Structure Operating and Manufacturing of AMLCD Devices
|
|
|
- Violet White
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 42 ACTA ELECTOTEHNICA Structure Operating and Manufacturing of AMLCD Devices Kada ENCHIKH, elabbes SOUDINI and achid ALLAM Abstract: This paper provides a state of the art review of Active Matrix Liquid Crystal Display (AMLCD) technology. After a short presentation of market dynamics in display technologies and the interest of LCDs in this field, we develop in more details the structure, operating and manufacturing process of AMLCD devices. The review is illustrated with recent achievements made in the field. Improvements and derivates of the devices are described, limitations inherent to technology and design are mentioned. Keywords: LCD, pixel, TFT, active matrix, color filter, time multiplexing. INTODUCTION As the information society develops, demands for various types of display devices increase. Accordingly, many efforts have been made to research and develop various flat display devices such as LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), PDP (Plasma Display Panel), OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), and FED (Field Emission Display). Flat display panel market has generated 74 billion USD in 2005 and should be more than 00 billion USD at the end of Further, LCD market has been of 60 billion USD in The trends in 200, for example, will be of 30 million and 00 million display devices for PDP and LCD respectively. Among various flat display devices, LCD devices have been used most widely replacing CTs (Cathode Tube ay) because of its advantages, such as excellent picture quality, light weight, thin profile and lower consumption. At the present time, CT devices trend to disappear by overgoing recent display technologies concurrence; OLED devices are used newly including only the small size displays; PDP devices are used for large size displays which are very expensive and LCD devices are in top growth covering all display ranges and upsetting PDP devices for large sizes. Moreover LCD manufacturer are making 8th generation plates (40 to 52 ) then reducing the costs for 30% []. Particularly, AMLCD devices are used in an increasingly wide variety of products, including consumer electronic, computer monitors, televisions and other communication devices. A large number of papers related to AMLCD devices have been published and the rate of publications are still growing regularly. We will try to contribute, in this way, with a synthesis work. It should be understood that the figures, in this paper, are merely schematic and are not drawn to scale. In particular certain dimensions, such as the thickness of layers, have been exaggerated while other dimensions have been reduced. 2. STUCTUE Fig. shows the structure of a conventional active matrix liquid crystal display device [2], [3], [4], [5] comprising a display panel, a plurality of picture elements (pixel) arranged in a matrix form. Only a few of the picture elements are shown for simplicity whereas in practice, the total number of picture elements (mxn) in the display area may be or more. The 2008 Mediamira Science Publisher. All rights reserved.
2 Volume 49, Number 4, Timing and Control unit Video processing Unit DATA DIVE n - TFT 2- Liquid crystal 3- Pixel electrode 4- Common electrode 5- ate line 6- Data line 7- round 8- Display panel ATE DIVE m ate signal ate Electrode Data signal Source Electrode Drain Electrode TFT round Pixel Electrode Liquid Crystal Fig.. Circuit diagram of a AMLCD panel. pixel array consists of m rows ( to m) and n columns ( to n). Each picture element is associated with a respective switching device such as a thin film transistor (TFT). The gate electrodes off all TFTs associated with pixels in the same row are connected to a common row conductor as gate line. Similarly the same electrodes associated with all pixels in the same column are connected to a common conductor as data line. The drain electrodes of the TFTs are each connected to a respective transparent pixel electrode. The gate lines, data lines, TFTs and pixel electrodes are carried on one transparent plate. A second transparent plate carries the common electrode to all the pixels. The first and second transparent plates are spaced and a liquid crystal is disposed therebetween. Each of the pixel electrodes together with the liquid crystal and the common electrode define a pixel of a LCD device. A pixel is formed at the intersection of a gate line and a data line so as to cross each other. Each pixel electrode has a necessary capacitance [6], [7 between the pixel electrode and the storage capacitance line. This capacitance serves as a storage capacitance. The gate lines are supplied successively with gate signals by a gate driver controlled by regulator timing pulses from a timing and control unit. Video information signals (data) are supplied to the data lines from a data driver. The data driver is supplied with video signals from a video processing unit and timing pulses from the timing and control unit in synchronism with row scanning. Fig.2 shows a cross-sectional view of an AMLCD panel. The device comprises [8], [3], [9], [7] a pair of glass or like transparent substrate facing each other and spaced apart by a spacer provided therebetween along the edges. Liquid crystal may be sealed between substrates. Alignment layers, made of polyimide, are formed on the transparent substrates. Formed on the inner surface of lower substrate is a plurality of driving electrodes. TFT layer is formed contiguous to driving electrodes. The drain of the TFT forms the pixel electrodes and the TFT serves as switching elements. Then a color filter with a black matrix and common electrode are sequentially formed on the inner surface of the upper transparent substrate. Three different types of color filters, for example, red filter, green filter and blue filter are formed on the upper transparent substrate in correspondence with the driving electrodes. Further, a transparent passivation layer (not shown) may be added on the color filter and then the common conductive electrode is formed on
3 44 ACTA ELECTOTEHNICA acklight - Polarizer 2- Transparent substrate or glass 3- Color filter and black matrix 4- Common electrode 5- Alignment layer 6- Liquid Crystal 7- Pixel electrode 8- TFT layer 9- Driving electrodes 20- Spacer 0 Fig. 2. Cross-sectional view of a AMLCD panel. the passivation layer for driving the liquid crystal. There is a construction where the common transparent electrode is formed directly onto the color film without the passivation layer. The coloring materials may be deteriorated or damaged when the common electrode is formed. This disadvantage is avoided by forming the passivation layer. Transparent spacers are scattered in the liquid crystal layer held by the two transparent substrates in order to keep the thickness (4 to 9 µm) of the liquid crystal layer uniform. Moreover, a sealing material (not shown) is applied to the surrounding section of the liquid crystal display panel except for a liquid crystal injection port. Furthermore, two polarizing films are respectively set on the substrates. Thereafter, liquid crystal is injected through the liquid crystal injection port, and the liquid crystal injection port is closed with an endsealing material. Then, packaging members such as a data driver, a gate driver, a control circuit and a backlight are installed, thereby completing the liquid crystal display device. The backlight, for transmission-type LCD, emits an incident light to produce an image by controlling the transmittance of the incident light. Fig.3 shows an example of the crosssectional view in the active region of the AMLCD panel. A gate electrode, a gate insulating film, a semiconductor layer, a n+si layer to be the source and drain electrodes, a metal layer, an interlayer insulating film, and a transparent conductive layer to be the pixel electrode are formed in this order on an insulating substrate. The pixel electrode is connected to the drain of the TFT. In this structure, the interlayer insulating film is formed between the gate line (the same layer as the gate electrode) and the pixel electrode and between the data line and the pixel electrode. Therefore, the pixel electrode can be arranged to overlap the data line. It is known that such an arrangement can improve the aperture ratio, and reduce an alignment defect of liquid crystal by shielding the electric field resulting from the data line. Fig.4 shows a structural example of a color filter [0],[7]. Three different types of color filters are formed on a glass substrate, for example, red filter, green filter and blue filter corresponding to the three primary colors. The color filters are arranged as a mosaic, delta or stripe pattern. Any color may be achieved by the primary colors mixing principle. In the case of color display one pixel
4 Volume 49, Number 4, Insulating substrate 3-ate electrode 32- ate insulating film 33- Semi-conducteur layer 34- n+si layer 35- Source/drain electrode 36- Passivation layer 37- Pixel electrode 38- Insulating layer Fig. 3. Cross-sectional view in the active region of AMLCD Panel. is formed by three sub-pixels, i.e, red, green and blue pixels. For example a panel for displaying a matrix consisting of 800 horizontal pixels and 600 vertical pixels, the number of sub-pixels displayed on one gate line is The color filter include a black matrix layer which is a light-blocking layer closing gaps between adjacent color filters. Furthermore, with the provision of lightblocking layer to close the gaps between adjacent color filters, there is no possibility of transmission of undesired light through the gaps between adjacent color filters. Then the black matrix layer serves to avoid blurring of the color at the filter boundary. This promotes the improvement of the contrast and color purity, and hence the image quality. 3. MANUFACTUIN POCESS TFT switching elements are usually realised with amorphous silicon (a-si) or polycrystalline silicon (poly-si) and processing temperatures under 300 C are used. Silicon thin film layer is formed on transparent substrate by Low Pressure Vapor lack matrix lue filter ed filter reen filter Transparent substrate Stripe Mosaïc Delta Fig. 4. Structure of a LCD color filter.
5 46 ACTA ELECTOTEHNICA Chemical Deposition (LPCVD) [8], [], [5]. ecently, the trend in LCD devices is to higher resolutions at larger sizes. The driving circuits should use thin film transistors having a high mobility as switching devices for high speed switching of video signals. A method for overcoming the switching problem is to use a poly-si TFT instead of a-si TFT [5]. More particularly, the poly-si TFTs are used in the driving circuits, which are integrated into the LCD panel. Also, active layers of the TFTs in the pixel, such as the semiconductor layer, are made of poly-si, thereby preventing image blur due to slow switching in the pixels. Channel length may be reduced, then decreasing the turn-on time of TFTs and increasing the drain current [9]. ate electrode, source electrode and drain electrode are made of a metal such as aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr) or molybdenum (Mo) [9], [5]. The driving electrodes and common electrode are made of a transparent conductive material like ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) so as to pass light through there [2], [7]. Driving electrodes have a thickness of 3 to 500 angstroms [9]. Semiconductor layer has a thickness of 0. to 0.5 microns. ate insulating film is made of SiO2 by oxidizing the silicon surface [7] or consists of SiNx and has a thickness of 0.5 micron or below [9]. Suitable insulating film is transparent and has a low dielectric constant. For instance, it is of SiO and has a thickness of 5000 angstroms to micron. Transparent substrate is made from material such as glass, pyrex, quartz or like having comparatively high melting point. The color filter manufacturing consists as follow. A water soluble organic resin layer, for example polyvinyl alcohol, gelatine, or the like, is formed on a transparent glass substrate. Then, the water soluble organic layer is colored with coloring materials of red, blue and green by printing these coloring materials in an arrangement having a predetermined pattern. As a result, each color filter is formed so as to be arranged in correspondence to each driving electrode (Fig.). The color filter includes red portions, blue portions and green portions. In addition, a black matrix layer [3], [7] is provided between the color filters by coloring the boundary of each primary color with a black pigment. The black matrix layer [9] may be made of aluminum (Al), or chromium (Cr) with a thickness of 2000 to 3000 angstroms and may be formed by means of deposition or spattering. AMLCD devices may be manufactured from a stock of standard blanks and shaped individually as appropriate. A laser may be use in the cutting step of a preformed active matrix device. In AMLCD devices the plates are typically formed of glass, which can be reliably fractured along straight lines using a scribe and break technique. However, more complex and/or curved shapes may be more readily cut in glass and other suitable plate materials by utilizing laser scribing [4]. On the other hand, while developing ever larger LCDs several interconnect technologies have been used [2]. Two technologies nowadays are used: TA (Tape Automated onding) and CO (Chip On lass) which employs wire bonding directly to the display electrodes. oth require metal bumps on top of the IC surface. CO technology bonds chips directly to the LCD electrodes, by means of bumps, usually grown galvanically on the bond pads of the IC. The extra processing is limited to growing of the bumps and to the bonding of the ICs to the LCD, but packaging of the ICs is removed from the normal production of these ICs. The disadvantage lies in the availability of a high performance bonding process, testability and quality assurance. However, film processing in the CO method requires small number of processes and low cost of materials, compared with the TA method. Therefore, the CO method is preferably used for small-scale liquid crystal display devices in which smaller number of pixels and lower cost are required to be achieved. TA technology operate by growing or transferring bumps on ICs with peripheral contacts, attaching them to a flexible foil and applying the foil to the LCD. This interconnect technology has all the advantages of application flexibility, testability, quality
6 Volume 49, Number 4, assurance, reliable low ohmic contacting and high production yield. TA also has the advantage of reducing the LCD glass size as compared to CO, allowing for larger LCDs from the same substrate. 4. OPEATIN LCD effect is well known [3], [2], [2]. The Twisted Nematic Liquid Crystal (TN-LC) in AMLCD has been arranged so, that in rest both molecular axes parallel to the electrodes gradually rotate over 90 going from one plate to the other opposite plate, and the polarization angle of light passing through, with it. When an electrical field of sufficient strength is applied, the induced dipole LC molecules are aligned perpendicular to the plates, thereby losing the polarizations rotation properties. The display panel is operated in conventional manner. Light from a light source disposed on one side enters the panel and is modulated according to the transmission characteristics of the picture elements. Particularly [5], when a scanning voltage is applied to the gate electrode (Fig.) through the gate line, the TFT is operated so as to apply a data voltage from the data line to the pixel electrode. The data voltage applied to the pixel electrode through the TFT generates a voltage difference between the pixel electrode and the common electrode. The voltage difference changes the arrangement of the liquid crystal between the pixel electrode and the common electrode such that light transmittance characteristics of the pixel are changed. Thus, a visual image can be created with the pixels of an LCD device according to data voltages applied to the pixels. In other manner, when the TFT turns on, a voltage is applied through the data line to the capacitor and the liquid crystal driving electrode. Then, an electrical charge is stored by the capacitor between opposite electrodes. The electrical charge can be kept for a long time because the current leakage of the TFT and the liquid crystal material is negligibly small. Therefore, a principle duty ratio can be the time of electrical charge retention in the capacitor divided by the time necessary for inputting a data signal [8]. The display panel is driven using the time multiplexing principle as shown, for simplicity in the example of Fig. 5. This method [4] operates on a row at a time basis by scanning the gate lines sequentially with a gating (selection) signal so as to turn on each row of TFTs in turn and applying data (video) signals to the data lines for each row of pixels in turn as appropriate and in synchronism with the gating signals so as to build up a complete display picture. Using one row at time addressing all TFTs of the addressed row are switched on for a period determined by the duration of the gating signal corresponding to a row time or less during 0 Strobe LCD matrix 5 Data 7 Pixel (6,5) 0 Pixel ON Pixel OFF 0 Fig. 5. Time multiplexing in AMLCD.
7 48 ACTA ELECTOTEHNICA which the video information signals are transferred from the data lines to the pixels. Upon termination of the gating signal, the TFTs of the row are turned off for the remainder of the field time thereby isolating the pixels from the data line and ensuring the applied charge is stored on the pixels until the next time they are addressed, usually in the next field period. eferring to figure and figure 5, the gate lines are supplied successively with gating signals by a gate driver circuit comprising a digital shift register controlled by regular timing pulses from a timing and control circuit. In the intervals between gating signals, the gate lines are supplied with a substantially constant reference potential by the gate driver circuit. Video information signals are supplied to the data lines from a data driver circuit. The data driver is supplied with video signals from a video processing unit and timing pulses from the timing and control unit in synchronism with row scanning to provide serial to parallel conversion appropriate to the time multiplexing principle of the panel. Data driver (Fig. 6), represent the next step in driver IC development for AMLCDs. Data driver is designed around few main functions []: data input, data storage, data conversion, data output and the shift register, realizing the serial to parallel conversion. Such functions are performed at the transitions of a clock pulse through the shift register during reading of data. A latch stores the assembled data, where a conversion to the appropriate voltage level occurs. On the other hand, an exemplary driving method of a color LCD [7] is shown in Fig.7, wherein respective colors,, and of the color filter are arranged in a mosaic pattern. In the video signal, the respective color signals V, V, and V are multiplexed in synchronism with clocks Ø, Ø2, Ø3. Thus it is necessary that the timing of these clocks Ø, Ø2, Ø3 correspond with the arrangement of each color filter allocated to the pixel. eferring to Fig.6 and Fig.7, when selecting, for example, the first row, a signal V is first supplied to the S output of the shift register (Fig.6) in synchronism with the clock signal Ø. Second, a color signal V is supplied to the S2 output in synchronism with the clock signal Ø2. Third, a color signal V is supplied to the S3 output in synchronism with the clock signal Ø3. Thus, it is necessary to shift the clock signals Ø, Ø2 and Ø3 going from one row to the next row in order to supply one of the three primary color signals to each driving electrode in correspondence with the three primary color filters arranged in the mosaic pattern. Cp Digital rayscale Data V V V Ø Ø 3 S SHIFT EISTE S2 S3 Sn Lp LATCH DAC UFFES O O 2 O 3 To data lines Fig. 6. Circuit diagram of a data driver. O n
8 Volume 49, Number 4, Cp Ø Ø2 Selected Subpixels Ø3 First row First row First row Fig. 7. Signal waveforms color filter subpixels in mosaïc pattern. 5. CONCLUSION Some improvements have been achieved in AMLCD devices and are listed as follow. LCD color filters are sized to prevent incident light leakage between pixels by means of a black matrix. The signal lines may be formed in any number of layers that may have a grounding line in between some or all of the layer to reduce the non-active or non-display area of an AMLCD panel. Further, by reduction of the channel length as well as the on-resistance and parasitic capacitance of TFTs, the switching speed and drain current increase, so an image display of high contrast and satisfactory image quality can be obtained. On other hand, recent innovations in plate formats, layer disposition steps and photolithography together with processing interconnect technology have positioned the AMLCDs as dominant leader in the display market, by a progressive decreasing of device costs, covering a wide variety of products such as portable devices and monitors for computers and TV. EFEENCES W. DEN OE, Active Matrix Liquid Crystal Displays, Fundamentals and applications, Newnes Edit. Oct I. ONNASSIEUX, Ecrans plats PHYS58a 2002, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France. 4. S.C. DEANE, Active Matrix Devices, United States Patent No Jun S.K. Hong, Flat Display Device, United States Patent No Aug N. LU, Active Matrix Display Device; United States Patent No , Oct S. MOOZUMI et al, LCD device having color filters sized to prevent light leakage between pixels, United States Patent No March S. MOOZUMI et al in and.5 in /W and Full-Color LC Vidéo Displays addressed by Poly- Si-TFTs, SID 84 Digest 984, pp S. AOKI et al, LCD device and method of manufacturing the same, United States Patent, No Aug.990. F. SELLA et X. MOAI, la fabrication des écrans à cristaux liquides à matrice active, eport 2003, Ecole des Mines d ALI, Carnaux, France. 2..H. VAN LEEVEN et al, A Digital Common Driver IC for AM-LCDs, Euro display 93 (993). 3..H. VAN LEEVEN et.a. HATMAN, Overview on Active Matrix Display Technology, ESSDEC 93 (993). 4..J. LECHNE et al, Liquid Crystal Matrix Displays; Proc.IEEE, Vol.59, No., Nov.97, pp J.M. SHANNON et al, AMLCD having a metal light shield for each switching device electrically connected to an adjacent row address conductor, United States Patent No , Jul.992
9 420 ACTA ELECTOTEHNICA Kada ENCHIKH Department of Electronics University of Sidi-el-Abbes (Algeria) elabbes SOUDINI achid ALLAM University of Poitiers (France) IOAPHY Kada ENCHIKH was born in Sidi-el-Abbes, Algeria, in 955. He received the Eng degree in Electronic Engineering from USTO University (Algeria) in 980, the MS degree in Microelectronic from University of Sidi-el-Abbes in 992. He is currently professor of Electronic at the University of Sidi-el-Abbes. His current research interests includes display technologies, flat panel displays and microelectronic. elabbes SOUDINI was born in Sidi-el-Abbes, Algeria, in 963. He received the Eng degree in Electronic Engineering from USTO University (Algeria) in 988, the MS degree in Microelectronic from University of Sidi-el-Abbes in 990 and the PhD from the University of Sidi-el-Abbes in 995. He is currently professor of Electronic at the University of Sidi-el-Abbes. His current research interest includes materials sciences, microelectronic and optoelectronic. achid ALLAM was born in Oujda, Morocco, in 955. He received the Dipl. Eng degree in Electronic Engineering from USTO University (Algeria) in 980, the Docteur-Ingenieur in 984 from the University of Lille (France). Currently, he is professor of Electronics at the University of Poitiers (France). His current researchs concerns microwave mixers, nonlinear CAD and millimeter-wave MMICs.
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Liquid Crystal Displays
 Liquid Crystal Displays Cosmin Ioniţă - Spring 2006 - A brief history 1888 - Friedrich Reinitzer, an Austrian chemist working in the Institute of Plant Physiology at the University of Prague, discovered
Liquid Crystal Displays Cosmin Ioniţă - Spring 2006 - A brief history 1888 - Friedrich Reinitzer, an Austrian chemist working in the Institute of Plant Physiology at the University of Prague, discovered
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) When coming into contact with grooved surface in a fixed direction, liquid crystal molecules line up parallelly along the grooves. When coming into contact with grooved surface
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) When coming into contact with grooved surface in a fixed direction, liquid crystal molecules line up parallelly along the grooves. When coming into contact with grooved surface
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VARIOUS DISPLAY TECHNOLOGIESS
 VARIOUS DISPLAY TECHNOLOGIESS Mr. Virat C. Gandhi 1 1 Computer Department, C. U. Shah Technical Institute of Diploma Studies Abstract A lot has been invented from the past till now in regards with the
VARIOUS DISPLAY TECHNOLOGIESS Mr. Virat C. Gandhi 1 1 Computer Department, C. U. Shah Technical Institute of Diploma Studies Abstract A lot has been invented from the past till now in regards with the
These are used for producing a narrow and sharply focus beam of electrons.
 CATHOD RAY TUBE (CRT) A CRT is an electronic tube designed to display electrical data. The basic CRT consists of four major components. 1. Electron Gun 2. Focussing & Accelerating Anodes 3. Horizontal
CATHOD RAY TUBE (CRT) A CRT is an electronic tube designed to display electrical data. The basic CRT consists of four major components. 1. Electron Gun 2. Focussing & Accelerating Anodes 3. Horizontal
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
Technology White Paper Plasma Displays. NEC Technologies Visual Systems Division
 Technology White Paper Plasma Displays NEC Technologies Visual Systems Division May 1998 1 What is a Color Plasma Display Panel? The term Plasma refers to a flat panel display technology that utilizes
Technology White Paper Plasma Displays NEC Technologies Visual Systems Division May 1998 1 What is a Color Plasma Display Panel? The term Plasma refers to a flat panel display technology that utilizes
the Most Popular Display Technology?
 Why is LCD the Most Popular Display Technology? History of Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) As early as 1889, scientists discovered that chemicals such as cholesteryl benzoate, when melted into liquid form,
Why is LCD the Most Popular Display Technology? History of Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) As early as 1889, scientists discovered that chemicals such as cholesteryl benzoate, when melted into liquid form,
Joint Development of Ultra-Bright, Inorganic EL Light-Emitting Materials. November 2, 2005 KURARAY CO., LTD.
 Joint Development of Ultra-Bright, Inorganic EL Light-Emitting Materials November 2, 2005 KURARAY CO., LTD. Sales Trends of Display-related Products (Kuraray (standalone)) FY1994 FY1999 FY2004 Sales Ratio
Joint Development of Ultra-Bright, Inorganic EL Light-Emitting Materials November 2, 2005 KURARAY CO., LTD. Sales Trends of Display-related Products (Kuraray (standalone)) FY1994 FY1999 FY2004 Sales Ratio
ID C10C: Flat Panel Display Basics
 ID C10C: Flat Panel Display Basics Renesas Electronics America Inc. Robert Dunhouse, Display BU Engineering Manager 12 October 2010 Revision 1.1 Robert F. Dunhouse, Jr. Displays Applications Engineering
ID C10C: Flat Panel Display Basics Renesas Electronics America Inc. Robert Dunhouse, Display BU Engineering Manager 12 October 2010 Revision 1.1 Robert F. Dunhouse, Jr. Displays Applications Engineering
 Chapter 1 Introduction --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.1 Overview of the Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Displays Flat
Chapter 1 Introduction --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.1 Overview of the Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Displays Flat
COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS
 COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS by Roberto W. Flores A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of George Mason University in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for
COMPENSATION FOR THRESHOLD INSTABILITY OF THIN-FILM TRANSISTORS by Roberto W. Flores A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of George Mason University in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for
Hitachi Europe Ltd. ISSUE : app084/1.0 APPLICATION NOTE DATE : 28/04/99
 APPLICATION NOTE DATE : 28/04/99 Design Considerations when using a Hitachi Medium Resolution Dot Matrix Graphics LCD Introduction Hitachi produces a wide range of monochrome medium resolution dot matrix
APPLICATION NOTE DATE : 28/04/99 Design Considerations when using a Hitachi Medium Resolution Dot Matrix Graphics LCD Introduction Hitachi produces a wide range of monochrome medium resolution dot matrix
28 North Lotts, Dublin 1, Ireland Tel: info [AT] phonevolts.com
![28 North Lotts, Dublin 1, Ireland Tel: info [AT] phonevolts.com 28 North Lotts, Dublin 1, Ireland Tel: info [AT] phonevolts.com](/thumbs/91/104995975.jpg) www.phonevolts.ie 28 North Lotts, Dublin 1, Ireland Tel: 01 8728722 Email: info [AT] phonevolts.com PhoneVolts is owned and operated by GSMsolutions.ie What is an LCD? A liquid crystal display (commonly
www.phonevolts.ie 28 North Lotts, Dublin 1, Ireland Tel: 01 8728722 Email: info [AT] phonevolts.com PhoneVolts is owned and operated by GSMsolutions.ie What is an LCD? A liquid crystal display (commonly
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
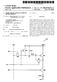 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
Flat Panel Displays: LCD Technologies and Trends
 Flat Panel Displays: LCD Technologies and Trends Robert Dunhouse, Sr. Engineering Manager, Display BU Class ID: 4C01B Renesas Electronics America Inc. Robert F. Dunhouse, Jr. Sr. Engineering Manager, Display
Flat Panel Displays: LCD Technologies and Trends Robert Dunhouse, Sr. Engineering Manager, Display BU Class ID: 4C01B Renesas Electronics America Inc. Robert F. Dunhouse, Jr. Sr. Engineering Manager, Display
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/24
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 068 378 A2 (43) Date of publication:.06.2009 Bulletin 2009/24 (21) Application number: 08020371.4 (51) Int Cl.: H01L 33/00 (2006.01) G02F 1/13357 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 068 378 A2 (43) Date of publication:.06.2009 Bulletin 2009/24 (21) Application number: 08020371.4 (51) Int Cl.: H01L 33/00 (2006.01) G02F 1/13357 (2006.01)
In-Cell Projected Capacitive Touch Panel Technology
 1384 INVITED PAPER Special Section on Electronic Displays In-Cell Projected Capacitive Touch Panel Technology Yasuhiro SUGITA a), Member, Kazutoshi KIDA, and Shinji YAMAGISHI, Nonmembers SUMMARY We describe
1384 INVITED PAPER Special Section on Electronic Displays In-Cell Projected Capacitive Touch Panel Technology Yasuhiro SUGITA a), Member, Kazutoshi KIDA, and Shinji YAMAGISHI, Nonmembers SUMMARY We describe
Alien Technology Corporation White Paper. Fluidic Self Assembly. October 1999
 Alien Technology Corporation White Paper Fluidic Self Assembly October 1999 Alien Technology Corp Page 1 Why FSA? Alien Technology Corp. was formed to commercialize a proprietary technology process, protected
Alien Technology Corporation White Paper Fluidic Self Assembly October 1999 Alien Technology Corp Page 1 Why FSA? Alien Technology Corp. was formed to commercialize a proprietary technology process, protected
Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix OLED Displays
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
Research & Development of Surface-Discharge Color Plasma Display Technologies. Tsutae Shinoda
 esearch & Development of Surface-Discharge Color Plasma Display Technologies Tsutae Shinoda Peripheral System Laboratories,Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. 64, Nishiwaki, Ohkubo-cho, Akashi 674-8555 Japan Abstract
esearch & Development of Surface-Discharge Color Plasma Display Technologies Tsutae Shinoda Peripheral System Laboratories,Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. 64, Nishiwaki, Ohkubo-cho, Akashi 674-8555 Japan Abstract
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
High-resolution screens have become a mainstay on modern smartphones. Initial. Displays 3.1 LCD
 3 Displays Figure 3.1. The University of Texas at Austin s Stallion Tiled Display, made up of 75 Dell 3007WPF LCDs with a total resolution of 307 megapixels (38400 8000 pixels) High-resolution screens
3 Displays Figure 3.1. The University of Texas at Austin s Stallion Tiled Display, made up of 75 Dell 3007WPF LCDs with a total resolution of 307 megapixels (38400 8000 pixels) High-resolution screens
Organic light emitting diode (OLED) displays
 Ultra-Short Pulse Lasers Enable Precision Flexible OLED Cutting FLORENT THIBAULT, PRODUCT LINE MANAGER, HATIM HALOUI, APPLICATION MANAGER, JORIS VAN NUNEN, PRODUCT MARKETING MANAGER, INDUSTRIAL PICOSECOND
Ultra-Short Pulse Lasers Enable Precision Flexible OLED Cutting FLORENT THIBAULT, PRODUCT LINE MANAGER, HATIM HALOUI, APPLICATION MANAGER, JORIS VAN NUNEN, PRODUCT MARKETING MANAGER, INDUSTRIAL PICOSECOND
1. Publishable summary
 1. Publishable summary 1.1. Project objectives. The target of the project is to develop a highly reliable high brightness conformable low cost scalable display for demanding applications such as their
1. Publishable summary 1.1. Project objectives. The target of the project is to develop a highly reliable high brightness conformable low cost scalable display for demanding applications such as their
Sep 09, APPLICATION NOTE 1193 Electronic Displays Comparison
 Sep 09, 2002 APPLICATION NOTE 1193 Electronic s Comparison Abstract: This note compares advantages and disadvantages of Cathode Ray Tubes, Electro-Luminescent, Flip- Dot, Incandescent Light Bulbs, Liquid
Sep 09, 2002 APPLICATION NOTE 1193 Electronic s Comparison Abstract: This note compares advantages and disadvantages of Cathode Ray Tubes, Electro-Luminescent, Flip- Dot, Incandescent Light Bulbs, Liquid
V6118 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
Organic Light Emitting Diodes
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Organic Light Emitting Diodes Badisa Sai Ram Krsihna Final Year B.Tech, Dept. of ECE, KL University, Vaddeswaram, AP, India Angadi Suresh Associate Professor B.Tech, Dept. of ECE,
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Organic Light Emitting Diodes Badisa Sai Ram Krsihna Final Year B.Tech, Dept. of ECE, KL University, Vaddeswaram, AP, India Angadi Suresh Associate Professor B.Tech, Dept. of ECE,
AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing. Research Division Almaden - Austin - Beijing - Haifa - India - T. J. Watson - Tokyo - Zurich
 RT0565 Engineering Technology 4 pages Research Report February 3, 2004 AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing Y. Sakaguchi, D. Nakano IBM Research, Tokyo Research Laboratory IBM Japan, Ltd.
RT0565 Engineering Technology 4 pages Research Report February 3, 2004 AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing Y. Sakaguchi, D. Nakano IBM Research, Tokyo Research Laboratory IBM Japan, Ltd.
Chapter 2 Circuits and Drives for Liquid Crystal Devices
 Chapter 2 Circuits and Drives for Liquid Crystal Devices Hideaki Kawakami 2.1 Circuits and Drive Methods: Multiplexing and Matrix Addressing Technologies Hideaki Kawakami 2.1.1 Introduction The liquid
Chapter 2 Circuits and Drives for Liquid Crystal Devices Hideaki Kawakami 2.1 Circuits and Drive Methods: Multiplexing and Matrix Addressing Technologies Hideaki Kawakami 2.1.1 Introduction The liquid
Digital time-modulation pixel memory circuit in LTPS technology
 Digital time-modulation pixel memory circuit in LTPS technology Szu-Han Chen Ming-Dou Ker Tzu-Ming Wang Abstract A digital time-modulation pixel memory circuit on glass substrate has been designed and
Digital time-modulation pixel memory circuit in LTPS technology Szu-Han Chen Ming-Dou Ker Tzu-Ming Wang Abstract A digital time-modulation pixel memory circuit on glass substrate has been designed and
Emiflective Display with Integration of Reflective Liquid Crystal Display and Organic Light Emitting Diode
 Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 46, No. 1, 2007, pp. 182 186 #2007 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Emiflective Display with Integration of Reflective Liquid Crystal Display and Organic Light
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 46, No. 1, 2007, pp. 182 186 #2007 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Emiflective Display with Integration of Reflective Liquid Crystal Display and Organic Light
Display Technologies CMSC 435. Slides based on Dr. Luebke s slides
 Display Technologies CMSC 435 Slides based on Dr. Luebke s slides Recap: Transforms Basic 2D Transforms: Scaling, Shearing, Rotation, Reflection, Composition of 2D Transforms Basic 3D Transforms: Rotation,
Display Technologies CMSC 435 Slides based on Dr. Luebke s slides Recap: Transforms Basic 2D Transforms: Scaling, Shearing, Rotation, Reflection, Composition of 2D Transforms Basic 3D Transforms: Rotation,
Challenges in the design of a RGB LED display for indoor applications
 Synthetic Metals 122 (2001) 215±219 Challenges in the design of a RGB LED display for indoor applications Francis Nguyen * Osram Opto Semiconductors, In neon Technologies Corporation, 19000, Homestead
Synthetic Metals 122 (2001) 215±219 Challenges in the design of a RGB LED display for indoor applications Francis Nguyen * Osram Opto Semiconductors, In neon Technologies Corporation, 19000, Homestead
Development of Simple-Matrix LCD Module for Motion Picture
 Development of Simple-Matrix LCD Module for Motion Picture Kunihiko Yamamoto* Shinya Takahashi* Kouki Taniguchi* * A1203 Project Team Abstract A simple-matrix LCD module (12.1-in. SVGA) has been developed
Development of Simple-Matrix LCD Module for Motion Picture Kunihiko Yamamoto* Shinya Takahashi* Kouki Taniguchi* * A1203 Project Team Abstract A simple-matrix LCD module (12.1-in. SVGA) has been developed
Display Devices & its Interfacing
 Display Devices & its Interfacing 3 Display systems are available in various technologies such as i) Cathode ray tubes (CRTs), ii) Liquid crystal displays (LCDs), iii) Plasma displays, and iv) Light emitting
Display Devices & its Interfacing 3 Display systems are available in various technologies such as i) Cathode ray tubes (CRTs), ii) Liquid crystal displays (LCDs), iii) Plasma displays, and iv) Light emitting
Transflective Liquid Crystal Display
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Transflective Liquid Crystal Display 6-29-2010 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Ju-Hyun Lee University of Central Florida Xinyu Zhu University
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Transflective Liquid Crystal Display 6-29-2010 Shin-Tson Wu University of Central Florida Ju-Hyun Lee University of Central Florida Xinyu Zhu University
TEPZZ 695A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 ( ) G06F 3/041 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 695A_T (11) EP 3 121 695 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 25.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/04 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 (2006.01) G06F 3/041 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 695A_T (11) EP 3 121 695 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 25.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/04 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 (2006.01) G06F 3/041 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits
 Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits Chapter 9 Objectives Selected areas covered in this chapter: Analyzing/using decoders & encoders in circuits. Advantages and disadvantages of LEDs and LCDs. Observation/analysis
Chapter 9 MSI Logic Circuits Chapter 9 Objectives Selected areas covered in this chapter: Analyzing/using decoders & encoders in circuits. Advantages and disadvantages of LEDs and LCDs. Observation/analysis
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD
 IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO., LTD., TOSHIBA CORPORATION, AND FUNAI ELECTRIC CO., LTD, Petitioners, v. GOLD CHARM LIMITED
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO., LTD., TOSHIBA CORPORATION, AND FUNAI ELECTRIC CO., LTD, Petitioners, v. GOLD CHARM LIMITED
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
Lecture Flat Panel Display Devices
 Lecture 1 6.976 Flat Panel Display Devices Outline Overview of 6.976 Overview Flat Panel Display Devices Course website http://hackman.mit.edu Reading Assignment: Article by Alt and Noda, IBM Journal of
Lecture 1 6.976 Flat Panel Display Devices Outline Overview of 6.976 Overview Flat Panel Display Devices Course website http://hackman.mit.edu Reading Assignment: Article by Alt and Noda, IBM Journal of
A NOVEL METHOD FOR TESTING LCD BY INTEGRATING SHORTING BAR AND TAGUCHI DOE TECHNOLOGIES
 This article has been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in JMST but has not yet been copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process. Please note that the publication version of
This article has been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in JMST but has not yet been copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process. Please note that the publication version of
Display Systems. Viewing Images Rochester Institute of Technology
 Display Systems Viewing Images 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology In This Section... We will explore how display systems work. Cathode Ray Tube Television Computer Monitor Flat Panel Display Liquid
Display Systems Viewing Images 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology In This Section... We will explore how display systems work. Cathode Ray Tube Television Computer Monitor Flat Panel Display Liquid
Lecture Flat Panel Display Devices
 Lecture 13 6.111 Flat Panel Display Devices Outline Overview Flat Panel Display Devices How do Displays Work? Emissive Displays Light Valve Displays Display Drivers Addressing Schemes Display Timing Generator
Lecture 13 6.111 Flat Panel Display Devices Outline Overview Flat Panel Display Devices How do Displays Work? Emissive Displays Light Valve Displays Display Drivers Addressing Schemes Display Timing Generator
Screens; media that use additive primaries
 Image display Display is the final stage in the image processing pipeline: Continuous scenes are acquired and digitally processed. The display process essentially converts the discrete image back to continuous
Image display Display is the final stage in the image processing pipeline: Continuous scenes are acquired and digitally processed. The display process essentially converts the discrete image back to continuous
Performance Comparison of Bilayer and Multilayer OLED
 Performance Comparison of Bilayer and Multilayer OLED Akanksha Uniyal, Poornima Mittal * Department of Electronics and Communication School of Engineering and Technology Graphic Era University, Dehradun-248002,
Performance Comparison of Bilayer and Multilayer OLED Akanksha Uniyal, Poornima Mittal * Department of Electronics and Communication School of Engineering and Technology Graphic Era University, Dehradun-248002,
Scalable self-aligned active matrix IGZO TFT backplane technology and its use in flexible semi-transparent image sensors. Albert van Breemen
 Scalable self-aligned active matrix IGZO TFT backplane technology and its use in flexible semi-transparent image sensors Albert van Breemen Image sensors today 1 Dominated by silicon based technology on
Scalable self-aligned active matrix IGZO TFT backplane technology and its use in flexible semi-transparent image sensors Albert van Breemen Image sensors today 1 Dominated by silicon based technology on
Wafer Thinning and Thru-Silicon Vias
 Wafer Thinning and Thru-Silicon Vias The Path to Wafer Level Packaging jreche@trusi.com Summary A new dry etching technology Atmospheric Downstream Plasma (ADP) Etch Applications to Packaging Wafer Thinning
Wafer Thinning and Thru-Silicon Vias The Path to Wafer Level Packaging jreche@trusi.com Summary A new dry etching technology Atmospheric Downstream Plasma (ADP) Etch Applications to Packaging Wafer Thinning
Basically we are fooling our brains into seeing still images at a fast enough rate so that we think its a moving image.
 Basically we are fooling our brains into seeing still images at a fast enough rate so that we think its a moving image. The formal definition of a Moving Picture... A sequence of consecutive photographic
Basically we are fooling our brains into seeing still images at a fast enough rate so that we think its a moving image. The formal definition of a Moving Picture... A sequence of consecutive photographic
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
Displays and framebuffers
 Reading Optional Displays and framebuffers Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 OpenGL Programming Guide (the red book available online): First four sections of chapter 2 First section of chapter 6 Foley
Reading Optional Displays and framebuffers Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 OpenGL Programming Guide (the red book available online): First four sections of chapter 2 First section of chapter 6 Foley
Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations.
 Wide View Compact LCD 6 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations. Compact body size: 19.0mm (.78 ) x 18.0mm (.709
Wide View Compact LCD 6 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Perfect for rack mount router and other applications with space limitations. Compact body size: 19.0mm (.78 ) x 18.0mm (.709
17. Optical detectors and displays. Optical displays. FPD (Flat panel display)
 17. Optical detectors and displays Optical displays FPD (Flat panel display) Display Resolutions High-definition television (HDTV): 720p (1280 720 progressive scan) 1080i (1920 1080 split into two interlaced
17. Optical detectors and displays Optical displays FPD (Flat panel display) Display Resolutions High-definition television (HDTV): 720p (1280 720 progressive scan) 1080i (1920 1080 split into two interlaced
Trial decision. Conclusion The trial of the case was groundless. The costs in connection with the trial shall be borne by the demandant.
 Trial decision Invalidation No. 2007-800070 Ishikawa, Japan Demandant Nanao Corporation Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SUGITANI, Tsutomu Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney TODAKA, Hiroyuki Osaka, Japan Patent
Trial decision Invalidation No. 2007-800070 Ishikawa, Japan Demandant Nanao Corporation Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SUGITANI, Tsutomu Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney TODAKA, Hiroyuki Osaka, Japan Patent
Solid State Devices 4B6
 Solid State Devices 4B6 Lecture 13 Projection and 3D displays: LCD, DLP and LCOS Daping Chu Lent 2016 Development of flat panel displays (FPDs) (LCD) in early days 1 A 105 inch TFT-LCD 4k2k curved panel
Solid State Devices 4B6 Lecture 13 Projection and 3D displays: LCD, DLP and LCOS Daping Chu Lent 2016 Development of flat panel displays (FPDs) (LCD) in early days 1 A 105 inch TFT-LCD 4k2k curved panel
TipatOr. Liquid metal switch (LMS) display technology. Avi Fogel
 TipatOr Liquid metal switch (LMS) display technology Avi Fogel 972-52-5702938 avifog@gmail.com Who is behind TipatOr TipatOr emerged from a merger of 2 expert groups in the fields of MEMS and Displays
TipatOr Liquid metal switch (LMS) display technology Avi Fogel 972-52-5702938 avifog@gmail.com Who is behind TipatOr TipatOr emerged from a merger of 2 expert groups in the fields of MEMS and Displays
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070176538A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0176538A1 Winters et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2007 (54) CONTINUOUS CONDUCTOR FOR OLED (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20070176538A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0176538A1 Winters et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2007 (54) CONTINUOUS CONDUCTOR FOR OLED (52) U.S. Cl....
Data Sheet. Electronic displays
 Data Pack F Issued November 0 029629 Data Sheet Electronic displays Three types of display are available; each has differences as far as the display appearance, operation and electrical characteristics
Data Pack F Issued November 0 029629 Data Sheet Electronic displays Three types of display are available; each has differences as far as the display appearance, operation and electrical characteristics
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
Semiconductors Displays Semiconductor Manufacturing and Inspection Equipment Scientific Instruments
 Semiconductors Displays Semiconductor Manufacturing and Inspection Equipment Scientific Instruments Electronics 110-nm CMOS ASIC HDL4P Series with High-speed I/O Interfaces Hitachi has released the high-performance
Semiconductors Displays Semiconductor Manufacturing and Inspection Equipment Scientific Instruments Electronics 110-nm CMOS ASIC HDL4P Series with High-speed I/O Interfaces Hitachi has released the high-performance
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
Characteristics of the liquid crystals market
 Characteristics of the liquid crystals market Information Day 2013 A Deep Dive into the LC&OLED Business Walter Galinat President of Performance Materials Darmstadt, Germany June 26, 2013 Disclaimer Remarks
Characteristics of the liquid crystals market Information Day 2013 A Deep Dive into the LC&OLED Business Walter Galinat President of Performance Materials Darmstadt, Germany June 26, 2013 Disclaimer Remarks
Flexible Electronics Production Deployment on FPD Standards: Plastic Displays & Integrated Circuits. Stanislav Loboda R&D engineer
 Flexible Electronics Production Deployment on FPD Standards: Plastic Displays & Integrated Circuits Stanislav Loboda R&D engineer The world-first small-volume contract manufacturing for plastic TFT-arrays
Flexible Electronics Production Deployment on FPD Standards: Plastic Displays & Integrated Circuits Stanislav Loboda R&D engineer The world-first small-volume contract manufacturing for plastic TFT-arrays
A New Overlap-Scan Circuit for High Speed and Low Data Voltage in Plasma-TV
 1218 A New Overlap-Scan Circuit for High Speed and Low Data Voltage in Plasma-TV Byung-Gwon Cho, Heung-Sik Tae, Senior Member, IEEE, Dong Ho Lee, and Sung-IL Chien, Member, IEEE Abstract A new overlap-scan
1218 A New Overlap-Scan Circuit for High Speed and Low Data Voltage in Plasma-TV Byung-Gwon Cho, Heung-Sik Tae, Senior Member, IEEE, Dong Ho Lee, and Sung-IL Chien, Member, IEEE Abstract A new overlap-scan
The LCD general specification provides outgoing inspection provision and its expected quality level based on outgoing inspection of LCD.
 Page 1 of 6 1. PURPOSE Issued By : Wilson Chan Audited By : Management : The LCD general specification provides outgoing inspection provision and its expected quality level based on outgoing inspection
Page 1 of 6 1. PURPOSE Issued By : Wilson Chan Audited By : Management : The LCD general specification provides outgoing inspection provision and its expected quality level based on outgoing inspection
Novel film patterned retarder utilizing in-plane electric field
 Novel film patterned retarder utilizing in-plane electric field Ji-Hoon Lee, 1 Il Hwa Jeong, 2 Ji Hoon Yu, 2 Ki Hoon Song, 2 Kwang-Un Jeong, 3 Shin- Woong Kang, 2 Myoung-Hoon Lee, 3,4 and Seung Hee Lee
Novel film patterned retarder utilizing in-plane electric field Ji-Hoon Lee, 1 Il Hwa Jeong, 2 Ji Hoon Yu, 2 Ki Hoon Song, 2 Kwang-Un Jeong, 3 Shin- Woong Kang, 2 Myoung-Hoon Lee, 3,4 and Seung Hee Lee
CCD 143A 2048-Element High Speed Linear Image Sensor
 A CCD 143A 2048-Element High Speed Linear Image Sensor FEATURES 2048 x 1 photosite array 13µm x 13µm photosites on 13µm pitch High speed = up to 20MHz data rates Enhanced spectral response Low dark signal
A CCD 143A 2048-Element High Speed Linear Image Sensor FEATURES 2048 x 1 photosite array 13µm x 13µm photosites on 13µm pitch High speed = up to 20MHz data rates Enhanced spectral response Low dark signal
FUJISAWA Toru, HAYASHI Masanao, HASEBE Hiroshi, TAKEUCHI Kiyofumi, TAKATSU Haruyoshi, and KOBAYASHI Shunsuke
 Novel PSV-FLCDs with High Response Speed, High Optical Throughput, and High Contrast Ratio with Small Voltage Shift by Temperature: Application to Field Sequential Full Color LCDs FUJISAWA Toru, HAYASHI
Novel PSV-FLCDs with High Response Speed, High Optical Throughput, and High Contrast Ratio with Small Voltage Shift by Temperature: Application to Field Sequential Full Color LCDs FUJISAWA Toru, HAYASHI
Technology Overview LTCC
 Sheet Code RFi0604 Technology Overview LTCC Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) is a multilayer ceramic substrate technology that allows the realisation of multiple embedded passive components (Rs,
Sheet Code RFi0604 Technology Overview LTCC Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) is a multilayer ceramic substrate technology that allows the realisation of multiple embedded passive components (Rs,
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays
 Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays Linrun Feng, Xiaoli Xu and Xiaojun Guo ECS Trans. 2011, Volume 37, Issue 1, Pages 105-112. doi:
Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays Linrun Feng, Xiaoli Xu and Xiaojun Guo ECS Trans. 2011, Volume 37, Issue 1, Pages 105-112. doi:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
THE CAPABILITY to display a large number of gray
 292 JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2006 Integer Wavelets for Displaying Gray Shades in RMS Responding Displays T. N. Ruckmongathan, U. Manasa, R. Nethravathi, and A. R. Shashidhara
292 JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2006 Integer Wavelets for Displaying Gray Shades in RMS Responding Displays T. N. Ruckmongathan, U. Manasa, R. Nethravathi, and A. R. Shashidhara
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION
 TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0220IT-1 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE DESCRIPTION FROM TO A 2008.03.10 First Release.
TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0220IT-1 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE DESCRIPTION FROM TO A 2008.03.10 First Release.
CCD Element Linear Image Sensor CCD Element Line Scan Image Sensor
 1024-Element Linear Image Sensor CCD 134 1024-Element Line Scan Image Sensor FEATURES 1024 x 1 photosite array 13µm x 13µm photosites on 13µm pitch Anti-blooming and integration control Enhanced spectral
1024-Element Linear Image Sensor CCD 134 1024-Element Line Scan Image Sensor FEATURES 1024 x 1 photosite array 13µm x 13µm photosites on 13µm pitch Anti-blooming and integration control Enhanced spectral
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
TFT Display Module. Part Number E43RG34827LW2M300-R
 Ph. 480-503-4295 NOPP@FocusLCD.com TFT CHARACTER UWVD FSC SEGMENT CUSTOM REPLACEMENT TFT Display Module Part Number E43RG34827LW2M300-R Overview 480x272(105.4x67.15), 8/16/18/24 bit RGB interface, WHITE
Ph. 480-503-4295 NOPP@FocusLCD.com TFT CHARACTER UWVD FSC SEGMENT CUSTOM REPLACEMENT TFT Display Module Part Number E43RG34827LW2M300-R Overview 480x272(105.4x67.15), 8/16/18/24 bit RGB interface, WHITE
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS-
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS- Fire Tom Wada What is semiconductor and LSIs Huge number of transistors can be integrated in a small Si chip. The size of the chip is roughly the size of nails. Currently,
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS- Fire Tom Wada What is semiconductor and LSIs Huge number of transistors can be integrated in a small Si chip. The size of the chip is roughly the size of nails. Currently,
Interactive Virtual Laboratories for Studying OLED Technology
 Interactive Virtual Laboratories for Studying OLED Technology Phillip I. Cherner 1 Abstract The paper describes a virtual OLED laboratory designed to introduce young people to one of the most contemporary
Interactive Virtual Laboratories for Studying OLED Technology Phillip I. Cherner 1 Abstract The paper describes a virtual OLED laboratory designed to introduce young people to one of the most contemporary
AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis
 IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): , ISSN (p): Volume 2, PP Organic Led. Figure 1.
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Volume 2, PP 46-51 www.iosrjen.org Organic Led Prof.Manoj Mishra 1, Sweety Vade 2,Shrutika Sawant 3, Shriwari Shedge 4, Ketaki
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Volume 2, PP 46-51 www.iosrjen.org Organic Led Prof.Manoj Mishra 1, Sweety Vade 2,Shrutika Sawant 3, Shriwari Shedge 4, Ketaki
Organic light emitting diodes for display technology
 Organic light emitting diodes for display technology Shamna Shamsudeen MScTI - ZITI-Heidelberg University OLED ZITI, Uni Heidelberg Page1 What s Light Light: Visible part of EM spectra. Ref:[1] Thermoluminescence:
Organic light emitting diodes for display technology Shamna Shamsudeen MScTI - ZITI-Heidelberg University OLED ZITI, Uni Heidelberg Page1 What s Light Light: Visible part of EM spectra. Ref:[1] Thermoluminescence:
SmartSwitch TM. Wide View LCD 36 x 24 Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS PART NUMBER & DESCRIPTION
 Wide View LCD 36 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced LED Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD Variety
Wide View LCD 36 x Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Standard with Enhanced LED Illumination: Broad and even light diffusion Consistent backlighting Low energy consumption Programmable LCD Variety
Chapter 3. Display Devices and Interfacing
 Chapter 3 Display Devices and Interfacing Monitor Details Collection of dots Matrix of dots creates character Monochrome monitor screen is collection of 350 *720 350 rows and each rows having 720 dots
Chapter 3 Display Devices and Interfacing Monitor Details Collection of dots Matrix of dots creates character Monochrome monitor screen is collection of 350 *720 350 rows and each rows having 720 dots
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS-
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS- Fire Tom Wada 2011/12/19 1 What is semiconductor and LSIs Huge number of transistors can be integrated in a small Si chip. The size of the chip is roughly the size of nails.
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY -CMOS- Fire Tom Wada 2011/12/19 1 What is semiconductor and LSIs Huge number of transistors can be integrated in a small Si chip. The size of the chip is roughly the size of nails.
Abstract 1. INTRODUCTION. Cheekati Sirisha, IJECS Volume 05 Issue 10 Oct., 2016 Page No Page 18532
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 10 Oct. 2016, Page No. 18532-18540 Pulsed Latches Methodology to Attain Reduced Power and Area Based
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 10 Oct. 2016, Page No. 18532-18540 Pulsed Latches Methodology to Attain Reduced Power and Area Based
Spatial Light Modulators XY Series
 Spatial Light Modulators XY Series Phase and Amplitude 512x512 and 256x256 A spatial light modulator (SLM) is an electrically programmable device that modulates light according to a fixed spatial (pixel)
Spatial Light Modulators XY Series Phase and Amplitude 512x512 and 256x256 A spatial light modulator (SLM) is an electrically programmable device that modulates light according to a fixed spatial (pixel)
New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 4, April 2010, pp. 1185 1189 New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED C. L. Fan, Y. Y. Lin, B. S. Lin
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 4, April 2010, pp. 1185 1189 New Pixel Circuit Compensating Poly-si TFT Threshold-voltage Shift for a Driving AMOLED C. L. Fan, Y. Y. Lin, B. S. Lin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20140098.078A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0098078 A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
Display Technologies. Corning: The Technology Behind the Glass
 Display Technologies Corning: The Technology Behind the Glass Dr. David Chen Director, Application Engineering and Asia Commercial Technology Taiwan Corning Display Technologies Taiwan June 13, 2008 Forward
Display Technologies Corning: The Technology Behind the Glass Dr. David Chen Director, Application Engineering and Asia Commercial Technology Taiwan Corning Display Technologies Taiwan June 13, 2008 Forward
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADPO1 1322 TITLE: Amorphous- Silicon Thin-Film Transistor With Two-Step Exposure Process DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release,
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADPO1 1322 TITLE: Amorphous- Silicon Thin-Film Transistor With Two-Step Exposure Process DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release,
Design of Active Matrix Micro-LED Display with CCCS Pixel Circuits
 Design of Active Matrix Micro-LED Display with CCCS Pixel Circuits Ke ZHANG 1, 2, Zhaojun LIU* 1, 2 and Hoi-Sing KWOK* 1 1 State Key Laboratory on Advanced Displays and Optoelectronics Technologies, The
Design of Active Matrix Micro-LED Display with CCCS Pixel Circuits Ke ZHANG 1, 2, Zhaojun LIU* 1, 2 and Hoi-Sing KWOK* 1 1 State Key Laboratory on Advanced Displays and Optoelectronics Technologies, The
Research Trends of Flexible Liquid Crystal Displays
 Research Trends of Flexible Liquid Crystal Displays Min Young Jin Research Institute of Information Displays Hanyang university Seoul 133-791 Korea minyjin@paran.com Jae-Hoon Kim Department of Electrical
Research Trends of Flexible Liquid Crystal Displays Min Young Jin Research Institute of Information Displays Hanyang university Seoul 133-791 Korea minyjin@paran.com Jae-Hoon Kim Department of Electrical
IC TECHNOLOGY Lecture 2.
 IC TECHNOLOGY Lecture 2. IC Integrated Circuit Technology Integrated Circuit: An integrated circuit (IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor
IC TECHNOLOGY Lecture 2. IC Integrated Circuit Technology Integrated Circuit: An integrated circuit (IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor
