(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
|
|
|
- Sarah Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 Jeon et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY Applicant: SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO.,LTD., Yongin-city (KR) Inventors: Mu-Kyung Jeon, Yongin-city (KR); Tae-Joon Kim, Yongin-city (KR) Assignee: Samsung Display Co., Ltd., Yongin-city (KR) Appl. No.: 13/804,474 Filed: Mar 14, 2013 Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 8, 2012 (KR) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G09G 3/32 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G09G 3/3208 ( ) USPC /205:345/82 (57) ABSTRACT An organic light emitting diode (OLED) display includes: a Substrate; a scan line formed on the Substrate and that trans fers a scan signal; a data line and a driving Voltage line that intersect the scan line and that transfer a data signal and a driving Voltage, respectively; a Switching thin film transistor (TFT) connected to the scan line and the data line; a driving TFT connected to the switching TFT and the driving voltage line; an OLED connected to the driving TFT, a storage capacitor connected between the driving Voltage line and a driving gate electrode of the driving TFT, and a boosting capacitor connected to the storage capacitor, wherein the storage capacitor has at least one capacitor opening. 172 ELVDDL A 123
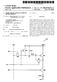
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 6 US 2014/ A1 FIG. 1 ELVDDL S2 D2 Dm cs \-G2 T2 Cb T S1 O D1 E Cb2 Cb1 G1 n Sn G3 T3. T5 G5 D3 S3 T6 S6 122 T4 D6 G6 D4 Sn-1 G4 S4 ld, VOLED
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 6 US 2014/ A1 s FIG. 2 ty X DX T4 DX X - Wint - Sn-1 X Cst X N-OLED X T2 T3 - Sn DX T5 T - En
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 6 US 2014/ A1 131a FIG l ) ( >124 DX ( \ d DXI. HDX DXN d S. y C 177d /N-122 I V a-N / Cst 127a -N-126 : 174b N NN u , 172b- SI f N N CEE V 1 / U IV E VI -25 N Y C 1/ N --125C T S- -I-1 131C 125d 1-176c. 177d K - 176a a C - N-125a 131at 125e E-st la -177a T53- N. 176f 176e N-D a 81 N -131f N-177f V-72
5 Patent Application Publication US 2014/ A1 91
6 Patent Application Publication Sheet 5 of 6 US 2014/ A1 FIG a 127a 174b b FN-191 ~-18O s De-160 / N-110 V A. W
7 Patent Application Publication Sheet 6 of 6 US 2014/ A1 FIG. 6
8 ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DODE DISPLAY CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims priority to and the benefit of Korean Patent Application No filed in the Korean Intellectual Property Office on Oct. 8, 2012, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND Field The described technology relates generally to an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display Description of the Related Technology An OLED display includes two electrodes and an organic emission layer that is positioned therebetween. Elec trons that are injected from one electrode and holes that are injected from the other electrode form excitons by coupling in the organic emission layer, and the excitons emit light while discharging energy Such an OLED display includes a plurality of pixels including an OLED, which is a self-luminance element. At each pixel, a plurality of thin film transistors (TFT) and at least one capacitor for driving the OLED are formed. The plurality of TFTs include a switching TFT and a driving TFT The capacitor includes a storage capacitor that stores a data signal and a boosting capacitor that performs a boosting operation according to a Voltage change of a signal line in order to more accurately express grayscales. Lumi nance of a pixel including the storage capacitor and the boost ing capacitor changes according to a capacitance ratio of the two capacitors The above information disclosed in this Back ground section is only for enhancement of understanding of the background of the described technology and therefore it may contain information that does not form the prior art that is already known in this country to a person of ordinary skill in the art. SUMMARY OF CERTAIN INVENTIVE ASPECTS The described technology has been made in an effort to provide an OLED display having advantages of being capable of preventing a stain due to a capacitance deviation between a storage capacitor and a boosting capaci tor that are provided in a plurality of pixels One embodiment provides an OLED display includ ing: a Substrate; a scan line formed over the Substrate and configured to transfer a scan signal; a data line and a driving Voltage line that intersect the Scanline and that are configured to transfer a data signal and a driving Voltage, respectively; a switching thin film transistor (TFT) connected to the scan line and the data line; a driving TFT connected to the switching TFT and the driving voltage line, the driving TFT including a driving gate electrode; an OLED that is connected to the driving TFT, a storage capacitor connected between the driv ing Voltage line and the driving gate electrode; and a boosting capacitor connected to the storage capacitor, wherein the storage capacitor has at least one capacitor opening The driving TFT may include a driving semiconduc tor layer formed over the substrate; the driving gate electrode formed on a first gate insulating layer and a second gate insulating layer that sequentially cover the driving semicon ductor layer, the driving gate electrode overlapped with the driving semiconductor layer The storage capacitor may include a first storage capacitor plate formed over the first gate insulating layer, a second gate insulating layer covering the first storage capaci torplate; and a second storage capacitor plate formed over the second gate insulating layer and overlapped with the first storage capacitor plate The capacitor opening may be formed in the second storage capacitor plate The OLED may further include an interlayer insu lating layer covering the second storage capacitor plate, wherein the driving gate electrode is connected to the first storage capacitor plate through a contact hole positioned within the capacitor opening and formed in the interlayer insulating layer and the second gate insulating layer The driving voltage line may be formed over the interlayer insulating layer and spaced apart from the capacitor opening A first side separation terminal and a second side separation terminal of the driving Voltage line may be con nected to the second storage capacitor plate through a first side contact hole and a second side contact hole, respectively, that are formed in the interlayer insulating layer The OLED display may further include a connec tion member formed in the same layer, and configured to be parallel to the driving Voltage line, and further configured to connect the driving gate electrode and the first storage capaci tor plate A first end of the connection member may be con nected to the driving gate electrode through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, and a first interme diate protruding portion of the connection member may be connected to the first storage capacitor plate through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer and the second gate insulating layer The OLED display may further include an initial ization TFT configured to be turned on according to a previ ous scan signal received through a previous scan line and further configured to transfer an initialization Voltage to a driving gate electrode of the driving TFT, wherein a second end of the connection member may be connected to an ini tialization semiconductor layer of the initialization TFT through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, the second gate insulating layer, and the first gate insu lating layer The OLED display may further include a compen sating TFT configured to compensate a threshold Voltage of the driving TFT and connected to the driving TFT, wherein a second intermediate protruding portion of the connection member may be connected to a compensation semiconductor layer of the compensation TFT through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, the second gate insulating layer, and the first gate insulating layer The boosting capacitor may include a first boosting capacitor plate extended from the first storage capacitor and a second boosting capacitor plate overlapped with the first boosting capacitor plate and protruded from the scan line The scan line and the driving gate electrode may be formed co-planar with the second storage capacitor plate The previous scan line may be formed co-planar with the first storage capacitor plate.
9 0024. The first storage capacitor plate may be formed co planar with the first boosting capacitor plate, and the second storage capacitor plate may be formed co-planar with the second boosting capacitor plate According to one embodiment, because a storage capacitor has at least one capacitor opening, a capacitance ratio of a storage capacitor and a boosting capacitor can be uniformly Sustained even in an over-etching phenomenon. Therefore, because a deviation does not occur in a capaci tance ratio between a storage capacitor and a boosting capaci tor that are provided in a plurality of pixels, a stain can be prevented from occurring Further, by separating a driving voltage line from a position corresponding to a capacitor opening, connecting one side separation terminal and the other side separation terminal of the driving Voltage line to the second storage capacitor plate through a first side contact hole and a second side contact hole, respectively, that are formed in an interlayer insulating layer, connecting a first storage capacitor plate and a driving gate electrode that are exposed through a capacitor opening using a connection member, a capacitor opening can be formed within the storage capacitor. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0027 FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel of an OLED display according to one embodiment FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a position of a plu rality of TFTs and a capacitor at one pixel of an OLED display according to one embodiment FIG. 3 is a specific layout view of one pixel of an OLED display according to one embodiment FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line IV-IV of FIG FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line V-V of FIG FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line VI-VI of FIG. 3. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF CERTAIN INVENTIVE EMBODIMENTS The present invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which certain embodiments of the invention are shown. As those skilled in the art would realize, the described embodi ments may be modified in various ways, without departing from the spirit or scope of the present invention The drawings and description are to be regarded as illustrative in nature and not restrictive. Like reference numerals generally designate like elements throughout the specification Further, in the drawings, a size and thickness of each element are represented for better understanding and ease of description, and the present invention is not limited thereto In the drawings, the thickness of layers, films, pan els, regions, etc., may be exaggerated for clarity. In the draw ings, for better understanding and ease of description, thick nesses of some layers and areas may be excessively displayed. It will be understood that when an element such as a layer, film, region, or Substrate is referred to as being on another element, it can be directly on the other element or intervening elements may also be present In addition, unless explicitly described to the con trary, the word comprise' and variations such as com prises' or comprising, will be understood to imply the inclusion of stated elements but not the exclusion of any other elements. Further, in the specification, an upper part of a target portion indicates an upper part or a lower part of the target portion, and the target portion is not always positioned at the upper side based on a gravity direction Further, in the attached drawings, an active matrix (AM) OLED display of a 6Tr2Cap structure having 6 TFTs and two capacitors at one pixel is illustrated, but the present invention is not limited thereto. Therefore, the OLED display may have a plurality of TFTs and at least one capacitor at one pixel, and as a separate wire is further formed or an existing wire is omitted, the OLED display may be formed to have various structures. Here, a pixel is a minimum unit that dis plays an image, and the OLED display displays an image through a plurality of pixels Hereinafter, an OLED display according to one embodiment will be described in detail with reference to FIGS 1 to In order to express uniform luminance, a capaci tance ratio of a storage capacitor and a boosting capacitor should be uniformly sustained between a plurality of pixels. When a deviation occurs in the capacitance ratio, a stain occurs by a luminance deviation and a color deviation. Par ticularly, because an area of the boosting capacitor is Smaller than that of the storage capacitor, a micro over-etching phe nomenon, i.e., a skew in a production process has a large influence on an area of the boosting capacitor and thus a stain may occur at a pixel FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel of an OLED display according to one embodiment As shown in FIG. 1, one pixel of an OLED display according to an embodiment includes a plurality of signal lines 121, 122,123,124,171, and 172, a plurality of TFTs T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, and T6 that are connected to the plurality of signal lines, capacitors Cst and Cb, and an OLED The TFTs includes a driving TFT T1, a switching TFTT2, a compensation TFT T3, and an initialization TFT T4, an operation control TFTT5, and a light emission control TFTT6, and the capacitors include a storage capacitor Cst and a boosting capacitor Cb. 0044) The signal lines includes a scan line 121 that trans fers a scan signal Snto the switching TFTT2 and the boosting capacitor Cb, a previous scan line 122 that transfers a previ ous scan signal Sn-1 to the initialization TFT T4, a light emission control line 123 that transfers a light emission con trol signal En to the operation control TFT T5 and the light emission control TFTT6, a data line 171 that intersects the scan line 121 and that transfers a data signal Dm, a driving voltage line 172 that transfers a driving voltage ELVDD and that is formed substantially parallel to the data line 171, and an initialization Voltage line 124 that transfers an initializa tion voltage Vint that initializes the driving TFTT A gate electrode G1 of the driving TFT T1 is con nected to one end Cst1 of a storage capacitor Cst. A source electrode S1 of the driving TFTT1 is connected to the driving voltage line 172 via the operation control TFT T5. A drain electrode D1 of the driving TFTT1 is electrically connected to an anode of the OLED via the light emission control TFT T6. The driving TFTT1 receives a data signal Dm according to a switching operation of the switching TFTT2 and supplies a driving current Id to the OLED A gate electrode G2 of the switching TFT T2 is connected to the scan line 121, the other end Cb2 of the
10 boosting capacitor Cb, and a gate electrode G3 of the com pensation TFT T3. A source electrode S2 of the switching TFTT2 is connected to the data line 171. A drain electrode D2 of the switching TFT T2 is connected to the driving voltage line 172 via the operation control TFTT5 while being con nected to a source electrode S1 of the driving TFT T1. The Switching TFTT2 is turned on according to a scan signal Sn received through the scan line 121, and performs a Switching operation that transfers a data signal Dm to the Source elec trode S1 of the driving TFTT A gate electrode G3 of the compensation TFTT3 is connected to the scan line 121, the gate electrode G2 of the switching TFTT2, the other end Cb2 of the boosting capaci tor Cb. A source electrode S3 of the compensation TFTT3 is connected to an anode of the OLED via the light emission control TFTT6 while being connected to a drain electrode D1 of the driving TFTT1. A drain electrode D3 of the compen sation TFT T3 is connected to one end Cst1 of the capacitor Cst, one end Cb1 of the boosting capacitor Cb, a gate elec trode G1 of the driving TFT T1, and a drain electrode D4 of the initialization TFTT4. The compensation TFTT3 is turned on according to a scan signal Sn received through the Scanline 121 to connect a gate electrode G1 and a drain electrode D1 of the driving TFTT1, and to perform a diode-connection of the driving TFTT A gate electrode G4 of the initialization TFT T4 is connected to the previous scanline 122. A source electrode S4 of the initialization TFT T4 is connected to the initialization voltage line 124. A drain electrode D4 of the initialization TFTT4 is connected to one end Cb1 of the boosting capacitor Cb, one end Cst1 of the storage capacitor Cst, a drain elec trode D3 of the compensation TFT T3, and a gate electrode G1 of the driving TFTT1. The initialization TFTT4 is turned on according to the previous scan signal Sn-1 received through the previous scan line 122, transfers an initialization voltage Vint to the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFTT1, and performs an initialization operation that initializes a Volt age of the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFTT A gate electrode G5 of the operation control TFTT5 is connected to the light emitting control line 123. A source electrode S5 of the operation control TFTT5 is connected to the driving voltage line 172. A drain electrode D5 of the operation control TFTT5 is connected to the source electrode S1 of the driving TFT T1 and the drain electrode S2 of the switching TFTT A gate electrode G6 of the light emitting control TFTT6 is connected to the light emitting control line 123. A source electrode S6 of the light emitting control TFTT6 is connected to a drain electrode D1 of the driving TFTT1 and a source electrode S3 of the compensation TFT T3. A drain electrode D6 of the light emitting control TFTT6 is electri cally connected to an anode of the OLED. The operation control TFT T5 and the light emission control TFTT6 are turned on according to the light emission control signal En received through the light emission control line 123 and thus a driving voltage ELVDD is transferred to the OLED to enable a driving current Id to flow to the OLED The other end Cst2 of the storage capacitor Cst is connected to the driving voltage line 172, and a cathode of the OLED is connected to a common voltage ELVSS. Accord ingly, the OLED receives a driving current Id from the driving TFTT1 and emits light, thereby displaying an image Hereinafter, a specific operation process of one pixel of an OLED display according to any embodiment will be described in detail First, for an initialization period, the previous scan signal Sn-1 of a low level is supplied through the previous scan line 122. Therefore, the initialization TFT T4 is turned on to correspond to the previous scan signal Sn-1 of a low level, the initialization voltage Vint is connected from the initialization voltage line 124 to the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFT T1 through the initialization TFT T4, and the driving TFTT1 is initialized by the initialization voltage Vint Thereafter, for a data programming period, a scan signal Sn of a low level is supplied through the scan line 121. Therefore, the switching TFTT2 and the compensation TFT T3 are turned on to correspond to the scan signal Sn of a low level In this case, the driving TFTT1 is diode-connected by the turned-on compensation TFT T3 and is biased in a forward direction Therefore, a compensation voltage (Dm+Vth) (where Vth is a negative (-) value) that is reduced by a threshold voltagevth of the driving TFTT1 from a data signal Dm that is supplied from the data line 171 is applied to the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFTT The driving voltage ELVDD and a compensation voltage Dm+Vth are applied to both ends of the storage capacitor Cst, and charges corresponding to a Voltage differ ence between the two ends of the capacitor are stored at the storage capacitor Cst Thereafter, while the supply of the scan signal Sn is stopped, whena Voltage level of the scan signal Sn is changed to a high level, a Voltage that is applied to the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFT T1 by a coupling operation of the boosting capacitor Cb is changed to correspond to a Voltage change width of the scan signal Sn. In this case, because a voltage that is applied to the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFT T1 is changed by charge sharing between the storage capacitor Cstand the boosting capacitor Cb, a Voltage change amount that is applied to the driving gate electrode G1 is changed proportional to a charge sharing value between the storage capacitor Cst and the boosting capacitor Cb together with a Voltage change width of the scan signal Sn Thereafter, for a light emitting period, a light emis sion control signal En that is Supplied from the light emission control line 123 is changed from a high level to a low level. Therefore, for a light emitting period, the operation control TFTT5 and the light emission control TFTT6 are turned on by the light emission control signal En of a low level Therefore, a driving current Id is generated accord ing to a Voltage difference between a Voltage of the gate electrode G1 of the driving TFT T1 and the driving voltage ELVDD, and the driving current Id is supplied to the OLED through the light emission control TFT T6. For a light emit ting period, a gate-source Voltage Vgs of the driving TFTT1 is sustained to Dm+Vth-ELVDD by the storage capacitor Cst, and a driving current Id is proportional to the square (Dm-ELVDD) of a value that subtracts a threshold voltage Vth from a gate-source Voltage Vgs according to a current voltage relationship of the driving TFT T1. Therefore, the driving current Id is determined regardless of the threshold voltage Vth of the driving TFTT Hereinafter, a detailed structure of a pixel of the OLED display that is shown in FIG. 1 will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 2 to 6.
11 0062 FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a position of a plu rality of TFTs and a capacitor at one pixel of an OLED display according to an embodiment, FIG. 3 is a specific layout view of one pixel of an OLED display according to an embodi ment, FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line IV-IV of FIG. 3, FIG. 5 is a cross sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line V-V of FIG.3, and FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an OLED display taken along line VI-VI of FIG As shown in FIGS. 2 to 6, a pixel of the OLED display according to an embodiment includes a Scanline 121, a previous Scanline 122, a light emission control line 123, and an initialization Voltage line 124 that apply a scan signal Sn, a previous scan signal Sn-1, a light emission control signal En, and an initialization Voltage Vint, respectively to the pixel, and that are formed in a row direction. The pixel of the OLED display also includes a data line 171 and a driving voltage line 172 that intersect all of the scan line 121, the previous scan line 122, the light emission control line 123, and the initialization Voltage line 124, and that apply a data signal Dm and a driving voltage ELVDD, respectively, to the pixel Further, at the pixel, the driving TFTT1, the switch ing TFTT2, the compensation TFTT3, the initialization TFT T4, the operation control TFT T5, the light emission control TFTT6, the storage capacitor Cst, the boosting capacitor Cb, and an OLED 70 are formed The driving TFT T1, the switching TFT T2, the compensation TFT T3, the initialization TFT T4, the opera tion control TFT T5, and the light emission control TFT T6 are formed along a semiconductor layer 131, and the semi conductor layer 131 is bent in various shapes. Such a semi conductor layer 131 is made of polysilicon and includes a channel area in which impurities are not doped and a source area and a drain area that are doped with impurities at both sides of the channel area. Such impurities change according to a kind of a TFT and may be an N type impurity or a P type impurity. The semiconductor layer includes a driving semi conductor layer 131a that is formed in the driving TFTT1, a switching semiconductor layer 131b that is formed in the switching TFTT2, a compensation semiconductor layer 131c that is formed in the compensation TFT T3, an initialization semiconductor layer 131d that is formed in the initialization TFT T4, and an operation control semiconductor layer 131e and a light emission control semiconductor layer 131f that are formed in the operation control TFTT5 and the light emission control TFTT6, respectively The driving TFTT1 includes the driving semicon ductor layer 131a, a driving gate electrode 125a, a driving source electrode 176a, and a driving drain electrode 177a. The driving source electrode 176a corresponds to a driving source area 176a that is doped with impurities in the driving semiconductor layer 131a, and the driving drain electrode 177a corresponds to a driving drain area 177a that is doped with impurities in the driving semiconductor layer 131a. The driving gate electrode 125a is overlapped with the driving semiconductor layer 131a and has a rectangular shape The driving gate electrode 125a is formed in the same layer and with the same material as that of the Scanline 121, the initialization Voltage line 124, a Switching gate elec trode 125b, a compensation gate electrode 125c, a second storage capacitor plate 127, and a second boosting capacitor plate The switching TFT T2 includes a switching semi conductor layer 131b, the switching gate electrode 125b, a switching source electrode 176b, and a switching drain elec trode 177b. The switching drain electrode 177b corresponds to a switching drain area 177b that is doped with impurities in the switching semiconductor layer 131b The compensation TFTT3 includes a compensation semiconductor layer 131c, a compensation gate electrode 125c, a compensation source electrode 176c, and a compen sation drain electrode 177c, and the compensation source electrode 176c corresponds to a compensation Source area that is doped with impurities in the compensation semicon ductor layer 131c. The compensation gate electrode 125c forms a separate dual gate electrode 25, thereby preventing a leakage current The initialization TFT T4 includes an initialization semiconductor layer 131d, an initialization gate electrode 125d, an initialization source electrode 176d, and an initial ization drain electrode 177d. One end of the initialization source electrode 176d is connected to the initialization volt age line 124 through a contact hole 61 that is formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160, and the other end of the ini tialization source electrode 176d is connected to the initial ization semiconductor layer 131d through a contact hole 62 that is continuously formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the interlayer insulating layer 160. The initialization drain electrode 177d is the other end of a connection member 174 and is connected to the initialization semiconductor layer 131d through the con tact hole 63 that is continuously formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the interlayer insulating layer The operation control TFTT5 includes an operation control semiconductor layer 131e, an operation control gate electrode 125e, an operation control source electrode 176e, and an operation control drain electrode 177e. The operation control source electrode 176e is a portion of the driving Voltage line 172, is connected to an operation control source area through a contact hole 71. The operation control drain electrode 177e corresponds to an operation control drain area 177e that is doped with impurities in the operation control semiconductor layer 131e The light emission control TFTT6 includes a light emission control semiconductor layer 131f a light emission control gate electrode 125f a light emission control source electrode 176f, and a light emission control drain electrode 177f. The light emission control source electrode 176f corre sponds to a light emission control source area 176f that is doped with impurities in the light emission control semicon ductor layer 131f One end of the driving semiconductor layer 131a of the driving TFT T1 is connected to the switching semicon ductor layer 131b and the operation control semiconductor layer 131e, and the other end of the driving semiconductor layer 131a is connected to the compensation semiconductor layer 131c and the light emission control semiconductor layer 131f. Therefore, the driving source electrode 176a is con nected to the switching drain electrode 177b and the opera tion control drain electrode 177e, and the driving drain elec trode 177a is connected to the compensation source electrode 176c and the light emission control source electrode 176f 0074 As shown in FIG. 5, the storage capacitor Cst includes a first storage capacitor plate 126 and a second storage capacitor plate 127 that together interpose the second
12 gate insulating layer 142 therebetween. The second gate insu lating layer 142 is a dielectric material, and storage capaci tance is determined by charges that are stored at the storage capacitor Cstanda Voltage between both capacitor plates 126 and The first storage capacitor plate 126 is formed in the same layer and with the same material as that of the previous scan line 122, the light emission control line 123, the opera tion control gate electrode 125e, the light emission control gate electrode 125f and the first boosting capacitor plate 128. The second storage capacitor plate 127 is formed in the same layer and with the same material as that of the scan line 121, the initialization Voltage line 124, the driving gate electrode 125a, the switching gate electrode 125b, the compensation gate electrode 125c, and the second boosting capacitor plate 129. The first storage capacitor plate 126 and the second storage capacitor plate 127 are formed with a gate wire including at least one metal of aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), titanium (Ti), tantalum (Ta), Al Ni-La alloy, and Al Nd alloy. Therefore, storage capacitance can be improved, compared with a structure that forms any one capacitor plate of the storage capacitor Cst with a semiconductor layer The storage capacitor Cst has at least one capacitor opening 126a, and specifically, a capacitor opening 126a is formed in the second storage capacitor plate 127. Therefore, because the inside of the storage capacitor Cst is over-etched together with the outside of the storage capacitor Cst by an over-etching phenomenon occurring in a production process, a skew area of the storage capacitor Cst is larger than that of the boosting capacitor Cb, and thus a capacitance ratio of the storage capacitor Cst and the boosting capacitor Cb may be uniformly Sustained even in an over-etching phenomenon. Therefore, because a deviation does not occur at a capaci tance ratio between the boosting capacitor Cb and the storage capacitor Cst, by minimizing a Voltage deviation of the driv ing gate electrode 125a of the driving TFT T1, a stain is prevented from occurring The driving voltage line 172 passing through to overlap with the storage capacitor Cst is separated at a posi tion at which the capacitor opening 126a is formed. The driving Voltage line 172 includes one side separation terminal 172a that is positioned at one side based on the capacitor opening 126a and the other side separation terminal 172b that is positioned at the other side based on the capacitor opening 126a. One side separation terminal 172a and the other side separation terminal 172b of the driving voltage line 172 are connected to the second storage capacitor plate 127 through one side contact hole 65 and the other side contact hole 66, respectively, that are formed in the interlayer insulating layer The connection member 174 is formed in the same layer to be parallel to the driving voltage line 172. The con nection member 174 connects the driving gate electrode 125a and the first storage capacitor plate 126. One end 174a of the connection member 174 is connected to the driving gate electrode 125a through the contact hole 67 that is formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160, and a first intermediate protruding portion 174b of the connection member 174 is connected to the first storage capacitor plate 126 through a contact hole 64 that is formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160 and the second gate insulating layer 142 that is positioned at the inside of the capacitor opening 126a The other end 177d of the connection member 174 corresponds to an initialization drain electrode 177d of the initialization TFT T4 and is connected to the initialization semiconductor layer 131d of the initialization TFT T4 through a contact hole 63 that is continuously formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the interlayer insulating layer 160. Further, the sec ond intermediate protruding portion 177c of the connection member 174 corresponds to the compensation drain electrode 177c of the compensation TFT T3 and is connected to the compensation semiconductor layer 131c of the compensation TFT T3 through the contact hole 68 that is continuously formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the interlayer insulating layer Therefore, the first storage capacitor plate 126 of the storage capacitor Cst is connected to the compensation semi conductor layer 125c and an initialization semiconductor layer 125d through the second intermediate protruding por tion 177c and the other end 177d of the connection member 174 and is connected to the driving gate electrode 125a through one end 174a of the connection member 174. The second storage capacitor plate 127 of the storage capacitor Cst is connected to the driving voltage line 172 through one side contact hole 65 and the other side contact hole 66 that is formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160. I0081. Therefore, the storage capacitor Cst stores storage capacitance corresponding to a difference between a gate Voltage of the driving gate electrode 125a and a driving Volt age ELVDD that is transferred through the driving voltage line 172. I0082 In this way, the driving voltage line 172 is separated from a position corresponding to the capacitor opening 126a, and one side separation terminal 172a and the other side separation terminal 172b of the driving voltage line 172 are connected to the second storage capacitor plate 127 through one side contact hole 65 and the other side contact hole 66, respectively, that are formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160 and connect the first storage capacitor plate 126 and the driving gate electrode 125a that are exposed through the capacitor opening 126a using the connection member 174, thereby forming the capacitor opening 126a at the inside of the storage capacitor Cst. In this case, an area and the number of the capacitor openings 126a that is formed in the storage capacitor Cst are determined by a capacitance ratio of the boosting capacitor Cb. I0083. The first boosting capacitor plate 128 of the boost ing capacitor Cb is extended from the first storage capacitor plate 126, and the second boosting capacitor plate 129 is protruded from the scan line 121. The first boosting capacitor plate 128 has a hammer shape, and a first boosting capacitor plate 133 includes a handle portion parallel to the driving voltage line 172 and a head portion that is formed in an end portion of the handle portion. The head portion of the first boosting capacitor plate 128 is positioned to overlap at the inside of the second boosting capacitor plate 129. I0084. The switching TFT T2 is used as a switch that selects a pixel to emit light. The switching gate electrode 125b is connected to the scan line 121, the Switching source elec trode 176b is connected to the data line 171, and the switching drain electrode 177b is connected to the driving TFT T1 and the operation control TFT T5. The light emission control drain electrode 177f of the light emission control TFTT6 is
13 directly connected to a pixel electrode 191 of the organic light emitting diode 70 through a contact hole 181 that is formed in a protective layer Hereinafter, a structure of an OLED display accord ing to an embodiment will be described in detail with refer ence to FIGS. 4 to 6. I0086 A structure of a TFT based on the driving TFT T1, the switching TFTT2, and the light emission control TFTT6 will be described, and a storage capacitor Cst and the connec tion member 174 will be described. The remaining TFTs T3, T4, and T5 have substantially the same stacked structure as that of the driving TFT T1, the switching TFT T2, and the light emission control TFT T6 and therefore a detailed description thereof will be omitted. I0087. A buffer layer 111 is formed on a substrate 110, and the substrate 110 is formed as an insulation substrate that is formed with glass, quartz, ceramic, and plastic The switching semiconductor layer 131b, the driv ing semiconductor layer 131a, and the light emission control semiconductor layer 131fare formed on the buffer layer 111. The switching semiconductor layer 131b includes a switch ing source area and a Switching drain area opposite to each other with a switching channel area interposed therebetween. The driving semiconductor layer 131a includes a driving Source area and a driving drain area opposite to each other with a driving channel area interposed therebetween. The light emission control TFTT6 includes a light emission con trol channel area 131f1, a light emission control source area 176f, and a light emission control drain area 133f The first gate insulating layer 141 that is formed with silicon nitride SiNX or silicon oxide SiO2 is formed on the Switching semiconductor layer 131a, the driving semi conductor layer 131b, and the light emission control semi conductor layer 131f The previous scan line 122 including an initializa tion gate electrode 125d, a light emission control line 123 including the operation control gate electrode 125e and the light emission control gate electrode 125f, and first gate wires 122, 123, 125d, 125e, 125f 126, and 128 including the first storage capacitor plate 126, and the first boosting capacitor plate 128 are formed on the first gate insulating layer A second gate insulating layer 142 is formed on the first gate wires 122, 123,125d, 125e, 125f 126, and 128 and the first gate insulating layer 141. The second gate insulating layer 142 is made of silicon nitride SiNx or silicon oxide SiO On the second gate insulating layer 142, a scan line 121 including the driving gate electrode 125a, the switching gate electrode 125b, and the compensation gate electrode 125c, the initialization voltage line 124, and the second gate wires 125a, 125b, 125c, 121, 124, 127, and 129 including the second storage capacitor plate 127 and the second boosting capacitor plate 129 are formed. A storage opening 127a for connecting the first storage capacitor plate 126 and the first intermediate protruding portion 174b of the connection mem ber 174 is formed at the inside of the second storage capacitor plate The interlayer insulating layer 160 is formed on the second gate wires 125a, 125b, 125c, 121, 124, 127, and 129 and the second gate insulating layer 142. The interlayer insu lating layer 160 is made of a ceramic-based material Such as silicon nitride SiNX or silicon oxide SiO2, as in the first gate insulating layer 141 and the second gate insulating layer On the interlayer insulating layer 160, a data wire including a data line 171 including the Switching Source elec trode 176b, the connection member 174 including the initial ization drain electrode 177d and the compensation drain elec trode 177c, and the driving voltage line 172 including the light emission control drain electrode 177f and the driving control source electrode 176e are formed. (0095. The light emission control drain electrode 177 fis connected to the light emission control drain area 133f of the light emission control semiconductor layer 131f through a contact hole 72 that is formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the interlayer insulating layer 160. The first intermediate protruding portion 174b of the connection member 174 is connected to the first storage capacitor plate 126 through the contact hole 64 that is continuously formed in the second gate insulating layer 142 and the interlayer insulating layer 160. One side separation terminal 172a and the other side separation terminal 172b of the driving voltage line 172 are connected to the second storage capacitor plate 127 through one side contact hole 65 and the other side contact hole 66, respectively, that are formed in the interlayer insulating layer 160. The second intermediate protruding portion 177c of the connection mem ber 174 is connected to the compensation semiconductor layer 125c of the compensation TFT T3 through a contact hole 68 that is continuously formed in the first gate insulating layer 141, the second gate insulating layer 142, and the inter layer insulating layer The protective layer 180 that covers data wires 171, 172,174, and 177f is formed on the interlayer insulating layer 160, and the pixel electrode 191 is formed on the protective layer 180. The pixel electrode 191 is connected to the light emission control drain electrode 177f through the contact hole 181 that is formed in the protective layer 180. (0097. A barrier rib 350 is formed on the protective layer 180 and an edge of the pixel electrode 191, and the barrier rib 350 has a barrier rib opening 351 that exposes the pixel electrode 191. The barrierrib350 may be made of a resin such as a polyacrylates resin and a polyimides resin or a silica based inorganic material An organic emission layer 370 is formed on the pixel electrode 191 that is exposed by the barrier rib opening 351, and a common electrode 270 is formed on the organic emission layer 370. In this way, the OLED 70 including the pixel electrode 191, the organic emission layer 370, and the common electrode 270 are formed. (0099. The pixel electrode 191 is an anode, which is a hole injection electrode, and the common electrode 270 is a cath ode, which is an electron injection electrode. However, embodiments are not limited thereto, and the pixel electrode 191 may be a cathode, and the common electrode 270 may be an anode according to a driving method of the OLED display. When holes and electrons from the pixel electrode 191 and the common electrode 270, respectively, are injected into the organic emission layer 370 and excitons in which the injected holes and electrons are coupled drop from an excited State to a ground State, light is emitted The organic emission layer 370 is made of a low polymer organic material or a high polymer organic material such as poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT). Further, the organic emission layer 370 may beformed as a multilayer including at least one of an emission layer, a hole injection layer (HIL), a hole transporting layer (HTL), an electron transporting layer (ETL), and an electron injection layer
14 (EIL). When the multilayer includes all of the emission layer, the HIL, the HTL, the ETL, and the EIL, the HIL is disposed on the pixel electrode 191, which is a positive electrode, and the HTL, the emission layer, the ETL, and the EIL are sequen tially stacked thereon. The common electrode 270 is made of a reflective conductive material and becomes a rear light emitting OLED display. As a reflective material, a material Such as lithium (Li), calcium (Ca), lithium fluoride/calcium (LiF/Ca), lithium fluoride/aluminum (LiF/Al), aluminum (Al), silver (Ag), magnesium (Mg), or gold (Au) may be used While this disclosure has been described in connec tion with certain embodiments, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but, on the contrary, is intended to cover various modifications and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit and scope of the appended claims. <Description of symbols-> 110: Substrate 121: scan line 122: previous scan line 123:light emission control line 124: initialization voltage line 125a: driving gate electrode 125b: Switching gate electrode 126: first storage capacitor plate 127: second storage capacitor plate 128: first boosting capacitor plate 129: Second boosting capacitor plate 131: semiconductor layer 141: first gate insulating layer 142: Second gate insulating layer 160: interlayer insulating layer 171: data line 172: driving voltage line 174: connection member What is claimed is: 1. An organic light emitting diode (OLED) display, com prising: a Substrate; a scan line formed over the Substrate configured to transfer a scan signal; a data line that intersects the scan line and is configured to transfer a data signal a driving Voltage line that intersects the scan line and is configured to transfer a driving Voltage; a switching thin film transistor (TFT) connected to the scan line and the data line; a driving TFT connected to the switching TFT and the driving Voltage line, the driving TFT comprising a driv ing gate electrode: an OLED connected to the driving TFT, a storage capacitor connected between the driving Voltage line and the driving gate electrode; and a boosting capacitor connected to the storage capacitor, wherein the storage capacitor has at least one capacitor opening. 2. The OLED display of claim 1, wherein the driving TFT further comprises a driving semiconductor layer formed on the Substrate, and wherein the driving gate electrode is formed on a first gate insulat ing layer and a second gate insulating layer that sequen tially cover the driving semiconductor layer, the driving gate electrode overlapped with the driving semiconduc tor layer. 3. The OLED display of claim 2, wherein the storage capacitor comprises: a first storage capacitor plate formed over the first gate insulating layer; a second gate insulating layer covering the first storage capacitor plate; and a second storage capacitor plate formed over the second gate insulating layer and overlapped with the first stor age capacitor plate. 4. The OLED display of claim 3, wherein the capacitor opening is formed in the second storage capacitor plate. 5. The OLED display of claim 4, further comprising an interlayer insulating layer covering the second storage capacitor plate, wherein the driving gate electrode is connected to the first storage capacitor plate through a contact hole positioned within the capacitor opening and formed in the inter layer insulating layer and the second gate insulating layer. 6. The OLED display of claim 5, wherein the driving volt age line is formed over the interlayer insulating layer and is spaced apart from the capacitor opening. 7. The OLED display of claim 6, wherein a first side sepa ration terminal and a second side separation terminal of the driving Voltage line are connected to the second storage capacitor plate through a first side contact hole and a second side contact hole, respectively, the first side and the second side contact holes formed in the interlayer insulating layer. 8. The OLED display of claim 7, further comprising a connection member formed in the same layer, and configured to be parallel to, the driving Voltage line, and further config ured to connect the driving gate electrode and the first storage capacitor plate. 9. The OLED display of claim 8, wherein a first end of the connection member is connected to the driving gate electrode through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, and a first intermediate protruding portion of the con nection member is connected to the first storage capacitor plate through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulat ing layer and the second gate insulating layer. 10. The OLED display of claim 8, further comprising an initialization TFT configured to be turned on according to a previous scan signal received through a previous Scanline and further configured to transfer an initialization Voltage to a driving gate electrode of the driving TFT, wherein a second end of the connection member is con nected to an initialization semiconductor layer of the initialization TFT through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, the second gate insulating layer, and the first gate insulating layer. 11. The OLED display of claim 8, further comprising a compensating TFT configured to compensate a threshold voltage of the driving TFT and connected to the driving TFT, wherein a second intermediate protruding portion of the connection member is connected to a compensation semiconductor layer of the compensation TFT through a contact hole formed in the interlayer insulating layer, the second gate insulating layer, and the first gate insulating layer. 12. The OLED display of claim 8, wherein the boosting capacitor comprises a first boosting capacitor plate extended from the first storage capacitor and a second boosting capaci torplate overlapped with the first boosting capacitorplate and protruded from the scan line. 13. The OLED display of claim 12, wherein the scan line and the driving gate electrode are formed co-planar with the second storage capacitor plate.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) United States Patent
 US00926.3506B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.263,506 B2 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (OLED) DISPLAY INCLUDING CURVED OLED (71) Applicant: SAMSUNG
US00926.3506B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.263,506 B2 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (OLED) DISPLAY INCLUDING CURVED OLED (71) Applicant: SAMSUNG
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011
 US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2011 0006327A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0006327 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0156062 A1 Kim et al. US 2011 O156062A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0156062 A1 Kim et al. US 2011 O156062A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE AND METHOD
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20150144925A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0144925 A1 BAEK et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY Publication Classification
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. KO (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008
 US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
US 2008O143655A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0143655 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070176538A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0176538A1 Winters et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2007 (54) CONTINUOUS CONDUCTOR FOR OLED (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20070176538A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0176538A1 Winters et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2007 (54) CONTINUOUS CONDUCTOR FOR OLED (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0039018 A1 Yan et al. US 201700390 18A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) DUAL DISPLAY EQUIPMENT WITH
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
32S N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States. Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 (19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(19) United States US 20090072251A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0072251A1 Chan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) LED SURFACE-MOUNT DEVICE AND LED DISPLAY INCORPORATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,760,165 B2
 USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
USOO776O165B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cok () Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 20 (54) CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STACKED OLED 6,844,957 B2 1/2005 Matsumoto et al. DEVICE 6,903,378 B2 6, 2005 Cok 7.463,222
III. (12) United States Patent US 6,995,345 B2. Feb. 7, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Timothy D. Gorbold, Scottsville, NY
 USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
USOO6995.345B2 (12) United States Patent Gorbold (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,995,345 B2 Feb. 7, 2006 (54) ELECTRODE APPARATUS FOR STRAY FIELD RADIO FREQUENCY HEATING (75) Inventor: Timothy
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2
 USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO8304743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,743 B2 Baik et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) ELECTRON BEAM FOCUSINGELECTRODE (58) Field of Classification Search... 250/396
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160.042965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0042965 A1 Ha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 11, 2016 (54) METHODS FOR FORMING FINE PATTERNS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20160.042965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0042965 A1 Ha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 11, 2016 (54) METHODS FOR FORMING FINE PATTERNS Publication Classification
AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis
 IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
IHS Electronics & Media Key Patent Report AMOLED compensation circuit patent analysis AMOLED pixel driving circuit with threshold voltage and IR-drop compensation July 2013 ihs.com Ian Lim, Senior Analyst,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/24
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 068 378 A2 (43) Date of publication:.06.2009 Bulletin 2009/24 (21) Application number: 08020371.4 (51) Int Cl.: H01L 33/00 (2006.01) G02F 1/13357 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 068 378 A2 (43) Date of publication:.06.2009 Bulletin 2009/24 (21) Application number: 08020371.4 (51) Int Cl.: H01L 33/00 (2006.01) G02F 1/13357 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2. Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013
 USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
USOO8492969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.492,969 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE 2002fOO15005 A1 2/2002 Imaeda... 34.5/5 DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014020431 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0204310 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2014 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE Publication Classification
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
(19) United States US 2002O125831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0125831 A1 Inukai et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazutaka Inukai, Kanagawa
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
 Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 3 Evaluated Results of Conventional Pixel Circuit, Other Compensation Circuits and Proposed Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes (AMOLEDs) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(73) Assignee. SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO.,LTD.(KR) ' ' ' ' " Gools
 USOO9420363B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.420,363 B2 Seo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2016 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USPC... 381/333 See application file for complete search history.
USOO9420363B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.420,363 B2 Seo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2016 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USPC... 381/333 See application file for complete search history.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
(19) United States US 2010.0020005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0020005 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING BRIGHTNESS
Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED)
 Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 2 Overview of All Pixel Circuits for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O157252A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0157252 A1 Yamazaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND METHOD Publication
US 2011 O157252A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0157252 A1 Yamazaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE AND METHOD Publication
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013
 USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
USOO8405582B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,405,582 B2 Kim (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 26, 2013 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND JP 2002-278513 9/2002 DRIVING METHOD THEREOF.. i;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix OLED Displays
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 3, MARCH 2008 1 Design of Organic TFT Pixel Electrode Circuit for Active-Matrix Displays Aram Shin, Sang Jun Hwang, Seung Woo Yu, and Man Young Sung 1) Semiconductor and
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) United States Patent Sanford et al. USOO6734636B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 11, 2004 (54) OLED CURRENT DRIVE PIXEL CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: James Lawrence Sanford, Hopewell Junction,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160O86557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0086557 A1 WATANABE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) CONTROL DEVICE, DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20160O86557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0086557 A1 WATANABE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) CONTROL DEVICE, DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(19) United States US 2012O133635A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0133635 A1 J et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND Publication Classification DRIVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0292213 A1 (54) (71) (72) (21) YOON et al. AC LED LIGHTINGAPPARATUS Applicant: POSCO LED COMPANY LTD., Seongnam-si (KR) Inventors:
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
s S (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.412,462 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 9, 2016
 USOO9412462B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (54) 3D STACKED MEMORY ARRAY AND METHOD FOR DETERMINING THRESHOLD VOLTAGES OF STRING SELECTION TRANSISTORS (71) Applicant: Seoul National University
USOO9412462B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (54) 3D STACKED MEMORY ARRAY AND METHOD FOR DETERMINING THRESHOLD VOLTAGES OF STRING SELECTION TRANSISTORS (71) Applicant: Seoul National University
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl O : --- I. all T
 (19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(19) United States US 20130241922A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0241922 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD OF DISPLAYING THREE DIMIENSIONAL STEREOSCOPIC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231566A1 Naugler US 20080231566A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) MINIMIZING DARK CURRENT IN LED DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231566A1 Naugler US 20080231566A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) MINIMIZING DARK CURRENT IN LED DISPLAY
III. USOO A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998
 III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
III USOO5741 157A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,741,157 O'Connor et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54) RACEWAY SYSTEM WITH TRANSITION Primary Examiner-Neil Abrams ADAPTER Assistant
O'Hey. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 SOHO (2. See A zo. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2016O139866A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0139866A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1. Murade (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2001
 US 2001 OO19384A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2001/0019384 A1 Murade (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2001 (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDIG LIGHT (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 OO19384A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2001/0019384 A1 Murade (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2001 (54) APPARATUS FOR PROVIDIG LIGHT (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 (19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070229418A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0229418 A1 Yun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR DRIVING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(19) United States US 200700296.58A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0029658 A1 Peng et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 8, 2007 (54) ELECTRICAL CONNECTION PATTERN IN Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
US 2006O114220A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0114220 A1 Wang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING Publication Classification OPEPRATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20020089492A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089492 A1 Ahn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY WITH INPUT DEVICE (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,044,949 B2
 USOO8044949B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Yamazaki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2011 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE AND 6,885,385 B2 4/2005 Ouchi et al. ELECTRONIC APPARATUS FOR 2001/0022565
USOO8044949B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Yamazaki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2011 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE AND 6,885,385 B2 4/2005 Ouchi et al. ELECTRONIC APPARATUS FOR 2001/0022565
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand
 United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
United States Patent (19) Ekstrand (11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: 5,055,743 Oct. 8, 1991 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58 56 NDUCTION HEATED CATHODE Inventor: Assignee: John P. Ekstrand,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011
 US 2011 0193817A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0193817 A1 BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS Publication Classification
US 2011 0193817A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0193817 A1 BYUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2011 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
 USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8026969B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays
 Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays Linrun Feng, Xiaoli Xu and Xiaojun Guo ECS Trans. 2011, Volume 37, Issue 1, Pages 105-112. doi:
Comparative Analysis of Organic Thin Film Transistor Structures for Flexible E-Paper and AMOLED Displays Linrun Feng, Xiaoli Xu and Xiaojun Guo ECS Trans. 2011, Volume 37, Issue 1, Pages 105-112. doi:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
(19) United States US 2002O080298A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0080298 A1 Fukayama (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE (76) Inventor: Norihisa Fukayama, Mobara
AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing. Research Division Almaden - Austin - Beijing - Haifa - India - T. J. Watson - Tokyo - Zurich
 RT0565 Engineering Technology 4 pages Research Report February 3, 2004 AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing Y. Sakaguchi, D. Nakano IBM Research, Tokyo Research Laboratory IBM Japan, Ltd.
RT0565 Engineering Technology 4 pages Research Report February 3, 2004 AM-OLED pixel circuits suitable for TFT array testing Y. Sakaguchi, D. Nakano IBM Research, Tokyo Research Laboratory IBM Japan, Ltd.
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
US0093.18074B2 (12) United States Patent Jang et al. (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING BACKLIGHT THEREOF (75) Inventors: Woo-Seok Jang, Gumi-si (KR); Jin-Sung
AMOLED Manufacturing Process Report SAMPLE
 AMOLED Manufacturing Process Report SAMPLE 2018 AMOLED Manufacturing Process Report The report analyzes the structure and manufacturing process by dividing AMOLED into small & medium-sized rigid OLED,
AMOLED Manufacturing Process Report SAMPLE 2018 AMOLED Manufacturing Process Report The report analyzes the structure and manufacturing process by dividing AMOLED into small & medium-sized rigid OLED,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008
 US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 20080290816A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0290816A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2008 (54) AQUARIUM LIGHTING DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1 O1585A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0101585 A1 YOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2014 (54) IMAGE PROCESSINGAPPARATUS AND (30) Foreign Application
