(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2
|
|
|
- Ira Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,026,969 B2 Mauritzson et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 27, 2011 (54) PIXEL FOR BOOSTING PIXEL RESET VOLTAGE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors: Richard A. Mauritzson, Boise, ID (US); 6, A * 4/2000 Afghahi w is ghahi ,208.1 Joey Shah, Boise, ID (US) 6, B1* 6/2001 Hoffman /308 6, B2 2/2004 Rhodes (73) Assignee: Aptina Imaging Corporation, George 7, B2 5/2007 Dierickx ,308 Town (KY) 7,233,353 B2 6/2007 Xue ,294 7,277,129 B1 * 10/2007 Lee ,308 c - r 2003, OO63206 A1 4/2003 Mabuchi (*) Notice: Still style hit." 2004/ A1* Shinohara ,308 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. 2006/ A1 12/2006 Mabuchi ,308 This patent is Subject to a terminal dis- FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS claimer. JP JP , /1999 (21) Appl. No.: 12/632,828 JP , 2003 (22) Filed: Dec. 8, 2009 OTHER PUBLICATIONS (65) O O Prior Publication Data Shunsuke Inoue et al. "A 3.25M-pixel APS-C size CMOS Image Sensor. IEEE 2001 Workshop on Charge-Coupled Devices and US 201O/OO97509 A1 Apr. 22, 2010 Advanced Image Sensors, Jun. 2001, pp * cited by examiner Related U.S. Application Data (63) Continuation of application No. 10/925,172, filed on Aug. 25, 2004, now Pat. No. 7,652,704. (51) Int. Cl. H04N3/14 ( ) HO)4N 5/217 ( ) HOIL 3L/II3 ( ) HOIL 27/00 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /308; 348/241; 257/292; 250/208.1 (58) Field of Classification Search /308, 348/301, 241; 257/291, 292; 250/208.1 See application file for complete search history. Primary Examiner Nhan T Tran (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Nancy Y. Ru (57) ABSTRACT A pixel cell in which a capacitance is coupled between a storage node and a row select transistor. The pixel cell utilizes a readout timing sequence between operation of a reset tran sistor and a row select transistor to boost a reset Voltage. 12 Claims, 7 Drawing Sheets 300 VCC 302 OUT
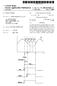
2 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 1 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2 ROWDRIVER DECODER OZZ
3 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 2 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2 3 g
4 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 3 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2
5 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 4 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2 S s s CN C cro
6 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 5 Of 7 US 8,026,969 B A flo
7 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 6 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2
8 U.S. Patent Sep. 27, 2011 Sheet 7 of 7 US 8,026,969 B2 cxd C co C s ar CD Lu CC 2C5 CD > CD S. OS O ac ad h S. S
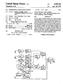
9 1. PXEL FOR BOOSTING PXEL RESET VOLTAGE REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 10/925,172 filed Aug. 25, 2004, now U.S. Pat. No. 7,652,704, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. FIELD OF THE INVENTION The invention relates generally to improving the control and operation of an imager pixel. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Various imager circuits have been proposed such as charge coupled device (CCD) arrays, complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) arrays, arrays combining both CCD and CMOS features, as well as hybrid infrared focal-plane arrays (IR-FPAS). Conventional arrays have light-sensing elements, typically referred to as pixels' and readout cir cuitry that outputs signals indicative of the light sensed by the pixels. ACMOS imager, for example, includes a focal plane array of pixel cells; each cell includes a photodetector (e.g., a pho togate, photoconductor or a photodiode) overlying a substrate for producing a photo-generated charge in a doped region of the substrate. A readout circuit is provided for each pixel cell and includes at least a source follower transistor and a row select transistor for coupling the source follower transistor to a column output line. The pixel cell also typically has a storage region, connected to the gate of the source follower transistor. Charge generated by the photodetector is sent to the storage region. The imager may also include a transistor for transferring charge from the photodetector to the storage region and another transistor for resetting the storage region to a predetermined charge level prior to charge transference. FIG. 1 illustrates a block diagram of a CMOS imager device 908 having a pixel array 200 with each pixel cell being constructed as described above, or as other known pixel cell circuits. Pixel array 200 comprises a plurality of pixels arranged in a predetermined number of columns and rows (not shown). The pixels of each row in array 200 are all turned on at the same time by a row select line, and the pixels of each column are selectively output by respective column select lines. A plurality of row and column lines are provided for the entire array 200. The row lines are selectively activated in sequence by a row driver 210 in response to row address decoder 220. The column select lines are selectively activated in sequence for each row activation by a column driver 260 in response to column address decoder 270. Thus, a row and column address is provided for each pixel. The CMOS imager908 is operated by a control circuit 250, which controls address decoders 220, 270 for selecting the appropriate row and column lines for pixel readout. Control circuit 250 also controls the row and column driver circuitry 210, 260 so that they apply driving voltages to the drive transistors of the selected row and column lines. The pixel output signals typically include a pixel reset signal V, taken off of the storage region when it is reset by the reset transistor and a pixel image signal V, which is taken off the storage region after photo-generated charges are transferred to it. The V, and V signals are readby a sample and hold circuit 265 and are subtracted by a differential amplifier 267, to produce a differential signal V, -V. for each pixel. V-V, repre sents the amount of light impinging on the pixels. This dif US 8,026,969 B ference signal is digitized by an analog-to-digital converter 275. The digitized pixel signals are fed to an image processor 280 to form a digital image output. The digitizing and image processing can be located on or off the imager chip. In some arrangements the differential signal V-V can be ampli fied as a differential signal and directly digitized by a differ ential analog to digital converter. FIG. 2 illustrates a four transistor (4T) CMOS imager pixel cell 100. Pixel cell 100 includes a photodiode 102 connected to a transfer transistor 104. The transfer transistor 104 is also connected to storage region 108. A reset transistor 106, a capacitor 107 and a gate of a source follower transistor 110 are connected to storage region 108. A row select transistor 112 is connected to source follower transistor 110. The active elements of pixel cell 100 perform the functions of (1) photon to charge conversion by photodiode 102; (2) resetting the storage region to a known state before the transfer of charge to it by reset transistor 106; (3) transfer of charge to the storage region 108 by the transfer transistor 104; (4) selection of the cell 100 for readout by row select transistor 112; and (5) output and amplification of a signal representing a reset Volt age (i.e., V) and a pixel signal Voltage (i.e., V) based on the charges present on storage region 108 by source follower transistor 110. Capacitor 107 is utilized because charges pro duced during an integration period by photodiode 102 may be greater than the capacity of storage region 108. Accordingly, capacitor 107 provides additional charge storage capacity. The pixel cell 100 of FIG. 2 is formed on a semiconductor Substrate as part of an imager device pixel array (e.g., array 200 of FIG. 1). FIG. 3 illustrates a timing diagram for the FIG. 2 circuit 300 during pixel readout. Initially, the storage regions 108 of all pixels in an imager array 200 (FIG. 1) are set to a prede termined voltage to ensure that all source follower transistors 110 remain turned off. The ROW signal of the pixel intended to be read is pulsed high at time t1 providing an operating voltage across source follower transistor 110. The storage region 108 of the pixel intended to be sampled is then reset at time t2 by briefly turning on reset transistor 106, which is supplied with operating voltage VCC plus a Vt threshold voltage of the reset transistor 106 when signal RST goes high, thereby resetting storage region 108 to a predetermined volt age. The reset voltage level on the storage region 108 is then applied to the gate of source follower transistor 110, which converts it to a reset output voltage V, on a column output line. The output signal is Subsequently sampled at time t3, for example by a sample and hold circuit 265 (FIG. 1), where a high pulse SHR is used to sample and hold the reset output Voltage V, onto a first sample and hold capacitor. Charge stored in photodiode 102 from an integration period is subsequently transferred to storage region 108 by signal TX going high at time tathereby, turning on transfer transistor 104. The transferred charge lowers the voltage on the storage region 108 to a pixel output signal level, which is applied to the gate of source follower transistor 110. Source follower transistor 110, which is supplied with operating Voltage VCC, converts the signal Voltage level to a signal output voltage V on the column output line. Sample and hold circuit 265 (FIG. 1) in response to a sample/hold pulse SHS at time t5 causes the pixel s signal output voltage V on the column line to be stored in a second sample and hold capacitor. After V is sampled, the ROW signal is set to a low Voltage and the pixel circuit is ready for a next image capture. Since transfer transistor 104 is positioned between photo diode 102 and storage region 108, the storage region 108 can
10 3 be reset prior to transferring electrons. This permits a corre lated double sampling operation resulting in reduced ktc noise and image noise. With the pixel circuit configuration of FIG. 2 during reset, in order to obtain a maximum Voltage Swing at storage region 108, the reset transistor gate voltage is boosted to VCC+Vt (a threshold voltage of reset transistor 106). By adding voltage Vt to the reset voltage, the storage region 108 can be reset to VCC allowing a greater output signal Swing from the Source follower transistor 110 in response to charges transferred to the storage region 108 from photodiode 102. This technique requires additional Supply Voltage boost circuits to boost the reset Voltage which increases the size, power consumption, design complexity and costs of the pixel and associated cir cuit. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Exemplary method and apparatus embodiments of the present invention provide a new pixel design for an imager in which the row transistor that selects the pixel row for opera tion and readout is electrically coupled to and is operated in a manner which boosts the reset Voltage applied to the storage region thereby eliminating the need for a Supply Voltage boosting circuit. In one exemplary embodiment, the pixel cell includes a photosensor, a storage region for receiving transferred charges from the photosensor, a reset transistor for the reset ting the storage region, which is operated by a reset control signal, a source follower output transistor having a gate coupled to the storage region for providing a selective readout in response to a row select signal, a row select transistor coupled between a power source and the source follower output transistor for providing an output signal onto an output column line and a capacitance coupled between the storage region and a source terminal of the row select transistor. When the row select transistor is turned on shortly after a reset transistor is turned on, the row select transistor boosts the reset Voltage on the storage region by adding the initial pulse Voltage to the reset Voltage Supplied by the reset transistor. The capacitance also provides increased charge storage for the storage region when charge is transferred to the storage region from the photosensor. The capacitance may be pro vided by parasitic capacitance or by an added capacitor In another exemplary embodiment, the pixel cell includes a photosensor, a storage region for receiving transferred charges from the photosensor, a reset transistor for the reset ting of the storage region, which is operated by a reset control signal, a source follower output transistor having a gate coupled to the storage region for providing a readout signal, a row select transistor connected to the Source of the Source follower output transistorin response to a row select signal to thereby output a readout signal onto an output column line and a capacitor coupled between the gates of the Source follower transistorand the row select transistor. When the row select transistor turns on, after the reset transistor turns on, a Voltage pulse to boost the reset Voltage on the storage region is provided. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS These and other features and advantages of the invention will be better understood from the following detailed descrip tion, which is provided in connection with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a conventional imager device; US 8,026,969 B FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a conventional four tran sistor pixel; FIG. 3 is a timing diagram for charge readout of a conven tional four transistor pixel; FIG. 4 is a schematic circuit diagram according to a first exemplary embodiment of the invention; FIG. 5 is a schematic circuit diagram according to a second exemplary embodiment of the invention; FIG. 6 is a timing diagram for charge readout of the FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 circuits; and FIG. 7 is a diagram of a processing system which employs an imager employing an array of pixels constructed in accor dance with the FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 circuits. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION In the following detailed description, reference is made to the accompanying drawings, which are a part of the specifi cation, and in which is shown by way of illustration various embodiments whereby the invention may be practiced. These embodiments are described in sufficient detail to enable those skilled in the art to make and use the invention. It is to be understood that other embodiments may be utilized, and that structural, logical, and electrical changes, as well as changes in the materials used, may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Additionally, certain processing steps are described and a particular order of processing steps is disclosed; however, the sequence of steps is not limited to that set forth herein and may be changed as is known in the art, with the exception of steps or acts necessarily occurring in a certain order. The terms "wafer and substrate are to be understood as interchangeable and as including silicon, silicon-on-insulator (SOI) or silicon-on-sapphire (SOS), doped and undoped semiconductors, epitaxial layers of silicon Supported by a base semiconductor foundation, and other semiconductor structures. Furthermore, when reference is made to a "wafer' or substrate in the following description, previous process steps may have been utilized to form regions, junctions or material layers in or on the base semiconductor structure or foundation. In addition, the semiconductor need not be sili con-based, but could be based on silicon-germanium, germa nium, gallium arsenide, or other known semiconductor mate rials. The term pixel refers to a photo-element unit cell con taining a photo-conversion device or photosensor, for example, a photogate, photoconductor or a photodiode and transistors for processing an electrical signal from electro magnetic radiation sensed by the photo-conversion device. The embodiments of pixels discussed herein are illustrated and described as employing four transistor (4T) pixel circuits which use a transfer transistor to gate charge from a photo sensor to a storage region for the sake of example only. It should be understood that the invention may be used with other pixel arrangements having more or less than four tran sistors and in arrangements which do not use a transfer tran sistor. Although the invention is described herein with reference to the architecture and fabrication of one pixel cell, it should be understood that this is representative of a plurality of pixels in an array of an imager device Such as array 200 of imager device 908 (FIG. 1). In addition, although the invention is described below with reference to a CMOS imager, the inven tion has applicability to any solid state imaging device having a storage node which is reset and then has charges transferred to it. The following detailed description is, therefore, not to be
11 US 8,026,969 B2 5 taken in a limiting sense, and the scope of the present inven tion is defined only by the appended claims. FIG. 4 illustrates a pixel circuit 300 according to a first exemplary embodiment of the invention. Pixel circuit 300 includes a photodiode 302 connected to a transfer transistor The transfer transistor 304 is also connected to storage region 308. A reset transistor 306 and a source follower tran sistor 310 are connected to storage region 308. However, unlike circuit 100, the drain of row select transistor 312 is connected to Voltage source VCC and the source is connected 10 to source follower transistor 310. Also, one end of capacitor 307 is connected to the source of the row select transistor 112, while the other is connected to the storage region 108. With this arrangement, when the row select transistor 312 is first turned on, a Voltage boost is applied to the storage region If the reset transistor 306 is pulsed (on/off) just prior to the row select transistor 312, the storage region will see both the reset voltage applied by reset transistor 306 and the voltage boost caused by the turn on of the row select transistor 312. Other voltage coupling devices may be utilized instead of 20 capacitor 307, such as a reverse biased diode. As noted above with respect to the pixel readout of circuit 100 (FIG. 3), the reset voltage level is created by turning on the reset transistor 106 thereby resetting the storage region 108. The reset voltage level is applied to the gate of the source 25 follower transistor 110, which converts it to a reset output Voltage V, on a column output line. The boosted Voltage provided by turning on the row select transistoris also applied to the storage region 108 and gate of source follower transis tor 110. The pixel circuit 300 configuration and timing during 30 pixel readout (FIG. 6) provides a boosted reset signal, which is sampled to provide V, during charge integration (a period in which photodiode 302 generates signal charge in response to incident light). Thus, it is not required to have a Voltage Supply boosting circuit. The reset signal on the storage region is boosted due to the operation of capacitor 307 when the row select transistor 312 turns on in response to the leading edge of a row select pulse. In addition, if only a slight boost is required to sample the reset signal, the capacitor 307 may be omitted in which case 40 the parasitic capacitance between the gate? source junction of the source follower transistor 310 may be utilized to provide a reset voltage boost to the storage region 308. FIG. 5 illustrates a pixel circuit 400 according to a second exemplary embodiment of the invention. Pixel circuit 400 is similar to pixel circuit 100; however, instead of having a capacitor coupled between the storage region 108 and VCC, one end of capacitor 407 is connected to the gate of the row select transistor 112, while the other is connected to the storage region 108. Accordingly, when the row select control signal is applied to the gate of the row select transistor 112, it provides a boosted reset signal at the storage region 108. Other voltage coupling devices may be utilized instead of capacitor 407, such as a reverse biased diode. FIG. 6 illustrates a timing diagram for circuit 300 and circuit 400 during pixel readout. During a readout operation, the reset enable signal RST applied to the gate of reset tran sistor 106 is pulsed (on/off) prior to row enable signal ROW being pulsed high. Initially, the storage region (308/108) of a pixel in an imager array 200 is set to a predetermined Voltage (near VCC). At time t1, the storage region (308/108) of the pixel intended to be sampled is then reset by briefly turning on reset transistor (306/106), which is supplied with operating voltage VCC when signal RST goes high, thereby resetting storage region (308/108) to a predetermined voltage. The reset volt age level on the storage region (308/108) is then applied to the gate of source follower transistor (310/110). After the RST pulse goes low, the ROW signal of the pixel intended to be read is pulsed high at time a providing a Voltage boost to the reset Voltage on the gate of the Source follower transistor (310/110). The boosted reset signal provided from the row select gate Voltage is Subsequently sampled at time t3, for example by a sample and hold circuit 265 (FIG. 1), where a high pulse SHR is used to sample and hold the reset output Voltage V, onto a first sample and hold capacitor. Charge stored in photodiode (302/102) during an integra tion period is subsequently transferred to storage region (308/ 108) by signal TX going high at time ta thereby, turning on transfer transistor (304/104). The transferred charge lowers the voltage on the storage region (308/108) to a pixel output signal level, which is applied to the gate of Source follower transistor (310/110). Source follower transistor (310/110), which is supplied with operating voltage VCC through the row select transistor (312/112), converts the signal voltage level to a signal output voltage V on the column output line. Sample and hold circuit 265 (FIG. 1) in response to a sample/ hold pulse SHS at time ts causes the pixel s signal output voltage V on the column line to be stored in a second sample and hold capacitor. After V is sampled, the ROW signal is set to a low Voltage and the pixel circuit is ready for a next image capture. By pulsing RST high attl prior to pulsing ROW high at t2. a boosting of the predetermined reset Voltage is achieved. This boost is attributed to a capacitive coupling between the storage region 308 (FIG. 4) and the source of the row select transistor 310 (FIG. 4), or capacitive coupling between the storage region 108 (FIG. 5) and the gate of the row select transistor 112 (FIG. 5). FIG. 7 illustrates a processor-based system 900 including an imaging device 908 of FIG. 1 modified to contain pixels in the array 200 which are constructed in accordance with the invention. The processor-based system 900 is exemplary of a system utilizing an imaging device 908 which includes a pixel array having pixels constructed and operated in accordance with the invention. Without being limiting, such a system could include a camera system, computer system, Scanner, machine vision system, vehicle navigation system, video phone, Surveillance system, auto focus system, star tracker system, motion detection system, and others. The processor-based system 900, for example a camera system, generally comprises a central processing unit (CPU) 902. Such as a microprocessor, that communicates with an input/output (I/O) device 906 over a bus 904. Imaging device 908 also communicates with the CPU902 over bus 904. The processor-based system 900 also includes random access memory (RAM) 910, and can include removable memory 915, such as flash memory, which also communicate with CPU902 over the bus 904. Imaging device 908 may be combined with a processor, Such as a CPU, digital signal processor, or microprocessor, with or without memory Stor age on a single integrated circuit or on a different chip than the processor. Various embodiments of the invention have been illus trated using a photodiode as the charge conversion device, and in the environment of a four transistor pixel. However, it should be appreciated that the invention is not so limited and can be used in any pixel architecture employing a row select transistor and source follower transistor coupled in the fash ion similar to the circuit described above, which is used for eliminating the need to boost the Voltage of a reset signal. Also, other types of photosensors may be used to generate image charge. The invention may also be used in a readout circuit for a CCD (charge coupled device) array. Accordingly,
12 7 it is not intended that the present invention be strictly limited to the above-described and illustrated embodiment. Any modifications, though presently unforeseeable, of the present invention that comes within the spirit and scope of the fol lowing claims should be considered part of the present inven tion. The invention claimed is: 1. A pixel, said pixel comprising: a photosensor for generating charge during an integration period; a storage node for receiving said generated charge from said photosensor, an output transistor coupled to said storage node for con Verting a charge signal at said storage node to an output Voltage; a reset transistor for applying a reset Voltage to said storage node: a row select transistor coupled to said output transistor for Selectively enabling said pixel circuit to output said out put Voltage; and a capacitive connection between said row select transistor and said storage node for boosting a reset Voltage applied to said storage node by said reset transistor when said row select transistor is activated, wherein said capacitive coupling comprises a capacitor directly con nected to said storage node and a source of said row Select transistor. 2. The pixel of claim 1, wherein said output transistor provides an output signal based on said charge at the storage node. 3. The pixel of claim 1 further comprising a transfer tran sistor connected to said photosensor for transferring charge from said photosensor to said storage node. 4. The pixel of claim 1, wherein said row select transistoris coupled between a Voltage source and a drain of said output transistor. 5. An imager, comprising: a pixel array comprising a plurality of pixels arranged in rows and columns, at least one of said pixels comprising: a photosensor for generating charge during an integration period; a storage node for receiving said generated charge from said photosensor, a reset transistor for applying a reset Voltage to said storage node: US 8,026,969 B a readout circuit for reading out a reset Voltage of said storage node, said readout circuit including a row select transistor for selectively enabling said pixel circuit to output an output Voltage; and a capacitor directly connected between a source of said row Select transistor and said storage node. 6. The imager of claim 5 further comprising a transfer transistor connected to said photosensor for transferring charge from said photosensor to said storage node. 7. A method of reading out signals from a pixel, said method comprising: resetting a storage node adapted to receive photogenerated charge to a predetermined Voltage state; with the storage node at said predetermined State, adding an additional Voltage to said storage node to produce a boosted reset Voltage; and reading out said boosted reset Voltage as said storage node as a reset level output signal, wherein the additional Voltage is added by a direct capacitive coupling between a row select transistor and said storage node and wherein the direct capacitive coupling comprises a capacitor con nected between said storage node and a source of said row select transistor. 8. The method of claim 7 further comprising the act of generating charges with a photosensor during an integration period and applying said generated charges to said storage node. 9. The method of claim 7, wherein the direct capacitive coupling comprises a capacitor, the method further compris ing the act of storing charges in the capacitor. 10. The method of claim 7, wherein said additional voltage is added in response to turning on a row select transistor of a pixel. 11. The method of claim 7 further comprising selectively transferring charge generated by a photosensor to said storage node. 12. The method of claim 7, further comprising: resetting the storage node to a reset level; with the storage node at the reset level, turning on a row Select transistor to output a signal from said pixel; and reading out said reset level as a reset level output signal, wherein a timing relationship between turning on said row select transistor and said resetting of said storage node boosts said reset level output signal. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
(19) United States US 2003O146369A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0146369 A1 Kokubun (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003 (54) CORRELATED DOUBLE SAMPLING CIRCUIT AND CMOS IMAGE SENSOR
12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US B2
 USOO87240O2B2 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 8.724.002 B2 9 9 Rajasekaran (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) IMAGING PIXELS WITH DUMMY 6,535,247 B1 3/2003 Kozlowski et al. TRANSISTORS
USOO87240O2B2 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 8.724.002 B2 9 9 Rajasekaran (45) Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) IMAGING PIXELS WITH DUMMY 6,535,247 B1 3/2003 Kozlowski et al. TRANSISTORS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
USOO7023408B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,023.408 B2 Apr. 4, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 21,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,803,770 B2. Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014
 US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
US00880377OB2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Jeong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) PIXEL AND AN ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING 20, 001381.6 A1 1/20 Kwak... 345,211 DISPLAY DEVICE USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0078354 A1 Toyoguchi et al. US 20140078354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) SOLD-STATE MAGINGAPPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
USOO8106431B2 (12) United States Patent Mori et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) (51) (52) (58) (56) SOLID STATE IMAGING APPARATUS, METHOD FOR DRIVING THE SAME AND CAMERAUSING THE SAME Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/001381.6 A1 KWak US 20100013816A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIXEL AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE USING THE SAME (76)
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098. J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999](/thumbs/90/103906389.jpg) US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
US005862098A United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,862,098 J eong [45] Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1999 [54] WORD LINE DRIVER CIRCUIT FOR 5,416,748 5/1995 P111118..... 365/23006 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,867,549 B2. Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005
 USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
USOO6867549B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2005 (54) COLOR OLED DISPLAY HAVING 2003/O128225 A1 7/2003 Credelle et al.... 345/694 REPEATED PATTERNS
(12) United States Patent
 US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
US00957 1775B1 (12) United States Patent Zu0 et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) IMAGE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY REECTION RATO IMPROVEMENT
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll
 illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
illlllllllllllilllllllllllllllllillllllllllllliilllllllllllllllllllllllllll USOO5614856A Unlted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,614,856 Wilson et al. [45] Date of Patent: Mar. 25 1997 9 [54] WAVESHAPING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
USOO6462508B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,508 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) CHARGER OF A DIGITAL CAMERA WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS DATA TRANSMISSION FUNCTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2. Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005
 USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
USOO6865123B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,865,123 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,272.672 A * 12/1993 Ogihara... 365/200 WITH ENHANCED REPAIR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Ali USOO65O1400B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) CORRECTION OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER GAIN ERROR IN PIPELINED ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (75) Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number:
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent (10) Patent Number: USOORE38379E Hara et al. (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY WITH 4,750,839 A * 6/1988 Wang et al.... 365/238.5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 004063758A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/063758A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 004 (54) LINE ON GLASS TYPE LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2. Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004
 USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
USOO6727486B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,727,486 B2 Choi (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2004 (54) CMOS IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A 6,040,570 A 3/2000 Levine et al.... 250/208.1 CHOPPER-TYPE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
US 2009017.4444A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0174444 A1 Dribinsky et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2009 (54) POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT HAVING ZERO (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,736,525 B2
 US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
US008736525B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kawabe (45) Date of Patent: *May 27, 2014 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE USING CAPACITOR USPC... 345/76 82 COUPLED LIGHTEMISSION CONTROL See application file
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2005O285825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0285825A1 E0m et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND DRIVING (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
(12) United States Patent USOO71 6 1 494 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,161,494 B2 AkuZaWa (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2007 (54) VENDING MACHINE 5,831,862 A * 11/1998 Hetrick et al.... TOOf 232 75 5,959,869
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER 3,467,839
 Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
Sept. 16, 1969 N. J. MILLER J-K FLIP - FLOP Filed May 18, 1966 dc do set reset Switching point set by Resistors 6O,61,65866 Fig 3 INVENTOR Normon J. Miller 2.444/6r United States Patent Office Patented
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,885,157 B1
 USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
USOO688.5157B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cok et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN AND OLED 6,504,530 B1 1/2003 Wilson et al.... 345/173 FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(19) United States US 2005O105810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0105810 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONDENSED IMAGE RECORDING AND REPRODUCTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2
 USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
USOO65708O2B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,570,802 B2 Ohtsuka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 27, 2003 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE 5,469,559 A 11/1995 Parks et al.... 395/433 5,511,033
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LOURIE ETAL 3,143,664
 Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
Aug. 4, 1964 N. M. LURIE ETAL 3,143,664 SELECTIVE GATE CIRCUItfizie TRANSFRMERS T CNTRL THE PERATIN F A BISTABLE CIRCUIT Filed Nov. 13, 196l. 2 Sheets-Sheet GANG SIGNAL FLIP - FLP CIRCUIT 477WAY Aug. 4,
United States Patent (19) Osman
 United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Osman 54) (75) (73) DYNAMIC RE-PROGRAMMABLE PLA Inventor: Fazil I, Osman, San Marcos, Calif. Assignee: Burroughs Corporation, Detroit, Mich. (21) Appl. No.: 457,176 22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2013 0100156A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0100156A1 JANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) PORTABLE TERMINAL CAPABLE OF (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) United States Patent Sung USOO668058OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,680,580 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE (75) Inventor: Chih-Feng Sung,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0084992 A1 Ishizuka US 20110084992A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) ACTIVE MATRIX DISPLAY APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) United States Patent USOO9678590B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,678,590 B2 Nakayama (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) PORTABLE ELECTRONIC DEVICE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Shusuke Nakayama,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
US 200701.20581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0120581 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) COMPARATOR CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/74 (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
United States Patent (19) Taylor 54 GLITCH DETECTOR (75) Inventor: Keith A. Taylor, Portland, Oreg. (73) Assignee: Tektronix, Inc., Beaverton, Oreg. (21) Appl. No.: 155,363 22) Filed: Jun. 2, 1980 (51)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,822,052 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
USOO5822052A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,212,376 5/1993 Liang... 250/208.1 COMPENSATING ILLUMINANCE ERROR 5,278,674
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2016O141348A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0141348 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE (52) U.S. Cl. DISPLAY
III... III: III. III.
 (19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2015 0084.912A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084912 A1 SEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 9 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,424,795 B1
 USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
USOO6424795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Takahashi et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 23, 2002 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,444,482 A 8/1995 Misawa et al.... 386/120 RECORDING AND REPRODUCING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2. na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006
 US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
US00704375OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.043,750 B2 na (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) SET TOP BOX WITH OUT OF BAND (58) Field of Classification Search... 725/111, MODEMAND CABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200800847.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0084743 A1 Grant et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2008 (54) MEMORY STUCTURE CAPABLE OF BT WISE WRITE OR OVERWRITE
(19) United States US 200800847.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0084743 A1 Grant et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 10, 2008 (54) MEMORY STUCTURE CAPABLE OF BT WISE WRITE OR OVERWRITE
Dm 200. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States. User. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2007.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0242068 A1 Han et al. US 20070242068A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) 2D/3D IMAGE DISPLAY DEVICE, ELECTRONIC IMAGING DISPLAY DEVICE,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(19) United States US 20150379938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0379938A1 (21) (22) (60) (51) Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. SELECT A PLURALITY OF TIME SHIFT CHANNELS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lee US 2006OO15914A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) RECORDING METHOD AND APPARATUS CAPABLE OF TIME SHIFTING INA PLURALITY OF CHANNELS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. CLK CK CLK2 SOUrce driver. Y Y SUs DAL h-dal -DAL
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0079669 A1 Huang et al. US 20090079669A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) FLAT PANEL DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Tzu-Chien Huang,
United States Patent 19 11) 4,450,560 Conner
 United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
United States Patent 19 11) 4,4,560 Conner 54 TESTER FOR LSI DEVICES AND DEVICES (75) Inventor: George W. Conner, Newbury Park, Calif. 73 Assignee: Teradyne, Inc., Boston, Mass. 21 Appl. No.: 9,981 (22
(12) United States Patent
 US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
US009076382B2 (12) United States Patent Choi (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,076,382 B2 Jul. 7, 2015 (54) PIXEL, ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY DEVICE HAVING DATA SIGNAL AND RESET VOLTAGE SUPPLIED
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998
 USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
USOO.5850807A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,850,807 Keeler (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 22, 1998 54). ILLUMINATED PET LEASH Primary Examiner Robert P. Swiatek Assistant Examiner James S. Bergin
Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 (12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent US007847763B2 (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DRIVING PASSIVE MATRIX (56) References Cited OLED U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Shang-Li
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,501,230 B1
 USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
USOO65O123OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Feldman (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) DISPLAY WITH AGING CORRECTION OTHER PUBLICATIONS CIRCUIT Salam, OLED and LED Displays with Autonomous
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,373,742 B1. Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002
 USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6373742B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kurihara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 2002 (54) TWO SIDE DECODING OF A MEMORY (56) References Cited ARRAY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1
 USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
USOO8707080B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,707,080 B1 McLamb (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2014 (54) SIMPLE CIRCULARASYNCHRONOUS OTHER PUBLICATIONS NNROSSING TECHNIQUE Altera, "AN 545:Design
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2004O184531A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0184531A1 Lim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) DUAL VIDEO COMPRESSION METHOD Publication Classification
A High-Speed CMOS Image Sensor with Column-Parallel Single Capacitor CDSs and Single-slope ADCs
 A High-Speed CMOS Image Sensor with Column-Parallel Single Capacitor CDSs and Single-slope ADCs LI Quanliang, SHI Cong, and WU Nanjian (The State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures, Institute
A High-Speed CMOS Image Sensor with Column-Parallel Single Capacitor CDSs and Single-slope ADCs LI Quanliang, SHI Cong, and WU Nanjian (The State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures, Institute
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
United States Patent (19) Mizomoto et al. 54 75 73 21 22 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER Inventors: Hiroyuki Mizomoto; Yoshiaki Kitamura, both of Tokyo, Japan Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan Appl. No.: 18,756
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,266 B1
 USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
USOO6275266B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Morris et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 14, 2001 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,8,208 9/1998 Samela... 348/446 AUTOMATICALLY DETECTING AND 5,841,418
(12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A)
 Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Case #: JP H9-102827A (19) JAPANESE PATENT OFFICE (51) Int. Cl. 6 H04 M 11/00 G11B 15/02 H04Q 9/00 9/02 (12) Publication of Unexamined Patent Application (A) Identification Symbol 301 346 301 311 JPO File
Exexex. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States DAT. CONTS Sense signol generotor Detection
 (19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(19) United States US 20070285365A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0285365A1 Lee (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD THEREOF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,479 B2. Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010
 US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
US007804479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Furukawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH A TOUCH SCREEN 2003/01892 11 A1* 10, 2003 Dietz... 257/79 2005/0146654
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al.
 United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
United States Patent 19 Yamanaka et al. 54 COLOR SIGNAL MODULATING SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Seisuke Yamanaka, Mitaki; Toshimichi Nishimura, Tama, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,605,794 B2
 USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
USOO7605794B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nurmi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) ADJUSTING THE REFRESH RATE OFA GB 2345410 T 2000 DISPLAY GB 2378343 2, 2003 (75) JP O309.2820
) 342. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States MAGE ANALYZER TMING CONTROLLER SYNC CONTROLLER CTL
 (19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
(19) United States US 20160063939A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0063939 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) DISPLAY PANEL CONTROLLER AND DISPLAY DEVICE INCLUDING
Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993
 United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5258937A Patent Number: 5,258,937 Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993 54 ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75 inventor: Fletcher
United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5258937A Patent Number: 5,258,937 Blackmon 45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1993 54 ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75 inventor: Fletcher
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
(19) United States US 20050008347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0008347 A1 Jung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2005 (54) METHOD OF PROCESSING SUBTITLE STREAM, REPRODUCING
32O O. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(19) United States US 2012O243O87A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0243087 A1 LU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) DEPTH-FUSED THREE DIMENSIONAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/478 DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) United States Patent Park USOO6256325B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TRANSMISSION APPARATUS FOR HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION USING HDLC (75) Inventor: Chan-Sik Park, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040041173A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0041173 A1 Takahashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEMICONDUCTOR STORAGE AND ITS REFRESHING METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20040041173A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0041173 A1 Takahashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEMICONDUCTOR STORAGE AND ITS REFRESHING METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
US 2010O283828A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0283828A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 11, 2010 (54) MULTI-VIEW 3D VIDEO CONFERENCE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
(12) United States Patent Alfke et al. USOO6204695B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2001 (54) CLOCK-GATING CIRCUIT FOR REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION (75) Inventors: Peter H. Alfke, Los Altos
o VIDEO A United States Patent (19) Garfinkle u PROCESSOR AD OR NM STORE 11 Patent Number: 5,530,754 45) Date of Patent: Jun.
 United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent (19) Garfinkle 54) VIDEO ON DEMAND 76 Inventor: Norton Garfinkle, 2800 S. Ocean Blvd., Boca Raton, Fla. 33432 21 Appl. No.: 285,033 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51) Int. Cl.... HO4N 7/167
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
United States Patent 19 Maeyama et al. (54) COMB FILTER CIRCUIT 75 Inventors: Teruaki Maeyama; Hideo Nakata, both of Suita, Japan 73 Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21) Appl. No.: 27,957
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
(19) United States US 20140176798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0176798 A1 TANAKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2014 (54) BROADCAST IMAGE OUTPUT DEVICE, BROADCAST IMAGE
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,825,438 Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998
 USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
USOO5825438A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Song et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,517,341 5/1996 Kim et al...... 349/42 DUPLICATE WRING AND A PLURALITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(19) United States US 2012.00569 16A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/005691.6 A1 RYU et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE AND DRIVING METHOD (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/691;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0230902 A1 Shen et al. US 20070230902A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) DYNAMIC DISASTER RECOVERY
con una s190 songs ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Feb. 27, 2018 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 905, 806 B2 Chen
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
( 12 ) United States Patent Chen ( 54 ) ENCAPSULATION STRUCTURES OF OLED ENCAPSULATION METHODS, AND OLEDS es ( 71 ) Applicant : Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, Guangdong
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,239,640 B1
 USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6239640B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Liao et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 (54) DOUBLE EDGE TRIGGER D-TYPE FLIP- (56) References Cited FLOP U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
USOO9024241 B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (54) PHOSPHORDEVICE AND ILLUMINATION SYSTEM FOR CONVERTING A FIRST WAVEBAND LIGHT INTO A THIRD WAVEBAND LIGHT WHICH IS SEPARATED INTO AT LEAST TWO COLOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070226600A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0226600 A1 gawa (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2007 (54) SEMICNDUCTR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (30) Foreign Application
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,639,057 B1. Su (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, (54) CLOCK GATER SYSTEM 6,232,820 B1 5/2001 Long et al.
 United States Patent USOO7639057B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Su (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 2009 (54) CLOCK GATER SYSTEM 6,232,820 B1 5/2001 Long et al. 6,377,078 B1 * 4/2002 Madland... 326,95 75 6,429,698
United States Patent USOO7639057B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Su (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 2009 (54) CLOCK GATER SYSTEM 6,232,820 B1 5/2001 Long et al. 6,377,078 B1 * 4/2002 Madland... 326,95 75 6,429,698
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) United States Patent Kim USOO6348951B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) CAPTION DISPLAY DEVICE FOR DIGITAL TV AND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Man Hyo Kim, Anyang (KR) (73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012
 US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
US 20120169931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169931 A1 MOHAPATRA (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) PRESENTING CUSTOMIZED BOOT LOGO Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0116196A1 Liu et al. US 2015O11 6 196A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 30, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) LED DISPLAY MODULE,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,525,932 B2
 US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
US00852.5932B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2013 (54) ANALOGTV SIGNAL RECEIVING CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search FOR REDUCING SIGNAL DISTORTION
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2014-24184 USA Appellant BRIDGELUX INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney SAEGUSA & PARTNERS The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
US 2010.0097.523A1. (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0097523 A1 SHIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS AND CONTROL (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0054800A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0054800 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2015 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR DRIVING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2. Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005
 USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
USOO6852965B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,852,965 B2 Ozawa (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 8, 2005 (54) IMAGE SENSORAPPARATUS HAVING 6,373,460 B1 4/2002 Kubota et al.... 34.5/100 ADDITIONAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO972O865 (10) Patent No.: US 9,720,865 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 1, 2017 (54) BUS SHARING SCHEME USPC... 327/333: 326/41, 47 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent USOO972O865 (10) Patent No.: US 9,720,865 Williams et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 1, 2017 (54) BUS SHARING SCHEME USPC... 327/333: 326/41, 47 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
USOO8462O86B2 (12) United States Patent Takasugi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,086 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) VOLTAGE COMPENSATION TYPE PIXEL CIRCUIT OF ACTIVE MATRIX ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
US 2011 0016428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0016428A1 Lupton, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NESTED SCROLLING SYSTEM Publication Classification O O
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 7700
 USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
USOO6141279A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Hur et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2000 54 REFRESH CONTROL CIRCUIT 56) References Cited 75 Inventors: Young-Do Hur; Ji-Bum Kim, both of U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2008O144051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0144051A1 Voltz et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISPLAY DEVICE OUTPUT ADJUSTMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004
 US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004O1946.13A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0194613 A1 Kusumoto (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 7, 2004 (54) EFFECT SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
US 2003O22O142A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0220142 A1 Siegel (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2003 (54) VIDEO GAME CONTROLLER WITH Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl.
 (19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(19) United States US 20060034.186A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0034186 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) FRAME TRANSMISSION METHOD IN WIRELESS ENVIRONMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
US 20150358554A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358554 A1 Cheong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) PROACTIVELY SELECTINGA Publication Classification
OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al...
 (12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent USOO73 04621B2 (10) Patent No.: OOmori et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) DISPLAY APPARATUS, SOURCE DRIVER 6,366,026 B1 * 4/2002 Saito et al.... 315/1693 AND DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent USOO7609240B2 () Patent No.: US 7.609,240 B2 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2009 (54) LIGHT GENERATING DEVICE, DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 345/82: 345/88:345/89 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl. M M 110 / <E
 (19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(19) United States US 20170082735A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0082735 A1 SLOBODYANYUK et al. (43) Pub. Date: ar. 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
US0093.7941 OB2 (12) United States Patent Thompson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,379.410 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) PREVENTING INTERNAL SHORT
OV µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor
 OmniVision OV5642 1.4 µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor Circuit Analysis of the Pixel Array, Row Control, Column Readout, Analog Front End, and Pipelined A/D Converter
OmniVision OV5642 1.4 µm Pixel Size Back Side Illuminated (BSI) 5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor Circuit Analysis of the Pixel Array, Row Control, Column Readout, Analog Front End, and Pipelined A/D Converter
