(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,090,075 B2
|
|
|
- Dwight Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USO B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,090,075 B2 Holm et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2012 (54) X-RAY TUBE WITH AN ANODE INSULATION (56) References Cited ELEMENT FOR LIQUID COOLING ANDA RECEPTACLE FOR A HIGH-VOLTAGE PLUG U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 2,067,139 A 1, 1937 Ehrke (75) Inventors: Kurt Holm, Baden (CH); Adrian FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS Riedo, Didingen (CH); Hans Reusser, Helgisried (CH) DE C 7, 1935 DE C 4f1939 GB * 4, 1972 (73) Assignee: Comet Holding AG, Flamatt (CH) GB A 4f1972 OTHER PUBLICATIONS *) Notice: Subject to any y disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 International Search Report for corresponding International Appli U.S.C. 154(b) by 137 days. cation PCT, EP2007/ * cited by examiner (21) Appl. No.: 12/595,697 Primary Examiner Courtney Thomas (22) PCT Filed: Jun. 6, 2007 (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm WRB-IP LLP (57) ABSTRACT (86). PCT No.: PCT/EP2007/ In a high-voltage X-ray tube, which a cathode, which is held S371 (c)(1) at negative high Voltage during operating conditions, and al (2), (4) Date. Oct. 13, 2009 anode, which is held at positive high Voltage during operating s e - a 9 conditions, are disposed opposite each other in a vacuumized inner space, the anode being attached to an anode insulation (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2008/ PCT Pub. Date: Dec. 11, 2008 element in Such a way that the anode insulation element has a cylindrical shape or a shape tapering toward the anode and includes an opening to receive a high-voltage plug, and a pipe (65) Prior Publication Data structure is provided by means of which a coolant is able to be Supplied to the anode. This coolant can be in particular insu US 2010/O A1 May 6, 2010 lating oil or another electrically non-conducting liquid. The pipe structure can, for example, be integrated completely into (51) Int. Cl. the interior of the anode insulation element, but can also be HOI 35/12 ( ) integrated into the Surface of the high-voltage plug. A solution (52) U.S. Cl /141 is also possible in which the pipe structure is integrated into (58) Field of Classification Search ,119, an intermediate element, which is situated between the anode 378/121, 130, 141 insulation element and the high-voltage plug. See application file for complete search history. 8 Claims, 8 Drawing Sheets
2 U.S. Patent Jan. 3, 2012 Sheet 1 of 8 US 8,090,075 B2
3 U.S. Patent Jan. 3, 2012 Sheet 2 of 8 US 8,090,075 B2 i
4 U.S. Patent Jan. 3, 2012 Sheet 3 of 8
5
6
7
8
9
10 1. X-RAY TUBE WITH AN ANODE INSULATION ELEMENT FOR LIQUID COOLING ANDA RECEPTACLE FOR A HIGH-VOLTAGE PLUG BACKGROUND AND SUMMARY The invention relates to a high-voltage X-ray tube, in which a cathode, held at negative high Voltage during oper ating conditions, and an anode, held at positive high Voltage during operating conditions, are disposed opposite each other in a vacuumized interior space. The invention relates in par ticular to such a high-voltage X-ray tube in which the anode is attached to an anode insulation element. X-ray tubes in metal are preferably produced nowadays in coaxial design, the outer jacket of the tube being held at ground and the cathode or respectively the anode being fixed in the interior by a ceramic insulator. These specially shaped ceramic insulators are primarily made of Al2O3 ceramic. In addition, with these so-called metal-ceramic X-ray tubes, a distinction is made between two designs, depending upon the structure of the ceramic insulator, namely between the use of disc-shaped ceramic on the one hand, and the use of cylindri cal or conical ceramic on the other hand. In the case of the ceramic disc X-ray tube, the insulation path lies transversely to the tube axis. So that sufficient volt age Sustaining capability can be ensured, the disc must there fore have an adequate diameter. A recommended value of 1 cm pro 50 kv thereby applies. The use of disc-shaped insu lators thus leads to tubes with large diameter but short overall length. With such X-ray tubes, the high voltage is supplied by way of a special insulating adapter, which receives the cable with the high-voltage plug and connects it in a suitable way to the tube anode, or respectively tube cathode, via the ceramic disc element. The drawbacks of this solution consist in that the tube is given a large diameter and owing to the lead covering necessary for reasons of radiation protection a large amount of weight. Furthermore, for reasons relating to high Voltage technology, the ceramic disc element is not ideal since the direction of field strength runs parallel to the ceramic surface, and thus there exists the risk of instability through flashover. Through the installation of a special adapter moreover two separate insulation bounding Surfaces occur, which represent additional risks of high Voltage flash OVer. To avoid this and further drawbacks of the ceramic disc element, cylindrical or respectively conical insulations are also used. These have the electrical advantage that the field strength runs to a large extent perpendicular to the Surface, and such a tube is therefore not as susceptible to electrical flashover. In addition, they make possible a narrow structural shape for the tube since the ceramic-insulation path runs parallel to the tube axis, and the dielectric strength is consid erably greater through the vacuum than parallel to the ceramic Surface. Since the commercially available high-voltage plugs can be directly connected to the ceramic element, a special adapter is not necessary, and the overall length can be kept short. Since the anode in an X-ray tube is heated up by the electron beam during operation, a special anode cooling is required. This can take place in a simple way by air or water, but only in those situations in which the anode is held at ground potential, however. The X-ray tubes in which the one electrode, preferably the anode, is held at ground potential, and the second electrode, preferably the cathode, is held at high Voltage are referred to as so-called unipolar X-ray tubes. Conversely, in so-called bipolar X-ray tubes, both electrodes are held at a high Voltage. US 8,090,075 B As already mentioned a little further above, the conical ceramic as insulator in X-ray tubes has been especially Suc cessful. It permits, on the one hand, a high degree of Voltage Sustaining capability, and, on the other hand, it also ensures a compact design. In unipolar tubes, such a ceramic is prefer ably employed on the cathode side. The anode is then grounded, and can be cooled with water (or, if need be, with air). A problem arises with bipolar tubes, however. Since the anode in these bipolar X-ray tubes is also held at high Voltage, like the cathode, the anode cooling must be carried out in an insulated way since a high potential difference exists between the anode and the cooling unit. Insulating oil is preferably used in this case for cooling the anode. In this design, the integration of the anode cooling system in the conical ceramic part represents a problem, however. According to the conven tional Solutions, a special adapter must again be used for this, which contains the insulated cooling lines and the high Volt age connection. This solution is complex and costly in manu facture; it also creates additional bounding Surfaces at risk from high Voltage, and leads moreover to an enlargement of the diameter of the tube. Thus the aims of simplicity in design, reliability and compactness of the X-ray tube cannot be achieved at all or only in insufficient measure. It is desirable to propose a new high-voltage X-ray tube which does not have the drawbacks of the state of the art. It is desirable to provide such a bipolar high-voltage X-ray tube, which, on the one hand, has an especially compact design, and which at the same time also ensures the cooling of the anode, held at high Voltage, such that reliability in operation is guaranteed at all times (in particular no oil leak possible, stable at high voltage), and that the tube is robust and is not damaged, even with transport and continuous operation. According to an aspect of the invention a high-voltage X-ray tube is provided in which a cathode, which is held at negative high Voltage during operating conditions, and an anode, which is held at positive high Voltage during operating conditions, are disposed opposite each other in a vacuumized inner space, the anode being attached to an anode insulation element, the anode insulation element has a cylindrical shape ora shape tapering toward the anode, and includes an opening to receive a high-voltage plug, and a pipe structure is provided by means of which a coolant is able to be supplied to the anode. The advantage of this invention lies in particular in that the X-ray tube according to the invention is able to combinea compact design with a simple and reliable anode cooling. By means of the shape tapering toward the anode, all advantages of X-ray tubes can be kept which are based on the principle of the conical or cylindrical ceramic element. Moreover a sig nificant reduction in size can be achieved, compared with conventional tubes, since the cooling of the anode can be achieved without additional adapter or other similar interme diate elements, thanks to the provided pipe structure. In an embodiment variant, the coolant is insulating oil or another electrically non-conducting liquid or fluid. This embodiment variant has above all the advantage that already tried and proven means of cooling and approaches to cooling can be used. Furthermore, through the use of an electrically non-conducting liquid or fluid, the problem of unwanted elec trical flashover is solved, so that the X-ray tube can be oper ated at all times with a high degree of safety and reliability. In still another embodiment variant, the pipe structure comprises at least one inflow channel and at least one outflow channel. The advantage of this embodiment variant lies above all in that a closed circuit is formed, through which the coolant may circulate unhampered. By means of a channel structure in which the coolant flows in each case in one direction only,
11 US 8,090,075 B2 3 oil bottlenecks or other problems of this kind in the cooling system can moreover be completely eliminated. Finally, also a greater flow rate and thus also a faster cooling of the anode can thereby be ensured. In a further embodiment variant, the pipe structure is inte- 5 grated completely into the interior of the anode insulation element. The advantage of this embodiment variant lies in particular in that absolutely no additional elements are needed for anode cooling. The pipe structure is located com pletely inside the anode insulation element, so that in particu- 10 lar no changes in the high-voltage plug are necessary. In this embodiment variant, therefore, the standard high Voltage plugs can continue to be used. Furthermore no special main tenance or special handling during operation is necessary since the pipe structure is well protected from external influ- 15 ences by the wall of the insulation layer. In another embodiment variant, the pipe structure is inte grated into the Surface of the anode insulation element turned toward the high-voltage plug, the pipe structure being at least partially open toward the outside. This embodiment variant 20 has in particular the advantage of very easy access to the pipe structure. In particular, this makes possible very simple con trol or respectively very simple upkeep of the pipe structure. Last but not least, the manufacture of such an anode insulation element is also considerably simplified. In addition, the main- 25 tenance is also further simplified since the grease otherwise used between the anode insulation element and the high Voltage plug resinifies, as a rule, over time and has to be renewed. In still another embodiment variant, the pipe structure is 30 able to be sealed off by the surface of the high-voltage plug. The advantage of this embodiment variant lies in particular in that the Surface of the high-voltage plug can be used auto matically for sealing off of the pipe structure. Thus also no additional elements or seals are needed. The coolant can then 35 circulate freely in the respective channels, without oil leaks occurring. In a further embodiment variant, provided on the high Voltage plug are sealing means, by means of which the pipe structure is able to be sealed off. This embodiment variant has 40 above all the advantage that the sealing can be improved and optimized through use of special sealing means. Thus it can be ensured at all times that the pipe structure is closed off optimally, and that the coolant does not come into contact with the outer air. Moreover the high-voltage plug can also be 45 pulled out even when the coolant is still in the pipe structure, for example, without this coolant escaping. The safety in use and the simplicity of handling of a high-voltage X-ray tube according to this embodiment variant are thereby brought to an especially high level. Likewise, in the case of damage to 50 the sealing means, only this element has to be replaced, while the same high-voltage plug can continue to be used. In still another embodiment variant, the pipe structure is integrated into the Surface of the high-voltage plug. The most important advantage of this embodiment variant lies above all 55 in the very easy access to the pipe structure, akin to the embodiment variant with the pipe structure in the surface of the anode insulation element. That makes possible above all very easy control or respectively very easy upkeep of the pipe structure, whereby the maintenance is also considerably sim- 60 plified. However, made possible by means of this embodi ment variant is the use of standardized anode insulation ele ments (i.e. Such as are also usable with unipolar X-ray tubes, for example), while the pipe structure comes to lie exclusively within the high-voltage plug. 65 In another embodiment variant, the pipe structure is inte grated into an intermediate element, the intermediate element 4 being disposed between the anode insulation element and the high-voltage plug. The advantage of this embodiment variant lies in particular in that both standardized high-voltage plugs and standardized anode insulation elements are usable. Thus the pipe structure for guiding of the coolant is integrated into a completely new element, which can be manufactured and also installed separately. Also the maintenance of such a pipe structure is thereby especially simplified. In the case of failure or massive damage to the pipe structure, the intermediate element can also be very easily replaced, without the entire anode insulation element and/or the high-voltage plug being used also being affected. In still another embodiment variant, the at least one inflow channel and/or the at least one outflow channel are of helical design. This embodiment variant has in particular the advan tage that by means of the helical shape, a much greater length is achievable for the conducting channels. The insulation path in the coolant can thereby be increased, and the Voltage Sus taining capability and reliability of the tubes improved. In a further embodiment variant, the at least one inflow channel and/or the at least one outflow channel are of recti linear design. The advantage of this embodiment variant is in particular that a pipe structure with straight channels is pro duced considerably more easily and can essentially be main tained considerably more easily. In addition, the possibility of bottlenecks of liquid in the pipe structure is clearly smaller with straight channels. The coolant can also be conducted very quickly to the anode, which can be an advantage at very high temperatures. In another embodiment variant, the pipe structure is pro ducible by boring and/or casting. The advantage of this embodiment variant lies above all in that standardized manu facturing methods can be applied to produce the pipe struc ture for the coolant (e.g. the cooling liquid). A Smooth Surface of the channels in the pipe structure can also be obtained by boring or by casting, which is decisive for a friction-free flow of the cooling liquid. In still another embodiment variant, the at least one inflow channel and/or the at least one outflow channel have a round or oval cross section. This embodiment variant has above all the advantage that an optimal channel shape is used for the circulation of the coolant in the pipe structure. Thus the pos sibility of a bottleneck or another difficulty is greatly reduced. It should be mentioned here that in addition to the high Voltage X-ray tube according to the invention, this invention also relates to a corresponding method for producing the high-voltage X-ray tube according to the invention. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS The embodiment variants of the present invention will be described in the following with reference to examples. The examples of the embodiments are illustrated by the following attached figures: FIG. 1a shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of a high-voltage X-ray tube from the state of the art having a design with disc-shaped ceramic insulators; FIG. 1b shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of a high-voltage X-ray tube from the state of the art having a design with conical ceramic insulators; FIG. 2 shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of a high-voltage X-ray tube according to the invention; FIG. 3 shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of the anode insulation element of the high-voltage X-ray tube with the corresponding high-voltage plug according to a first embodiment variant of the invention;
12 5 FIG. 4 shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of the anode insulation element of the high-voltage X-ray tube with the corresponding high-voltage plug according to a second embodiment variant of the invention; FIG. 5 shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of the anode insulation element of the high-voltage X-ray tube with the corresponding high-voltage plug according to a third embodiment variant of the invention; FIG. 6a shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of the anode insulation element of the high-voltage X-ray tube with the corresponding high-voltage plug according to a fourth embodiment variant of the invention; and FIG. 6b shows a diagrammatic cross-sectional view of the anode insulation element of the high-voltage X-ray tube with the corresponding high-voltage plug according to a fifth embodiment variant of the invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION FIG.1a shows diagrammatically a high-voltage X-ray tube R from the state of the art. The high-voltage X-ray tube Rhas, among other things, an outer jacket or lead covering 1, by means of which an inner space 11 is closed off and sealed off. Normally the high-voltage X-ray tube R is of coaxial design, as is shown by a central axis in FIG. 1a. The inner space 11 is essentially under vacuum, which vacuum is generated once during the manufacture of the high-voltage X-ray tube R. In this inner space 11, an anode 2 and a cathode 8 are situated opposite one another. By means of applied high Voltage, electrons e- are accelerated from the cathode 8 to the anode 2. X-rays 10 are thereby created at the anode 2, which X-rays are emitted through an exit aperture 9 in the lead covering 1 into the Surrounding area. The anode 2 and the cathode 8 are insulated by disc-shaped insulation elements from the lead covering 1. The anode insulation element 3a and the cathode insulation element 3b thereby have a particular radius so that sufficient voltage Sustaining capability can be ensured. In such a high-voltage X-ray tube R from the state of the art, the high Voltage is Supplied using specially designed insulating adapters 4a and 4b. These adapters 4a and 4b each have openings. 5a and 5b, in which high-voltage plugs can be plugged in, which Supply the tube anode 2 or respectively tube cathode 8 in a suitable way with high voltage via the ceramic disc element. With a bipolar high-voltage X-ray tube R, a special cool ant, for example an insulating cooling oil, must be used for cooling of the anode 2. The cooling oil will be thereby con ducted through the adapter 4a through specially designed channels 6,7. One channel 6 serves thereby as inflow channel for the cooling oil, while the channel 7 is used as outflow channel. A circuit is thereby created for the coolant which flows through the channel 6 to the anode, absorbs here the excess heat, and then flows through the channel 7 out again out of the adapter 4a. The two reference numerals 12a and 12b, or respectively 12a" and 12b', refer to two separated insulation bounding Surfaces, which occur owing to the con struction of the adapter 4a, or respectively 4b, and which represent additional risks for high Voltage flashover. Illustrated diagrammatically in FIG. 1b is a different high voltage X-ray tube R from the state of the art. This high Voltage X-ray tube R now comprises conical electrode insu lation elements 3a and3b. The elements described in FIG.1a are given the same reference numerals also in FIG. 1b. Thus the reference numeral 1 refers to the outer jacket or respec tively the lead covering of the high-voltage X-ray tube R, the reference numeral 2 to the anode, the reference numerals 6 US 8,090,075 B and 7 to the inflow channel, respectively to the outflow chan nel, the reference numeral 9 to the exit aperture for the X-rays 10, and the reference numeral 11 to the vacuumized inner space of the high-voltage X-ray tube R. With the high-voltage X-ray tube R from FIG.1b, the field strength runs to a large extent perpendicular to the Surface, thanks to the conical or respectively cylindrical electrode insulators 3a and 3b. Thus this high-voltage X-ray tube R is also not as susceptible to electrical flashover. The cathode insulation element 3b in FIG.1b has an opening 5b, which can receive a commercially available high-voltage plug. Since the high-voltage plug can in principle be connected directly to the cathode insulation element 3b, a special adapter is not neces sary, and the overall length can be kept short. However, on the anode-side another special adapter 4 has to be used, which contains the insulated cooling lines 6 and 7 and the connec tion 5a for the high-voltage plug. An additional bounding surface 12b, at risk from high voltage, also results with this high-voltage X-ray tube. FIG.2 shows diagrammatically the structure of an embodi ment variant of a high-voltage X-ray tube Raccording to the invention. Elements known from FIGS. 1a and 1b are desig nated using the same reference numerals also in FIG. 2. Thus the reference numeral 1 refers once again to the outerjacket or respectively to the lead covering of the high-voltage X-ray tube R, the reference numeral 2 to the anode, the reference numerals 3a and 3b to the anode insulation element, respec tively to the cathode insulation element, the reference numer als 5a and 5b to the high-voltage plug connections, the refer ence numeral 8 to the cathode, the reference numeral 9 to the exit aperture for the X-radiation 10, and the reference numeral 11 to the inner space of the high-voltage X-ray tube R. In FIG. 2, the anode insulation element 3a likewise has a cylindrical shape or respectively a shape tapering toward the anode 2. In addition, the anode insulation element 3a com prises Such an opening 5a for receiving a high-voltage plug 12, making possible a direct connection without adapters or Such intermediate elements being needed. According to the invention, a pipe structure is also provided by means of which a coolant can be supplied to the anode 2. The different embodiment variants of the invention will be shown in the Subsequent figures. FIG. 3 illustrates a first embodiment variant of the inven tion, in which the pipe structure with the inflow channel 6, and the outflow channel 7, is integrated into the surface of the high-voltage plug 12. In this first embodiment variant, the conical high-voltage plug 12 has in its Surface open, groove shaped channels 6 and 7 through which the coolant (in par ticular the cooling oil or another Suitable cooling liquid) can be conducted. Through the press fit of the rubber cone 12 in the ceramic cone 3a, the oil channels 6, 7 are sealed off laterally, so that no oil leaks can occur. At its end, the inflow channel 6 has an opening 6', through which the cooling liquid can escape to the anode 2. On the other side, the cooling liquid can reach the outflow channel 7 through the opening 7", after the exchange of heat. In particular, these openings 6' and 7" can be situated partially or completely in the anode insulation element 3a. The channels 6 and 7 can be disposed rectilin early, but also helically. It is also possible moreover to run a plurality of inflow and/or outflow channels 6, 7 parallel, in order to reduce the drop in pressure or respectively increase the flow rate of the cooling liquid. A second embodiment variant of the invention, in which the pipe structure with the inflow channel 6 and the outflow channel 7 is completely integrated into the interior of the anode insulation element 3a, is shown in FIG. 4. In this
13 7 second embodiment variant, the conical ceramic anode insu lation element3a is provided with bores 6, 7, which run in the ceramic wall and serve to guide the coolant flow. These bores 6, 7 are advantageously made in the preform before firing of the ceramic. If need be, the channels 6, 7 can also be inte grated into the anode insulation element 3a by casting or another suitable production method. The coolant enters the inflow channel 6, and leaves it through the opening 6'. After wards the coolant can flow into the outflow channel 7 through the opening 7". In this embodiment variant, above all the bounding surface between the insulation element 3a and the high-voltage plug is not changed. Standard plugs can thereby be used. Also in this embodiment variant, the pipe structure can have rectilinear or also helical channels 6,7. Moreover it is also possible in this embodiment variant to runa plurality of channels 6, 7 parallel in order to reduce the drop in pressure or respectively increase the oil flow rate. FIG.5 shows a third embodiment variant of the invention in which the pipe structure with the inflow channel 6 and the outflow channel 7 is integrated into an intermediate element 13, the intermediate element 13 being disposed between the anode insulation element 3a and the high-voltage plug 12. This third embodiment variant thus comprises an intermedi ate element 13, which is inserted between the anode insula tion element 3a and the high-voltage plug 12. This interme diate element 13 now contains the inflow and outflow channels 6, 7 for the supply and removal of the coolant to the anode 2. The intermediate part 13 can be sealed off by means of a Suitable method in a gap-free way with respect to the ceramic cone of the anode insulation element 3a. This can take place e.g. with oil, grease or a thin silicon sleeve. Of course other sealing means and methods are absolutely con ceivable as well. In this embodiment variant, the intermediate element 13 is plugged directly into a standard anode insulation element 3a. Consequently this intermediate element 13 must be length ened outwardly in Such a way (the extension 13a) that once again a standardized high-voltage plug 12 may be used. Oth erwise the anode insulation element 3a can be made some what broader in order to make space for the intermediate element 13. Standardized high-voltage plugs 12 can thereby continue to be used. FIGS. 6a and 6b show respectively the fourth and fifth embodiment variants of the present invention. In these embodiment variants, the pipe structure 6, 7 in both cases is integrated as a groove or channel structure in the Surface of the anode insulation element 3a turned toward the high-volt age plug 12, it being at least partially open toward the outside. Shown in FIG. 6a is the embodiment variant in which the channels 6 and 7 are sealed off directly by the surface of the high-voltage plug 12. Alternatively (as shown in FIG. 6b). additional, thin-walled sealing means 13 can also be used, which seal off the oil-conducting channels 6, 7 on the one side, and, on the other side, provide the guiding means for the high-voltage plug 12. Also in these two cases, the channels 6, 7 can be run straight or in a helical way. Likewise a plurality of grooves can also be used in parallel. By installing the cooling channels in the boundary layer between the anode insulation element 3a and high-voltage plug 12, or respectively in the anode insulation element 3a itself, it is possible, even with conical or cylindrical insula tors, to Supply the cooling oil to the anode 2, which is under high Voltage, with simple components or even completely without separate components. The advantages of this design are not thereby lost, i.e. the high-voltage X-ray tube R remains compact, robust and reliable. The invention is not limited to the embodiment variants described. It will be immediately clear to one skilled in that art US 8,090,075 B that further developments and modifications within the scope of the protected invention are possible by implication. Ele ments of the device can be substituted, depending upon need, by other elements that fulfill the same or similar functions. Likewise additional devices and elements can be provided. For example, the anode insulation element 3a can also have a cylindrical inner bore in which the high-voltage plug 12 can then be inserted. The connection between the plug 12 and the ceramic element3a is made in this case by means of a flexible intermediate element 13, which fits snugly on the ceramic element 3a. In particular, a constant pressing pressure is ensured by the cylindrical shape. The flexible intermediate element 13 can be advantageously designed in Such away that channels 6, 7 are created for the supply and removal of cool ant, which run along between the high-voltage plug 12 and the ceramic anode insulation element 3a in a straight or helical way. A maintenance-free high-voltage plug 12 can thereby be achieved. These and many other measures and elements fall within the scope of protection of the invention which is defined by the following claims. The invention claimed is: 1. A high-voltage X-ray tube, comprising a cathode, the cathode being held at negative high Voltage during operating conditions, an anode, the anode being held at positive high Voltage during operating conditions, the cathode and the anode being disposed opposite each other in a vacuumized inner space, the anode being attached to an anode insu lation element, a high Voltage plug, the anode insulation element having a cylindrical shape or a shape tapering toward the anode, the anode insulation element including an opening to receive the high-volt age plug, a pipe structure through which a coolant is adapted to be Supplied to the anode, and an intermediate element into which the pipe structure is integrated, the pipe structure being at least partially defined by one or more grooves formed in an external surface of the intermediate element, the intermediate element being disposed between the anode insulation element and the high Voltage plug, the intermediate ele ment being directly plugged into the anode insulation element. 2. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim 1, wherein the coolant is insulating oil or another electrically non-conduct ing liquid. 3. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim 1, wherein the pipe structure comprises at least one inflow channel and at least one outflow channel. 4. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim 3, wherein at least one of the at least one inflow channel and the at least one outflow channel are of helical design. 5. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim 3, wherein at least one of the at least one inflow channel and the at least one outflow channel are of rectilinear design. 6. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim3, wherein the pipe structure is produced by boring and/or casting. 7. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim 3, wherein at least one of the at least one inflow channel and the at least one outflow channel have a round or oval cross section. 8. The high-voltage X-ray tube of claim wherein the inter mediate element is in direct contact with both the anode insulation element and the high Voltage plug.
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand
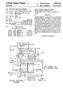 United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1
 USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Laubscher & Laubscher Conyers, Ga. 57 ABSTRACT
 USOO5863414A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,863,414 Tilton (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 1999 54) PLASTIC, FLEXIBLE FILM AND 4.261.462 4/1981 Wysocki. PAPERBOARD PRODUCT-RETENTION 4,779,734
USOO5863414A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,863,414 Tilton (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 1999 54) PLASTIC, FLEXIBLE FILM AND 4.261.462 4/1981 Wysocki. PAPERBOARD PRODUCT-RETENTION 4,779,734
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
Assistant Examiner Kari M. Horney 75 Inventor: Brian P. Dehmlow, Cedar Rapids, Iowa Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Kyle Eppele; James P.
 USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
US 7,872,186 B1. Jan. 18, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent Tatman (54) (76) Kenosha, WI (US) (*)
 US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
(19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
US 6,817,895 B2. Kiely. Nov. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent (54)
 (12) United States Patent Kiely USOO6817895B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) COLOR CODED SHIELDED CABLE AND CONDUIT CONNECTORS
(12) United States Patent Kiely USOO6817895B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) COLOR CODED SHIELDED CABLE AND CONDUIT CONNECTORS
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311612 A1 Qiao et al. US 2015 0311612A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) CABLE-TO-BOARD CONNECTOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311612 A1 Qiao et al. US 2015 0311612A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) CABLE-TO-BOARD CONNECTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
( InfoSystems Translation )
 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110247855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0247855A1 AMATO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) COAXAL CABLE SHIELDING Inventor:
(19) United States US 20110247855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0247855A1 AMATO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) COAXAL CABLE SHIELDING Inventor:
United States Patent
 United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, B1
 USOO6487273B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takenaka et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE HAVING AN INTEGRAL 4,884,292 A 11/1989 Klostermann... 378/127 HOUSING ASSEMBLY
USOO6487273B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takenaka et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE HAVING AN INTEGRAL 4,884,292 A 11/1989 Klostermann... 378/127 HOUSING ASSEMBLY
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201700.52256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0052256A1 Delfs et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) 3D LASER SCANNER HOIS 5/83 (2006.01) GO2B 26/08 (2006.01) (71)
(19) United States US 201700.52256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0052256A1 Delfs et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) 3D LASER SCANNER HOIS 5/83 (2006.01) GO2B 26/08 (2006.01) (71)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2
 USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2 i :
 US008 167253B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,167.253 B2 i : Smith 45) Date of Patent May 1, 2012 (54) FLAT PANEL TV STAND PROVIDING 2.477,735 A * 8/1949 Gentile... 248,220.31 FLOATINGAPPEARANCE
US008 167253B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,167.253 B2 i : Smith 45) Date of Patent May 1, 2012 (54) FLAT PANEL TV STAND PROVIDING 2.477,735 A * 8/1949 Gentile... 248,220.31 FLOATINGAPPEARANCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
s\ OJII <*S Illl INI II III IIMI 1 1 llll I II I II Eur Pean Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1
 s\ OJII
s\ OJII
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
NES 2NS () United States Patent (19) Trebes et al. 7 / 17 \, T 7-17N. 11 Patent Number: 6,134,300 (45) Date of Patent: Oct.
 United States Patent (19) Trebes et al. 54 MINIATURE X-RAY SOURCE 75 Inventors: James E. Trebes, Livermore; Perry M. Bell, Tracy; Ronald B. Robinson, Modesto, all of Calif. 73 Assignee: The Regents of
United States Patent (19) Trebes et al. 54 MINIATURE X-RAY SOURCE 75 Inventors: James E. Trebes, Livermore; Perry M. Bell, Tracy; Ronald B. Robinson, Modesto, all of Calif. 73 Assignee: The Regents of
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100173523A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0173523 A1 MAGNEZ. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 8, 2010 (54) DUAL-DIRECTION CONNECTOR AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20100173523A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0173523 A1 MAGNEZ. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 8, 2010 (54) DUAL-DIRECTION CONNECTOR AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, Ireland /1958 Fed. Rep. of Germany...
 IIIHIIIHIIIHIII USOO5326297A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 (54) LIFE JACKET 4,241,459 12/1980 Quayle... 2102 O 5,029,293 7/1991 Fontanille...
IIIHIIIHIIIHIII USOO5326297A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,326,297 Loughlin 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 1994 (54) LIFE JACKET 4,241,459 12/1980 Quayle... 2102 O 5,029,293 7/1991 Fontanille...
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,093 B1. Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006
 United States Patent US007 112093B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) POSTLESS COAXIAL COMPRESSION 5,073,129 A * 12/1991 Szegda... 439,585 CONNECTOR 5,632,651 A * 5/1997...
United States Patent US007 112093B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) POSTLESS COAXIAL COMPRESSION 5,073,129 A * 12/1991 Szegda... 439,585 CONNECTOR 5,632,651 A * 5/1997...
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al.
 United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Herriott et al.
 United States Patent (19) Herriott et al. (54) 75 (73) 21 22 51 52) (58) 56) ELECTRON GUN WITH IMPROVED CATHODE AND SHADOW GRO CONFIGURATION Inventors: Assignee: Ronald W. Herriott, San Bruno; Johann R.
United States Patent (19) Herriott et al. (54) 75 (73) 21 22 51 52) (58) 56) ELECTRON GUN WITH IMPROVED CATHODE AND SHADOW GRO CONFIGURATION Inventors: Assignee: Ronald W. Herriott, San Bruno; Johann R.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS
 3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Complete Fine Beam Tube System 1013843 Instruction sheet 10/15 SD/ALF If it is to be expected that safe operation is impossible (e.g., in case of visible damage), the apparatus is
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Complete Fine Beam Tube System 1013843 Instruction sheet 10/15 SD/ALF If it is to be expected that safe operation is impossible (e.g., in case of visible damage), the apparatus is
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B2
 US009327469B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,327.469 B2 Heinrich et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 2016 (54) ROTARY TABLET PRESS AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited PRESSING TABLETS IN
US009327469B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,327.469 B2 Heinrich et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 2016 (54) ROTARY TABLET PRESS AND METHOD FOR (56) References Cited PRESSING TABLETS IN
THE X-RAY ADVANTAGE Pros and cons X-ray and Gamma
 THE X-RAY ADVANTAGE Pros and cons X-ray and Gamma NDTMA - February 12, 2015 NILS HASE Sales Manager IXT 1 THE COMET GROUP COMET, AG is a 65 year- old Swiss company and a leading supplier of advanced system
THE X-RAY ADVANTAGE Pros and cons X-ray and Gamma NDTMA - February 12, 2015 NILS HASE Sales Manager IXT 1 THE COMET GROUP COMET, AG is a 65 year- old Swiss company and a leading supplier of advanced system
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
Up to 85% higher Service Life due to efficient sealing method.
 Robot Accessories Feeding through Up to 85% higher Service Life due to efficient sealing method. 346 Robot Accessories Feeding through Feeding through DDF 2 Rotary Feed-through Series Size Page DDF 2 348
Robot Accessories Feeding through Up to 85% higher Service Life due to efficient sealing method. 346 Robot Accessories Feeding through Feeding through DDF 2 Rotary Feed-through Series Size Page DDF 2 348
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
 Patented Nov. 14, 1950 2,529,485 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 1 This invention relates to television systems and more particularly to methods of and means for producing television images in their natural
Patented Nov. 14, 1950 2,529,485 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 1 This invention relates to television systems and more particularly to methods of and means for producing television images in their natural
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,790,981 B2
 US007790981B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,790,981 B2 Vaupotic et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 2010 (54) SHIELDED PARALLEL CABLE 5,142,100 A * 8/1992 Vaupotic... 174/24 5,293,146
US007790981B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,790,981 B2 Vaupotic et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 2010 (54) SHIELDED PARALLEL CABLE 5,142,100 A * 8/1992 Vaupotic... 174/24 5,293,146
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
Design, Fabrication and Testing of Gun-Collector Test Module for 6 MW Peak, 24 kw Average Power, S-Band Klystron
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2014, 1(1): 11-15 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Design, Fabrication and Testing of Gun-Collector Test Module
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2014, 1(1): 11-15 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Design, Fabrication and Testing of Gun-Collector Test Module
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O172366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0172366 A1 Popp (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CORN SEED SIZING (52) U.S. Cl.... 800/320.1;
US 2005O172366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0172366 A1 Popp (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CORN SEED SIZING (52) U.S. Cl.... 800/320.1;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
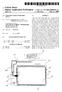 (19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
III. USOO A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998
 III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
352,26,362.25:36:50:32:3:32:3: A. E. "N'io E
 USOO6976777B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: HerOld (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 20, 2005 (54) SIMULATED NEON-LIGHT TUBE 6,231,207 B1 5/2001 Kennedy et al.... 362/158 6,337,946 B1 1/2002 McGaffigan......
USOO6976777B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: HerOld (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 20, 2005 (54) SIMULATED NEON-LIGHT TUBE 6,231,207 B1 5/2001 Kennedy et al.... 362/158 6,337,946 B1 1/2002 McGaffigan......
