(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
|
|
|
- Marybeth Webb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
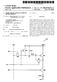
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1 Ishizuka US A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: 12/994,079 Shinichi Ishizuka, Mitaka (JP) PIONEER CORPORATION, Kawasaki-shi, Kanagawa (JP) PCT Fled: May 23, 2008 PCT NO.: S371 (c)(1), (2), (4) Date: PCT/UP2008/ Nov. 22, 2010 VIDE ODATA Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G09G 5/10 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /690 (57) ABSTRACT A display apparatus comprises an average luminance calcu lating unit that calculates average luminance of a display screen based on a video signal; and a drive Voltage adjuster that adjusts a drive Voltage of drive transistors each driving a light-emitting element provided in a pixel unit according to the calculated average luminance. 10 CONTROLLER APL CALCULA TION O D Z U 20 C U VOLTAGE SOURCE (PS)
2 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 1 of 12 US 2011/ A1
3 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 2 of 12 US 2011/ A1 VOLTAGE SOURCE (PC) SCAN DRIVER
4 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 3 of 12 US 2011/ A1 (dq) TVNOIS LVCI e?ep A
5 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 4 of 12 US 2011/ A1 FG.4 AP
6 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 5 of 12 US 2011/ A1 O 3 ch 8 > D D n C - D Se E s
7 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 6 of 12 US 2011/ A1 VOLTAGE SOURCE (PC) S CAN DRIVER
8 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 7 of 12 US 2011/ A1
9 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 8 of 12 US 2011/ A1 g
10 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 9 of 12 US 2011/ A1 a as a re we pulli is r (dg) TVNºIS LVCI e?ep/\ TV/NS) S N\/OS (ds)
11 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 10 of 12 US 2011/ A1 FIG.10 AP
12 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 11 of 12 US 2011/ A1 VOLTAGE SOURCE (PC) SCAN DRIVER
13 Patent Application Publication Apr. 14, 2011 Sheet 12 of 12 US 2011/ A1 F.G. 12 APL
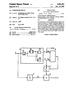
14 US 2011/ A1 Apr. 14, 2011 ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a display apparatus including active elements for driving light-emitting elements such as EL (electroluminescent) elements or LEDs (light emitting diodes) and particularly to a display apparatus including thin film transistors (TFTs) as active elements. BACKGROUND ART 0002 TFTs are widely used as active elements for driving an active matrix display Such as an organic EL display or a liquid crystal display. FIG. 1 shows an example equivalent circuit of a drive circuit for an organic electroluminescent element (OEL) or an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) 100 for one pixel PLi,j Referring to FIG. 1, this equivalent circuit includes two p-channel TFT 101, 102 that are active elements, and a capacitor (Cs) 104. A scan line Wis is connected to the gate of the selecting transistor 101; a data line Wa is connected to the Source of the selecting transistor 101; and a power Supply line WZ for Supplying a constant Supply Voltage Vdd is connected to the source of the drive transistor 102. The drain of the selecting transistor 101 is connected to the gate of the drive transistor 102, and a capacitor 104 is formed between the gate and the source of the drive transistor 102. The anode and the cathode of the OEL 100 are respectively connected to the drain of the drive transistor 102 and ground potential (or common potential) When a selecting pulse is applied to the scan line Ws, the selecting transistor 101 as a switch is turned on so as to render it conductive between its source and drain. At this time, a data voltage is supplied from the data line Wa through the selecting transistor 101 between the source and the drain and is stored in the capacitor 104. Because the data voltage stored in the capacitor 104 is applied between the gate and source of the drive transistor 102, a drain current Id corre sponding to the gate-to-source Voltage Vgs of the drive tran sistor 102 flows and is supplied to the OEL 100 to emit light In the active matrix display, by supplying a data signal corresponding to input video data to each pixel PLi, via the data line while the selecting pulse (scan pulse) being applied sequentially to the scan lines, an image is displayed For the active matrix display, for example, Refer ence 1 discloses imparting a peak luminance characteristic to suppress white luminance to a low level to video of which the entire screen is bright. Specifically, it is disclosed that using the fact that the potential difference between the input end potential and the terminal end potential of the power Supply line in a display apparatus varies according to the screen luminance, the potential on the other end of the data-holding capacitor, one end of which is connected to the gate of the drive transistor, is controlled according to the potential dif ference (i.e., image luminance), thereby imparting the above mentioned peak luminance characteristic As such, for the active matrix display, it is becoming a very important capability to reduce power consumption from the viewpoint of saving energy, Suppressing heat gen eration, making the apparatus thinner, and so on. Hence, providing a display apparatus of low power consumption is strongly desired Reference 1: Japanese Patent Application Laid Open Publication No (p. 19, FIGS. 1, 2) DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION Problem to be Solved by the Invention One example of the problems to be solved by the present invention is the above defect in the conventional art. An object of the present invention is to provide a display apparatus of low power consumption that imparts a peak luminance characteristic to suppress white luminance to a low level to video whose entire screen is bright. Means for Solving the Problem According to the present invention, there is provided a display apparatus which has an active matrix type of display panel comprising a plurality of pixel units each having a light-emitting element and a drive transistor driving the light emitting element, a scan drive unit for sequentially scanning scan lines of the display panel, and a data drive unit for Supplying a data signal based on a video signal to a control electrode of each of the drive transistors in association with scanning by the scan drive unit, the display apparatus com prises a capacitor provided in each of the plurality of pixel units to hold the data signal, a first terminal of the capacitor being connected to the control electrode of the drive transis tor; a capacitor Voltage generating unit which generates a capacitor Voltage to be applied to a second terminal of each of the capacitors; an average luminance calculating unit which calculates average luminance of a display screen based on the Video signal; and a drive Voltage adjuster which adjusts a drive Voltage of the drive transistors according to the average luminance. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS 0011 FIG. 1 shows an example equivalent circuit of a conventional light-emitting element drive circuit; 0012 FIG. 2 shows a display apparatus using an active matrix display panel according to a first embodiment of the present invention; (0013 FIG. 3 shows a pixel unit PL associated with data line Xi and scan line Y from among a plurality of pixel units PL to PL FIG. 4 is a graph showing schematically a relation ship of a drive voltage VD of a drive transistor against a calculated APL value; (0015 FIG. 5 shows the forward voltage (Vf) of an EL element and a drain-source Voltage Vds; 0016 FIG. 6 shows a display apparatus using an active matrix display panel according to a second embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 7 shows a pixel unit PL, of a display panel according to a third embodiment of the present invention; 0018 FIG.8 shows the ON/OFF states of switches SW1 to SW3 of FIG.7; (0019 FIG. 9 shows a pixel unit PL, of a display panel according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention; (0020 FIG. 10 shows a relationship of the drive voltage VD of a drive transistor against the APL value; 0021 FIG. 11 shows a display panel having a black level adjusting circuit according to a fifth embodiment of the present invention; and
15 US 2011/ A1 Apr. 14, FIG. 12 shows a relationship of a black level voltage BL against the APL value. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION 0023 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below in detail with reference to the drawings. The same reference numerals are used to denote substantially equivalent parts throughout the figures cited below. First Embodiment 0024 FIG. 2 shows a display apparatus 10 using an active matrix display panel according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The display apparatus 10 comprises a dis play panel 11, a scan driver 12, a data driver 13, a capacitor voltage source (PC) 14, a controller 15, a light-emitting ele ment drive Voltage source (PS) 16, and an average luminance calculating unit (hereinafter also referred to as an APL calcu lating unit) The display panel 11 is an active matrix type of display panel comprising 'n' rows and m columns of pix els, where 'm' and n are integers greater than or equal to two, and has a plurality of data lines X1 to Xm (Xi, i=1 to m) arranged parallel, a plurality of scan lines Y1 to Yin (Y.j=1 to n) arranged parallel, and a plurality of pixel units PL to PL. The pixel units PL to PL, are arranged at the intersections of the data lines X1 to Xm and the scan lines Y1 to Yin and all have the same configuration Further, as described in detail later, the pixel units (or pixel circuits) PL to PL, are connected to a light emitting element drive Voltage line (hereinafter simply referred to as a drive Voltage line) Z and a capacitor Voltage line W Note that in this embodiment, description will be made taking as an example the case where the display panel 11 is a monochrome display panel and where each of the pixel units constitutes one pixel FIG. 3 shows a pixel unit associated with data line Xi (i-1,2,..., m) and Scanline Yi (=1,2,..., n) from among the plurality of pixel units (pixel circuits) PL to PL, of the display panel 11. That is, the pixel unit PL is connected to the data line Xi and the scan line Y, and more specifically, comprises TFTs (thin film transistors) 21, 22 that are respec tively a selecting transistor (Tr1) and a drive transistor (Tr2), a data-holding capacitor (Cs) 24, and an organic EL (elec troluminescent) light-emitting element (OEL) 25. The select ing transistor 21, the drive transistor 22, and the capacitor 24 constitute a drive circuit for the light-emitting element (EL element) 25. Note that description will be made below taking as an example the case where the two TFTs 21, 22 are P-chan nel TFTs The gate of the selecting transistor (Tr1) 21 is con nected to the scan line Y, and its source is connected to the data line Xi. The drain of the selecting transistor 21 is con nected to the control electrode (i.e., gate) of the drive transis tor (Tr2) 22. The source of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is connected to the drive voltage line Z so that a drive voltage VD (a variable voltage) is supplied thereto from the drive voltage source (PS) 16. The drain of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is connected to the anode of the EL element 25. The cathode of the EL element 25 is connected to a potential Vcom common to the plurality of pixel units (pixel circuits) PL to PL navas for example, ground potential (Vcom=0) In the present embodiment, one end of the capacitor (Cs) 24 (a first terminal; electrode E1) is connected to the gate, that is the control electrode, of the drive transistor 22 (and to the drain of the selecting transistor 21), and the other end thereof (a second terminal; electrode E2) is connected to the capacitor Voltage source (PC) 14 via the capacitor Voltage line W. The connection is made Such that a capacitor Voltage Vcap (a fixed Voltage) is applied to the capacitor (Cs) 24 associated with the scan line Y from the capacitor Voltage source (PC) 14 via the capacitor voltage line W The scan lines Y1 to Yn of the display panel 11 are connected to the scan driver 12, and the data lines X1 to Xm are connected to the data driver 13. The controller 15 gener ates a scan control signal SC and a data control signal DD to gradation-drive control the display panel 11 according to an input video signal. The scan control signal is Supplied to the scan driver 12, and the data control signal is Supplied to the data driver The scan driver 12 supplies scan pulses for display on the Scanlines Y1 to Yin at predetermined timings according to the scan control signal sent from the controller 15 to per form line sequential scanning The data driver 13 supplies respective pixel data signals for the pixel units located on the scan line onto which the scan pulse is being Supplied, to the pixel units (i.e., selected pixel units) via the data lines X1 to Xm according to the data control signal sent from the controller 15. For non light-emitting pixel units, the pixel data signal of a level which does not make their EL element emit light is supplied. In other words, the data signals indicating emission lumi nance respectively for the pixels are applied via the data lines X1 to Xm in association with the line sequential scanning so as to control the image display of the display panel The controller 15 controls the entire display appa ratus 10, that is, the scan driver 12, the data driver 13, the capacitor Voltage source (PC) 14, the light-emitting element drive voltage source (PS) 16, and the APL calculating unit 17. (0035) Next, the circuit operation of the pixel unit PL will be described When the scan pulse SP is applied to the j-th scan line Y to select the scan line Y, the selecting transistor 21 becomes conductive (i.e., turned on), and a data signal DP (data Voltage Vdata) corresponding to the luminance of the pixel unit PL, from the data driver 13 is supplied to the gate (i.e., the first terminal; electrode E1) of the capacitor voltage 22 via the selecting transistor 21. Then, the data voltage Vdata is stored in the data-holding capacitor (CS)24, and the Voltage is held Meanwhile, the capacitor voltage V cap (a fixed volt age) is applied to the second terminal (i.e., electrode E2) of the capacitor 24 via the capacitor voltage line W. Thus, even when the selecting transistor 21 is turned off due to the line sequential scanning, the gate potential of the drive transistor 22 is fixed at the Vdata As described above, the variable voltage VD is applied to the source of the drive transistor 22, and the drain thereof is connected to the anode of the organic EL element 25. The cathode of the EL element 25 is connected to the common electrode Vicom. Thus, the current Id flowing through the drive transistor 22 is proportional to VD-Vdata, and the EL element 25 emits light with luminance corre sponding to the data signal Voltage DP and the source Voltage VD of the drive transistor 22.
16 US 2011/ A1 Apr. 14, Next, the operation of adjusting peak luminance (white luminance) according to the brightness of the entire screen of video data will be described The average luminance calculating unit (APL cal culating unit) 17 calculates an average luminance of the screen, i.e., APL (Average Picture Level) that is the brightness of the entire screen from the input video data (display data). The method of calculating the average luminance (APL) may be to add together the data to take the average of them where the input video data is digital data, or to integrate it where the input video data is an analog signal. Then, the calculated APL is supplied to the drive voltage source (PS) FIG. 4 is a graph showing schematically a relation ship of the drive voltage VD of the drive transistor 22, that is, the drive voltage (source voltage) VD in this embodiment against the calculated APL value. The drive voltage source (PS) 16 adjusts the drive voltage (i.e., source voltage) VD of the drive transistor 22 according to the calculated APL value. Namely, the drive voltage source (PS) 16 functions as a drive voltage adjuster. The drive voltage source (PS) 16 adjusts the variable voltage VD to be larger when the entire screen is dark, i.e., the APL is small, and to be smaller when the entire screen is bright with the APL being large That is, as described above, because a current (drive current Id) proportional to VD-Vdata flows through the drive transistor 22, the adjustment of the drive voltage VD can impart a peak luminance characteristic where white lumi nance is made low when video whose entire screen is bright is displayed and becomes higher for video whose background is darker Next, the fact that reduction in electric power con sumed in the drive transistor 22 together with the peak lumi nance characteristic can be achieved by adjusting the drive voltage VD according to the brightness (APL) of the entire screen of video data to impart the peak luminance character istic, will be described specifically with reference to the draw 1ngS An EL element such as the organic EL element 25 exhibits a diode characteristic as well known. That is, the higher the emission luminance is (or the larger the drive currentis), the higher the forward voltage (Vf) is (see FIG. 5). In the conventional configuration, the drive Voltage (Source voltage) of the drive transistor is fixed, and hence the drive Voltage is set according to the highest peak luminance. With this conventional configuration, white luminance is made low when video whose entire Screen is bright is displayed, and hence the forward voltage (Vf) of the EL element becomes lower, while power consumed by the drain-source Voltage Vds of the drive transistor 22 increases because the drive Voltage (Source Voltage) of the drive transistor 22 is constant In contrast, as described above, in the present embodiment the drive voltage (source voltage) VD of the drive transistor 22 is adjusted according to the APL. Specifi cally, when video whose entire screen is bright is displayed, i.e., when the APL is large, the drive voltage VD is decreased, and thus power consumed corresponding to the drain-source voltage Vds of the drive transistor 22 can be suppressed to a low level. Second Embodiment 0046 FIG. 6 shows a display apparatus 10 using an active matrix display panel according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In this display apparatus 10, the display panel 11 is configured as a color organic EL panel More specifically, three pixel units of red, green, blue (R,G,B) are arranged sequentially in a repeated pattern in a row direction. That is, the three pixel units of red, green, blue (R,G,B) form one pixel, and a plurality of the pixels are arranged in a row direction. More specifically, pixels (PR, PG, PB), (PR, PG, PB),..., (PR, PG, PB) are sequentially arranged in the j-th row of the display panel The circuit configurations of the pixel units of red, green, blue (R, G, B) are the same as in the above first embodiment (see FIG. 3) except that EL elements 25 emitting lights of red, green, blue (R,G,B) are respectively used. (0049. In each row, the red pixel units PR, (k=1 to n) are connected to a common connection line ZR, and the green pixel units PG, (k-1 to n) are connected to a common con nection line ZG, and the blue pixel units PB (k=1 to n) are connected to a common connection line ZB. More specifi cally, the connection lines ZR, ZG, ZB are connected to the source of the drive transistor(tr2) 22 in respective pixel units. Drive voltages VD(R), VD(G), VD(B) are supplied respec tively onto these connection lines (light-emitting element drive voltage lines) ZR. ZG, ZB from the light-emitting ele ment drive voltage source (PS) 16. Of course, the light-emit ting element drive voltage source (PS) 16 may be formed of individual variable voltage sources PS16(R), PS16(G), PS16 (B) for the respective colors In the present embodiment, the light-emitting ele ment drive voltage source (PS) 16 adjusts each of the drive voltages VD(R), VD(G), VD(B) according to the brightness (APL) of the entire screen of video data. That is, also where the forward voltage is different for each emission color, power consumed by the drive transistor can be reduced. Fur ther, where the forward voltage of the EL element is different for each emission color, by adjusting the drive Voltage of the drivetransistor for eachemission color, the EL element can be driven with a minimum power Supply Voltage required, and hence the effect of reducing power consumption is larger. Third Embodiment An embodiment which uses a current program scheme will be described below. FIG. 7 shows a pixel unit PL, connected to data line Xi (i-1,2,..., m) and scan line Yi (=1, 2,..., n) from among a plurality of pixel units of a display panel 11 according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Note that in this embodiment, description will be made taking as an example the case where the display panel 11 is a monochrome display panel and where each of the pixel units constitutes one pixel The configuration of the display apparatus 10 is the same as that in the first embodiment (FIG. 2) except that the data driver 13 and the pixel unit PL, have circuit configura tions adapted for the current program scheme as described later The display panel 11 has a circuit configuration adapted for the current program scheme as shown in FIG. 7. More specifically, the pixel unit PL comprises a drive tran sistor (Tr2) 22, a capacitor (Cs) 24, a current source 31, and switches SW1 to SW3. The data driver 13 is configured as a constant current source, and the pixel unit PL is supplied with a data current Idata from the current source 31 corre sponding to the data line Xi of the data driver As in the first embodiment, the source of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is connected to the data line Xi, and the second terminal (i.e., electrode E2) of the capacitor (Cs) 24 is
17 US 2011/ A1 Apr. 14, 2011 connected to a capacitor Voltage line W. That is, a capacitor Voltage Vcap (a fixed Voltage) is applied to the capacitor (Cs) 24 from a capacitor Voltage source 14 via the capacitor Volt age line W. Although during the period of a write mode of the current program operation, the drive Voltage (source Voltage) VD of the transistor (Tr2) 22 is made to be a constant (or fixed) voltage as described later, the fixed voltage VD may be the same in value as the capacitor Voltage V cap applied to one end of the data-holding capacitor, or may be different from it FIG. 7 shows an example of the pixel circuit con figuration of a four-transistor (4-Tr) current program Scheme. The current program scheme will be briefly described below. In the current program Scheme, the pixel circuit can be set in a write mode and a light-emission mode The switches SW1 to SW3 are made open and closed according to a scan pulse signal from the scan driver 12 and/or a control signal from the controller 15. More specifi cally, their ON/OFF is controlled depending on the write mode of writing data to the capacitor (Cs) 24 or the light emission mode of making the light-emitting element (OEL) 25 emit light FIG. 8 shows the ON/OFF states of the switches SW1 to SW3. First, in the data write mode, the switches SW1, SW2 are closed (ON) in response to the scan control signal to select the j-th scan line Y with the switch SW3 being opened (OFF). Thereby, the data current Idata is supplied into the data line Xi to write data. Namely, charge corresponding to a voltage V cap-vdata is stored in the capacitor 24 due to the Supply of the data current Idata, and this Voltage is held across the capacitor. At this time, because the switch SW3 is OFF, the light-emitting element (OEL) 25 does not emit light Then, the pixel circuit switches to the light-emission mode, where the switches SW1, SW2 are made open (OFF) with the switch SW3 being closed (ON), and during the light-emission mode period, the drive Voltage (Source Volt age) is set at an adjusted voltage value VD. Namely, the drive voltage source (PS) 16 sets the drive voltage (source voltage) VD to correspond to the APL value calculated by the APL calculating unit 17 and outputs this Voltage That is, as in the previously-described embodiment, the variable voltage VD is adjusted such that the VD is increased when the entire screen is dark, i.e., when the APL is small, and that the VD is decreased when the entire screen is bright and the APL is large Namely, because a current (drive current Id) propor tional to VD-Vdata flows through the drive transistor 22 as described above, the adjustment of the drive voltage VD can impart the peak luminance characteristic where white lumi nance is made low when video whose entire screen is bright is displayed and becomes higher for video whose background is darker Thus, as described above, the adjustment drive of the drive voltage VD can be applied to the display apparatus of the current program scheme as well, and the same peak luminance characteristic as in the Voltage write type of dis play apparatus described in the above embodiments can be imparted. Fourth Embodiment 0062 Although in the above embodiments description has been made taking as an example the case where the selecting transistor (Tr1) 21 and the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 are P-channel TFTs, the adjustment drive of the drive voltage VD can also be applied to cases where either or both of the two transistors are N-channel TFTs. For example, it can also be applied to cases where the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is an N-channel TFT FIG. 9 shows a pixel unit associated with data line Xi (i-1,2,..., m) and Scanline Yi (=1,2,..., n) from among a plurality of pixel units (pixel circuits) PL to PL, of a display panel 11. That is, the pixel unit is connected to the data line Xi and the Scanline Y, and more specifically, comprises TFTs (thin film transistors) 21, 22 that are respectively a selecting transistor (Tr1) and a drive transistor (Tr2), a data holding capacitor (Cs) 24, and an organic EL (electrolumi nescent) light-emitting element (OEL) 25. The selecting tran sistor 21, the drive transistor 22, and the capacitor 24 form a drive circuit for the light-emitting element (EL element) The gate of the selecting transistor (Tr1) 21 is con nected to the scan line Y, and its source is connected to the data line Xi. The drain of the selecting transistor 21 is con nected to the control electrode (gate) of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22. The drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is an N-channel TFT, and the source of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is connected to a drive voltage line Z so that a drive voltage VD is supplied thereto from the drive voltage source (PS) 16. The drain of the drive transistor (Tr2) 22 is connected to the cathode of the EL element 25. The anode of the EL element 25 is connected to a potential Vcom common to the plurality of pixel units (pixel circuits) PL to PL In the present embodiment, one end of the capacitor (Cs) 24 (a first terminal; electrode E1) is connected to the gate, that is the control electrode, of the drive transistor 22 (and to the drain of the selecting transistor 21), and the other end thereof (a second terminal; electrode E2) is connected to the capacitor Voltage source (PC) 14 via the capacitor Voltage line W. The connection is made Such that a capacitor Voltage Vcap (a fixed Voltage) is applied to the capacitor (Cs) 24 associated with the scan line Y from the capacitor Voltage source (PC) 14 via the capacitor voltage line W In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10, the drive voltage VD of the drive transistor 22 is adjusted accord ing to the APL. Specifically, the drive voltage VD is increased when video whose entire screen is bright is displayed, i.e., when the APL is large, and thus power consumed correspond ing to the drain-source voltage Vds of the drive transistor 22 can be Suppressed to a low level. Fifth Embodiment In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 11, the display panel 11 is provided with a black-level adjusting circuit 31. The configuration of pixel unit PL, of the display panel 11 is the same as in the first embodiment (FIG. 3) It is more effective to vary video data according to the APL with adjusting the drive voltage VD according to the brightness (APL) of the entire screen of the video data as described in the first embodiment The APL value calculated by the APL calculating unit is supplied to the black-level adjusting circuit 31. The black-level adjusting circuit 31 adjusts the black level BL of the input video signal according to the calculated APL value to generate an adjusted data control signal DDA, which is supplied to the data driver The black-level adjusting circuit 31 may adjust, for example, the gain of an amplifier (not shown) amplifying the input video data when the input video data is an analog signal to generate the adjusted data control signal DDA, and may adjust the gain of a multiplier (not shown) multiplying the
18 US 2011/ A1 Apr. 14, 2011 input video data by a multiplier factor when the input video data is digital data to generate the adjusted data control signal DDA (0071 FIG. 12 shows a relationship of the black level volt age BL against the APL value. The black level voltage BL is adjusted Such that when the entire screen is dark, i.e., when the APL value is small, the BL is increased, and that when the entire screen is bright and the APL is large, the VD is decreased. By this adjustment, peak luminance processing can be performed with Suppressing black floating. 1. A display apparatus which has an active matrix type of display panel comprising a plurality of pixel units each hav ing a light-emitting element and a drive transistor whose drive electrode is Supplied with drive Voltage driving said light emitting element, a scan drive unit for sequentially scanning scan lines of said display panel, and a data drive unit for Supplying a data signal based on a video signal to a control electrode of each of said drive transistors in association with scanning by said scan drive unit, said display apparatus com prising: a capacitor provided in each of said plurality of pixel units to hold said data signal, a first terminal of said capacitor being connected to said control electrode of said drive transistor, a capacitor Voltage generating unit which generates a capacitor Voltage to be applied to a second terminal of each of said capacitors; an average luminance calculating unit which calculates average luminance of a display screen based on said video signal; and a drive Voltage adjuster which adjusts the drive Voltage driving said light-emitting element of said drive transis tors according to said average luminance. 2. A display apparatus according to claim 1, wherein said drive Voltage adjuster adjusts said drive Voltage such that white luminance of said display screen increases according to decrease in said average luminance. 3. A display apparatus according to claim 1, wherein said display panel is a color light-emitting panel in which a light emitting element of one color of red, green, and blue is con nected between the scan line and the drive line at each of intersections of scan lines and drive lines arranged in a matrix, and said drive Voltage adjuster adjusts the drive Voltage for said light-emitting elements on a per emission color basis. 4. A display apparatus according to claim 1, wherein said data drive unit comprises a current source that Supplies said capacitor with a current corresponding to said data signal. 5. A display apparatus according to claim 1, comprising: a black-level adjuster that increases a black level for said video signal according to decrease in said average lumi nance so as to generate said data signal. 6. A display apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the capacitor Voltage to be applied to the second terminal of each of said capacitors is a fixed Voltage. c c c c c
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2002O097208A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0097208A1 Hashimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF DRIVING A COLOR LIQUID (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,760,165 B2
 USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1
 USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
USOO6657619B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,619 B1 Shiki (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) CLAMPING FOR LIQUID 6.297,791 B1 * 10/2001 Naito et al.... 34.5/102 CRYSTAL DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis
 IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
United States Patent (19) Stein
 United States Patent (19) Stein 54) PULSE GENERATOR FOR PRODUCING FIXED WIDTH PUISES (75) Inventor: Marc T. Stein, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 967,769 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Stein 54) PULSE GENERATOR FOR PRODUCING FIXED WIDTH PUISES (75) Inventor: Marc T. Stein, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 967,769 22 Filed:
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0176566A1 Yoshida et al. US 2012O176566A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) BACKLIGHT DEVICE AND IMAGE DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0176566A1 Yoshida et al. US 2012O176566A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) BACKLIGHT DEVICE AND IMAGE DISPLAY
United States Patent 19 11) 4,450,560 Conner
 United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013
 USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
-/9. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 POWER.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198009 A1 Morita US 2006O1980.09A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT, DISPLAY DRIVER,
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999
 USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
USOO5923134A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,134 Takekawa (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 1999 54 METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRIVING DC 8-80083 3/1996 Japan. BRUSHLESS MOTOR 75 Inventor: Yoriyuki
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Jun. 28, 2005 (JP) LEVEL DETECTION CIRCUIT IMAGE DATA
 (19) United States US 20070064162A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0064162 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20070064162A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0064162 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,501,230 B1
 USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,918,462 Apr. 17, 1990 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING A SOLID SCAN TYPE RECORDNG HEAD 75 Inventors: Satoru Tomita, Yokohama;
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,918,462 Apr. 17, 1990 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING A SOLID SCAN TYPE RECORDNG HEAD 75 Inventors: Satoru Tomita, Yokohama;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl O : --- I. all T
 (19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090 184902A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0184902 A1 TOMIDA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SELF-LUMINOUS DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD
(19) United States US 20090 184902A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0184902 A1 TOMIDA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SELF-LUMINOUS DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. filed on Jan. Jan. 31, 2002 (JP) A IAININ VAZZZZAZ L
 (19) United States US 200600502O1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0050201 A1 Kato (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY (76) Inventor: Yoshifumi Kato, Kariyashi (JP) Correspondence
(19) United States US 200600502O1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0050201 A1 Kato (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY (76) Inventor: Yoshifumi Kato, Kariyashi (JP) Correspondence
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160O86557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0086557 A1 WATANABE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) CONTROL DEVICE, DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20160O86557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0086557 A1 WATANABE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) CONTROL DEVICE, DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. KO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008
 US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2
 USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2. Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013
 USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2
 USOO8427462B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.427.462 B2 Miyamoto (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS (56) References Cited AND LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
USOO8427462B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.427.462 B2 Miyamoto (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2013 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY APPARATUS (56) References Cited AND LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix OLED Displays
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
