(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
|
|
|
- Dwain Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
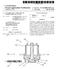
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Kline et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) LARGESCALE LED DISPLAY (76) Inventors: Daniel S. Kline, Encinitas, CA (US); Matthew W. Shankle, Greenwood Village, CO (US); David F. Cox, Escondido, CA (US); James C. Lee, San Diego, CA (US); Sam R. Sarcia, San Diego, CA (US) Correspondence Address: MCANDREWS HELD & MALLOY, LTD 500 WEST MADISON STREET, SUITE 3400 CHICAGO, IL (21) Appl. No.: 12/001,315 (22) Filed: Dec. 11, 2007 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G09G 3/14 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /46 (57) ABSTRACT A large scale LED display has a cable and rigid link support structure for a number of LED modules. The cable and rigid link support structure is flexible but has sufficient structural integrity to prevent misalignment of the pixel modules. The LED modules are removable from the support structure indi vidually and as a group so as to facilitate repair of the display. The LED modules are rugged so as to withstand harsh out door conditions and they provide sufficient luminescence for use in Sunlight.
2 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 1 of 12 US 2009/ A1 al U -IV No.4 it ul ritu W 2
3 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 2 of 12 US 2009/ A1 Fig. 2 f" This II, L-12 (N-S) (9 NILS), O C C d s
4 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 3 of 12 US 2009/ A1 Fig. 3
5 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 4 of 12 US 2009/ A1 Fig. 4
6 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 5 of 12 US 2009/ A1 f
7 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 6 of 12 US 2009/ A1
8 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 7 of 12 US 2009/ A1 s
9 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 8 of 12 US 2009/ A1 Fig
10
11 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 10 of 12 US 2009/ A1 144
12 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 11 of 12 US 2009/ A1
13 Patent Application Publication Jun. 11, 2009 Sheet 12 of 12 US 2009/ A1
14 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 LARGESCALE LED DISPLAY CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS The present application is related to co-pending patent applications U.S. Ser. No. entitled "Data And Power Distribution System and Method For A Large Scale Display; U.S. Ser. No. entitled "Enumeration Sys tem. And Method For A LED Display; and U.S. Ser. No. entitled Large Scale LED Display System. each filed concurrently herewith. STATEMENT REGARDING FEDERALLY SPONSORED RESEARCH ORDEVELOPMENT 0002 N/A TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention is directed to a large scale display and more particularly to the LED modules, segments and Support structure for a large scale LED display. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0004 Large scale displays on the order of 10x20 ft. or 40x60 ft. are known to employ a net formed of intersecting cables to structurally support a number of pixel units as shown in Temple U.S. Patent Application Publication No. US 2006/ A1. Because of its flexible nature, this net display may be supported on curved or irregular Surfaces as well as flat surfaces. However, this net display is so flexible that the pixel units can twist about the cables, impairing the visibility of the pixels. Moreover, the horizontal cables of the net flex so that the pixel units become misaligned resulting in distortions in the displayed image. The pixel units of this net display include a housing for a circuit board that Supports a cluster of red, green and blue LEDs wherein a potting mate rial seals the circuit board from the environment. U.S. patent Yoksza et al. U.S. Pat. No. 5,410,328 shows similar pixel modules for a large scale LED display wherein each module is individually removable from the display by removing a few screws or twisting the module. One wall of the housing of the pixel module in Yoksza et al. extends beyond the LEDs so as to provide a sunshade for the module. Another LED module for a display, as shown in U.S. patent Simon et al. U.S. Pat. No. 4,887,074, uses a heat sinking potting compound in con tact with the circuit board supporting the LEDs and heat spreader plates to dissipate heat from the module housing. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In accordance with the present invention, the disad Vantages of prior art large scale LED displays have been overcome. The LED display system of the present invention includes a novel support structure for a number of LED mod ules wherein the support structure is sufficiently flexible so that the display can conform to curved or irregular Surfaces and yet the Support structure has sufficient structural integrity to prevent twisting and sagging of the LED modules, prevent ing misalignment of the modules so that a distortion free image can be displayed In accordance with one feature of the present inven tion, the display includes a plurality of LED modules wherein each LED module includes a module housing that Supports a plurality of color LEDs. The support structure for the LED modules includes a first pair of parallel cables; a first set of rigid links, extending between the cables of the first cable pair, a second pair of parallel cables, the cables of the second cable pair being parallel to the cables of the first cable pair; and a second set of rigid links extending between the cables of the second cable pair wherein each of the LED modules is mounted on one cable of the first cable pair and one cable of the second cable pair In accordance with another feature of the present invention, the rigid links are H-shaped links that are over molded onto a pair of cables. The links are such that they locate the position of the LED modules along the cables In accordance with another feature of the present invention, the Support structure includes a plurality of plates wherein the plates are mounted on one cable of the first cable pair adjacent to at least one rigid link of the first set and on one cable of the second cable pair adjacent to at least one link of the second set wherein a LED module is removably mounted on a plate In accordance with still a further feature of the present invention, a LED module for a display includes at least two red LEDs; two green LEDs; two blue LEDs; a circuit board on which the LEDs are mounted and an over-molded housing encasing the circuitboard, the LEDs protruding from a front surface of the housing and the front surface of the housing including a plurality of heat sink fins In accordance with another feature of the present invention, a LED display comprises a plurality of linear seg ments of LED modules in each of a plurality of columns or rows of the display, each LED module having a housing Supporting a plurality of multi-color LEDs and each segment including a plurality of LED modules coupled together so that the LED modules of a segment are removable from the dis play only as a group and each segment of LED modules is removable from the display independent of the LED modules of another segment. In this embodiment the LED display may include individual LED modules that are connected between segments of LED modules In accordance with another feature of the present invention, a segment of LED modules for use in a display comprises a first electrical connector fixedly attached to a first end of the segment; a second electrical connector fixedly attached to a second end of the segment; a plurality of spaced LED modules connected between the first electrical connec tor and the second electrical connector, the spaced LED mod ules being connected end-to-end by at least one cable capable of carrying power and/or data to each of the LED modules: and a further cable connected directly between the first con nector and the second connector for carrying data directly between the first and second connectors These and other advantages and novel features of the present invention, as well as details of an illustrated embodiment thereof, will be more fully understood from the following description and drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL VIEWS OF THE DRAWINGS 0013 FIG. 1 is a front view of a large scale display in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention; (0014 FIG. 2 is a partial front view of the display of FIG. 1, illustrating a number of LED modules mounted on the Sup port structure for the display of the present invention; 0015 FIG. 3 is a partial perspective view of the support structure for the display of FIGS. 1 and 2:
15 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, FIG. 4 is a back view of the support structure depicted in FIG. 3: 0017 FIG.5 is a partial front view of a pair of master LED modules and a pair of slave LED modules mounted on the support structure depicted in FIGS. 2-4; 0018 FIG. 6 is a perspective view of a segment of slave LED modules in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention; 0019 FIG. 7 is a side perspective view of the segment of slave LED modules depicted in FIG. 6 with the housing of one of the modules removed; 0020 FIG. 8 is a back view of a segment of slave LED modules as depicted in FIG. 6; 0021 FIG. 9 is a front perspective view of a master LED module in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention; 0022 FIG. 10 is an illustration of the circuit boards and connectors for the master LED module depicted in FIG. 9; 0023 FIG. 11 is a back perspective view of the master LED module of FIG. 9; and 0024 FIG. 12 is a back view of a pair of slave LED module segments connected between respective master LED mod ules. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION A large scale LED display 10 in accordance with the present invention, as shown in FIG. 1, has height by width dimensions on the order of 3 mx6 m to 24 mx32 m or approxi mately 10 ft.x20 ft. to 80 ft.x105 ft. However, it should be appreciated, that the present invention can be used for dis plays that are larger or Smaller as well. A display that is approximately 24 mx32 m has 480 pixelsx640 pixels or a total of 307,200 pixels. These large scale LED displays are intended for both indoor use and outdoor use. The large scale display in accordance with the present invention is extremely robust and can withstand harsh outdoor environments while providing distortion free displayed images. Moreover, seg ments of the display can be readily replaced Each pixel of the display 10 is generated by a mod ule 12 or 14 having two red LEDs 16, two blue LEDs 18 and two green LEDs 20 mounted in a respective housing of the modules 12 or 14 as shown in FIG. 2. A circuit board con tained within the housings of the modules 12 and 14 controls the intensities of the red, blue and green LEDs in order to generate pixels of a large number of different colors as is well known in the art. Although each of the modules 12 and 14 is depicted in FIG. 2 having pairs of red, green and blue LEDs, the number of red, green and blue LEDs can vary depending upon the spacing between the individual modules and the flux density of the individual LEDs. For example, where the cen ter-to-center spacing between adjacent LED modules is 50 mm or greater, one or more red, one or more blue and one or more green LEDs can provide a light output for the display of 5,000 nits or greater depending upon the flux density of the LEDs so that the display 10 is suitable for use outdoors in Sunlight. For a display in which the center-to-center spacing between adjacent LED modules is 75 mm or greater, it is preferable to use a plurality of red LEDs, a plurality of green LEDs and a plurality of blue LEDs, such as three LEDs of each color, although the number of LEDs may be reduced depending upon the flux density of the individual LEDs. It should be appreciated that all of the LEDs of the modules as well as the entire display may be monochromatic as well. When monochromatic LEDs are used, changeable graphics and/or text can be displayed by turning on selected LEDs or modules. Moreover, to enhance the light output of the mod ules, it is preferred that the housing of each of the modules be black or a dark color as described in detail below. In accor dance with another feature of the invention, however, the color of the housing is selected to match the color of the structure, such as a building, on which the display is mounted. Moreover, a single display can employ modules with differ ent colored housings so that when the LEDs of the display are turned off, the different colored housings depict a fixed logo, graphic and/or text message There are two types of pixel modules employed in the display 10, master LED modules 12 and slave LED mod ules 14. Each master module is associated with a group of slave modules in a segment 24 of the display. Although FIG. 2 illustrates a segment as including one master LED module and three slave LED modules for simplicity, in a preferred embodiment of the present invention, each segment has one master module and fifteen slave modules to generate sixteen pixels of the display. It should be apparent, however, that the number of slave modules can vary from Zero to any number depending upon the aspects of the present invention that are used. In a preferred embodiment, the segments 24 of the display 10 are linear, extending in a column of the display 10. However, segments can extend in rows of the display as well. For a 480x640 display having linear segments of sixteen pixels, there are thirty segments in each column of the display. The segments are preferably aligned so that each master module is in a row of master modules. As such, there are thirty rows of master modules with 640 master modules in each row of a 480x640 display with fifteen rows of slave modules between each of the rows of master modules The support structure for each of the LED modules 12 and 14 of the display 10, as shown in FIGS. 2-5, includes a first pair of parallel cables 24 and 26 and a first set of rigid links 28 wherein each link 28 extends between the cable 24 and the cable 26. The support structure for each of the LED modules 12 and 14 also includes a second pair of parallel cables 30 and 32 and a second set of rigid links 34 wherein each link 34 extends between the cable 30 and the cable 32. Each of the LED modules in a first column of the display 10 is mounted on one cable 26 of the first cable pair and on one cable 30 of the second cable pair adjacent at least one link 28 from the first set and adjacent at least one link 34 from the second set. Each of the LED modules in the second column of the display 10 is mounted on the second cable 32 of the second cable pair and a cable 36 adjacent at least one link34 of the second set of links and adjacent at least one link 38 in a third set of links that extends between cables 38 and 40 of a third cable pair. For a display having N columns, the Support structure includes N+1 pairs of cables, such as cables 24 and 26, and N--1 sets of rigid links. If the display has M LED modules in each column, each set of links would include M links. (0029. In a preferred embodiment, the links 28, 34, 38 are H-shaped links that are over-molded onto the cables of each cable pair. More specifically, the two cables of a cable pair are placed in a mold into which plastic is injected around the cable to form the rigid H-shaped links connecting the two cables of a pair. A reel to reel molding process is employed in which the over-molded links are indexed through the mold and the previously molded links are used to datum and posi tion the Subsequent links. The molding process ensures that the spacing between the links along the length of the cables is
16 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 constant. The H-shaped links are used to precisely and easily locate the LED modules along the lengths of the cables so that the spacing between the LED modules in a column and the spacing between the LED modules in a row of the display 10 remains constant. Moreover, the H-shaped links provide structural integrity to the cable support structure of the dis play 10 to prevent sagging and misalignment of the LED modules when the display is in use. It is noted that the cables are preferably steel cables that are of a gauge sufficient to bear the load of all of the LED modules in a column of the display More particularly, as depicted in FIGS. 3 and 4, the rigid H-shaped links serve to locate steel back plates 42 of the master LED modules 12 and steel back plates 44 of the slave LED modules 14. The back plate 42 of each of the master LED modules has four arms on each side of the plate 42 wherein the arms are crimped onto the cables of the support structure. The two inner arms 46 and 47 of the back plate 42 are crimped onto a respective cable on either side of a leg of the H-link 38 such that the arms 46 and 47 abut the H-link with some tolerance therebetween. Similarly, the back plate 44 of the slave LED modules has two arms 50 and 52 on each side of the plate 44 wherein the arms 50 and 52 are crimped onto the cables of the support structure on either side of the H-link such that the arms 50 and 52 abut the H-link with some tolerance therebetween. Because the arms of the back plates 42 and 44 of the LED modules are crimped onto the support cables of the display 10, the arms and thus the back plates can rotate somewhat about the cables to provide enough flexibility for the display 10 so that the display 10 can conform to curved surfaces even though the H-links cannot rotate about the cables. The rigid H-links and LED module back plates provide structural integrity for the Support struc ture and prevent twisting, sagging and misalignment of the LED modules of the display 10. Moreover, the location of the links along the horizontal centerline of the back plates pro vides a structure that can be tensioned. This allows side ten Sioning of the mesh structure to cause the mesh to conform to a curved surface or to remove by tension any incidental wrinkles for a flat configuration Both the master LED modules 12 and the slave LED modules 14 are removably mounted on the respective back plates 42 and 44 so that the individual master LED modules 12 and/or a slave module segment 54 can be removed and replaced after the display 10 is installed. As seen in FIGS. 6-8, a slave module segment 54 includes a first electrical connec tor 56 that is fixedly attached to one end of the segment 54 and a second electrical connector 58 that is connected to a second end of the segment 54. A number of spaced slave LED mod ules 14 are connected between the first and second electrical connectors 56 and 58 via ribbon cables 60. The ribbon cables 60 carry power and data to each of the slave LED modules 14 of the segment 54 from a master module 12 that is connected to one of the electrical connectors As seen in FIGS. 7 and 8, each of the electrical connectors 56 and 58 of a slave module segment 54 includes a pair of downwardly extending rubber or elastomeric prongs 62 and 64. The prongs 62 of the electrical connector 56 snap through apertures 66 formed in the master LED module back plate 42. After the electrical connector 56 of the slave module segment 54 is Snapped into the apertures 66 of a master module back plate 42, each of the slave modules of the seg ment 54 are Snapped on to respective back plate 44. As a slave LED module 14 is snapped on to its back plate 44, a pair of module retaining members 72 are forced apart. When the slave module 14 is Snapped into its back plate, the lower edge 73 of the retaining members 72 abuts the tops of a pair of protrusions 74 formed on the side walls of the slave LED module housing 100 to retain the slave module 14 securely on the back plate 44. The electrical connector 58 on the second end of the slave module segment 54 is inserted in apertures 67 of a master LED module back plate 42 in the next row of master modules. After the slave module segment 54 is mounted on the back plates of the cable Support structure, a master LED module 12 is mounted on the back plate 42. Specifically, a master LED module 12 is mounted on the back plate 42 on top of the connector 56 with mating connector pins 68 of the module 12 extending into the apertures 70 of the electrical connector 56. Each of the master LED modules 12 is secured to a back plate 42 by four screws 78 that extend through apertures 80 of the back plate 42. In a preferred embodiment, the back plate 42 of the master LED modules is formed of steel or the like so that the back plate forms a heat sink that is in contact with the ground plane 82 of the printed circuit board 128 contained in the master LED module hous ing 124 as discussed in detail below. It is noted, that when the master LED module 12 is bolted onto the back plate 42, the over-molded elastomeric pads 86 of the electrical connector 56 are compressed so as to provide a water tight seal between the master LED module 12 and the electrical connector 56 of the slave module segment 54 to protect the connector from environmental effects The master LED module connected to the slave LED module segment 54 via the connector 56 provides data and power to the slave LED modules 14 of the segment 54 via the ribbon connector 60. A LVDS cable 88 that extends from the first electrical connector 56 and the second electrical connector 58 provides a direct electrical connection between a pair of master LED modules 12 and 12" of adjacent segments 24 in a column of the display 10 to allow the master LED modules of adjacent segments in a column to communicate directly as discussed in detail in the copending patent appli cation Ser. No. entitled Data And Power Distribution System And Method For A Large Scale Display, filed con currently herewith and incorporated herein by reference. Adjacent master LED modules 12 and 12" in a row of the display 10 communicate directly via a flex cable 90. In a preferred embodiment, the flex cable 90 overlies a H-link 34 connecting the support cables 32 and 30 as depicted in FIG ). Each of the slave LED modules 14 includes a hous ing 100 that is over-molded about the slave module printed circuit board 102 on which the LEDs of the module are mounted and about a portion of the ribbon cables 60 con nected to the printed circuit board 102 by a IDC connector 104. Each slave LED module is connected to the ribbon cable in a common-bus manner so that a failure of any connection does not affect the other slave modules. In order to over-mold the housings of the slave LED modules 14, a string of, for example, fifteen printed circuit boards 102 supporting the LEDs for respective slave modules are placed in a mold wherein the fifteen printed circuit boards are connected by respective ribbon connectors 60 in a string. Thereafter, a thermoset or thermoplastic resin is injected into the mold to form a casing or housing 100 about the printed circuit boards 102 and ribbon connectors 104. The over-molded housing of the LED modules provides extremely robust modules that can withstand harsh outdoor weather. Prior to injecting the resin to form the housing 100 of the slave LED modules 14, a flash memory contained on the circuit board 102 is programmed with the address of the slave LED module. For a slave module segment 54 having fifteen slave LED modules, the slave modules will have an address of 1 to 15 starting in sequence with the slave LED module that is closest to the electrical connector 56 to be attached to the master LED module that
17 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 will control the slave modules in a segment 24 of the display. It is noted that, while the printed circuit boards are in the molding fixture, the electronics on the boards 102 can be tested prior to over-molding. It is noted, that the mold for the slave LED module housings supports the printed circuitboard 102 for the LEDs at a 10 angle from the back surface 106 of the housing. As such, when the slave LED module segment 54 is mounted vertically, the LEDs are angled downward by 10 for better viewing of the pixels generated by the slave mod ules when the display is in use. It should be appreciated, however, that the angle of the LEDs can be 0 to 20 where the LEDs are angled up, down or to the side depending upon the use of the display Each of the housings 100 for the slave LED modules 14 has integrally formed heat sink fins on a front surface of the housing between a first column 112 of red, green and blue LEDs and a second column 114 of red, green and blue LEDs. Placing the heat sink fins 108 between the LEDs of the mod ule, which are actuated to form a single pixel, does not inter fere with the light generated by the LEDs to form the pixel. It is noted, in a preferred embodiment, the LEDs in the first column have an order of red, green and blue; whereas the LEDs in the second column have an order of green, blue and red so as to provide better color mixing to generate the various colors of a pixel. 0036) Each of the housings 100 for the slave LED modules 14 also has integrally formed sunshades 110 that project outwardly above each of the LEDs 16, 18 and 20. It is noted, that in an alternate embodiment that does not have the heat sink fins 108 on the front surface of the housing 100, one sunshade 110 may be positioned above each row of LEDs. The Sunshades 110 as well as the black or dark resin used to form the housing 100 of the LEDs enhances the contrast or conspicuity of the pixels generated by the modules 14 when the display 10 is used outdoors As shown in FIG. 8, the housing 100 of each of the slave LED modules 14 is molded so as to form a channel 116 in the back surface 106 of the housing 100. The channel 116 is sufficiently wide so as to be able to accommodate the cable 88 therein as well as a pair of power cables 118 and 120. The channels 116 of the housings 100 are aligned with the ribbon cables 60 so that the LVDS cable 88 and the power cables 118 and 120 are aligned in back of the ribbon cables 60. Thus, when viewed from the front of the display 10, the cables and 120 are not readily visible. Further, because the cables 88, 118 and 120 are aligned behind the ribbon cables 60, the display still has open areas between the modules so that if the display 10 is hung in an open area outdoors, there is relief for wind. Moreover, the open areas permit viewing through the display. Such a semi-transparent display will not block the view out of windows of a building upon which the display is hung The housing 124 for each of the master LED mod ules is over-molded about the master module printed circuit boards 126 and 128. The LEDs 16, 18 and 20 for the master module 12 are mounted on the printed circuit board 126 which is similar to the printed circuit board 102 of the slave LED modules for controlling the illumination of the LEDs of a module. The printed circuit board 128 of the master LED module includes additional circuitry for controlling the func tions of the master LED module that are unique thereto, such as extracting the data intended for the master module and its associated slave LED modules in a segment 24 of the display as described in the co-pending patent application Ser. No. entitled Data and Power Distribution System And Method For A Large Scale Display, filed concurrently here with and incorporated herein by reference. In a preferred embodiment, the printed circuit board 126 is soldered to the circuit board 128 at a 10 angle so that when the boards 126 and 128 are placed in the mold for the master LED module housing 124, the LEDs 16, 18 and 20 will be at a 10 angle to the back surface 130 of the module 12 as described above for the LEDs of the slave module The front surface of the housing 124 for each of the master LED modules 12 is the same as the front surface of the housing 100 for the slave LED modules 110 so that both types of modules have the same LED order, the same heat sink fins 108 and the same sunshades 110, providing a uniform appear ance of pixels throughout the display regardless of whether they are generated by a master or a slave module. However, the sides and the back surface 130 of the master LED module housing 124 are different than those of the housing 100 for the slave modules 102. In particular, the sides 129 and 131 of the master module housing 124 are formed with projections 132 having apertures 134 therein for the screws 78 that attach the master LED module 12 to the back plate 42 of the master LED module. The back surface 130 of the master LED module housing 124 includes a number of integrally formed heat sinks 136 so as to further aid in the heat dissipation of the master module. It is noted that the housings for the master LED modules as well as the housings for the slave LED modules are over-molded with a thermally conductive resin. The resin conducts heat away from components and the geometry of the housing spreads the heat and provides a maximized surface area for heat transfer. Moreover, the back plate 42 is thermally and electrically connected to the ground plane on the master LED module's printed circuit board to allow the back plate 42 to act as an additional and independent heat sink for the master LED module The back surface 130 of the housing 124 of the master LED module 12 is also formed with two pairs of grooves 138 and 140 through which power cable connectors 142 and 144 extend. When power cables 118 and 120 are seated in the grooves 138 and 140 of the housing 124, the prongs of the connectors 142 and 144, pierce the rubber insulation of the power cables So as to make electrical contact with the cables. The power cables are continuous and the insulation piercing connectors 142 and 144 are formed with sharp prongs to minimize the force required to penetrate the rubber insulation on the cables. The preferred insulation is a thermoplastic elastomer because of its resilience and tough ness. This insulation tends to close around the penetrating prongs forming a seal. It is noted that when the screws 78 that attach a master LED module 12 to a back plate 42 are tight ened, the prongs of the connectors 142 and 143 are driven into the power cables. A redundant set of power connections are provided for the master LED modules so that there are two positive and two neutral connections spread apart as far as possible Such that the system is tolerant to a connection fail ure. The master LED module 12 also includes Z-axis connec tors 148 and 150 surrounded by elastomeric pads 152. These connectors are commercially available flexible connectors that are designed to conduct along a single Z-axis. The back plate 42 compresses the Z-axis connector between contacts on the printed circuit board 128 and contacts on the flex circuit 90. The flex circuit 90 is designed as a stripline circuit with conductors and conductor spacing adjusted to achieve the desired impedance (75 ohms). The stripline configuration also provides shielding for the data conductors. The Z-axis connectors connect to the flex cables 90 so as to allow adja cent master LED modules 12 in a row of a display panel to communicate directly as discussed above In accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the display 10 is arranged in a number of
18 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 panels for easy deployment. Each panel, may have, for example, sixteen columns wherein a full height panel has 480 rows, although, each of the display panels can have any height and width desired. The support cables, 24, 26, 30, and 40 for the LED modules of each display panel are attached to a steel bar 60 wherein each of the steel bars 160 of a display 10 are clamped together to Support the multiple display pan els forming the display 10. The steel bar 160 is then attached to a support structure 162 which is used to hoist the display 10 on to a Support structure Such as a building or frame. Each of the display panels forming the display 10 includes a data hub 164 that provides the video data to the display panel of the display 10. Power to the display panel 10 may also be pro vided to the display 10 through the data hubs 164 so that the data hubs can monitor the power supply. Details of the data hubs and power hubs for the display 10 are disclosed in the co-pending patent application Ser. No. entitled Data And Power Distribution System And Method For A Large Scale Display, filed concurrently herewith and incor porated herein by reference The large scale LED display of the present invention is extremely robust, readily repairable and suitable for out door as well as indoor use. Many modifications and variations of the present invention are possible in light of the above teachings. Thus, it is to be understood that, within the scope of the appended claims, the invention may be practiced other wise than as described hereinabove. What is claimed and desired to be secured by Letters Patent 1S 1. A LED display comprising: a plurality of LED modules, each LED module including a module housing Supporting a plurality of colored LEDs; a support structure for the plurality of LED modules of the display comprising: a first pair of parallel cables: a first set of rigid links, extending between the cables of the first cable pair; a second pair of parallel cables, the cables of the second cable pair being parallel to the cables of the first cable pair; a second set of rigid links, extending between the cables of the second cable pair; wherein each LED module is mounted on one cable of the first cable pair and one cable of the second cable pa1r. 2. A LED display as recited in claim 1 wherein each LED module is mounted adjacent at least one link from the first set of links and adjacent at least one link from the second set of links, the links locating the position LED module along the cables. 3. A LED display as recited in claim 1 wherein the rigid links are H shaped links over-molded onto a pair of cables. 4. A LED display as recited in claim 1 wherein the rigid links do not pivot about the cables. 5. A LED display as recited in claim 1 further comprising a plurality of plates, each plate mounted on one cable of the first cable pair and one cable of the second cable pair and each plate supporting an LED module thereon to mount the LED module on the cables. 6. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein the rigid links are H shaped links over-molded onto a pair of cables. 7. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein the plates and cables are formed of steel. 8. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein the plates are at least slightly pivotable about the cables on which they are mounted. 9. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein at least one LED module is removably mounted on an associated plate. 10. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein at least one of the LED modules includes red, green and blue LEDs, the LEDs extending outwardly from a first surface of the LED module housing and the first surface of the LED module housing including a plurality of heat sink fins. 11. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein the hous ing of the at least one of the LED modules has at least one Surface with at least one protrusion that Snaps into an aperture of a plate to removably mount the LED module to the plate. 12. A LED display as recited in claim 5 wherein the hous ing of at least one of the LED modules has a back surface abutting the plate when the module is mounted thereon, the back surface of the module having a channel formed therein through which one or more cables pass. 13. A LED display comprising: a plurality of LED modules, each LED module including a module housing Supporting a plurality of colored LEDs; a support structure for the plurality of LED modules of the display comprising: a first pair of parallel cables; a first set of rigid links extending between the cables of the first cable pair; a second pair of parallel cables, the second pair of par allel cables being parallel to the first cable pair; a second set of rigid links extending between the cables of the second cable pair; and a plurality of plates, the plates being mounted on one cable of the first cable pair adjacent at least one link of the first set and on one cable of the second cable pair adjacent at least one link of the second set, wherein an LED module is removably mounted on a plate. 14. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the rigid links are H shaped links over-molded onto a pair of cables. 15. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the LED modules include a first set of modules and a second set of modules, a LED module in the first set being secured to a respective plate by a plurality of screws and a LED module in the second set being Snapped onto a respective plate. 16. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the LED modules include a first set of modules and a second set of modules, a LED module in the first set being individually replaceable and a LED module in the second set being fixedly connected to a plurality of LED modules in the second set to form a segment of modules that are removable from the display together. 17. A LED display as recited in claim 16 wherein a LED module in the first set is secured to a respective plate by a plurality of screws and a LED module in the second set being Snapped onto a respective plate. 18. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein each plate includes a first member and a second member that abut oppo site sides of one link from the first set and each plate includes a third member and a fourth member that abut opposite sides of one link from the second set. 19. ALED display as recited in claim 13 wherein each plate abuts a link from the first set of links and abuts a link from the second set of links. 20. A LED display as recited in claim 19 wherein the links are spaced along the respective cable such that the spacing
19 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 between adjacent links on a cable is constant, the links locat ing the position of the plates along the cables. 21. An LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the plates and cables are formed of steel. 22. ALED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the plates are at least slightly pivotable about the cables on which they are mounted. 23. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein at least one LED module is removably mounted on an associated plate by Snapping the module onto the plate. 24. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein at least one of the LED modules includes red, green and blue LEDs, the LEDs extending outwardly from a first surface of the LED module housing and the first surface of the LED module housing including a plurality of heat sink fins. 25. A LED display as recited in claim 24 wherein a plural ity of the LED module housings include a plurality of heat sink fins on a back Surface of the housing. 26. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein each of a plurality of the plates form a heat sink for the LED module that is mounted thereon. 27. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the housing of the at least one of the LED modules has at least one Surface with at least one protrusion that Snaps into an aperture of a plate to retain the LED module on the plate. 28. A LED display as recited in claim 13 wherein the housing of at least one of the LED modules has a back surface abutting the plate when the module is mounted thereon, the back surface of the module having a channel formed therein through which one or more cables pass. 29. A LED module for a display comprising: one or more red LEDs; one or more green LEDs; one or more blue LEDs; a circuit board on which the LEDs are mounted; and an over-molded housing encasing the circuit board, the LEDs protruding through a front Surface of the housing, and the front Surface of the housing including a plurality of heat sink fins. 30. A LED module as recited in claim 29 wherein the housing is formed of a black resin. 31. ALED module as recited inclaim 29 wherein the LEDs are arranged in at least two columns, each column having a red LED, a green LED and a blue LED wherein the columns are separated by one or more of the heat sink fins. 32. ALED module as recited inclaim 29 wherein the LEDs are arranged in columns including a first column having an order of red, green and blue LEDs and a second column having an order of green, blue and red LEDs. 33. A LED module as recited in claim 32 wherein the first and second columns of LEDs are separated by one or more of the heat sink fins. 34. A LED module as recited in claim 29 wherein the front Surface of the housing includes a plurality of Sunshade pro trusions, each protrusion extending outwardly above one or more of the LEDs of the module. 35. A LED module as recited in claim 34 wherein each LED has an individual Sunshade protrusion extending out wardly above the LED. 36. A LED module as recited in claim 29 wherein the housing has a back Surface with at least one channel formed therein to accommodate at least one cable in the channel. 37. A LED display comprising: a plurality of linear segments of LED modules in each of a plurality of columns or rows of the display, each LED module having a housing Supporting a plurality of mul ticolor LEDs and each segment including a plurality of LED modules coupled together so that the LED modules of a segment are removable from the display only as a group and each segment of LED modules is removable from the display independent of the LED modules of another segment. 38. A LED display as recited in claim 37 including an individual LED module connected between a first segment of LED modules and a second segment of LED modules. 39. A LED display as recited in claim 38 wherein each segment includes at one end a first electrical connector adapted to be connected to one individual LED module and a second electrical connectoratan opposite end of the segment, the second electrical connector adapted to be connected to another individual LED module, each LED module of a seg ment having a module housing with a back wall having a channel formed therein for at least one data cable to pass therethrough, the data cable extending directly between the first electrical connector and the second electrical connector so as to directly connect one individual LED module to another individual LED module. 40. A LED display as recited in claim 39 wherein the channel formed in the module housing of the LED modules of a segment allows at least one power cable to pass there through as well as the data cable. 41. A segment of LED modules for use in a display com prising: a first electrical connector fixedly attached to a first end of the segment; a second electrical connector fixedly attached to a second end of the segment. a plurality of spaced LED modules connected between the first electrical connector and the second electrical con nector, the spaced LED modules being connected end to end by at least one cable capable of carrying power and data to each of the LED modules; a further cable connected directly between the first connec tor and the second connector for carrying data directly between the first and second connectors. 42. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 41 wherein each LED module includes a housing with a back wall having a channel formed therein for the further cable to pass therethrough under the LED module housing. 43. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 41 wherein each LED module includes: one or more red LEDs; one or more green LEDs; one or more blue LEDs; a circuit board on which the LEDs are mounted; and an over-molded housing encasing the circuit board, the LEDs protruding through a front Surface of the housing, and the front Surface of the housing including a plurality of heat sink fins. 44. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 43 wherein the LEDs are arranged in at least two columns, each column having a red LED, a green LED and a blue LED wherein the columns are separated by one or more of the heat sink fins. 45. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 43 wherein the LEDs are arranged in columns including a first
20 US 2009/O A1 Jun. 11, 2009 column having an order of red, green and blue LEDs and a second column having an order of green, blue and red LEDs. 46. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 45 wherein the first and second columns of LEDs are separated by one or more of the heat sink fins. 47. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 43 wherein the front surface of the housing includes a plurality of Sunshade protrusions, each protrusion extending outwardly above one or more of the LEDs of the module. 48. A segment of LED modules as recited in claim 47 wherein each LED has an individual sunshade protrusion extending outwardly above the LED. 49. A large scale LED display comprising: a cable Support structure; and a plurality of LED modules mounted on and structurally supported by the cable support structure, the LED mod ules including at least one red LED. at least one green LED and at least one blue LED supported on a dark color module housing, wherein the center to center spacing between adjacent LED modules is 50 mm or greater and the light output is 5,000 nits or greater. 50. A LED display as recited in claim 49 wherein the LED modules include a plurality of red LEDs, a plurality of green LEDs and a plurality of blue LEDs and the center to center spacing between adjacent LED modules is 75 mm or greater. 51. A large scale LED display comprising: a cable Support structure; and a plurality of LED modules mounted on and structurally Supported by the cable support structure, each LED module having at least one LED Supported on a module housing wherein at least two of the module housings of the display have different colors. 52. A large scale LED display as recited in claim 51 wherein the different color module housings depict a fixed graphic and/or text when the LEDs of the modules are off. 53. A large scale LED display comprising: a cable Support structure; and a plurality of LED modules mounted on and structurally supported by the cable support structure, the LED mod ules including at least one LED supported on a module housing, the LEDs of the display having the same color and wherein the center to center spacing between adja cent LED modules is 50 mm or greater and the light output is 5,000 nits or greater. 54. A LED display comprising: a plurality of LED modules, each LED module including a module housing Supporting a plurality of colored LEDs; a flexible support structure on which the LED modules are mounted, the Support structure including a plurality of parallel cables and a plurality of rigid members, each rigid member being mounted on and extending between a pair of adjacent cables, wherein the LED display is capable of conforming to a curved surface. 55. A LED display as recited in claim 54 wherein a plural ity of the rigid members are rigid links. 56. A LED display as recited in claim 55 wherein the rigid links extending between a pair of adjacent cables are spaced at approximately equal distances along the length of the cables. 57. A LED display as recited in claim 54 wherein a plural ity of the rigid members are back plates on which LED mod ules are mounted. 58. A LED display as recited in claim 54 wherein a group of the rigid members are rigid links and another group of the rigid members are module supports on which LED modules are mounted. 59. A LED display as recited in claim 58 wherein a module Support is mounted on a pair of cables adjacent a rigid link mounted on one cable of the cable pair and adjacent a rigid link mounted on the other cable of the cable pair. 60. A LED display as recited in claim 54 wherein a group of the rigid members are capable of at least Some rotation about the cables on which the members are mounted and another group of rigid members are not rotatable about the cables on which the members are mounted. 61. A LED display as comprising: a plurality of LED modules, each LED module including a module housing Supporting a plurality of colored LEDs; a support structure for the plurality of LED modules of the display, the Support structure including a plurality of parallel cables and a plurality of spacers mounted on and extending between a pair of adjacent cables, each LED module being mounted on a pair of adjacent cables adja cent to at least one spacer. 62. A LED display as recited in claim 61 wherein the spacers are spaced at approximately equal distances along the length of the cables. 63. A LED display as recited in claim 61 wherein the Support structure is flexible and capable of conforming to a curved Surface. 64. A LED display comprising: a plurality of LED modules, each LED module including a module housing Supporting a plurality of colored LEDs; a support structure for the plurality of LED modules of the display, the Support structure including a plurality of parallel cables, a plurality of spacers mounted on and extending between a pair of adjacent cables, and a plu rality of back plates mounted on a pair of adjacent cables, each back plate Supporting an LED module and each spacer maintaining the spacing between adjacent LED modules. 65. A LED display as recited in claim 64 wherein each back plate is mounted adjacent at least one spacer Such that the spacer extends along a centerline of the back plate. 66. A LED display as recited in claim 64 wherein the spacers extending between a pair of adjacent cables are spaced at approximately equal distances along the length of the cables. 67. A LED display as recited in claim 64 wherein the Support structure is flexible and capable of conforming to a curved Surface. 68. A LED display as recited in claim 64 wherein a plural ity of the LED modules snap onto the back plates. 69. A LED display as recited in claim 68 wherein a plural ity of the LED modules are secured to the back plates by SCCWS. 70. A LED display as recited in claim 64 wherein the spacers are rigid links. c c c c c
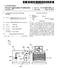
iii. PCA (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 (19) United States ly GbE 1 Dis si O GbE 1
 (19) United States US 20090146931A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146931 A1 Kharrati et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) LARGESCALE LED DISPLAY SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20090146931A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146931 A1 Kharrati et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) LARGESCALE LED DISPLAY SYSTEM (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
US 2004O195471A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0195471 A1 Sachen, JR. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) DUAL FLAT PANEL MONITOR STAND Publication Classification
III. USOO A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998
 III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311612 A1 Qiao et al. US 2015 0311612A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) CABLE-TO-BOARD CONNECTOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311612 A1 Qiao et al. US 2015 0311612A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (60) CABLE-TO-BOARD CONNECTOR
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
s\ OJII <*S Illl INI II III IIMI 1 1 llll I II I II Eur Pean Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1
 s\ OJII
s\ OJII
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1
 USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
USOO6406325B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,406,325 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) CONNECTOR PLUG FOR NETWORK 6,080,007 A * 6/2000 Dupuis et al.... 439/418 CABLING 6,238.235
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
US 6,817,895 B2. Kiely. Nov. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent (54)
 (12) United States Patent Kiely USOO6817895B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) COLOR CODED SHIELDED CABLE AND CONDUIT CONNECTORS
(12) United States Patent Kiely USOO6817895B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 16, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) COLOR CODED SHIELDED CABLE AND CONDUIT CONNECTORS
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
(19) United States US 2003.01.06057A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0106057 A1 Perdon (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2003 (54) TELEVISION NAVIGATION PROGRAM GUIDE (75) Inventor: Albert
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100173523A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0173523 A1 MAGNEZ. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 8, 2010 (54) DUAL-DIRECTION CONNECTOR AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20100173523A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0173523 A1 MAGNEZ. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 8, 2010 (54) DUAL-DIRECTION CONNECTOR AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Williams (54 CONNECTION APPARATUS FOR OPTICAL FBERS 75) Inventor: Russell H. Williams, Flemington, 73) Assignee: Thomas & Betts Corporation, Bridgewater, N.J. (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Williams (54 CONNECTION APPARATUS FOR OPTICAL FBERS 75) Inventor: Russell H. Williams, Flemington, 73) Assignee: Thomas & Betts Corporation, Bridgewater, N.J. (21) Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Hultermans
 United States Patent (19) Hultermans 54) OPTICAL FIBER CONNECTOR INCLUDING A BASING MEANS IN HOUSING (75 Inventor: Antonius P. C. M. Hultermans, Tilburg, Netherlands 73) Assignee: The Whitaker Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Hultermans 54) OPTICAL FIBER CONNECTOR INCLUDING A BASING MEANS IN HOUSING (75 Inventor: Antonius P. C. M. Hultermans, Tilburg, Netherlands 73) Assignee: The Whitaker Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/20
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 43 301 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/20 (1) Int Cl.: G02F 1/1337 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11103.3 (22) Date of filing: 22.02.2011
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 43 301 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/20 (1) Int Cl.: G02F 1/1337 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11103.3 (22) Date of filing: 22.02.2011
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 7,872,186 B1. Jan. 18, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent Tatman (54) (76) Kenosha, WI (US) (*)
 US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
US007872186B1 (12) United States Patent Tatman (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2011 (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) BASSOON REED WITH TUBULAR UNDERSLEEVE Inventor: Notice: Thomas
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand
 United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
( Socarras Publication )
 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O165814A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165814 A1 Parrish (43) Pub. Date: (54) TRELLIS SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A0IG 17/06 (2013.01); A0IG 2017/065
US 2016O165814A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165814 A1 Parrish (43) Pub. Date: (54) TRELLIS SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A0IG 17/06 (2013.01); A0IG 2017/065
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Laubscher & Laubscher Conyers, Ga. 57 ABSTRACT
 USOO5863414A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,863,414 Tilton (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 1999 54) PLASTIC, FLEXIBLE FILM AND 4.261.462 4/1981 Wysocki. PAPERBOARD PRODUCT-RETENTION 4,779,734
USOO5863414A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,863,414 Tilton (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 1999 54) PLASTIC, FLEXIBLE FILM AND 4.261.462 4/1981 Wysocki. PAPERBOARD PRODUCT-RETENTION 4,779,734
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
United States Patent (19) Gartner et al. 54) LED TRAFFIC LIGHT AND METHOD MANUFACTURE AND USE THEREOF 76 Inventors: William J. Gartner, 6342 E. Alta Hacienda Dr., Scottsdale, Ariz. 851; Christopher R.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2
 US007620287B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2 Appenzeller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 17, 2009 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS HOUSING WITH 5,167,001. A 1 1/1992 Debortoli et al....
US007620287B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.620,287 B2 Appenzeller et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 17, 2009 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS HOUSING WITH 5,167,001. A 1 1/1992 Debortoli et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0131504 A1 Ramteke et al. US 201401.31504A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) AUTOMATIC SPLICING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,881,898 B2
 USOO688.1898B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,881,898 B2 Baker et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) REMOTE DISTRIBUTION CABINET 4,783,718 A 11/1988 Raabe et al.... 361/652 RE33,220
USOO688.1898B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,881,898 B2 Baker et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) REMOTE DISTRIBUTION CABINET 4,783,718 A 11/1988 Raabe et al.... 361/652 RE33,220
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003OO3O269A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030269 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE RECEIPT DIARY WITH (52) U.S. Cl.... 283/63.1 ADHESIVE STRIP
US 2003OO3O269A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030269 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXPENSE RECEIPT DIARY WITH (52) U.S. Cl.... 283/63.1 ADHESIVE STRIP
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
352,26,362.25:36:50:32:3:32:3: A. E. "N'io E
 USOO6976777B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: HerOld (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 20, 2005 (54) SIMULATED NEON-LIGHT TUBE 6,231,207 B1 5/2001 Kennedy et al.... 362/158 6,337,946 B1 1/2002 McGaffigan......
USOO6976777B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: HerOld (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 20, 2005 (54) SIMULATED NEON-LIGHT TUBE 6,231,207 B1 5/2001 Kennedy et al.... 362/158 6,337,946 B1 1/2002 McGaffigan......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
MAGNETIC CARD READER DESIGN KIT TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
 MAGNETIC CARD READER DESIGN KIT TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Part Number: D99821002 Rev 212 MAY 2017 REGISTERED TO ISO 9001:2008 1710 Apollo Court Seal Beach, CA 90740 Phone: (562) 546-6400 FAX: (562) 546-6301
MAGNETIC CARD READER DESIGN KIT TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Part Number: D99821002 Rev 212 MAY 2017 REGISTERED TO ISO 9001:2008 1710 Apollo Court Seal Beach, CA 90740 Phone: (562) 546-6400 FAX: (562) 546-6301
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
US 2013 0083040A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0083040 A1 Prociw (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OVERLAPPING (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O172366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0172366 A1 Popp (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CORN SEED SIZING (52) U.S. Cl.... 800/320.1;
US 2005O172366A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0172366 A1 Popp (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CORN SEED SIZING (52) U.S. Cl.... 800/320.1;
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
Serial Number 09/311.900 Filing Date 14 May 1999 Inventor Gair P. Brown Yancy T. Jeleniewski Robert A. Throm NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
E. R. C. E.E.O. sharp imaging on the external surface. A computer mouse or
 USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
USOO6489934B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Klausner (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 2002 (54) CELLULAR PHONE WITH BUILT IN (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Darby & Darby OPTICAL PROJECTOR FOR DISPLAY
United States Patent 19 11) 4,450,560 Conner
 United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
( InfoSystems Translation )
 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,093 B1. Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006
 United States Patent US007 112093B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) POSTLESS COAXIAL COMPRESSION 5,073,129 A * 12/1991 Szegda... 439,585 CONNECTOR 5,632,651 A * 5/1997...
United States Patent US007 112093B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Holland (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) POSTLESS COAXIAL COMPRESSION 5,073,129 A * 12/1991 Szegda... 439,585 CONNECTOR 5,632,651 A * 5/1997...
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
Assistant Examiner Kari M. Horney 75 Inventor: Brian P. Dehmlow, Cedar Rapids, Iowa Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Kyle Eppele; James P.
 USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
USOO59.7376OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,973,760 Dehmlow (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 26, 1999 54) DISPLAY APPARATUS HAVING QUARTER- 5,066,108 11/1991 McDonald... 349/97 WAVE PLATE POSITIONED
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2
 US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100116521A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0116521 A1 Nordin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 13, 2010 (54) COMMUNICATION CABLE WITH (21) Appl. No.: 12/613,695
(19) United States US 20100116521A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0116521 A1 Nordin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 13, 2010 (54) COMMUNICATION CABLE WITH (21) Appl. No.: 12/613,695
OPTIMIZED LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (LED) DEVICES THAT HAVE A HIGH COLOR RENDERING INDEX (CRI) FOR LIGHTING APPLICATIONS
 The contents of U.S. Patent Pub. No. 20100001648, entitled LED lighting that has continuous and adjustable color temperature (CT), while maintaining a high CRI, published on January 7, 2010 is based in
The contents of U.S. Patent Pub. No. 20100001648, entitled LED lighting that has continuous and adjustable color temperature (CT), while maintaining a high CRI, published on January 7, 2010 is based in
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO82696.72B2 (12) United States Patent Tinaphong et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL MULTI-POLARITY, LOW PROFILE
USOO82696.72B2 (12) United States Patent Tinaphong et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL MULTI-POLARITY, LOW PROFILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
SECTION 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Contents Introduction LC, SC and ST Series...4-2 Markets and Applications...4-2 International Standard Documents Compliance...4-2 LC Series Features and Benefits...4-3 LC Standard... 4-4 to 4-5 LC for
Contents Introduction LC, SC and ST Series...4-2 Markets and Applications...4-2 International Standard Documents Compliance...4-2 LC Series Features and Benefits...4-3 LC Standard... 4-4 to 4-5 LC for
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
US 20030216785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0216785 A1 Edwards et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2003 (54) USER INTERFACE METHOD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US007563131B2 (12) United States Patent Sullivan et al. (54) INTEGRATED WALL PLATE ASSEMBLY AND PREMISE WIRING SYSTEM NCORPORATING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Thomas Sullivan, Brookville, OH (US); Gary Hess,
US007563131B2 (12) United States Patent Sullivan et al. (54) INTEGRATED WALL PLATE ASSEMBLY AND PREMISE WIRING SYSTEM NCORPORATING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Thomas Sullivan, Brookville, OH (US); Gary Hess,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
Automatic Connector MHV Connectors MHV Introduction MHV series connectors Contents Polarized mating interfaces Anti-Rock mating interfaces
 Automatic s 2004 Automatic. All rights reserved. pdf 1.0 3-18-04 Contents Specifications........................... 2 Straight Cable Plugs...................... 3 Right Angle Cable Plugs...................
Automatic s 2004 Automatic. All rights reserved. pdf 1.0 3-18-04 Contents Specifications........................... 2 Straight Cable Plugs...................... 3 Right Angle Cable Plugs...................
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
US 200901 22515A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0122515 A1 O0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2009 (54) USING MULTIPLETYPES OF PHOSPHOR IN Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al.
 United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2 i :
 US008 167253B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,167.253 B2 i : Smith 45) Date of Patent May 1, 2012 (54) FLAT PANEL TV STAND PROVIDING 2.477,735 A * 8/1949 Gentile... 248,220.31 FLOATINGAPPEARANCE
US008 167253B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,167.253 B2 i : Smith 45) Date of Patent May 1, 2012 (54) FLAT PANEL TV STAND PROVIDING 2.477,735 A * 8/1949 Gentile... 248,220.31 FLOATINGAPPEARANCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
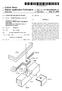 (19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
(19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
Oct. 4, 1960 M. L, HEG 2,955,156 STEREOSCOPIC-TELEVISION APPARATUS FOR INDIVIDUAL USE. s NVENTOR 23.7/4 -4, ATTORNEYS
 Oct. 4, 1960 M. L, HEG 2,9,16 Filed May 24, 197 3. Sheets-Sheet s NVENTOR 23.7/4-4, ATTORNEYS Oct. 4, 1960 M. L. HELIG 2,9,16 Filed May 24, 197 3. Sheets-Sheet 2 III S S Eri S R As l I e E. isie anss B
Oct. 4, 1960 M. L, HEG 2,9,16 Filed May 24, 197 3. Sheets-Sheet s NVENTOR 23.7/4-4, ATTORNEYS Oct. 4, 1960 M. L. HELIG 2,9,16 Filed May 24, 197 3. Sheets-Sheet 2 III S S Eri S R As l I e E. isie anss B
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
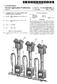 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0032405 A1 Braxton US 2013 OO32405A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) OFFSHORE DRILLING RIG FINGERBOARD
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0032405 A1 Braxton US 2013 OO32405A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) OFFSHORE DRILLING RIG FINGERBOARD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
FLAT AND ROUND CABLE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION DESIGN ADVANTAGES. IDC Systems Cable
 Cable PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Thomas & Betts flat cable provides the means to reduce mass and weight in flexible wiring assemblies. Available with PVC, TPE or FEP insulation, the cable is extruded to provide
Cable PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Thomas & Betts flat cable provides the means to reduce mass and weight in flexible wiring assemblies. Available with PVC, TPE or FEP insulation, the cable is extruded to provide
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240506 A1 Glover et al. US 20140240506A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DISPLAY SYSTEM LAYOUT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240506 A1 Glover et al. US 20140240506A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DISPLAY SYSTEM LAYOUT
Facedown Terminations Improve Ripple Current Capability
 Facedown Terminations Improve Ripple Current Capability John Prymak 1,Peter Blais 2, Bill Long 3 KEMET Electronics Corp. PO Box 5928, Greenville, SC 29606 1 66 Concord St., Suite Z, Wilmington, MA 01887
Facedown Terminations Improve Ripple Current Capability John Prymak 1,Peter Blais 2, Bill Long 3 KEMET Electronics Corp. PO Box 5928, Greenville, SC 29606 1 66 Concord St., Suite Z, Wilmington, MA 01887
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
