(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
|
|
|
- Mitchell Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
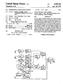
1 (19) United States US 2004O1796O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1 Le Meur et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DEVICE AND PROCESS FORESTIMATING NOISE LEVEL, NOISE REDUCTION SYSTEMAND CODING SYSTEM COMPRISING SUCH A DEVICE (76) Inventors: Olivier Le Meur, Talensac (FR); Jean-Yves Babonneau, L'Hermitage (FR); Georges Joulaud, Liffre (FR) Correspondence Address: Joseph S Tripoli Thomson Licensing Inc Patent Operations CN 5312 Princeton, NJ (US) (21) Appl. No.: 10/487,197 (22) PCT Filed: Aug. 6, 2002 (86) PCT No.: PCT/EP02/08810 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 21, 2001 (FR)... 01/10977 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... H04N 7/12 (52) U.S. Cl /240.12; 375/ (57) ABSTRACT The present invention relates to a device and a process for estimating the noise level of Video images before coding. The device comprises in particular means of Storage of at least one input image, a blockwise motion estimation mod ule, designed to produce, blockwise, first quantities repre Sentative of motion-compensated image variations, on the basis of a current input image and of at least one input image Stored previously in the Said means of Storage, means of estimation of a global noise level for each image as a function of at least certain of the Said quantities represen tative of motion-compensated image variations,the Said device comprises means of estimation of a for each block of the image as a function of Second quan tities representative of motion-compensated image varia tions and of the global noise level. Blockwise motion estination Estimation of a noise level global to the image Estimation of a for a block Motion-adapted and/or compensated noise reduction process
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 2 US 2004/ A1 Blockwise motion estination Estimation of a noise level global to the image Estimation of a for a block Motion-adapted and/or compensated noise reduction process FG. Threshold 2 O Threshold ----> ERRORDFD increase or. increase or Decrease Decrease or upper limitation lower limitation lower limitation lobal of Oglobal ofoglobal g ofoglobal FG3
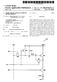
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 2 US 2004/ A1 Calculation of ERRORDFD ERRORDFD29 CERRORDFDS2 E3 ERRORDFDCS1 E8 YES increase in the local noise fevel Decrease in the -- thresholdinc EO YES Decrease in the E9 increase in the increase in the + thresholding Smoothing of the Go to the next DFD (x,y'it) FIG 2
4 DEVICE AND PROCESS FORESTIMATING NOISE LEVEL, NOISE REDUCTION SYSTEMAND CODING SYSTEM COMPRISING SUCH A DEVICE The present invention pertains to a device and to a process for estimating noise level as well as to a noise reduction System and to a coding System comprising Such a device It relates to noise level estimation techniques applied to digital video Signals. These techniques for esti mating noise level are used in noise reduction techniques. Noise reduction techniques are generally applied to digital Video images taking the form of a matrix of Samples, each Sample is composed of a luminance Signal and, for a colour Signal, of a chrominance Signal The acquisiton of video image sequences is today Still widely carried out in analogue form So that the images, once acquired and possibly forwarded and Stored in ana logue formats, exhibit an appreciable share of noise in their content. Once digitized, these images are also often Sub jected to Storage/editing operations which, in their turn, introduce noise of a digital nature, this time. Finally, an image Sequence generally undergoes a Succession of trans formations resulting in Spatio-temporal noise of a Strongly random nature. 0004) To obtain high-performance functioning, noise reduction methods calling upon recursive filtering consider the very strong temporal correlation of the images of a video Sequence. Consequently, the concepts of motion and of displacement are important in the fine-tuning of effective noise reduction The term <<displacement>> is understood to mean the change in position of an object in a Scene, this change in position being localized and Specific to this object. The term <<motion>> is understood to mean the entire Set of dis placements of objects in a Video Sequence Motion is conventionally detected either by simple image-to-image differencing, or by using a motion estimator When a motion estimator is used, the displace ments are taken into account by computing image differ ences at distinct instants as well as by moving Spatially within the frames. These displacements are represented by motion vector fields applied to pixels (pixelwise motion estimation) or to blocks (blockwise motion estimation). Motion-compensated image differences, called DFDS (Dis placement Frame Differences), are thus obtained pixelwise or blockwise In known systems, the estimation of the noise level is done at the level of the image frames. This estimation leads to the noise being made uniform over the frame, and consequently the filtering also, this possibly giving rise to certain defects Such as loss of definition over certain noise free Zones, the appearance of blur or the Smoothing of certain textures (lawns for example). Such Systems are for example described in French Patent Application filed on 24 Jul in the name of the Thomson Multi média Company The present invention relates to a device for esti mating noise level based on local estimation of noise thus taking into account its Strongly random character. The negative effects Set forth hereinabove are then considerably reduced contributing to an increase in image quality The invention also pertains to a noise reduction System and to a coding System comprising Such a device as well as to a corresponding motion-compensated recursive filtering process To this end, the invention concerns a device for estimating the noise level of Video images before coding comprising: 0012) means of Storage of at least one input image, 0013 a blockwise motion estimation module, designed to produce, blockwise, quantities represen tative of motion-compensated image variations, on the basis of a current input image and of at least one input image Stored previously in the Said means of Storage, 0014) means of estimation of a global noise level for each image as a function of at least the Said quantities representative of motion-compensated image varia tions, 0015 according to the invention this device com prises: 0016 means of estimation of a for each block of the image as a function of quantities representative of motion-compensated image varia tions and of the global noise level The expression <<quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations>> is understood to mean quantities which gauge temporal modifications in an image sequence (preferably blockwise) by taking account of motion estimation. These quantities advantageously consist of the DFDS The DFDS are fairly well representative of the amount of noise contained in a Video Sequence. The DFDS even give an exact expression for it if the motion compen sation is ideal (that is to say if the compensation is perfect, regardless of the nature of the motion and the deformations) By taking account of the strongly random nature of the noise, the estimation of a makes it possible to decrease the filtering artefacts; the latter are the direct consequence of a uniform noise level over the frame Synonymous with identical filtering over a noisy block and over a noise-free block Thus, the estimation of the noise level at the local level makes it possible to reduce in particular the StrongloSS of definition over the noise-free Zones of the image, the appearance of blur and the Smoothing of certain textures, for example, lawns By estimating the as a function of the global noise level of the frame, it is possible to situate the noise level of the current block with respect to the global noise level of the frame and thus to improve the estimation of the global noise level Preferably, the said quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations for determining the Said global noise level are a minimum quantity and a mean quantity which are calculated by the blockwise motion estimation module.
5 0023 Preferably, the said quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations for determining the Said are a local quantity and a mean quantity which are calculated by the blockwise motion estimation module According to a preferred embodiment, the means of estimation of a are designed to determine the as a function of the difference between the mean DFD and the local DFD and as a function of the ratio of the said difference to the mean DFD Preferably, the is adjusted differ ently as a function of the comparison between the values of the Said difference and at least one predetermined threshold value This makes it possible to adjust the noise level as a function of predetermined thresholds and thus to limit the fluctuations in the by prohibiting the local noise level from departing from a range of predefined values The invention also relates to a noise reduction device comprising a device for estimating noise level in accordance with the invention The invention also pertains to a coding system comprising a device for estimating the noise level in accor dance with the invention It applies also to a process for estimating the noise level of Video images before coding in which: 0030) at least one current input image is Stored, 0031 a blockwise motion estimation is performed So as to produce, blockwise, quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations, on the basis of a current input image and of at least one input image Stored previously in the Said means of Storage, 0032 a global noise level is determined for each image as a function of at least the Said quantities representative of motion-compensated image varia tions, According to the invention, 0034) a is determined for each block of the image as a function of quantities rep resentative of motion-compensated image variations and of the global noise level. 0035) The invention will be better understood and illus trated by means of wholly nonlimiting, advantageous exem plary embodiments and modes of implementation, with reference to the appended figures in which: FIG. 1 represents a noise level estimation device comprising a estimation module in accor dance with the invention, 0037 FIG. 2 shows a flow chart of the functioning of the module for estimating a for a block, and FIG.3 represents a diagram showing the modifi cations made to the global noise level to obtain the local noise level as a function of predetermined thresholds The following notation is employed: 0040 x, y and t respectively denote the abscissa, the ordinate and time, 0041 u(x,y,t) denotes a current input signal, 0042 u(x,y;t-t) denotes an input signal retarded by a delay T (T represents a delay of one video frame for example), 0043 d(dx.dy) denotes a displacement vector, dx Standing for the offset (shift) in displacement along the abscissa axis and dy the offset in displacement along the ordinate axis, 0044 v(x,y; t) denotes the output of the filter, 0045 Oetal denotes a noise level estimated for the entire image, 0046 O. denotes a noise level estimated for a block of the image, The filtering device comprises a memory 1, designed to Store an input image (signal u(x,y,t)) and a blockwise motion estimator 2, designed to produce, block wise, motion vectors d(dx.dy) and DFDS, on the basis of a current input image (signal u(x,y,t)) and of an input image previously stored (signal u(x,y ;t-t)) in the memory The device is also provided with a module 3 for estimating a noise level global to the image as a function of the mean DFD (DFD) and minimum DFD (DFD) It also comprises a memory 5 for storing the local DFDS for the instant t. The mean DFD is calculated after having traversed all the local DFDS of the frame It also comprises a module 4 for estimating a local noise level for a block as a function of the noise level O. calculated by the module 3 for estimating a noise level global to the image, of the local DFD (DFD(x,y,t)) and of the mean DFD (DFD). The functioning of this module is detailed in FIG The mean DFD (DFD) and the minimum DFD (DFD) are calculated previously, before calculating the local DFD (DFD(x,y;t)) It finally comprises a module 6 for reducing the motion-adapted and/or compensated noise level, as a func tion of the displacement vector d(dx,dy) and of the local noise level Oil (x,y,t) The module 6 outputs the current filtered image V(x,y,t) The module 6 can be a filtering module applied to the noise reduction or more generally an image processing module The minimum DFD (DFD) output by the block wise motion estimation module 2 can be calculated in various ways According to a first embodiment, it can represent the minimum DFD of the frame. This solution is simple and inexpensive but inaccurate Since it Suffices for one of the DFDS to be Small in order to have a small minimum DFD. This therefore gives:
6 DFD min = MINet block (DFDlocalx, y, t) with 0059 resx (respectively resy) the horizontal (respectively vertical) resolution, 0060 blockx (respectively blocky) the size of the horizontal block generally 16 pixels in size (respec tively vertical block generally 8 pixels in size) According to a second embodiment, the DFD, represents a percentage of the minimum DFDS of the frame. In this embodiment, the DFD, is therefore calculated on the basis of a set of values and hence does not represent a Single value as in the previous embodiment. This Solution is therefore more accurate but more complex Since it requires that all the DFDS of the frame be ranked. 0062) The mean DFD, DFD, represents the mean of all the DFDS of the frame. The mean DFD is therefore the Sum of the local DFDS over the number of DFDS in the frame. This therefore gives: X. X. DFDlocaly, y; t) DFD x=l y=l i8c esy resx blocky block X By way of illustrative example, for a frame with resolution and blocks of 16*8, there are (720/ 16)*(288/8) DFDs i.e DFDs. In this case, the mean is computed over these 1620 DFDS and is assigned to the mean DFD This module receives as input the local DFD of the block being processed DFD(x,y;t), the mean DFDDFD g3. as well as the global noise level O global This module carries out a local adaptation of the noise level as a function of the mean DFD DFD, and of the local DFD DFD(x,y ;t) of the current block. This adaptation is controlled on the one hand by the difference (ERRORDFD) between the mean DFD and the local DFD and on the other hand by the ratio (Ratio DFD) of this difference to the mean DFD The difference between the mean DFD and the local DFD determines the direction of variation of the adaptation; specifically, when the error is positive (signify ing that the local DFD is less than the mean DFD) the noise level must be decreased. Conversely, when the error is negative, it brings. about an increase in the noise level The ratio of the difference between the mean DFD and the local DFD to the mean DFD marks, in a form normalized with respect to the mean DFD, the error incurred So as not to make a binary correction which would create Visible artefacts on the image, one Solution is to make a correction as a function of the thresholds. The range of variation of the error ERRORDFD is therefore partitioned into Several Zones The example, given by way of illustration herein below, defines two thresholds partitioning this range into four Zones, as is represented in FIG When the error lies between 0 and Threshold 1 (S1), the local DFD is less than the mean DFD. The noise level must therefore be decreased; for an error close to 0, the decrease is Small and for an error close to Threshold 1 the decrease is a maximum over this interval, as is indicated during step E9 of FIG ) When the error lies between 0 and Threshold2 (S2), the local DFD is greater than the mean DFD. The noise level must therefore be increased; for an error close to 0, the increase is small and for an error close to Threshold2 (S2) the increase is a maximum over this interval, as is indicated during step E4 of FIG ) When the error is greater than Threshold1 (S1), the decrease in the noise level is limited to a maximum value as a function of parameters, as is indicated during Step E10 of FG, When the error is less than Threshold2 (S2), the local DFD is greater than the mean DFD, the local noise level must therefore be increased. To carry out the local adaptation of the noise level, two cases are considered: In the presence of considerable motion, the assumption is made that the motion estimator has performed a poor compensaton. The local DFD therefore represents a mixture of noise and of useful Signal. The local increase in the noise level is then limited by a maximum value as is indicated during step E6 of FIG In the converse case, that is to say in the presence of Slight motion, the motion estimator is regarded as very reliable. The motion compensation is deemed to be of good quality. Consequently, the local DFD represents noise. The increase in the local noise level is therefore not limited as is indicated during step E7 of FIG Weighting coefficients B and B allow greater or lesser accentuation of the effect of the local adjustment. Various ways of effecting this weighting are possible and the exemplary embodiment proposed is given merely by way of illustration We shall now describe FIG. 2 describing an embodiment of the module 4 for estimating a local noise level for a block The module 4 receives as input the mean DFD DFD and the local DFD (DFD(x,y,t)) and calculates during step E1 the difference between the mean DFD and the local DFD called ERRORDFD In the course of step E2, it performs a comparison test to determine whether this difference is positive or negative. 0080) If this difference is negative, it goes to step E3 of comparing this difference with the threshold S ) If ERRORDFD is greater than or equal to the threshold S2, then it goes to step E4. In the course of step E4, the is increased. By way of illustration, the increase can be performed using the following formula: Olocal-Oslobal-Ratio DFDxf32
7 0082) If ERRORDFD is less than S2, then it goes to step E5. In the course of step E5, it performs a test and compares the value of the displacement vector d(x,y) with a motion threshold S3. If d(x,y) is greater than S3, then it goes to step E7. In the course of step E7, the is increased and thresheld. By way of illustration, this can be done in the following manner: Olocal-Oglobalt? 2/2 0083) If d(x,y) is less than or equal to S3, then it goes to step E6 in the course of which the is increased. By way of illustration, this may be done as follows: Olocal-O,eal-Ratio DFDxf ) If, in the course of step E2, ERRORDFD is negative, then it goes to Step E8 of comparing this difference with the threshold S If ERRORDFD is less than or eqaul to the thresh old S1, then it goes to step E9. In the course of step E9, the is decreased. By way of illustration, the decrease can be performed using the following formula: Olocal-Oslobal-Ratio DFDxf1 0086). If ERRORDFD is greater than the threshold S1, then it goes to step E10. In the course of step E10 the local noise level is decreased and a thresholding performed according to the following formula given by way of illus tration: Olocal-Oglobal-B1/ Next it goes to step E11 in the course of which the value of the is Smoothed by imposing a minimum value C and a maximum value C. The final value of the noise level which is obtained is either the value obtained during steps E4, E6, E7, E9 or E10 or C, if this Value is greater than C, or C, if this Value is less than O. min In certain particular embodiments, by way of illus tration, the following values may be taken for the various thresholds To reveal a symmetry, it will be possible to take S1=S2 and B=B. S1=0.5xDFD mean, S2=-0.5xDFD mean, f=f31=6, (these coefficients are akin to f) S3=20. Cimin3.5 C flax 1. Device for estimating the noise level of Video images before coding comprising: means of Storage (1) of at least one input image u(x,y,t) a blockwise motion estimation module (2), designed to produce, blockwise, first quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations (DFD), on the basis of a current input image (u(x,y,t)) and of at least one input image Stored previously (u(x,y ;t-t)) in the Said means of Storage (1), means (3) of estimation of a global noise level (Oba) for each image as a function of at least certain of the Said first quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations (DFD), characterized in that the Said device comprises means (4) of estimation of a (O) for each block of the image as a function of Second quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations (DFD) and of the global noise level (Oba). 2. Device according to claim 1, characterized in that the Said certain first quantities representative of motion-com pensated image variations (DFD) for determining the said global noise level (Oba) are a minimum quantity (DFD i) and a mean quantity (DFD) which are calculated by the blockwise motion estimation module (4). 3. Device according to claim 2, characterized in that the Said Second quantities representative of motion-compen Sated image variations (DFD) for determining the said local noise level (O) are a local quantity (DFD(x,y,t)) and a mean quantity (DFD) which are calculated by the block wise motion estimation module (2). 4. Device according to one of claims 1 or 2, characterized in that the means (4) of estimation of a (O) are designed to determine the as a function of the difference (ERRORDFD) between the mean DFD (DFD) and the local DFD (DFD(x,y,t)) and as a function of the ratio of the said difference to the mean DFD (DFDea). 5. Device according to claim 4, characterized in that the (O) is adjusted differently as a function of the comparison between the values of the said difference (ERRORDFD) and at least one predetermined threshold value (S1, S2, S3). 6. System for reducing noise, characterized in that it comprises a device for estimating the noise level according to one of claims 1 to Coding System comprising a device for estimating the noise level according to one of claims 1 to Process for estimating the noise level of video images before coding in which: at least one current input image (u(x,y,t)) is stored, a blockwise motion estimation is performed So as to produce, blockwise, first quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations (DFD), on the basis of a current input image (u(x,y,t)) and of at least one input image Stored previously (u(x,y ;t-t)) in the Said means of Storage (1), a global noise level (Oba) is determined for each image (u(x,y,t)) as a function of at least certain of the said quantities representative of motion-compensated image variations (DFD), characterized in that a (O) is determined (E4, E6, E7, E9, E10, E11) for each block of the image as a function of Second quantities representative of motion-compen sated image variations (DFD) and of the global noise level (oglobal).
Compute mapping parameters using the translational vectors
 US007120 195B2 (12) United States Patent Patti et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct., 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORESTIMATING MOTION BETWEEN IMAGES (75) Inventors: Andrew Patti, Cupertino,
US007120 195B2 (12) United States Patent Patti et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct., 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORESTIMATING MOTION BETWEEN IMAGES (75) Inventors: Andrew Patti, Cupertino,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
United States Patent: 4,789,893. ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,789,893 Weston December 6, Interpolating lines of video signals
 United States Patent: 4,789,893 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,789,893 Weston December 6, 1988 Interpolating lines of video signals Abstract Missing lines of a video signal are interpolated from the
United States Patent: 4,789,893 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,789,893 Weston December 6, 1988 Interpolating lines of video signals Abstract Missing lines of a video signal are interpolated from the
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
III. United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 5,329,314. Jul. 12, ) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: FILTER FILTER P2B AVERAGER
 United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
United States Patent (19) Correa et al. 54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VIDEO SIGNAL INTERPOLATION AND PROGRESSIVE SCAN CONVERSION 75) Inventors: Carlos Correa, VS-Schwenningen; John Stolte, VS-Tannheim,
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sims USOO6734916B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,734,916 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) VIDEO FIELD ARTIFACT REMOVAL (76) Inventor: Karl Sims, 8 Clinton St., Cambridge, MA
(12) United States Patent Sims USOO6734916B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,734,916 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) VIDEO FIELD ARTIFACT REMOVAL (76) Inventor: Karl Sims, 8 Clinton St., Cambridge, MA
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,628,712 B1
 USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
USOO6628712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Le Maguet (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) SEAMLESS SWITCHING OF MPEG VIDEO WO WP 97 08898 * 3/1997... HO4N/7/26 STREAMS WO WO990587O 2/1999...
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
US 7,319,415 B2. Jan. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Gomila. (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 USOO73194B2 (12) United States Patent Gomila () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan., 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) CHROMA DEBLOCKING FILTER Inventor: Cristina Gomila,
USOO73194B2 (12) United States Patent Gomila () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan., 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) CHROMA DEBLOCKING FILTER Inventor: Cristina Gomila,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
Superpose the contour of the
 (19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(19) United States US 2011 0082650A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0082650 A1 LEU (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR UTILIZING FABRICATION (57) ABSTRACT DEFECT OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2011 0320948A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0320948 A1 CHO (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND USER Publication Classification INTERFACE
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Roberts et al. USOO65871.89B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,189 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) ROBUST INCOHERENT FIBER OPTC
(12) United States Patent Roberts et al. USOO65871.89B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,189 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) ROBUST INCOHERENT FIBER OPTC
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
(12) United States Patent Swan USOO6304297B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANIPULATING DISPLAY OF UPDATE RATE (75) Inventor: Philip L. Swan, Toronto
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nishijima et al. US005391.889A 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 1995 54) OPTICAL CHARACTER READING APPARATUS WHICH CAN REDUCE READINGERRORS AS REGARDS A CHARACTER
United States Patent (19) Nishijima et al. US005391.889A 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 1995 54) OPTICAL CHARACTER READING APPARATUS WHICH CAN REDUCE READINGERRORS AS REGARDS A CHARACTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060222067A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0222067 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR SCALABLY ENCODING AND DECODNG VIDEO SIGNAL (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,020,022 B2. Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited
 United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
United States Patent US008020022B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Tokuhiro (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2011 (54) DELAYTIME CONTROL OF MEMORY (56) References Cited CONTROLLER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(19) United States US 2003O152221A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0152221A1 Cheng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2003 (54) SEQUENCE GENERATOR AND METHOD OF (52) U.S. C.. 380/46;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(19) United States US 2001.0056361A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0056361A1 Sendouda (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2001 (54) CAR RENTAL SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Mitsuru Sendouda,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2
 US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
US007952748B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,952,748 B2 Voltz et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD 358/296, 3.07, 448, 18; 382/299,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0233648 A1 Kumar et al. US 20140233648A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0233648 A1 Kumar et al. US 20140233648A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Penney (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN INDICATION THAT A COLOR REPRESENTED BY A Y, R-Y, B-Y COLOR TELEVISION SIGNALS WALDLY REPRODUCIBLE ON AN RGB COLOR DISPLAY DEVICE 75) Inventor:
AUDIOVISUAL COMMUNICATION
 AUDIOVISUAL COMMUNICATION Laboratory Session: Recommendation ITU-T H.261 Fernando Pereira The objective of this lab session about Recommendation ITU-T H.261 is to get the students familiar with many aspects
AUDIOVISUAL COMMUNICATION Laboratory Session: Recommendation ITU-T H.261 Fernando Pereira The objective of this lab session about Recommendation ITU-T H.261 is to get the students familiar with many aspects
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
USOO8594204B2 (12) United States Patent De Haan (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR BASIC AND OVERLAY VIDEO INFORMATION TRANSMISSION (75) Inventor: Wiebe De Haan, Eindhoven (NL) (73) Assignee: Koninklijke Philips
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0023964 A1 Cho et al. US 20060023964A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 2, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) TERMINAL AND METHOD FOR TRANSPORTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20080232191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0232191 A1 Keller (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) STATIC MIXER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2. Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016
 USOO938913 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2 Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016 (54) ASSEMBLY, SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR G01L 5/042; G01L 5/06; G01L 5/10; A01 K CABLE
USOO938913 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,389,130 B2 Teurlay et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2016 (54) ASSEMBLY, SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR G01L 5/042; G01L 5/06; G01L 5/10; A01 K CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0303331 A1 Yoon et al. US 20090303331A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS OF LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY MODULE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
(19) United States US 20060288846A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0288846A1 Logan (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 28, 2006 (54) MUSIC-BASED EXERCISE MOTIVATION (52) U.S. Cl.... 84/612
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1. Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012
 United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
United States Patent US008205607B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8.205,607 B1 Darlington (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW 7,690.372 B2 * 4/2010 Cooper et al.... 124/25.6 7,721,721
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(19) United States US 2005.0089284A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0089284A1 Ma (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING CABLE WIRE (76) Inventor: Ming-Chuan Ma, Taipei
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
s S (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.412,462 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 9, 2016
 USOO9412462B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (54) 3D STACKED MEMORY ARRAY AND METHOD FOR DETERMINING THRESHOLD VOLTAGES OF STRING SELECTION TRANSISTORS (71) Applicant: Seoul National University
USOO9412462B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (54) 3D STACKED MEMORY ARRAY AND METHOD FOR DETERMINING THRESHOLD VOLTAGES OF STRING SELECTION TRANSISTORS (71) Applicant: Seoul National University
FRAME RATE CONVERSION OF INTERLACED VIDEO
 FRAME RATE CONVERSION OF INTERLACED VIDEO Zhi Zhou, Yeong Taeg Kim Samsung Information Systems America Digital Media Solution Lab 3345 Michelson Dr., Irvine CA, 92612 Gonzalo R. Arce University of Delaware
FRAME RATE CONVERSION OF INTERLACED VIDEO Zhi Zhou, Yeong Taeg Kim Samsung Information Systems America Digital Media Solution Lab 3345 Michelson Dr., Irvine CA, 92612 Gonzalo R. Arce University of Delaware
ECE3296 Digital Image and Video Processing Lab experiment 2 Digital Video Processing using MATLAB
 ECE3296 Digital Image and Video Processing Lab experiment 2 Digital Video Processing using MATLAB Objective i. To learn a simple method of video standards conversion. ii. To calculate and show frame difference
ECE3296 Digital Image and Video Processing Lab experiment 2 Digital Video Processing using MATLAB Objective i. To learn a simple method of video standards conversion. ii. To calculate and show frame difference
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al.
 United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent (19) Starkweather et al. H USOO5079563A [11] Patent Number: 5,079,563 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1992 54 75 73) 21 22 (51 52) 58 ERROR REDUCING RASTER SCAN METHOD Inventors: Gary K.
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2
 USOO8498332B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.498.332 B2 Jiang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 30, 2013 (54) CHROMA SUPRESSION FEATURES 6,961,085 B2 * 1 1/2005 Sasaki... 348.222.1 6,972,793
USOO8498332B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.498.332 B2 Jiang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 30, 2013 (54) CHROMA SUPRESSION FEATURES 6,961,085 B2 * 1 1/2005 Sasaki... 348.222.1 6,972,793
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
USOO9578298B2 (12) United States Patent Ballocca et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,578,298 B2 Feb. 21, 2017 (54) METHOD FOR DECODING 2D-COMPATIBLE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO FLOWS (75) Inventors:
An Overview of Video Coding Algorithms
 An Overview of Video Coding Algorithms Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Video coding can be viewed as image compression with a temporal
An Overview of Video Coding Algorithms Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Video coding can be viewed as image compression with a temporal
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
Dec. 22, 1995 FR France (51) Int. Cl... H04N 7/01 348/450; 348/ Field of Search /448, 449, 910,911. filter.
 United States Patent (19) Heimburger 54 PROCESS FOR INTERPOLATING PROGRESSIVE FRAMES 75 Inventor: Catherine Heimburger, Strasbourg, France 73 Assignee: Thomson multimedia S.A., Boulogne Cedex, France 21
United States Patent (19) Heimburger 54 PROCESS FOR INTERPOLATING PROGRESSIVE FRAMES 75 Inventor: Catherine Heimburger, Strasbourg, France 73 Assignee: Thomson multimedia S.A., Boulogne Cedex, France 21
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(19) United States US 20060097752A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Bhatti et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2006 (54) LUT BASED MULTIPLEXERS (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060095317A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0095317 A1 BrOWn et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORMONITORING (22) Filed: Nov.
US 20060095317A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0095317 A1 BrOWn et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FORMONITORING (22) Filed: Nov.
( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / A1
 THAI MAMMA WA MAI MULT DE LA MORT BA US 20180013978A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / 0013978 A1 DUAN et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Jan. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) VIDEO SIGNAL
THAI MAMMA WA MAI MULT DE LA MORT BA US 20180013978A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication 10 Pub No.: US 2018 / 0013978 A1 DUAN et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Jan. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) VIDEO SIGNAL
STANDARDS CONVERSION OF A VIDEOPHONE SIGNAL WITH 313 LINES INTO A TV SIGNAL WITH.625 LINES
 R871 Philips Res. Repts 29, 413-428, 1974 STANDARDS CONVERSION OF A VIDEOPHONE SIGNAL WITH 313 LINES INTO A TV SIGNAL WITH.625 LINES by M. C. W. van BUUL and L. J. van de POLDER Abstract A description
R871 Philips Res. Repts 29, 413-428, 1974 STANDARDS CONVERSION OF A VIDEOPHONE SIGNAL WITH 313 LINES INTO A TV SIGNAL WITH.625 LINES by M. C. W. van BUUL and L. J. van de POLDER Abstract A description
APPLICATIONS OF DIGITAL IMAGE ENHANCEMENT TECHNIQUES FOR IMPROVED
 APPLICATIONS OF DIGITAL IMAGE ENHANCEMENT TECHNIQUES FOR IMPROVED ULTRASONIC IMAGING OF DEFECTS IN COMPOSITE MATERIALS Brian G. Frock and Richard W. Martin University of Dayton Research Institute Dayton,
APPLICATIONS OF DIGITAL IMAGE ENHANCEMENT TECHNIQUES FOR IMPROVED ULTRASONIC IMAGING OF DEFECTS IN COMPOSITE MATERIALS Brian G. Frock and Richard W. Martin University of Dayton Research Institute Dayton,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
Chapter 2 Introduction to
 Chapter 2 Introduction to H.264/AVC H.264/AVC [1] is the newest video coding standard of the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). The main improvements
Chapter 2 Introduction to H.264/AVC H.264/AVC [1] is the newest video coding standard of the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). The main improvements
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
(19) United States US 2003O126595A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0126595 A1 Sie et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING MARKETING MESSAGES
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A 7001Ö
 Serial Number 09/678.881 Filing Date 4 October 2000 Inventor Robert C. Higgins NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
Serial Number 09/678.881 Filing Date 4 October 2000 Inventor Robert C. Higgins NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9369636B2 (12) United States Patent Zhao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2016 (54) VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD AND CAMERADEVICE (71) Applicant: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen
USOO9369636B2 (12) United States Patent Zhao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2016 (54) VIDEO SIGNAL PROCESSING METHOD AND CAMERADEVICE (71) Applicant: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen
Colour Reproduction Performance of JPEG and JPEG2000 Codecs
 Colour Reproduction Performance of JPEG and JPEG000 Codecs A. Punchihewa, D. G. Bailey, and R. M. Hodgson Institute of Information Sciences & Technology, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand
Colour Reproduction Performance of JPEG and JPEG000 Codecs A. Punchihewa, D. G. Bailey, and R. M. Hodgson Institute of Information Sciences & Technology, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand
Temporal Error Concealment Algorithm Using Adaptive Multi- Side Boundary Matching Principle
 184 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.8 No.12, December 2008 Temporal Error Concealment Algorithm Using Adaptive Multi- Side Boundary Matching Principle Seung-Soo
184 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.8 No.12, December 2008 Temporal Error Concealment Algorithm Using Adaptive Multi- Side Boundary Matching Principle Seung-Soo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS Lesson 24 MPEG-2 Standards Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. State the basic objectives of MPEG-2 standard. 2. Enlist the profiles
Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS Lesson 24 MPEG-2 Standards Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. State the basic objectives of MPEG-2 standard. 2. Enlist the profiles
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20060227O61A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0227061 A1 Littlefield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 12, 2006 (54) OMNI-DIRECTIONAL COLLINEAR ANTENNA (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8891 632B1 (12) United States Patent Han et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Nov. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORENCODING VIDEO AND METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DECODINGVIDEO, BASED ON HERARCHICAL
USOO8891 632B1 (12) United States Patent Han et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Nov. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORENCODING VIDEO AND METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DECODINGVIDEO, BASED ON HERARCHICAL
Reduced complexity MPEG2 video post-processing for HD display
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Reduced complexity MPEG2 video post-processing for HD display Virk, Kamran; Li, Huiying; Forchhammer, Søren Published in: IEEE International Conference on
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Reduced complexity MPEG2 video post-processing for HD display Virk, Kamran; Li, Huiying; Forchhammer, Søren Published in: IEEE International Conference on
(12) United States Patent
 USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
USO09522407B2 (12) United States Patent Bettini (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2016 (54) DISTRIBUTION DEVICE FOR COLORING PRODUCTS (71) Applicant: COROB S.P.A. CON SOCIO UNICO, San Felice
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
A Novel Approach towards Video Compression for Mobile Internet using Transform Domain Technique
 A Novel Approach towards Video Compression for Mobile Internet using Transform Domain Technique Dhaval R. Bhojani Research Scholar, Shri JJT University, Jhunjunu, Rajasthan, India Ved Vyas Dwivedi, PhD.
A Novel Approach towards Video Compression for Mobile Internet using Transform Domain Technique Dhaval R. Bhojani Research Scholar, Shri JJT University, Jhunjunu, Rajasthan, India Ved Vyas Dwivedi, PhD.
Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS Lesson 27 H.264 standard Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. State the broad objectives of the H.264 standard. 2. List the improved
Module 8 VIDEO CODING STANDARDS Lesson 27 H.264 standard Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. State the broad objectives of the H.264 standard. 2. List the improved
SUMMIT LAW GROUP PLLC 315 FIFTH AVENUE SOUTH, SUITE 1000 SEATTLE, WASHINGTON Telephone: (206) Fax: (206)
 Case 2:10-cv-01823-JLR Document 154 Filed 01/06/12 Page 1 of 153 1 The Honorable James L. Robart 2 3 4 5 6 7 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF WASHINGTON AT SEATTLE 8 9 10 11 12
Case 2:10-cv-01823-JLR Document 154 Filed 01/06/12 Page 1 of 153 1 The Honorable James L. Robart 2 3 4 5 6 7 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF WASHINGTON AT SEATTLE 8 9 10 11 12
