of an AMOLED circuit that drives a corresponding pixel in the prior art. Referring to FIG. 1, the driving circuit comprises transistors 100 and 102. The transistor is Such as the thin film transistor (TFT). A gate of the transistor 100 connects to the scanning line and receives a Scanning Voltage VScan at an appropriate point of time, and a source of the transistor 100 also receives a digital data Voltage Vdata Sent from the data line at this point of time. A drain of the transistor 100 connects to a gate of the transistor 102. Generally Speaking, the Source and the US 6,680,580 B drain of the transistor are Swappable. The case shown in the present invention is only exemplified here for description. In addition, a Storage capacitor 106 is connected in between the gate of the transistor 102 and a grounded Voltage. The drain of the transistor 102 connects to a Voltage Source V, the Source of the transistor 102 further connects to an anode of the organic light emitting device 104, and a cathode of the organic light emitting device 104 connects to a correspond ing low Voltage Vss. The operation principle of the driving circuit shown in FIG. 1 mentioned above is described as follows. When the gate of the transistor 100 is activated by receiving the Vscan provided by the Scanning line, the digital data Voltage Vdata is input into the gate of the transistor 100, so as to activate the transistor 102. Meanwhile, the voltage source V, flows into the organic light emitting device 104 via the transistor 102, and makes it emit the light. The transistor 102 is also generally called a driving device. When the circuit is operating, the Scanning line clock Vscan is input into the transistor 100 with a pre-determined frequency, and the time period between its clock pulses is also called a frame. A pre-determined image data block is input into the corre sponding pixel during a time period of the frame. When the Scanning line clock pulse VScan activates the transistor 100, the transistor 102 is also subsequently activated by the digital data Voltage, and the digital data Voltage Vdata is also Stored in the Storage capacitor 106, So as to maintain the activation of the transistor 102. Therefore, the conventional organic light emitting device 104 always stays in the activation state in any of the frames. The variance only exists in the fact that the conventional Voltage Vdata has different display gray Scales in different frames. In other words, the light emitting device of the TFT-AMOLED always makes it stay at the emitting state in the conventional design. Conventionally, Such emitting method complies with the image display effect and is able to avoid the picture flicking. In order to have the light emitting device continuously be driven, relatively, the transistor 102 must maintain its activation State. However, when the light emitting device 104, such as the organic light emitting diode, is operated for a long time period, there is a driving current continuously flowing through the light emitting device 104. Therefore, its char acteristic Such as the driving Voltage V, increases Over time. Thus, the light emitting State of the light emitting device, Such as the variances of the brightness and color, are impacted as shown in FIG. 2. The relationship between the effect caused by the deviation of the driving Voltage V and the driving circuit cooperated with the TFT is described hereinafter. When the organic light emitting device 104 is activated, the TFT driving current I has a relationship as shown in formula (1) (4): I=/2k(V- Vs- V.)? (2) Vs=Votep--Vss (3) I=/2k(V- Votep-Vss- V.)? (4) where k is a TFT characteristic constant, V=Vdata, and V is the driving voltage of the light emitting device 104. As shown in the formula (1) (4) above, when the driving Voltage Vo increases, Since it is activated for a long time, the driving current I flowing through the organic light emitting device 104 reduces accordingly, thus impacts
6 3 the light emitting condition of the organic light emitting device 104, and the brightness is also reduced accordingly. The life of the organic light emitting device 104 depends on its light emitting capability. Therefore, the variance of the driving Voltage Vo greatly impacts the organic light emitting device 104. In addition, similarly, when the transistor 102 is activated for a long time, its threshold Voltage Vth increases accord ingly. The threshold voltage Vth is the same as the driving voltage V, the current flowing through the light emit ting device 102 reduces when the threshold voltage Vth increases. Therefore, the threshold voltage Vth further dete riorates the light emitting quality. SUMMARY OF INVENTION Therefore, the present invention provides a driving circuit for the light emitting device, able to avoid the deviation of the driving Voltage V of the light emitting device, and at least maintaining the driving Voltage V on a stable value even under a long time operation of displaying image, So as to efficiently improve the display product quality. Furthermore, the threshold voltage Vth can also maintain a stable value without any deviation. The present invention provides a driving circuit for a light emitting device, Suitable for use in an active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED), which has a scanning line to be input with a Scanning clock Signal, So as to control the driving circuit. The driving circuit includes a driving circuit main part which includes a light emitting device driven by a driving transistor as well as a Scanline connection terminal and a data line connection terminal. The Scan line connec tion terminal receives a Scanning clock signal. A first tran Sistor has a gate connected to this Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to the data line connection terminal, and a drain connected to a gate electrode of the driving transistor. A Second transistor has a gate electrode connected to the Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to a common Voltage, and a drain connected to an anode of the light emitting device. The common Voltage has a high Voltage level and a low Voltage level, alternating by a frequency, wherein the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is higher than a System low Voltage and the low voltage level is smaller than the system low voltage. When the first transistor and the Second transistor are Simulta neously activated by the Scanning clock signal, the data line can be input with an image digital data Voltage or a negative turning-off Voltage. When the common Voltage is at the low Voltage level, the negative turning-off voltage is input, So as to turn off the driving transistor and the light emitting device. AS described above, the light emitting device mentioned above comprises an organic light emitting diode. AS described above, the high Voltage level of the common voltage mentioned above is 0 V, and the low voltage level mentioned above is a negative Voltage. AS described above, the negative turning-off voltage mentioned above is smaller than the low voltage level of the common Voltage mentioned above. AS described above, when the first transistor and the Second transistor mentioned above are simultaneously acti Vated by the Scanning clock signal mentioned above, the data line mentioned above can be input with an image digital data Voltage mentioned above to display an image. AS described above, the frequency of the common Voltage mentioned above varies in a period of one frame to drive an ON/OFF state of the corresponding multiple scanning lines, So as to achieve a frame inverse operation. US 6,680,580 B1 1O AS described above, the frequency of the common Voltage mentioned above uses the Scanning line as one unit accord ing to the Scanning clock Signal mentioned above, So as to achieve a line inverse operation. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS The accompanying drawings are included to provide a further understanding of the invention, and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this Specification. The drawings illustrate embodiments of the invention, and together with the description, Serve to explain the principles of the inven tion. In the drawings, FIG. 1 schematically shows a sketch map of a AMOLED circuit that drives a corresponding pixel in the prior art; FIG. 2 Schematically shows a sketch map of a variance of the driving Voltage of the light emitting device when it is varied with the activation time in the prior art, FIG.3 schematically shows a sketch map of a variance of the driving Voltage of the light emitting device when it is varied with the activation time according to the present invention; FIG. 4 schematically shows asketch map of an AMOLED circuit that drives a corresponding pixel according to the present invention; FIG. 5 schematically shows a clock controlling relation ship of the driving circuit for the light emitting device shown in FIG. 4 when it is cooperated with the input voltage clock; FIG. 6A schematically shows a mechanism of a frame inverse operation according to the present invention; and FIG. 6B schematically shows a mechanism of a line inverse operation according to the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION One of the major characteristics of the present invention is providing a driving circuit for the light emitting device, able to avoid the deviation of the driving Voltage V of the light emitting device, and at least maintain the driving Voltage Vol. On a stable Value even under a long time operation of displaying image, So as to efficiently improve the display product quality. Furthermore, the threshold volt age Vth can also maintain a stable value without any deviation. Considering the characteristics of the eye, the present invention can turn off the driving transistor of the light emitting device such as the TFT for a short time period without impacting the vision quality, So as to reset the threshold voltage. Therefore, the threshold voltage is not activated for a long time, and the threshold Voltage tends to be stable without any deviation. According to medical reports, a transient effect exists for human eyes. Human eyes cannot perceive the flickering when the image flickering frequency is above 60 Hz. That is, for example, the human eyes can not differentiate the light flickering of general light that is operated with a 60 HZ alternating current. When a frame is displaying an image, if the transient variance is faster than the frame variance, So as to turn off the light emitting device of the corresponding pixel, under Such a situation, even though the total bright ness may be reduced, the human eyes cannot perceive the flicking of the dark picture generated by the turn-off. However, the reduction of the brightness can be easily adjusted to compensate and achieve an expected brightness. Comparatively, Such a problem is not So critical. FIG.3 schematically shows a sketch map of a variance of the driving Voltage of the light emitting device when it is
7 S varied with the activation time according to the present invention. The driving Voltage of the light emitting device increases along with the increase of the display operation time when it is compared with the operation of the conven tional driving circuit of FIG. 2. Contrarily, the present invention can achieve a stable driving Voltage Vol. In order to obtain a stable V, the present invention modi fies the design used in the conventional driving circuit as shown in FIG. 4. FIG. 4 schematically shows asketch map of an AMOLED circuit that drives a corresponding pixel according to the present invention. AS shown in FIG. 4, when it is compared with a circuit structure of FIG. 1, the present invention particularly adds a Field Effect Transistor (FET), such as a TFT 108. In addition, when it is cooperated with the clock variance, the present invention can temporarily turn off the light emitting device and the driving transistor 102, So that the driving Voltage V of the light emitting device 108 and the threshold voltage Vth of the transistor 102 can be reset. Therefore, it does not increase along with the increase of the display operation time. The TFT 108 has a gate connected to the gate of the transistor 100 to simultaneously accept control from the scanning voltage. In addition, the drain of the TFT 108 connects to a control point of the light emitting device 104, Such as connecting to an anode of the light emitting diode. The general transistor 102 and the light emitting device 104 constitute a light emitting path that is connected in between a System high Voltage V, and a System low Voltage Vss. The source Vs of the transistor 102 and the anode of the light emitting diode 104 are jointly coupled to a node. Furthermore, the Source of the TFT 108 also connects to a common Voltage Vol. Regarding the maintain capacitor 106, an electrode of the capacitor 106 may be connected to the gate of the transistor 102, and the other electrode of the capacitor 106 can be grounded. However, it is also acceptable as shown in FIG. 4, to have the other electrode of the capacitor 106 connect to the source of the transistor 102 without impacting the characteristic of the present invention. In addition to adding a TFT 108, the present invention can further achieve the function of temporarily turning off the transistor 102 and the light emitting device by cooperating with the Voltage values and the clock relationship among the digital data Voltage Vdata, the Scanning Voltage Vscan and the common Voltage Vcom. FIG. 5 schematically shows a clock controlling relation ship of the driving circuit for the light emitting device shown in FIG. 4 when it is cooperated with the input voltage clock. The general display operation uses one frame as a time unit. Some corresponding Scanning lines are activated within a frame. A Scanning Signal is input into the Scanning line when it is cooperated with the frame size, providing a Scanning Voltage Vscan with a frequency along with the time variance for inputting into the gates of the transistors 100 and 108, so as to activate the transistors 100 and 108. In FIG. 5, a clock Signal CLK is a clock having a frequency, and a frame is defined as a range between pulses. AS to an image pixel unit, the variance of the Scanning Signal is the same as the variance of the clock signal CLK. FIG. 5 is an example using the frame as a unit. With the Same mechanism, the Scanning line also can be used as a unit to perform the control operation. As shown in FIG. 5, in an example of using the frame as a unit, the frame State is Set as an alternating relationship. When the frame is at an ON State, the corresponding Scanning lines Sequentially accept US 6,680,580 B control from the Scanning Voltage VScan, So as to activate the transistors 100 and 108. Meanwhile, the data lines are also Sequentially input with the image data Vdata, So as to provide it to the transistor 100 of the corresponding pixel unit. The image data Vdata are the Signals having different gray Scales. Since the transistor 100 is activated, the image data Vdata can further activate the transistor 102. In addition, its Voltage can be temporarily Stored in the main tain capacitor 106, so as to maintain the transistor 102 in an ON state. When the transistor 102 is activated, a system high Voltage V, flows through the light emitting device 104, and arrives at a System low Voltage Vss, So that the light emitting device 104 can emit the light. As to the conven tional driving method mentioned above, the transistor 102 and the light emitting device 104 are all kept in an ON state. Therefore, deviations of the threshold voltage of the tran Sistor 102 and the driving Voltage V of the light emitting device 104 are generated. The transistor 108 according to the present invention is further designed to cooperate with the operating Voltage, So as to temporarily turn off the transistor 102 and the light emitting device 104 during a period when the frame is in an OFF state. The Source of the transistor 108 connects to a common Voltage Vcom, and the Voltage level of the com mon Voltage Vcom comprises a voltage high level and a Voltage low level, which varies with a pre-determined frame ON/OFF state. For example, the voltage high level is a grounded Voltage, and the Voltage low level is a negative Voltage. Furthermore, the digital data Voltage Vdata is also cooperated with the common Voltage Vcom, So as to be input with a negative Voltage when it is at a Voltage low level State. Therefore, it can achieve an objective of temporarily turning off the transistor 102 and the light emitting device 104 when the frame is in an OFF state. The operating mechanism is described hereinafter. During the pre-determined frame OFF state, the common voltage Vcom is input with a negative Voltage, Such as -10 V. Meanwhile, a turning-off voltage, Such as -20 V, is input into an input terminal of the digital data Voltage. The System low Voltage VSS is Set as a grounded Voltage, or a negative voltage, such as -5 V. The system low voltage VSS is generally designed to be in between the high level and low level of the common voltage Vcom. When the voltage low level of the common Voltage Vcom is inversely input into the anode of the light emitting device 104, Since the Voltage low level of the common voltage Vcom is smaller than the system low voltage Vss, the light emitting device 104 can be deactivated. Furthermore, the relationship between the gate voltage Vg of the transistor 102 and the Source Voltage (i.e. anode voltage) Vs of the transistor 102 has to be kept on a relationship of Vg-Vs. Meanwhile, the digital data voltage Vdata is input with a Voltage, i.e. turning-off voltage, Such as -20 V that is smaller than the voltage low level of the common Voltage Vcom. A frame inverse operation can be achieved by using the operating mechanism mentioned above. The So-called frame inverse operation is as shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6A, The ON/OFF is sequentially operated with a frame unit. A frame is generally corresponded to a whole image picture or a picture having different blocks. Therefore, a frame may comprise the pixels corresponding to multiple Scanning lines. In FIG. 6A, all the corresponding Scanning lines in frame 1 are at the ON state, so as to normally display the image. Contrarily, when it is cooperated with the operation of the turning-off voltage and the common Voltage Vcom, those scanning lines in frame 2 are all at the OFF state. This is the so-called frame inverse operation. With the same
8 7 driving circuit and the driving method, the clock of the turning-off voltage and the common. Voltage Vcom can be adjusted, So as to achieve the line inverse operation. The so-called line inverse operation is as shown in FIG. 6B. In FIG. 6B, all the corresponding Scanning lines in frame 1 are ON and OFF alternatively, and the corresponding scanning lines in frame 2 are also ON and OFF alternatively. However, frame 1 and frame 2 are just in reverse. This is the So-called line inverse operation. The driving circuit and the driving method applied is Similar to the method shown in FIG. 6A, the only difference is in the clock adjustment. Regarding the circuit design, the light emitting device 104 may be an organic light emitting diode. The transistor may be an N type or a Ptype transistor in terms of the conductive type. AS to the integration of the driving method, the present invention is based on a conventional driving circuit, and further adding a transistor 108, when it is cooperated with the operating Voltage and is operated with an appropriate clock, the frame inverse operation or the line inverse opera tion can be achieved. The present invention at least can avoid the deviation of the threshold voltage of the driving transistor 102 and the driving voltage of the light emitting device 104, wherein the deviation is generated when the display operation time increases. The driving circuit for the light emitting device provided by the present invention at least can maintain the driving Voltage V, on a stable value even it is under a long image display operation time, So as to efficiently improve the display product quality. Furthermore, the threshold Voltage Vth can be maintained on a constant value without any deviation. Although the invention has been described with reference to a particular embodiment thereof, it will be apparent to one of the ordinary skill in the art that modifications to the described embodiment may be made without departing from the Spirit of the invention. Accordingly, the Scope of the invention will be defined by the attached claims not by the above detailed description. What is claimed is: 1. A driving circuit for a light emitting device, Suitable for use in an active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) display, which has a scanning line to be input with a Scanning clock Signal, So as to control the driving circuit, the driving circuit comprising: a driving transistor, having a gate connected to a first node, a light emitting device, Serially connected to the driving transistor at a Second node, So as to constitute a light emitting path, wherein, the light emitting path is connected in between a System high Voltage and a System low Voltage, when the driving transistor is activated, the System high Voltage drives the light emitting device to make it emit the light; maintain capacitor, connected to the first node, is able to maintain the driving transistor in an ON/OFF state according to a potential; a first transistor, having a gate connected to a Scanning line, a Source connected to a data line, and a drain connected to the first node, and a Second transistor, having a gate connected to the Scanning line, a Source connected to a common Voltage, and a drain connected to the Second node, wherein, the common Voltage has a high Voltage level and a low Voltage level, alternating by a frequency, and the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is higher than a System low Voltage and the low Voltage level is Smaller than the System low Voltage, US 6,680,580 B wherein, when the first transistor and the Second transistor are simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock Signal, the data line is input either with an image digital data Voltage or a negative turning-off Voltage, when the common Voltage is at the low Voltage level, the nega tive turning-off voltage is input, So as to turn off the driving transistor and the light emitting device. 2. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is OV, and the low Voltage level is a negative Voltage. 3. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 2, wherein the low voltage level is about -10 V, the system low Voltage is about -5 V, and the turning-off Voltage is about -20 V. 4. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the negative turning-off voltage is Smaller than the low Voltage level of the common Voltage. 5. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein when the first transistor and the Second transistor are simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock signal, the data line is input with the image digital data Voltage, So as to display an image. 6. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the frequency of the common Voltage is varied with a period of one frame, so as to drive an ON/OFF state of the corresponding multiple Scanning lines to achieve a frame inversion operation. 7. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the frequency of the common Voltage is based on the Scanning clock signal, So as to use the Scanning line as a unit to achieve a line inversion operation. 8. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the light emitting device comprises an organic light emitting diode. 9. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the first transistor, the Second transistor, and the driving transistor, are either an N type TFT transistor or a P type TFT transistor. 10. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the maintain capacitor is connected in between the first node and the Second node. 11. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 1, wherein the Second node is an anode of the light emitting device. 12. A driving circuit for a light emitting device, Suitable for use in an active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) display, which has a scanning line to be input with a Scanning clock Signal, So as to control the driving circuit, the driving circuit comprising: a driving circuit main part, including a light emitting device driven by a driving transistor as well as a data line connection terminal and a Scan line connection terminal, wherein, the Scan line connection terminal receives a Scanning clock signal; a first transistor, having a gate connected to the Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to the data line connection terminal, and a drain connected to a gate electrode of the driving transistor, and a Second transistor, having a gate electrode connected to the Scanline connection terminal, a Source connected to a common Voltage, and a drain connected to an anode of the light emitting device; wherein, the common Voltage has a high Voltage level and a low Voltage level, alternating by a frequency, and the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is higher than a System low voltage and the low voltage level is Smaller than the System low Voltage,
9 when the first transistor and the Second transistor are Simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock Signal, the data line is input either with an image digital data Voltage or a negative turning-off Voltage, when the common Voltage is at the low voltage level, the turning off voltage is input, So as to turn off the driving transistor and the light emitting device. 13. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein the light emitting device comprises an organic light emitting diode. 14. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is 0 V, and the low Voltage level is a negative Voltage. 15. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein the negative turning-off voltage is Smaller than the low Voltage level of the common Voltage. 16. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein when the first transistor and the Second transistor are simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock Signal, the data line is input with the image digital data Voltage, So as to display an image. 17. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein the frequency of the common Voltage is varied with a period of one frame, so as to drive an ON/OFF State of the corresponding multiple Scanning lines to achieve a frame inversion operation. 18. The driving circuit for the light emitting device of claim 12, wherein the frequency of the common Voltage is based on the Scanning clock Signal, So as to use the Scanning line as a unit to achieve a line inversion operation. 19. A driving method for a light emitting device, Suitable for use in an active matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) display, which has a scanning line to be input with a Scanning clock Signal, So as to control the driving circuit, the driving method comprising: providing a driving circuit main part, wherein the driving circuit main part includes a light emitting device driven by a driving transistor as well as a data line connection US 6,680,580 B terminal and a Scan line connection terminal, and the Scan line connection terminal receives a Scanning clock Signal; providing a first transistor, wherein the first transistor has a gate connected to the Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to the data line connection terminal, and a drain connected to a gate electrode of the driving transistor; providing a Second transistor, wherein the Second tran Sistor has a gate electrode connected to the Scan line connection terminal, a Source connected to a common Voltage, and a drain connected to an anode of the light emitting device; providing a high Voltage level and a low Voltage level that are alternating by a frequency, and the high Voltage level of the common Voltage is higher than a System low Voltage and the low Voltage level is Smaller than the System low Voltage; and when the first transistor and the Second transistor are Simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock signal, the data line is input either with an image digital data Voltage or a negative turning-off Voltage, when the common Voltage is at the low voltage level, the turning off voltage is input, So as to turn off the driving transistor and the light emitting device. 20. The driving method for the light emitting device of claim 19, wherein the high voltage level of the common Voltage is 0 V, and the low Voltage level is a negative Voltage. 21. The driving method for the light emitting device of claim 19, wherein the negative turning-off voltage is Smaller than the low Voltage level of the common Voltage. 22. The driving method for the light emitting device of claim 19, wherein when the first transistor and the second transistor are simultaneously activated by the Scanning clock Signal, the data line is input with the image digital data Voltage, So as to display an image. k k k k k
10 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 6,680,580 B1 Page 1 of 1 DATED : January 20, 2004 INVENTOR(S) : Paul Rudeck It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: Column 6 Line 31, replace fabricated as unshaped with -- fabricated as u-shaped -- Signed and Sealed this Thirteenth Day of April, 2004 WDJ JON W. DUDAS Acting Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
11 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 6,680,580 B1 Page 1 of 1 DATED : January 20, 2004 INVENTOR(S) : Chih-Feng Sung It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: This certificate Supersedes Certificate of Correction issued April 13, 2004, the number was erroneously mentioned and should be vacated since no Certificate of Correction was granted. Signed and Sealed this Fifteenth Day of June, 2004 WDJ JON W. DUDAS Acting Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis
 IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix OLED Displays
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS
 COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS by Roberto W. Flores A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of George Mason University in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for
COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS by Roberto W. Flores A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of George Mason University in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al.
 United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LOURIE ETAL 3,143,664
 Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 4, April 2010, pp. 1185 1189 New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED C. L. Fan, Y. Y. Lin, B. S. Lin
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 4, April 2010, pp. 1185 1189 New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED C. L. Fan, Y. Y. Lin, B. S. Lin
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al.
 United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
United States Patent 19 Majeau et al. 1 1 (45) 3,777,278 Dec. 4, 1973 54 75 73 22 21 52 51 58 56 3,171,082 PSEUDO-RANDOM FREQUENCY GENERATOR Inventors: Henrie L. Majeau, Bellevue; Kermit J. Thompson, Seattle,
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
ORGANIC light-emitting diode (OLED) displays are
 100 IEEE/OSA JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 1, NO. 1, SEPTEMBER 2005 A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors
100 IEEE/OSA JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 1, NO. 1, SEPTEMBER 2005 A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.07565A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0107565A1 Libsch et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX OLED VOLTAGE DRIVE PXEL CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2003.01.07565A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0107565A1 Libsch et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX OLED VOLTAGE DRIVE PXEL CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent
 US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al.
 (12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(12) United States Patent Nagashima et al. US006953887B2 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2005 (54) SESSION APPARATUS, CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR, AND PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CONTROL METHOD
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
-/9. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 POWER.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013
 USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,733,141 B2
 USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
USOO7733141B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Oh (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 8, 2010 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND 2007/0080732 A1* 4/2007 Cho... 327/175 OPERATING METHOD THEREOF 2008. O191757
P_02_1011:A Novel Pixel Circuit to Compensate for the Degradation of OLED Luminance in High-Resolution AMOLED Displays
 P_0_1011:A Novel Pixel Circuit to Compensate for the Degradation of OLED Luminance in High-Resolution AMOLED Displays National Cheng Kung University Department of Electrical Engineering IDBA Lab. Advisor..
P_0_1011:A Novel Pixel Circuit to Compensate for the Degradation of OLED Luminance in High-Resolution AMOLED Displays National Cheng Kung University Department of Electrical Engineering IDBA Lab. Advisor..
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999
 USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
