User s Manual of ET-TFT240320TP-2.8: GRAPHIC-LCD COLOR+TOUCH SCREEN ET- TFT240320TP-2.8. Header 1x20. LCD+Touch DIP SW1. TSC SEL DIP SW2.
|
|
|
- Angel Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
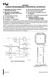
1 ET- TFT240320TP Specifications of Board ET-TFT240320TP Use Display Module TFT LCD Color + Touch Screen 240x320 Pixel - Be 2.8 wide TFT screen - Use Single Chip Driver No.HX8347-D - Has high resolution of colors(rgb=r:5bit,g:6bit,b:5bit) - Has 2 modes of Interface GLCD through DIP SW2.(MODE) 1) Parallel Mode 16-bit Interface 2) Parallel Mode 8-bit Interface Has 2 Interface Modes for controlling Touch Screen by using DIP SW1.TSC SEL. Firstly, it is SPI Interface that is interfaced through Chip Touch Screen Controller #ADS7846 (12BIT ADC). Secondly, it directly interfaces through Pin X-,X+,Y-,Y+ with Pin ADC of MCU (however, it is difficult to write program for controlling). When using this board but user does not require using Touch Screen, user can control in the particular part of LCD only. Can summarize amount of I/O of MCU for controlling the part of GLCD and Touch Screen as follows; 1) When using Parallel Mode 16-Bit Interface, it uses 27-PIN I/O. 2) When using Parallel Mode 8-Bit Interface, it uses 19-PIN I/O. - Can interface with MCU that uses either 5V or 3.3V (read more information in the part of How to use ) - Use Pin Header 2x20, 2.54mm Pitch to be Connector for using Parallel Mode 8Bit and 16Bit. - Use +5VDC Power Supply for board 2. Feature and Structure of Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 Header 1x20 LCD+Touch DIP SW1. TSC SEL DIP SW2. MODE Header 2x20 Figure 2.1 (A) Front board Figure 2.1 (B) Back board -1-
2 +5V 2 RS-H 3 LCD CS-H 6 WR/SCL-H BL-H 7 DB1-H RD-H 10 DB3-H DB5-H DB6-H DB7-H DB0-H RES-H DB2-H DB8-H DB9-H DB13-H DB15-H DB12-H DB14-H Y- Y+ X- X+ TOUCH-CS TOUCH-SCLK TOUCH-MOSI TOUCH-MISO TPUCH-PEN VTSC +3V3 VBAT VREF VTSC AUX +3V3 GND LCD CS-H RES-H BL-H Y- X- X+ Y+ TOUCH-SCLK TOUCH-CS TOUCH-BUSY TOUCH-PEN - LCD+Touch: It is area of LCD with 240x320 Pixel. The top of Screen is shielded by plate of Resistance Touch Screen. - Header 1x20: It is Connector 1x20 Pin MALE to interface with Pin Control LCD and Pin that is used to control IC Touch Screen is interfaced to other side. These pins are interfaced in parallel with pins on the side of Header 2x V 2 34 Figure2.2 pin position at Header 1X20 (referred to front board in the figure 2.1 (A)). - Header 2x20: It is Connector 2x20 Pin MALE to interface signal in the format of Parallel-Mode (8-Bit and 16-Bit) from MCU to control the operation of LCD and Touch Screen. Function of each pin is shown in the table 2.1, and GND DB4-H DB11-H DB10-H TOUCH-BUSY +5V 5 6 WR/SCL-H Figure 2.3 pin position at Header 2x20 (Parallel-Mode: 8Bit, 16Bit) (referred to front board in the figure 2.1 (A)). -2-
3 No.PIN Table 2.1: Details of PIN for controlling GLCD -3- Header2x2 Header1 PIN- 0 x20 NAME (Parallel (SPI I/O Mode) Mode) 1 4 GND Power LCD V Power LCD 3 8 LCD CS-H 4 - RS-H I 5 7 WR-H I I Pin Ground Pin +5V for board Description FFH). Pin Write Strobe: It is used to write Data when it has already received Signal Low in Parallel Mode. 6 8 RD-H I Pin Read Strobe: It is used to read Data when it has already received Signal Low. 7 9 RES-H I Pin RESET: It is used to initial LCD Module when it has already received Signal Low BL-H I Pin Black Light: The Black Light of LCD is lit up when this pin has already received Signal High Pin Chip-Select: It is used to Enable LCD Display (it can be used with both SPI Mode and Parallel Mode). Low = LCD Module Enable High = LCD Module Disable Pin Register-Select: Low = It accesses Index(IR) or Status(SR) Register. High = It accesses Control Register(Address 00H- DB0- DB15 I/O Pin Data Bus Bi-Directional 16 Bit: It is used to pass/send data or point to the Address position of Register; it is used for Parallel Mode. Table 2.2: Details of Pins for controlling Touch Screen No. PIN Header2x2 0 (Parallel Mode) Header1 x20 (SPI Mode) PIN-NAME I/O 25*-28 * 11*-14* Y-,X-,Y+,X TOUCH- SCLK TOUCH-CS I * 18* TOUCH- MOSI TOUCH- BUSY TOUCH- MISO Description Pin Y-,X-,Y+,X+: These pins are used to read position I of Touch Screen directly, not through Chip ADS7846. It has to shift all DIP SW1.TSC SCL to the position OFF. I It is Pin DCLK of ADS7846 for Synchronizes Serial Data I/O. It is Pin CS of ADS7846. When it has received Signal Low, it Enables Serial I/O Register of Chip to start running. It is Pin DIN of ADS7846. When Pin CS is Low, data is I latched at the Rising Edge Pin of Signal DCLK. It is Pin BUSY of ADS7846. It is High Impedance when O Pin CS is High. It is Pin DOUT of ADS7846. When Pin CS is Low, data is O shifted at the Falling Edge Pin of DCLK and this Output is High Impedance when CS is High.
4 No. PIN Header2x2 0 (Parallel Mode) Header1 x20 (SPI Mode) ,36,37 1,2,3-4- PIN- NAME TOUCH- PEN VTSC, +5V, +3V3 Table 2.2 (Continued) I/O O Power Touch Description It is Pin PENIRQ of ADS7846. When Touch Screen is touched, it gives Signal Logic Low (it has already set Pull-Up R10K on Board). These 3 pins are used to choose Power Supply for ADS7846. If it is used with MCU 5V, it has to jump Pin VTSC with Pin +5V; on the other hand, if it is used with MCU 3.3V, it has to jump Pin VTSC with Pin +3V3 (37). Screen 38* - VBAT I It is Pin Vbat of ADS7846 but it is unused in the part of Touch Screen. 39* - VREF I/O It is Pin Vref of ADS7846 but it is unused in the part of Touch Screen. 40* - AUX I (*)= Unused pin, referred to the examples of ETT It is Pin AUX input to ADC of ADS7846 but it is unused in this part. - DIP SW1.TSC SEL on the back of board: There are 4 DIP SW. If using Touch Screen in the format of SPI Interface through Chip Touch Screen Controller #ADS7846, it has to shift all 4 DIP SW. to the position ON (Default Value). Referred to the example program, it writes the program to support the communication of this operation mode as well. If using Interface Mode that interfaces Pin X-,X+,Y-,Y+ to with Pin ADC of MCU directly (ADS7846 is unused), it has to shift all 4 DIP SW. to position Default (OFF). - DIP SW2.MODE on the back of Board: There are 4 DIP SW. In this case, it uses only one switch that is S1. This DIP SW2 is used to choose the Interface Modes between Board GLCD and MCU that is interfaced for controlling the operation. In this case, it should choose the operation modes as shown in the Table 2.3 Table 2.3: How to choose Mode Interface LCD by DIP SW.2 DIP SW.2 MODE Format of setting SW2. MODE Interface S1 S2 S3 S4 OFF X X X Parallel 8-bit Mode ON X X X Parallel 16-bit Mode X= whatever value SW2. MODE ON= 0 ON CTS SW2. MODE ON= 0 ON CTS OFF= 1 OFF= 1
5 3. How to interface Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU Now, we would like to describe about the method to interface Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 that supports the example program of ETT; in this case, it uses MCU AVR MEGA128, PIC18F8722 (for MCU 5V) and uses MCU ARM7 LPC2138 (for MCU 3.3V). Moreover, user can modify the circuit of interfacing MCU below to use with other MCU numbers or other series. Be careful with Pin VTSC, it has to jump Pin VTSC with Pin +5V or +3V3 correctly according to the actual connection, otherwise it makes MCU damaged. For example, if MCU runs by +5V, it has to jump Pin VTSC with Pin +5V correctly. There are 2 Interface Modes; 8-Bit Parallel Interface Mode and 16- bit Parallel Interface Mode; in this case, user can shift DIP-SW2 on the back of board to choose Interfaces Mode. We can summarize example of interfacing circuits as follows; 3.1) 8-bit Parallel Interface MODE How to set Interface Mode SW2. MODE ON= 0 ON CTS OFF= 1 Interface Mode : Parallel 8 bit data (Use PIN I/O = 19 PIN) This 8-bit Parallel Interface Mode uses Pin Data to only sendreceive 8bit Data that is DB8-DB15. However, the part of PIN Interface LCD that is DB0-DB7 is unused; it should be interfaced with Ground as shown in the dotted line in the picture below (if it is floated, problem maybe happen). How to interface with MCU 3.3V Referred to this circuit, it interfaces Pin P0.2, P0.3, P0.11, and P0.14 of MCU with R Pull-Up because this Pin Port is Open Drain. If using MCU that has not any Pin Open Drain, it is unnecessary to interface with R Pull-Up. -5-
6 VCC+5V +3V3 J1 (Header 2x20) Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X Vbat 40 Vref AUX ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V LCD CS-H RS-H WR-H RD-H RES-H BL-H DB0-H DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 SCLK 29 TC CS 30 MOSI 31 BUSY 32 MISO 33 PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V V3 10Kx2 Jump For MCU 3.3V P1.18 P1.19 P1.20 P1.21 P1.22 P1.23 P0.8 P0.9 P0.10 P0.11 P0.12 P0.13 P0.14 P0.15 P0.16 P0.17 P0.18 P0.19 P0.20 P0.21 P0.22 P0.23 P0.4 P0.7 P0.3 P0.5 P0.2 P0.6 MCU ARM7 LPC2138 ARM7 LPC 2138 Vref VDDA VDD1 VDD2 VDD3 RESET XTAL1 XTAL2 VSSA VSS1 VSS2 VSS3 VSS4 VSS MHz 22K 0.1uF 22pF 22pF Figure 3.1A example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU ARM7 #LPC2138(3.3V) How to interface with MCU 5V VCC+5V VCC+5V J1 (Header 2x20) ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X Vbat 40 Vref AUX Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V RD-H 6 RES-H 7 BL-H 8 DB0-H 9 DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H LCD CS-H RS-H WR/SCL-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 Touch-SCLK 29 Touch-TC CS 30 Touch-MOSI 31 Touch-BUSY 32 Touch-MISO 33 Touch-PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V Jump For MCU 5V PE2 PE3 PE4 PE5 PE6 PE7 PA0 PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 PA6 PA7 PF0 PF1 PF2 PF3 PF4 PF5 PF6 PF7 PD4 PD7 PD3 PD5 PD2 PD6 GND VCC MCU AVR MEGA 128 AVR Mega128 10K PEN RESET XTAL1 XTAL2 10K 22pF 16MHz 22pF Figure 3.1B example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU AVR #Mega128 (5V). -6-
7 VCC+5V Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X+ J1 (Header 20x2) Vbat 40 Vref AUX ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V RD-H 6 RES-H 7 BL-H 8 DB0-H 9 DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H LCD CS-H RS-H WR-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 SCLK 29 TC CS 30 MOSI 31 BUSY 32 MISO 33 PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V Jump For MCU 5V RC0 RC1 RC2 RC3 RC4 RC5 RD0 RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RE0 RE1 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RJ2 RJ5 RJ1 RJ3 RJ0 RJ4 MCU PIC18F8722 PIC18F8722 VDD 12 AVDD 25 VDD 32 VDD 48 VDD 71 RG5/MCLR OSC1/CLKI/RA7 OSC2/CLKO/RA6 VSS AVSS VSS VSS VSS VCC+5V 10K 10MHz 22pF 22pF Figure 3.1C example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU PIC #18F8722 (5V). 3.2) 16-bit Parallel Interface MODE How to Set Interface Mode SW2. MODE ON= 0 ON CTS OFF= 1 Interface Mode : Parallel 16 bit data (Use PIN I/O = 27 PIN) How to interface with MCU 3.3V Referred to this circuit, it interfaces Pin P0.2, P0.3, P0.11, and P0.14 of MCU with R Pull-Up because this Pin Port is Open Drain. If this MCU that is used has not any Pi Open Drain, it is unnecessary to interface R Pull-Up. -7-
8 VCC+5V +3V Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X+ J1 (Header 2x20) Vbat 40 Vref AUX ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V LCD CS-H RS-H WR-H RD-H RES-H BL-H DB0-H DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 SCLK 29 TC CS 30 MOSI 31 BUSY 32 MISO 33 PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V V3 10Kx2 10Kx2 Jump For MCU 3.3V P1.18 P1.19 P1.20 P1.21 P1.22 P1.23 P0.8 P0.9 P0.10 P0.11 P0.12 P0.13 P0.14 P0.15 P0.16 P0.17 P0.18 P0.19 P0.20 P0.21 P0.22 P0.23 P0.4 P0.7 P0.3 P0.5 P0.2 P0.6 MCU ARM7 LPC2138 ARM7 LPC 2138 Vref VDDA VDD1 VDD2 VDD3 RESET XTAL1 XTAL2 VSSA VSS1 VSS2 VSS3 VSS4 VSS MHz 22K 0.1uF 22pF 22pF Figure 3.2A example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU ARM7 #LPC2138(3.3V) How to interface with MCU 5V VCC+5V VCC+5V J1 (Header 2x20) Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X+ ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD Vbat 40 Vref AUX PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V RD-H 6 RES-H 7 BL-H 8 DB0-H 9 DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H LCD CS-H RS-H WR/SCL-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 Touch-SCLK 29 Touch-TC CS 30 Touch-MOSI 31 Touch-BUSY 32 Touch-MISO 33 Touch-PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V Jump For MCU 5V PE2 PE3 PE4 PE5 PE6 PE7 PA0 PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 PA6 PA7 PF0 PF1 PF2 PF3 PF4 PF5 PF6 PF7 PD4 PD7 PD3 PD5 PD2 PD6 GND VCC MCU AVR MEGA 128 AVR Mega128 10K PEN RESET XTAL1 XTAL2 10K 22pF 16MHz 22pF Figure 3.2B example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU AVR #Mega128 (5V). -8-
9 VCC+5V Y- 27 X+ 28 Y+ X+ J1 (Header 20x2) Vbat 40 Vref AUX ET-TFT240320TP-3.2 Rev.B Pin Interface Touch-Screen Pin Interface LCD PARALLEL MODE GND 1 +5V RD-H 6 RES-H 7 BL-H 8 DB0-H 9 DB1-H 10 DB2-H 11 DB3-H 12 DB4-H 13 DB5-H 14 DB6-H 15 DB7-H 16 DB8-H LCD CS-H RS-H WR-H DB9-H DB10-H 19 DB11-H 20 DB12-H 21 DB13-H 22 DB14-H 23 DB15-H 24 SCLK 29 TC CS 30 MOSI 31 BUSY 32 MISO 33 PEN 34 VTSC +5V +3V Jump For MCU 5V RC0 RC1 RC2 RC3 RC4 RC5 RD0 RD1 RD2 RD3 RD4 RD5 RD6 RD7 RE0 RE1 RE2 RE3 RE4 RE5 RE6 RE7 RJ2 RJ5 RJ1 RJ3 RJ0 RJ4 MCU PIC18F8722 PIC18F8722 VDD 12 AVDD 25 VDD 32 VDD 48 VDD 71 RG5/MCLR OSC1/CLKI/RA7 OSC2/CLKO/RA6 VSS AVSS VSS VSS VSS VCC+5V 10K 10MHz 22pF 22pF Figure 3.2C example of connecting Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8 with MCU PIC #18F8722 (5V) 4. Basic Principles to Communicate with LCD and Touch Screen When user writes program to communicate with Board ET-TFT240320TP- 2.8, it is easier if user divides the operation into 2 parts that are LCD Display and Touch Screen. Firstly, there are 2 Interface Modes in the part of LCD Display; Parallel 8-bit and Parallel 16-bit. Secondly, it uses SPI Interface in the part of Touch Screen. Next, we will describe the basic principle of writing program to control the operation; in this case, we will refer to the example program of ETT that has been provided with CD-ROM. Each example program in CD-ROM uses the same basic principles to communicate with board, but it is only different in the part of results that will be shown through the Display. We can summarize the principle of both parts as follows; 4.1) Interface Control LCD: User can read more information about commands for controlling LCD from Data Sheet HX8347-D.pdf in CD-ROM. In this case, we divide the principle of sending command or Data to LCD into 3 formats according to Interface Mode and we will describe about it in the next minor section. First of all, user has to understand that whatever format of Interface Mode always sends 2 sets of Data to LCD. The first set is Register that will be accessed; it is Address Position of Register Index of the 8-Bit Instruction. For example, the Instruction Write Data to GRAM(R22h) has the Address Position of Register Index of the instruction as 0x22 ; so, it has to send out the value of 22H. The second set that will be sent out is 16-bit Data of the instruction. For example, when user has already sent out the Instruction of 0x22h, the -9-
10 second data set that will be sent out is data of color or other values of the instruction. If user requires displaying a white dot on LCD Display, it has to send out the Data as 0xFFFF. When user has understood the basic principles of sending Instructions well; next, we will describe how to arrange data inside LCD, especially how to arrange the incoming Instruction and Data, and including the Timing Diagram of Read-Write Data from MCU to LCD of both Interface Modes as follows; 4.1.1) 8-bit Parallel Interface MODE LCD in this operation mode arranges data in the part of internal Instruction and Data as shown in the figure 4.1.1A and 4.1.1B. In this case, it sends the 8-Bit(1Byte) Instruction or Data per 1 Signal Write (WR) in each time. 1 ST Transfer Input Data D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 8 bit- LCD Register data CB7 CB6 CB5 CB4 CB3 CB2 CB1 CB0 Figure 4.1.1A shows how to arrange bit of the incoming Instruction. Referred to the figure 4.1.1A above, it only sends out 1-Byte Instruction because the Address Register of the Instruction is only 1-Byte and it is set at the position of Byte Low (D7 D0). 1 ST Transfer 2 nd Transfer Input Data D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Data 16 bit- LCD GRAM DATA (RGB Mapping) R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 G5 G4 G3 G2 G1 G0 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Data 18 bit- LCD Figure 4.1.1B shows how to arrange the incoming Data Bit that is 16Bit 65K Colors. Referred to the figure 4.1.1B, it arranges colored Data Bit from Upper Bit to Lower Bit in the format of RGB, according to the example program of ETT. However, user can modify and change the arrangement of colored Data Bit to the format of BGR as required; in this case, it uses the Instruction Memory Access Control (R16H) to set the new arrangement of colored Data Bit. Read more information from Data Sheet of HX8347-D. When user requires sending data to show any dot on the LCD Display, user can to mix colors by self by referring to the arrangement of colored Data Bit in the figure above. In this case, Data D15-D11(5Bit) is red; Data D10-D5(6Bit) is green; and Data D4- D0(5Bit) is blue. When user has sent Data into LCD completely, Data will be automatically arranged in the new format of 18Bit Data as shown in the figure. The contrast of colors is arranged from darker to lighter that is from lower bit to upper bit. For example, if user requires the lightest shade of red, it is Data = 0xF800 ; or if user requires the darkest shade of green, it is Data = 0x0020. If user requires using other colors that are not these 3 main colors, user has to set the Data Bit in the range of each color -10-
11 suitably; and finally, user will get the preferable color. For example, if user requires white, it should set the value as Data=0xFFFF ; or if user requires black, it should set the value as Data=0x0000. Procedures for writing Instruction and Data from MCU to control LCD by 8-Bit Parallel MODE When user requires sending Instruction or Data from MCU to LCD through this operation mode, it always sends Data Bit to Pin DB8- DB15 of Board LCD of ETT according to the circuit above. First of all, it has to send out 1Byte Instruction or Address Register; next, it has to send out 1Byte or 2Byte Data of the instruction, depending on Data of the instruction. In case of sending 2Byte Data, the first byte should be Byte High and the second Byte should be Byte Low. User should determine the following Timing Diagram for reading-writing Instruction or Data into LCD. Figure 4.1.1C shows Timing Diagram for Read-Write Instruction and Data to LCD in the format of 8-bit Parallel Mode. Referred to the Timing diagram above, we only describe the part of Write Data but we do not describe the part of Read Data because the example program does not Read Data from LCD. In this case, it uses Delay instead and it can control the LCD as well. Referred to the Timing Diagram in the part of Write Data, the first Byte that will be sent out is Instruction or Register Address; in this case, it is 22H that is the Instruction Write SRAM. Next, it sends out 1Byte or 2Byte Data of the instruction, depending on amount of Data of each instruction. We can summarize the procedures of writing Instruction and Data as follows; 1) Set Pin RD, CS as 1. 2) Set Pin CS as 0 to enable LCD for receiving data. 3) Send Byte of Instruction or Address Register to Pin DB8-DB15 (referred to the actual pins on board). 4) Set Pin RS as 0 to set value for sending out; in this case, it is Instruction. 5) Set Pin PWR as 0 to start writing the first Byte Instruction. -11-
12 6) Set Pin WR as 1 ; the first Byte Instruction has been sent completely. 7) Set Pin RS as 1 to finish writing the Instruction and it sets the next value for sending out that is Data. After sent the Instruction completely, it has to send out the data of the Instruction as follows; 8) Still set Pin CS as 0 and Pin RS and RD as 1 to send Data. 9) Send out Data Byte High to Pin DB8-DB15 (in case of sending 2Byte Data). 10)Set Pin WR as 0 to start Write Data Byte High. 11)Set Pin WR as 1 ; the Data Byte has been sent completely. 12)Send out Data Byte Low to Pin DB8-DB15. 13)Set Pin WR as 0 to start Write Data Byte Low. 14)Set Pin WR as 1 ; the Data Byte Low has been sent completely. 15)Set Pin CS as 1 to finish sending the Instruction and Data. If user requires sending the next Instruction, please repeat the first procedure bit Parallel Interface MODE This operation mode sets new arrangement of LCD, especially in the part of Instruction and Data as same as the operation Mode above. It is only different in the part of sending Instruction or Data because it sends 16Bit Instruction or Data (2Byte) per 1 Signal Write (WR) in each time according to Timing Diagram in the figure 4.1.2C. 1 ST Transfer Input Data D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 16 bit- LCD Register data CB15 CB14 CB13 CB12 CB11 CB10 CB9 CB8 CB7 CB6 CB5 CB4 CB3 CB2 CB1 CB0 Figure 4.1.2A shows bit arrangement of the incoming Instruction. 1 ST Transfer Input Data D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Data 16 bit- LCD GRAM DATA (RGB Mapping) R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 G5 G4 G3 G2 G1 G0 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Data 18 bit- LCD Figure 4.1.2A shows arrangement of 16Bit 65K Colored Data Bit that has been received. Referred to the figure 4.1.2B, it arranges the colored Data Bit from upper bit to lower bit as RGB according to the examples of ETT. However, user can modify and change the arrangement of colored Data Bit as BGR as required; in this case, it uses the Instruction Memory Access Control (R16H) to set the new arrangement of colored Data Bit. Read more information in Data Sheet of SPFD5408A. When user requires sending data to show any dot on the LCD Display, user can to mix colors by self by referring to the arrangement of colored Data Bit in the figure above. In this case, -12-
13 Data D15-D11(5Bit) is red; Data D10-D5(6Bit) is green; and Data D4- D0(5Bit) is blue. When user has sent Data into LCD completely, Data will be automatically arranged in the new format of 18Bit Data as shown in the figure. The contrast of colors is arranged from darker to lighter that is from lower bit to upper bit. For example, if user requires the lightest shade of red, it is Data = 0xF800 ; or if user requires the darkest shade of green, it is Data = 0x0020. If user requires using other colors that are not these 3 main colors, user has to set the Data Bit in the range of each color suitably; and finally, user will get the preferable color. For example, if user requires white, it should set the value as Data=0xFFFF ; or if user requires black, it should set the value as Data=0x0000. Procedures for writing Instruction and Data from MCU to control LCD by 16-Bit Parallel MODE When user requires sending Instruction or Data from MCU to LCD through this operation mode, it always sends Data Bit to Pin DB0- DB15 of Board LCD of ETT according to the circuit above. It sends out 2Byte Data per sending 1 Instruction or Data in each time; in this case, the first 2Byte is Instruction that must be sent out first and then it follows by the second 2Byte that is Data of the instruction. If there is only 1Byte Instruction or Data, in the part of Byte High has to send out 0x00 instead. User should determine the following Timing Diagram for reading-writing Instruction or Data into LCD. Figure 4.1.2C shows Timing Diagram for Read-Write Instruction and Data from MCU to LCD in the format of 16-Bit Parallel Mode, -13-
14 Referred to the Timing diagram above, we only describe the part of Write Data but we do not describe the part of Read Data because the example program does not Read Data from LCD. In this case, it uses Delay instead and it can control the LCD as well. Referred to the Timing Diagram in the part of Write Data, there are 2 sets of data that are sent out to LCD in each time. The first set (2Byte) is the Instruction that is 00H+Address position of Register Index (Register No.); and the second set (2Byte) is 16Bit Data of the instruction. Next, user can send out the instruction according to the Timing Diagram and we can summarize the procedures as follows; 1) Set Pin RD, CS as 1. 2) Set Pin CS as 0 to enable LCD for receiving data. 3) Send 16Bit Instruction Set to Data Bus (DB0-DB15); in this case, Data Bus 8Bit Upper (DB8-DB15) is set as 0x00. 4) Set Pin RS as 0 to set value for sending out; in this case, it is Instruction. 5) Set Pin WR as 0 to start writing the first 2Byte Instruction. 6) Set Pin WR as 1, the first 2Byte Instruction has been sent completely. 7) Set Pin RS as 1 to finish writing the Instruction and it sets the next value for sending out that is Data. After sent the Instruction completely, it has to send out the data of the Instruction as follows; 8) Still set Pin CS as 0 and Pin RS and RD as 1 to send Data. 9) Send out 16Bit Data of the Instruction to all 16Bit Data Bus (DB0- DB15). If it sends out 8Bit Data (1Byte), it has to set 8Bit Data Bus Upper (DB8-DB15) to be 0x00. 10)Set Pin WR as 0 to start writing the latter 2Byte Data. 11)Set Pin WR as 1 ; the latter 2Byte Data has been sent completely 12)Set Pin CS as 1 to finish sending the Instruction and Data. If user requires sending the next Instruction, please repeat the first procedure. Referred to the procedures above, user can repeat the first step if user requires sending other instructions. While writing program, user can writes function to receive Instruction and value of Data into the function simultaneously; and then user can send Instruction and Data according to steps above. Moreover, user can write function according to the examples of ETT; in this case, it separates the function into 2 parts; function for sending Instruction and function for sending Data. 4.2) Interface Control Touch Screen: In the part of this Touch Screen, it separates Control from LCD. There are 2 Interface Modes that can be chosen for this Control. Firstly, it interfaces Pin Y-,Y+,X-,X+ with Pin ADC of MCU directly and user has to write program to control the process of reading values by self. However, it is difficult to write program because user has to learn and understand the operating principles of Touch Screen well and user has to write the program correctly. In this case, we do not suggest user to choose this Interface Mode. -14-
15 The Interface Mode that we will suggest user to choose and use is to interface signal through Chip ADS7846 according to the example of ETT. When user has chosen this Interface Mode, it has to shift all DIP SW(S1- S2) at the back of board to the position ON to interface Pin X+,Y+,X-,Y- of Touch Screen with Chip ADS7846 (normally, it has already been set to be default position). The Interface Mode that uses Chip ADS7846 is SPI Interface between MCU and Chip; user can read more information about communicating data with Chip for reading-writing position of Touch Screen correctly from Data Sheet Touch_ADC7846N.pdf. First of all, we should look at the co-operation between Touch Screen with ADS Co-operation between Touch Screen and ADS7846: It starts to read position of Touch Screen when user touched the Touch Screen, Chip ADS7846 converts the incoming Signal Analog through Pin X+,Y+,X-,Y-; and then it sends out Digital through Pin Serial Data Out. The ADC value that is read is 12Bit Resolution; so, the value that is read on both X- axis and Y-axis is in the range of While touching the Touch Screen, Pin PENNIRQ of Chip sends out Signal Interrupt Logic 0 for a while; user has to read status of this Signal Interrupt while writing program to check whether it is touching the Touch Screen. It saves much time because it does not loop to read the position of Touch Screen all the time, it only reads the value when it is touching the Touch Screen only; so, program can run in other parts independently. Figure shows how to interface circuit in the part of Touch Screen and ADS7846. X-Axis(ADC=0-4096) 4096 Y-Axis (ADC=0-4096) Figure extent Touch Screen and ADC value that has happened on the X,Y axis -15-
16 Referred to the figure above, it shows the direction of X-axis and Y-axis of Touch Screen and the ADC value that is read on positions while touching Touch Screen. Normally, the ADC value that is read through ADS7846 has the minimum value at 600 (not 0); it is the Offset value of the Display. However, the Offset value of each Touch Screen is read unequally; so, user always writes program to calibrate the Touch screen. In this case, user can copy the example of ETT to calibrate the Touch Screen instantly. It uses principle of matrix to calculate the coefficient from calibrating the Touch Screen of user. The example program forces user to touch 3 positions on the Touch Screen; in this case, if user can touch the mark position accurately, it also makes the operation be greater accuracy. - Timing Diagram for Read-Write data through ADS7846: When user understood the basic principles in the part of Touch Screen; next, we will describe how to read ADC Value from Touch Screen by using Chip ADS7846. First of all, user has to understand that ADC Value that is read from the Touch Screen is not the actual Address position; it cannot be used to refer to any position on LCD. User has to calculate this value to find out the actual position of LCD by self. When user has already got the actual Address position of LCD, user can use this value to replace the Instruction for controlling position of LCD Display. User can see and read all procedures from examples of ETT. Figure Conversion Timing Diagram, 16 Clock-per-Conversion, 8bit bus Interface. This Timing Diagram shows process of reading the ADC value from Touch Screen through Chip ADS7846; it uses SPI Interface between MCU and ADS7846 according to the example of ETT. Referred to the SPI Interface in the example, it uses Pin I/O of MCU, it does not use Module SPI internal MCU; so, user can edit or modify program easily. The principle of sending data in format of SPI Interface is to send out 1-bit data to Pin MOSI(Dout) and then follows by 1 Clock, it shifts 1Bit data into the Chip. Meanwhile, the Chip also shifts 1-bit data out to Pin MISO(Din), it is data that user has to read and save. Referred to the example of ETT, function tcs_wr() is used to write and read 1Byte data (8bit) serially. When user has created this function completely, user can send Control Byte and read the ADC value to store through this function. The procedures of reading the ADC value from Touch Screen are listed below. -16-
17 The method to read the ADC value from ADS7846 is to send Control Byte to ADS7846 first; it sets specifications for Chip before reading the value. The format of Control Byte is shown below; Bit7(MSB) Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 S A2 A1 A0 MODE SER/DFR PD1 PD0 Figure shows Control Byte of ADS7846. User can read more details of Control Byte for each Bit from Data Sheet by self. Referred to the Control Byte in the example, it is 0xD0 for reading the ADC value on the X-axis of Touch Screen and 0x90 for reading the ADC value on the Y-axis of Touch Screen. Summarize procedures to read ADC from ADS7846 1) Read Status from Pin PEN of ADS7846. If it is 0 (touching the Touch Screen), user can go to the next step to start the process of reading value; on the other hand, if it is 1 (has not touched the Touch Screen yet), it has to repeat reading. 2) Set Pin DCLK, CS, DOUT as 0 3) Send Control Byte 0xD0 to Pin DIN (MOSI) of ADS7846, it specifies and reads the 12Bit ADC on X-axis. 4) Send Data 0x00 to Pin DIN (MOSI) of ADS7846. Meanwhile, it is sending data in each bit, ADS7846 also shifts the ADC value to Pin DOUT(MISO). The firsts Data Bit that is shifted out is the 11 th Bit and it begins at Falling Edge Pin of the 2 nd DCLK. When all of 8 DCLK has already been sent completely, the data that is read on X-axis is 0x0ddddddd (d=data bit11-bit5). 5) Send Control Byte 0x90 to Pin DIN (MOSI) of ADS7846, it specifies and reads the 12Bit ADC on Y-axis. Meanwhile, it is sending out this Control Byte, the last 5Bit of Data ADC on X-axis will be sent out; in this case, it begins from Bit4 to Bit0. It arranges Data in the format of 0xddddd000 (d=data bit4-bit0). 6) Send Data 0x00 to Pin DIN (MOSI) of ADS7846. Meanwhile, it is sending data in each bit, ADS7846 also shifts thee ADC value to Pin DOUT(MISO). The firsts bit that is shifted out is the 11 th Bit and it begins at the Falling Edge Pin of the 2 nd DCLK. When all of 8 DCLK has been sent completely, the Data that is read on Y-axis is 0x0ddddddd (d=data bit11-bit5). 7) Send Data 0x00 to Pin DIN (MOSI) of ADS7846. Meanwhile, it is sending out this Data, the last 5bit of data ADC on Y-axis will be sent out; in this case, it begins from bit4 to bit0. It arranges data in the format of 0xddddd000 (d=data bit4-bit0). 8) When it has read the ADC value on both axes completely, it has to set Pin CS as 1 to finish reading the value from DAS ) If user requires reading other value, please repeat the step 1. 10) When it has read the ADC value on each axis completely, user has to rearrange the value. It uses 16Bit Variable for storing the ADC value that is read; the first 7Bit Data that is stored in the 16Bit Variable is 0x ddddddd, while the latter 5Bit Data that is stored in the 16Bit Variable is 0x ddddd000. Next, it shifts the Data that is read; in this case, it shifts 5Bit of the first 7Bit to the left side for and it shifts 3Bit of the latter 5Bit data the right side. Next, it has to do OR( ) data of both sets and user will get the 12Bit ADC value of the axis for using; in this case, it is 0x000ddddddddddddd. -17-
18 Referred to all principles of Control LCD and Touch Screen above, it is the general operation of using Board ET-TFT240320TP-2.8. When user understood the basic principles of Control well, user can copy functions in the examples of ETT to paste and use in the program s user instantly. Read more information about how to copy and use the functions from Description of Example Program. 5. How to use Program Embedtools 3.31 to Convert image file into HEX Code Now, we describe how to convert image file into HEX Code that will be send and display on the LCD Display as required; in this case, it uses Program Embedtools The process of converting this HEX Code supports the example from ETT; it uses function plot_picture() (it is in the example Ex3_Touch_Button ) to send the HEX Code from MCU to LCD Display. If user does not do initial lcd according to the example of ETT and does not set Program Embedtools to convert image file as mentioned below, user cannot use function plot_picture() because the direction of sending and receiving data incorrectly. In this case, user has to write program to plot image file by self according to the values that user has already set. Procedures to use Program Embedtools to convert image file into HEX Code 1. Install Program Embedtools.exe into the computer PC (it is in the Folder Embedtools3.31). 2. After user has installed the program successfully, it appears the ICON( ) at the Taskbar as shown in the picture 5.1. Next, click right on the ICON, TAB appears; click left on Image2LCD to run Program Embedtools; and finally, it shows a window as shown in the picture 5.2. Picture 5.1 Picture
19 3. Click ICON OPEN( ) on top of program to choose the preferable photo to convert; in this case, the image file should be the file surname as.jpg or.bmp. When user has opened the preferable photo, it shows window as shown in the picture 5.3. Picture After loaded the photo into the program successfully, it has to set following values (please look at picture 5.4 to be your guideline). Picture 5.4 Actual Pixel of photo (Width, Height) - Output file type: C array (*.C) = It sets data in the format of Array of C Language and then saves File Output as.c. - Scand mode: Horizon Scan = It sets initial direction of scanning data. When using data, it has to send data to LCD according to the direction of scanning data. -19-
20 - Bits Pixel: 16-bit TrueColor = It sets resolution of colored Bit (there are 2 the same values in the program, please choose the upper value). - Max Width and Height: Width, Height = Set width and height for the preferable picture. Click Button( ) after setting the values completely, user can see the change of picture, especially the picture size is in the unit of Pixel. However, it is not the actual picture size. If user calls and uses the function plot_picture() from example of ETT, it requires the actual width and height of the picture; in this case, user can look the actual Pixel of picture in the box Output Image below. - Include head data = Remove the check sign from the box. - TAB 16-bit Color = Click TAB 16-bit color in the box of Color Bit, it should choose the value in the box of R:5bit,G:6bit,B:5bit ; and in the blank of Order of Colors (WORD bit[15~0], it arranges colors in the format of RGB. For other Tabs, user does not set any value. 5. When user has already set all values, click ICON Save ( ) to save file hex code. If user requires using this file, it uses note pad to open this file; next, user can copy the hex code and then paste in the editor for writing program instantly. 6. How to run Example Programs Example Programs of ETT are written by C Language, it can support 3 MCU Series; AVR(Mega128), PIC(18F8722), and ARM7(LPC2138). There are 2 formats of Control LCD that can be found in this example; vertical line and horizontal line. It depends on user to choose the preferable format to display data and then user looks at the corresponding the example program mainly. Examples of each MCU series have the same format; all examples refer to the initial Address position on X,Y axis of the screen as shown in the picture below; X-Address(0-239) X-Address(0-319) Address Start Y-Address (0-319) Y-Address(0-239) DISPLAY 240x320(Hor.) DISPLAY 240x320(Ver.) Address Start Picture 6.1 reference to the initial Address on LCD Display in vertical line and horizontal line. -20-
21 Referred to the pictures above, if using function in the example program of ETT and setting any Address position of X,Y to plot picture or character, user should look at the reference address in the figure above. There are 4 main example programs in both formats of vertical line and horizontal line as described below; - Ex1_Touch_Position: Referred to this example program, when it is run in the first time use, it forces user to touch 3 plus signs (+) accurately to calibrate the Touch Screen. After calibrated, MCU can read Address position correctly according to the actual Address position of LCD every time user touches the Screen as shown in the picture 16. After calibrated, it always shows the position of X,Y that has been touch at the bottom every time user touched any position on LCD Display. - Ex2_Touch_Draw: Referred to this example program, when it is run in the first time use, it forces user to calibrate Touch Screen as same as the first example program. Next, user can draw or write any character on the screen and it will display lines according to writing or drawing. Moreover, user can touch Icon Musical Note( ) to change color of line and user can touch Icon HOME ( ) to Clear Screen. - Ex3_Touch_Button: Referred to this example program, when it is run in the first time use, it forces user to calibrate Touch Screen as same as the first example program; next, it shows buttons. When user has touched any button on the screen, the blank window will show pictures according to the pressing button. Referred to the example in the part of calibrate touch Screen, every time when user has RESET MCU, user has to calibrate the screen as well. However, user can calibrate the screen only one time in case of actual use. The method to edit this function is described below; The 1 st method: It has to interface more E2Prompt with MCU (if the MCU has no any E2PROMPT inside). Next, user should write program in Function touch_calibrate() after the line of calling Function set_matrix() by writing the value in the Variable divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn to store in E2Prompt, and then user should write any more 1Byte Data to store in E2Prompt to be Flag Status. This Flag Status is used to check whether it has been calibrated completely. Next, in the part of main program before calling Function touch_calibrate(), user should read Status Flag from E2Prompt to check whether it is the same value as user has written and stored. If yes, it is unnecessary to call Function touch_calibrate() anymore; user can read the value of the Variable divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn that has been stored in E2Prompt, and replace the value in the Variable divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn; and finally, it can run in other parts of program. This method saves much time because user does not calibrate LCD Display every time using it. The 2 nd method: It does not use E2Prompt for his method. User should add more Instruction printf() into the Function touch_calibrate() after the line of calling Function set_matrix() (referred to the example, it has written this Instruction but it is disabled). It prints the value of Variable divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn to show the result through RS232; in this case, it uses Program Hyper Terminal to receive the value of the -21-
22 Variable that has been printed to display the result for user. Next, user should note down and remember the value of each variable because it will be used to set value for the Variable divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn that has been declared above main(). While using, user can remove this Function touch_calibrate() and does not call it any more. In case of using this method with many LCD Displays, user has to write program to find out the value of divider,an,bn,cn,dn,en,fn to calibrate the display separately; because user has to find out the new value to calibrate the LCD Display every time user changes the new LCD Display although using the same LCD Display type. Remember, user cannot use the value of the old LCD Display to read the new LCD Display because the address position that is read does not accord with the actual address position of the new LCD Display. NOTE: While calibrating, user has to touch the nearest marked position because it makes the operation more accurate. - Ex4_Font_TH_EN: Referred to this example program, when it is run in the first time use, it forces user to calibrate Touch Screen as same as the first example program; next, it shows text in both Thai and English. Then, it shows Button Test Position and Button Example TH ; when user has touched any button on the screen, the blank box at the bottom will show text in both Thai and English. It uses Function printstr_te(char *str,int cur_x,int cur_y,unsigned int fg_color,unsigned int bg_color) to plot Font in both Thai and English. In this case, *str X Y = Text in both Thai and English. = Position of pixel on X-axis that user requires displaying the character on the LCD Display. = Position of pixel on Y-axis that user requires displaying the character on the LCD Display. fg_color = Color of character or color of Pixel that is plotted to be character. bg_color = Color of background of character or color of pixel in the part that is not plotted (0x0001 = colorless) + :7dot :9dot :4dot Y X X,Y=(0,15) Back ground Picture 6.2 shows how to place position of the character that is plotted on LCD Display. -22-
23 Referred to the picture 6.2 above, the position of X, Y that has been replaced in the function is the initial position to display the preferable character on the Display. In this case, it refers to the bottom on the left corner of the character mainly; and the upper-lower vowel and a tone mark in Thai writing are added automatically. It uses the general principle to type Thai character into the function above to display result on the Display. For example, = -, -, = = = - - -, = In the part of ASCII CODE that is used to refer to Thai and English characters in the example program, user can refer to the Table of ASCI CODE below. -23-
24 -24- Dec Hex Char Dec Hex Char Dec Hex Char Dec Hex Char Dec Hex Char Dec Hex Char A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F A 1B C 1D 1E 1F A 2B! # $ % & ( ) + * C 2D 2E 2F A 3B 3C 3D E 3F A 4B 4C 4D E 4F , / > = < ; : C B F E D I H G L K J O N M R Q P U T S W V A 5B 5C 5D 5E 5F A 6B 6C 6D 6E 6F A 7B 7C 7D 7E 7F Y X \ [ Z _ ^ ] b a e d c h g f j i k n m l q p o s r t w v u z y x { } ~ A 8B 8C 8D 8E 8F A 9B 9C 9D 9E 9F A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 AA AB AC AD AE AF B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9 BA BB BC BD BE BF C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 CA CB CC CD CE CF D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 DA DB DC DD DE DF E0 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 E7 E8 E9 EA EB EC ED EE EF F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 FA FB FC FD FE FF * : Table Font ASCII Code. O O...,,,,,, _ -
25 2.8 Picture 6.3 shows the size of Board ET-TFT240320TP
26 Picture 6.4 shows Circuit of ET-TFT240320TP
ET-REMOTE DISTANCE. Manual of ET-REMOTE DISTANCE
 ET-REMOTE DISTANCE ET-REMOTE DISTANCE is Distance Measurement Module by Ultrasonic Waves; it consists of 2 important parts. Firstly, it is the part of Board Ultrasonic (HC-SR04) that includes sender and
ET-REMOTE DISTANCE ET-REMOTE DISTANCE is Distance Measurement Module by Ultrasonic Waves; it consists of 2 important parts. Firstly, it is the part of Board Ultrasonic (HC-SR04) that includes sender and
APPLICATION NOTE VACUUM FLUORESCENT DISPLAY MODULE
 AN-E-3237A APPLICATION NOTE VACUUM FLUORESCENT DISPLAY MODULE GRAPIC DISPLAY MODULE GP92A1A GENERAL DESCRIPTION FUTABA GP92A1A is a graphic display module using a FUTABA 128 64 VFD. Consisting of a VFD,
AN-E-3237A APPLICATION NOTE VACUUM FLUORESCENT DISPLAY MODULE GRAPIC DISPLAY MODULE GP92A1A GENERAL DESCRIPTION FUTABA GP92A1A is a graphic display module using a FUTABA 128 64 VFD. Consisting of a VFD,
Alice EduPad Board. User s Guide Version /11/2017
 Alice EduPad Board User s Guide Version 1.02 08/11/2017 1 Table OF Contents Chapter 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Welcome... 3 1.2 Launchpad features... 4 1.3 Alice EduPad hardware features... 4 Chapter 2. Software
Alice EduPad Board User s Guide Version 1.02 08/11/2017 1 Table OF Contents Chapter 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Welcome... 3 1.2 Launchpad features... 4 1.3 Alice EduPad hardware features... 4 Chapter 2. Software
LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION
 TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0220IT-1 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE DESCRIPTION FROM TO A 2008.03.10 First Release.
TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0220IT-1 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE DESCRIPTION FROM TO A 2008.03.10 First Release.
4.3inch 480x272 Touch LCD (B) User Manual
 4.3inch 480x272 Touch LCD (B) User Manual Chinese website: www.waveshare.net English Website: www.wvshare.com Data download: www.waveshare.net/wiki Shenzhen Waveshare Electronics Ltd. Co. 1 目录 1. Overview...
4.3inch 480x272 Touch LCD (B) User Manual Chinese website: www.waveshare.net English Website: www.wvshare.com Data download: www.waveshare.net/wiki Shenzhen Waveshare Electronics Ltd. Co. 1 目录 1. Overview...
TV Character Generator
 TV Character Generator TV CHARACTER GENERATOR There are many ways to show the results of a microcontroller process in a visual manner, ranging from very simple and cheap, such as lighting an LED, to much
TV Character Generator TV CHARACTER GENERATOR There are many ways to show the results of a microcontroller process in a visual manner, ranging from very simple and cheap, such as lighting an LED, to much
AMP DISPLAY INC. SPECIFICATIONS AMP DISPLAY INC 9856 SIXTH STREET RANCHO CUCAMONGA CA TEL: FAX:
 AMP DISPLA INC. SPECIFICATIONS CUSTOMER CUSTOMER PART NO. AMP PART NO. APPROVED B DATE Approved For Specifications Approved For Specifications & Sample AMP DISPLA INC 9856 SITH STREET RANCHO CUCAMONGA
AMP DISPLA INC. SPECIFICATIONS CUSTOMER CUSTOMER PART NO. AMP PART NO. APPROVED B DATE Approved For Specifications Approved For Specifications & Sample AMP DISPLA INC 9856 SITH STREET RANCHO CUCAMONGA
S6B CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
64 CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June. 2000. Ver. 0.0 Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The (TQFP type: S6B2108) is a LCD driver LSI with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the
SPI Serial Communication and Nokia 5110 LCD Screen
 8 SPI Serial Communication and Nokia 5110 LCD Screen 8.1 Objectives: Many devices use Serial Communication to communicate with each other. The advantage of serial communication is that it uses relatively
8 SPI Serial Communication and Nokia 5110 LCD Screen 8.1 Objectives: Many devices use Serial Communication to communicate with each other. The advantage of serial communication is that it uses relatively
Modbus Register Tables for SITRANS RD300 & WI100
 AG021414 Modbus Register Tables for SITRANS RD300 & WI100 WARNING: As is typical with most instruments, the addition of serial communications carries an inherent risk; it allows a remote operator to change
AG021414 Modbus Register Tables for SITRANS RD300 & WI100 WARNING: As is typical with most instruments, the addition of serial communications carries an inherent risk; it allows a remote operator to change
ZR x1032 Digital Image Sensor
 Description Features The PixelCam is a high-performance CMOS image sensor for digital still and video camera products. With its Distributed-Pixel Amplifier design the pixel response is independent of its
Description Features The PixelCam is a high-performance CMOS image sensor for digital still and video camera products. With its Distributed-Pixel Amplifier design the pixel response is independent of its
2.13inch e-paper HAT (D) User Manual
 2.13inch e-paper HAT (D) User Manual OVERVIRE This is a flexible E-Ink display HAT for Raspberry Pi, 2.13inch, 212x104 resolution, with embedded controller, communicating via SPI interface, supports partial
2.13inch e-paper HAT (D) User Manual OVERVIRE This is a flexible E-Ink display HAT for Raspberry Pi, 2.13inch, 212x104 resolution, with embedded controller, communicating via SPI interface, supports partial
Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/ SSD1331. Advance Information
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ SSD1331 Advance Information 96RGB x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ SSD1331 Advance Information 96RGB x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common
Alice EduPad for Tiva or MSP432 TI ARM Launchpad. User s Guide Version /23/2017
 Alice EduPad for Tiva or MSP432 TI ARM Launchpad User s Guide Version 1.02 08/23/2017 1 Table OF Contents Chapter 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Welcome... 3 1.2 Tiva Launchpad features... 4 1.3 Alice EduPad hardware
Alice EduPad for Tiva or MSP432 TI ARM Launchpad User s Guide Version 1.02 08/23/2017 1 Table OF Contents Chapter 1. Overview... 3 1.1 Welcome... 3 1.2 Tiva Launchpad features... 4 1.3 Alice EduPad hardware
Vorne Industries. 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual Industrial Drive Itasca, IL (630) Telefax (630)
 Vorne Industries 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60143-1849 (630) 875-3600 Telefax (630) 875-3609 . 3 Chapter 1 Introduction... 1.1 Accessing Wiring Connections
Vorne Industries 87/719 Analog Input Module User's Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60143-1849 (630) 875-3600 Telefax (630) 875-3609 . 3 Chapter 1 Introduction... 1.1 Accessing Wiring Connections
DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY 1:
 PAGE 2 OF 22 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY 1: DOCUMENT REVISION FROM TO DATE DESCRIPTION CHANGED BY A 2007.10.30 First Release. PHILIP CHENG CHECKED BY PHILIP HO PAGE 3 OF 22 CONTENTS Page No. 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PAGE 2 OF 22 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY 1: DOCUMENT REVISION FROM TO DATE DESCRIPTION CHANGED BY A 2007.10.30 First Release. PHILIP CHENG CHECKED BY PHILIP HO PAGE 3 OF 22 CONTENTS Page No. 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
HD66840/HD LVIC/LVIC-II (LCD Video Interface Controller) Description. Features
 HD6684/HD6684 LVIC/LVIC-II (LCD Video Interface Controller) Description The HD6684/HD6684 LCD video interface controller (LVIC/LVIC-II) converts standard RGB video signals for CRT display into LCD data.
HD6684/HD6684 LVIC/LVIC-II (LCD Video Interface Controller) Description The HD6684/HD6684 LCD video interface controller (LVIC/LVIC-II) converts standard RGB video signals for CRT display into LCD data.
USER MANUAL Nokia 5110 LCD
 USER MANUAL Nokia 5110 LCD Introduction: This 84x48 pixel black and white LCDs are what you might have found in an old Nokia 3310 or 5110 cell phone. They re not flashy, not colorful and there s no touch
USER MANUAL Nokia 5110 LCD Introduction: This 84x48 pixel black and white LCDs are what you might have found in an old Nokia 3310 or 5110 cell phone. They re not flashy, not colorful and there s no touch
HD66766 Rev. 1.0 / 30 November 2001 HD (132 x 176-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors)
 HD66766 Rev.. / 3 November 2 HD66766 (32 x 76-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors) Rev.. November, 2 Description The HD66766, color-graphics LCD controller and driver LSI, displays 32-by-76-dot
HD66766 Rev.. / 3 November 2 HD66766 (32 x 76-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver for 65K Colors) Rev.. November, 2 Description The HD66766, color-graphics LCD controller and driver LSI, displays 32-by-76-dot
Logic Analyzer Auto Run / Stop Channels / trigger / Measuring Tools Axis control panel Status Display
 Logic Analyzer The graphical user interface of the Logic Analyzer fits well into the overall design of the Red Pitaya applications providing the same operating concept. The Logic Analyzer user interface
Logic Analyzer The graphical user interface of the Logic Analyzer fits well into the overall design of the Red Pitaya applications providing the same operating concept. The Logic Analyzer user interface
AIS CUBE 2.83 AMOLED DISPLAY. Datasheet & Application Note Preliminary Release
 AIS CUBE 2.83 AMOLED DISPLAY Datasheet & Application Note Preliminary Release TECHNICAL OVERVIEW Diagonal Size 2.83 Driving Mode Active Matrix Colour Mode 16bit RGB 5/6/5262K Colours Interface Mode 16bit
AIS CUBE 2.83 AMOLED DISPLAY Datasheet & Application Note Preliminary Release TECHNICAL OVERVIEW Diagonal Size 2.83 Driving Mode Active Matrix Colour Mode 16bit RGB 5/6/5262K Colours Interface Mode 16bit
SSD1305. Advance Information. 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1305 Advance Information 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1305 Advance Information 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Simple implementation featuring the ATmega88PA from Atmel Complete software solution
 DKAN0003A Controlling the SmartDisplay with a SPI Peripheral 09 June 009 Features IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Simple implementation featuring the ATmega88PA from Atmel Complete software
DKAN0003A Controlling the SmartDisplay with a SPI Peripheral 09 June 009 Features IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Simple implementation featuring the ATmega88PA from Atmel Complete software
Rfid Based Attendance System
 Rfid Based Attendance System Raj Kumar Mistri 1, Kamlesh Kishore 2, Priyanka Nidhi 3, Pushpakumari 4, Vikrantkumar 5 1, 2 Assistant Professor, 3,4,5 B.Tech Scholar 1,2,3,4,5 Dept. of ECE, RTC Institute
Rfid Based Attendance System Raj Kumar Mistri 1, Kamlesh Kishore 2, Priyanka Nidhi 3, Pushpakumari 4, Vikrantkumar 5 1, 2 Assistant Professor, 3,4,5 B.Tech Scholar 1,2,3,4,5 Dept. of ECE, RTC Institute
V6118 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA 2, 4 and 8 Mutiplex LCD Driver Description The is a universal low multiplex LCD driver. The version 2 drives two ways multiplex (two blackplanes) LCD, the version 4, four
7inch Resistive Touch LCD User Manual
 7inch Resistive Touch LCD User Manual Chinese website: www.waveshare.net English website: www.wvshare.com Data download: www.waveshare.net/wiki Shenzhen Waveshare Electronics Ltd. Co. 1 Contents 1. Overview...
7inch Resistive Touch LCD User Manual Chinese website: www.waveshare.net English website: www.wvshare.com Data download: www.waveshare.net/wiki Shenzhen Waveshare Electronics Ltd. Co. 1 Contents 1. Overview...
SignalTap Plus System Analyzer
 SignalTap Plus System Analyzer June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Simultaneous internal programmable logic device (PLD) and external (board-level) logic analysis 32-channel external logic analyzer 166
SignalTap Plus System Analyzer June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Simultaneous internal programmable logic device (PLD) and external (board-level) logic analysis 32-channel external logic analyzer 166
USER'S MANUAL. Getting started with ALEXAN ATMEL AT89C2051/AT89C4051 Training Module - 1
 USER'S MANUAL Getting started with ALEXAN ATMEL AT89C05/AT89C405 Training Module - Version.0 Copyright 006 Ace Electronic Technology Inc. All Rights Reserved Alexan 05/405 TM- v..0 Page of 7 About This
USER'S MANUAL Getting started with ALEXAN ATMEL AT89C05/AT89C405 Training Module - Version.0 Copyright 006 Ace Electronic Technology Inc. All Rights Reserved Alexan 05/405 TM- v..0 Page of 7 About This
LCD MODULE DEM B SYH
 DISPLAY Elektronik GmbH LCD MODULE DEM 128064B SYH Product specification Version:0 09/Okt/2006 GENERAL SPECIFICATION MODULE NO. : DEM 128064B SYH CUSTOMER P/N VERSION NO. CHANGE DESCRIPTION DATE 0 ORIGINAL
DISPLAY Elektronik GmbH LCD MODULE DEM 128064B SYH Product specification Version:0 09/Okt/2006 GENERAL SPECIFICATION MODULE NO. : DEM 128064B SYH CUSTOMER P/N VERSION NO. CHANGE DESCRIPTION DATE 0 ORIGINAL
JTAGcable II In Circuit Emulator for Atmel AVR microcontrollers. User s Guide REV 1.0. Many ideas one solution
 JTAGcable II In Circuit Emulator for Atmel AVR microcontrollers REV 1.0 User s Guide Evalu ation Board s for 51, AVR, ST, PIC microcontrollers Sta- rter Kits Embedded Web Serve rs Prototyping Boards Minimodules
JTAGcable II In Circuit Emulator for Atmel AVR microcontrollers REV 1.0 User s Guide Evalu ation Board s for 51, AVR, ST, PIC microcontrollers Sta- rter Kits Embedded Web Serve rs Prototyping Boards Minimodules
262,144-color, 240RGB x 320-dot Graphics Liquid Crystal Controller Driver for Amorphous-Silicon TFT Panel. Description Features...
 262,144-color, 240RGB x 320-dot Graphics Liquid Crystal Controller Driver for Amorphous-Silicon TFT Panel REJxxxxxxx-xxxx Rev. 1.01 April 9, 2009 Description... 6 Features... 6 Power Supply... 8 Block
262,144-color, 240RGB x 320-dot Graphics Liquid Crystal Controller Driver for Amorphous-Silicon TFT Panel REJxxxxxxx-xxxx Rev. 1.01 April 9, 2009 Description... 6 Features... 6 Power Supply... 8 Block
82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
 Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
Y Y Y Y Y 82C55A CHMOS PROGRAMMABLE PERIPHERAL INTERFACE Compatible with all Intel and Most Other Microprocessors High Speed Zero Wait State Operation with 8 MHz 8086 88 and 80186 188 24 Programmable I
64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION FEATURES 100 QFP-1420C
 INTRODUCTION The KS0108B is a LCD driver LSl with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the display RAM, 64 bit data latch, 64 bit drivers and
INTRODUCTION The KS0108B is a LCD driver LSl with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. This device consists of the display RAM, 64 bit data latch, 64 bit drivers and
LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION
 MULTIINNO TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0350D1T2 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference MODULE NO.: MI0350D1T2 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE FROM TO DESCRIPTION
MULTIINNO TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. LCD MODULE SPECIFICATION Model : MI0350D1T2 Revision Engineering Date Our Reference MODULE NO.: MI0350D1T2 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE FROM TO DESCRIPTION
IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Low cost implementation featuring the ATtiny13A from Atmel Complete software solution
 DKAN0002A Bit-banging the SmartDisplay 09 June 2009 Features IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Low cost implementation featuring the ATtiny13A from Atmel Complete software solution Introduction
DKAN0002A Bit-banging the SmartDisplay 09 June 2009 Features IS01BFRGB LCD SmartDisplay from NKK Switches Low cost implementation featuring the ATtiny13A from Atmel Complete software solution Introduction
The World Leader in High Performance Signal Processing Solutions. Section 15. Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI)
 The World Leader in High Performance Signal Processing Solutions Section 5 Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) L Core Timer 64 Performance Core Monitor Processor ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Instruction Memory
The World Leader in High Performance Signal Processing Solutions Section 5 Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) L Core Timer 64 Performance Core Monitor Processor ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Instruction Memory
NT7108. Neotec Semiconductor Ltd. 新德科技股份有限公司 NT7108 LCD Driver. Copyright: NEOTEC (C)
 Copyright: NEOTEC (C) 2002 http:// All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electric or mechanical,
Copyright: NEOTEC (C) 2002 http:// All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electric or mechanical,
with Carrier Board OSD-232+ TM Version 1.01 On-screen composite video character and graphic overlay Copyright 2010 Intuitive Circuits, LLC
 OSD-232+ TM with Carrier Board On-screen composite video character and graphic overlay Version 1.01 Copyright 2010 Intuitive Circuits, LLC D escription OSD-232+ is a single channel on-screen composite
OSD-232+ TM with Carrier Board On-screen composite video character and graphic overlay Version 1.01 Copyright 2010 Intuitive Circuits, LLC D escription OSD-232+ is a single channel on-screen composite
ANDpSi025TD-LED 320 x 240 Pixels TFT LCD Color Monitor
 320 x 240 Pixels TFT LCD Color Monitor The ANDpSI025TD-LED is a 2.5 active matrix color TFT LCD module, that is suitable for applications such as a portable television (NTSC), camcorder, digital camera
320 x 240 Pixels TFT LCD Color Monitor The ANDpSI025TD-LED is a 2.5 active matrix color TFT LCD module, that is suitable for applications such as a portable television (NTSC), camcorder, digital camera
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROCONTROLLER BASED PORTABLE ECG MONITOR
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Physics Vol. 4, No.1, 2011 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROCONTROLLER BASED PORTABLE ECG MONITOR Nahian Rahman 1, A K M Bodiuzzaman, A Raihan Abir, K Siddique-e Rabbani Department
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Physics Vol. 4, No.1, 2011 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MICROCONTROLLER BASED PORTABLE ECG MONITOR Nahian Rahman 1, A K M Bodiuzzaman, A Raihan Abir, K Siddique-e Rabbani Department
Spare Parts, Accessories, Consumable Material for Older Design Recorders
 Spare Parts, Accessories, Consumable Material for Older Design Recorders 4/2 Summary 4/2 Accessories for multipoint and line recorders SIREC 2010 4/2 Accessories for hybrid recorders VARIOGRAPH 4/2 Accessories
Spare Parts, Accessories, Consumable Material for Older Design Recorders 4/2 Summary 4/2 Accessories for multipoint and line recorders SIREC 2010 4/2 Accessories for hybrid recorders VARIOGRAPH 4/2 Accessories
Configuring the Élan SC300 Device s Internal CGA Controller for a Specific LCD Panel
 Configuring the Élan SC300 Device s Internal CGA Controller for a Specific LCD Panel Application Note This application note explains how to determine if a specific LCD panel is supported by the Élan TM
Configuring the Élan SC300 Device s Internal CGA Controller for a Specific LCD Panel Application Note This application note explains how to determine if a specific LCD panel is supported by the Élan TM
1 Watt, MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.40 x 0.387
 MN-3-52-X-S4 1 Watt, 3 52 MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.4 x.387 Typical Applications Military Radios Military Radar SATCOM Test and Measurement Equipment Industrial and Medical
MN-3-52-X-S4 1 Watt, 3 52 MHz, SMT Tunable Band Pass Filter (MINI-ERF ) 1.75 x 2.4 x.387 Typical Applications Military Radios Military Radar SATCOM Test and Measurement Equipment Industrial and Medical
Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff, OSSI F, Water Level Sensor With 0-5V, RS232 & Alarm Outputs, 1 to 20 Meter Staff
 Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff, OSSI-010-002F, Water Level Sensor With 0-5V, RS232 & Alarm Outputs, 1 to 20 Meter Staff General Description The OSSI-010-002E Wave Staff is a water level sensor that
Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff, OSSI-010-002F, Water Level Sensor With 0-5V, RS232 & Alarm Outputs, 1 to 20 Meter Staff General Description The OSSI-010-002E Wave Staff is a water level sensor that
4 x 4 VGA Matrix Switch
 Hall Research Technologies, Inc. 4 x 4 VGA Matrix Switch Model VSM-404 User s Manual With Serial Keypad CUSTOMER SUPPORT INFORMATION Order toll-free in the U.S. 800-959-6439 FREE technical support, Call
Hall Research Technologies, Inc. 4 x 4 VGA Matrix Switch Model VSM-404 User s Manual With Serial Keypad CUSTOMER SUPPORT INFORMATION Order toll-free in the U.S. 800-959-6439 FREE technical support, Call
Simple PICTIC Commands
 The Simple PICTIC Are you an amateur bit by the Time-Nut bug but can t afford a commercial time interval counter with sub nanosecond resolution and a GPIB interface? Did you find a universal counter on
The Simple PICTIC Are you an amateur bit by the Time-Nut bug but can t afford a commercial time interval counter with sub nanosecond resolution and a GPIB interface? Did you find a universal counter on
SmartSwitch TM. Wide View Compact LCD 64 x 32 Pushbutton DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS PART NUMBER & DESCRIPTION
 Wide View Compact LCD x Pushbutton SmartSwitch TM DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Combined with High Resolution High resolution of x pixels colors of backlighting can be controlled dynamically
Wide View Compact LCD x Pushbutton SmartSwitch TM DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS Compact Size Combined with High Resolution High resolution of x pixels colors of backlighting can be controlled dynamically
Design and Implementation of an AHB VGA Peripheral
 Design and Implementation of an AHB VGA Peripheral 1 Module Overview Learn about VGA interface; Design and implement an AHB VGA peripheral; Program the peripheral using assembly; Lab Demonstration. System
Design and Implementation of an AHB VGA Peripheral 1 Module Overview Learn about VGA interface; Design and implement an AHB VGA peripheral; Program the peripheral using assembly; Lab Demonstration. System
Specification Sheet. Mode: Transmissive Type, Negative mode, 3.97 LTPS LCD module 16.7M color. Checked by PM QA BU
 Specification Sheet Customer Part No. Product type ZRoHS Remarks TVL-55806GD040J-LW-G-AAN Mode: Transmissive Type, Negative mode, 3.97 LTPS LCD module 16.7M color Non-compliance Compliance Preliminary
Specification Sheet Customer Part No. Product type ZRoHS Remarks TVL-55806GD040J-LW-G-AAN Mode: Transmissive Type, Negative mode, 3.97 LTPS LCD module 16.7M color Non-compliance Compliance Preliminary
PCIe-FRM21. User s Manual
 PCIe-FRM21 User s Manual Windows, Windows2000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations mentioned in this document
PCIe-FRM21 User s Manual Windows, Windows2000, Windows NT and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft. We acknowledge that the trademarks or service names of all other organizations mentioned in this document
Outline Dimension. View Angle
 320 x 234 Pixels LCD Color Monitor The is a compact full color TFT LCD module, whose driving board is capable of converting composite video signals to the proper interface of LCD panel and is suitable
320 x 234 Pixels LCD Color Monitor The is a compact full color TFT LCD module, whose driving board is capable of converting composite video signals to the proper interface of LCD panel and is suitable
DOGM GRAPHIC SERIES 132x32 DOTS
 DOGM GRAPHIC SERIES 132x32 DOTS 6.2009 flexible display content! EA DOGM132B-5 + EA LED55x31-W TECHNICAL DATA EA DOGM132W-5 + EA LED55x31-A EA DOGM132W-6 + EA LED55x31-W * HIGH-CONTRAST LCD SUPERTWIST
DOGM GRAPHIC SERIES 132x32 DOTS 6.2009 flexible display content! EA DOGM132B-5 + EA LED55x31-W TECHNICAL DATA EA DOGM132W-5 + EA LED55x31-A EA DOGM132W-6 + EA LED55x31-W * HIGH-CONTRAST LCD SUPERTWIST
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT /12/14 BIT 10 TO 105 MSPS ADC
 LTC2280, LTC2282, LTC2284, LTC2286, LTC2287, LTC2288 LTC2289, LTC2290, LTC2291, LTC2292, LTC2293, LTC2294, LTC2295, LTC2296, LTC2297, LTC2298 or LTC2299 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 851 supports a
LTC2280, LTC2282, LTC2284, LTC2286, LTC2287, LTC2288 LTC2289, LTC2290, LTC2291, LTC2292, LTC2293, LTC2294, LTC2295, LTC2296, LTC2297, LTC2298 or LTC2299 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 851 supports a
Checkpoint 2 Video Interface
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Fall 1998 R. Fearing and Kevin Cho 1. Objective Checkpoint 2 Video Interface
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Fall 1998 R. Fearing and Kevin Cho 1. Objective Checkpoint 2 Video Interface
Section 14 Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI)
 Section 14 Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) 14-1 a ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance Monitor JTAG/ Debug Core Processor LD 32 LD1 32 L1 Data Memory SD32 DMA Mastered
Section 14 Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) 14-1 a ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance Monitor JTAG/ Debug Core Processor LD 32 LD1 32 L1 Data Memory SD32 DMA Mastered
Evaluation Board for CS4954/55
 Evaluation Board for CS4954/55 Features l Demonstrates recommended layout and grounding practices l Supports both parallel and serial digital video input l On-board test pattern generation l Supports NTSC/PAL
Evaluation Board for CS4954/55 Features l Demonstrates recommended layout and grounding practices l Supports both parallel and serial digital video input l On-board test pattern generation l Supports NTSC/PAL
Design and implementation (in VHDL) of a VGA Display and Light Sensor to run on the Nexys4DDR board Report and Signoff due Week 6 (October 4)
 ECE 574: Modeling and synthesis of digital systems using Verilog and VHDL Fall Semester 2017 Design and implementation (in VHDL) of a VGA Display and Light Sensor to run on the Nexys4DDR board Report and
ECE 574: Modeling and synthesis of digital systems using Verilog and VHDL Fall Semester 2017 Design and implementation (in VHDL) of a VGA Display and Light Sensor to run on the Nexys4DDR board Report and
C8188 C8000 1/10. digital audio modular processing system. 4 Channel AES/EBU I/O. features. block diagram. 4 balanced AES inputs
 features 4 balanced AES inputs Input Sample Rate Converters (SRC) 4 balanced AES outputs Relay bypass for pairs of I/Os Relay wait time after power up Master mode (clock master for the frame) 25pin Sub-D,
features 4 balanced AES inputs Input Sample Rate Converters (SRC) 4 balanced AES outputs Relay bypass for pairs of I/Os Relay wait time after power up Master mode (clock master for the frame) 25pin Sub-D,
uresearch GRAVITECH.US GRAVITECH GROUP Copyright 2007 MicroResearch GRAVITECH GROUP
 GRAVITECH.US uresearch GRAVITECH GROUP Description The I2C-7SEG board is a 5-pin CMOS device that provides 4-digit of 7-segment display using I 2 C bus. There are no external components required. Only
GRAVITECH.US uresearch GRAVITECH GROUP Description The I2C-7SEG board is a 5-pin CMOS device that provides 4-digit of 7-segment display using I 2 C bus. There are no external components required. Only
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT /12/14 BIT 10 TO 65 MSPS DUAL ADC
 LTC2286, LTC2287, LTC2288, LTC2290, LTC2291, LTC2292, LTC2293, LTC2294, LTC2295, LTC2296, LTC2297, LTC2298 or LTC2299 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 816 supports a family of s. Each assembly features
LTC2286, LTC2287, LTC2288, LTC2290, LTC2291, LTC2292, LTC2293, LTC2294, LTC2295, LTC2296, LTC2297, LTC2298 or LTC2299 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 816 supports a family of s. Each assembly features
Combo Board.
 Combo Board www.matrixtsl.com EB083 Contents About This Document 2 General Information 3 Board Layout 4 Testing This Product 5 Circuit Diagram 6 Liquid Crystal Display 7 Sensors 9 Circuit Diagram 10 About
Combo Board www.matrixtsl.com EB083 Contents About This Document 2 General Information 3 Board Layout 4 Testing This Product 5 Circuit Diagram 6 Liquid Crystal Display 7 Sensors 9 Circuit Diagram 10 About
DiD. LCD Video Monitor & Video Wall Universal User Manual. Digital Information Display
 LCD Video Monitor & Video Wall Universal User Manual DiD Digital Information Display Video Monitor Models M82S1/M70S1/M65S1/M55S1/M46S1/M40S1/M32S1/M24S1/M19S2/M19S1 Video Wall Models PD55N3/PD46N4/PD46N3/PD46N2/PD40N2
LCD Video Monitor & Video Wall Universal User Manual DiD Digital Information Display Video Monitor Models M82S1/M70S1/M65S1/M55S1/M46S1/M40S1/M32S1/M24S1/M19S2/M19S1 Video Wall Models PD55N3/PD46N4/PD46N3/PD46N2/PD40N2
Chrontel CH7015 SDTV / HDTV Encoder
 Chrontel Preliminary Brief Datasheet Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Features 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION VGA to SDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 104x768 Analog YPrPb or YCrCb outputs for
Chrontel Preliminary Brief Datasheet Chrontel SDTV / HDTV Encoder Features 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION VGA to SDTV conversion supporting graphics resolutions up to 104x768 Analog YPrPb or YCrCb outputs for
TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller
 TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller With the widespread conversion of the TV transmission and coding standards, from the early analog (NTSC, PAL, SECAM) systems to the modern digital formats
TV Synchronism Generation with PIC Microcontroller With the widespread conversion of the TV transmission and coding standards, from the early analog (NTSC, PAL, SECAM) systems to the modern digital formats
M66004SP/FP M66004SP/FP MITSUBISHI DIGITAL ASSP ASSP 16-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT VFD CONTROLLER 16-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT VFD CONTROLLER
 ASSP M664SP/FP M664SP/FP 6-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER 6-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER DESCRIPTION The M664 is a 6-digit 5 7-segment vacuum fluorescent display (FD) controller using the silicon gate
ASSP M664SP/FP M664SP/FP 6-DIGIT 5X7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER 6-DIGIT 5 7-SEGMENT FD CONTROLLER DESCRIPTION The M664 is a 6-digit 5 7-segment vacuum fluorescent display (FD) controller using the silicon gate
KS0108B 64CH SEGMENT DRIVER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION 100 QFP
 INTRODUCTION 100 QFP The KS0108B is a LCD driver LSl with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display system. This device consists of the display RAM, 64 bit data latch 64 bit drivers
INTRODUCTION 100 QFP The KS0108B is a LCD driver LSl with 64 channel output for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display system. This device consists of the display RAM, 64 bit data latch 64 bit drivers
Model 5240 Digital to Analog Key Converter Data Pack
 Model 5240 Digital to Analog Key Converter Data Pack E NSEMBLE D E S I G N S Revision 2.1 SW v2.0 This data pack provides detailed installation, configuration and operation information for the 5240 Digital
Model 5240 Digital to Analog Key Converter Data Pack E NSEMBLE D E S I G N S Revision 2.1 SW v2.0 This data pack provides detailed installation, configuration and operation information for the 5240 Digital
EM6126 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA. Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver. Features. Typical Applications
 EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA EM616 Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver Features Slim IC for COG, COF and COB technologies I C & Serial bus interface Internal display
EM MICROELECTRONIC - MARIN SA EM616 Digitally programmable 65 and 81 multiplex rate LCD Controller and Driver Features Slim IC for COG, COF and COB technologies I C & Serial bus interface Internal display
Programmable High Resolution LCD Switches
 Programmable High Resolution DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS High resolution of x pixels colors of backlighting can be controlled dynamically Pushbutton switch or display with LCD, RGB LED backlighting General
Programmable High Resolution DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS High resolution of x pixels colors of backlighting can be controlled dynamically Pushbutton switch or display with LCD, RGB LED backlighting General
TFT Display Module TFT CHARACTER UWVD FSC SEGMENT CUSTOM REPLACEMENT. Part Number. Overview. Ph E24RG12432LWIM800-C
 Ph. 480-503-4295 NOPP@FocusLCD.com TFT CHARACTER UWVD FSC SEGMENT CUSTOM REPLACEMENT TFT Display Module Part Number E24RG12432LWIM800-C Overview 2.4 inch TFT: 240x320(42.72x60.26), 18- bit RGB; 8/16-bit
Ph. 480-503-4295 NOPP@FocusLCD.com TFT CHARACTER UWVD FSC SEGMENT CUSTOM REPLACEMENT TFT Display Module Part Number E24RG12432LWIM800-C Overview 2.4 inch TFT: 240x320(42.72x60.26), 18- bit RGB; 8/16-bit
ILI9322. a-si TFT LCD Single Chip Driver 320RGBx240 Resolution and 16.7M color. Datasheet Preliminary
 Datasheet Preliminary Version: Preliminary V1.16 Document No.: DS_V1.15.pdf ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 4F, No. 2, Tech. 5 th Rd., Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. Tel.886-3-5670095; Fax.886-3-5670096
Datasheet Preliminary Version: Preliminary V1.16 Document No.: DS_V1.15.pdf ILI TECHNOLOGY CORP. 4F, No. 2, Tech. 5 th Rd., Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan 300, R.O.C. Tel.886-3-5670095; Fax.886-3-5670096
ARM HOW-TO GUIDE Interfacing Traffic Light with LPC2148
 ARM HOW-TO GUIDE Interfacing Traffic Light with LPC2148 Contents at a Glance ARM7 LPC2148 Primer Board... 3 Traffic Light Control... 3 About the colors of Traffic Light Control... 4 Interfacing Traffic
ARM HOW-TO GUIDE Interfacing Traffic Light with LPC2148 Contents at a Glance ARM7 LPC2148 Primer Board... 3 Traffic Light Control... 3 About the colors of Traffic Light Control... 4 Interfacing Traffic
bit TFT Digital Driver Board Specification
 OZDISAN ELECTRONIC A.S. 3.5 16 bit TFT Digital Driver Board Specification TDDB-SSD-3.5-54P-16B-V2 Doc.Version : 1.0 OLAB Ozdisan Electronic R&D and Technical Support Department Email: ts@ozdisan.com Tel:
OZDISAN ELECTRONIC A.S. 3.5 16 bit TFT Digital Driver Board Specification TDDB-SSD-3.5-54P-16B-V2 Doc.Version : 1.0 OLAB Ozdisan Electronic R&D and Technical Support Department Email: ts@ozdisan.com Tel:
RGB Encoder For the availability of this product, please contact the sales office. VIDEO OUT Y/C MIX DELAY CLAMP
 MATRIX Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite video outputs and
MATRIX Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite video outputs and
Lab 3 LCD Mar
 Lab 3 LCD Mar. 2016 1 Objective 1. To be familiar with advanced output devices that can be connected to microcontroller. 2. To be able to work with many input/output devices together. Alphanumeric LCD
Lab 3 LCD Mar. 2016 1 Objective 1. To be familiar with advanced output devices that can be connected to microcontroller. 2. To be able to work with many input/output devices together. Alphanumeric LCD
Complete 10-Bit, 25 MHz CCD Signal Processor AD9943
 a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
a FEATURES 25 MSPS Correlated Double Sampler (CDS) 6 db to 40 db 10-Bit Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) Low Noise Optical Black Clamp Circuit Preblanking Function 10-Bit, 25 MSPS A/D Converter No Missing
CHANGED BY A First Release. ZHANG YAN FANG
 VLPSCOGT350MCQH01 REV.A (COGT350MCQH01) PAGE 2 OF 20 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE FROM TO DESCRIPTION CHANGED BY A 2007.05.15 First Release. ZHANG YAN FANG CHECKED BY LIN GUO HUI VLPSCOGT350MCQH01
VLPSCOGT350MCQH01 REV.A (COGT350MCQH01) PAGE 2 OF 20 DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY DOCUMENT REVISION DATE FROM TO DESCRIPTION CHANGED BY A 2007.05.15 First Release. ZHANG YAN FANG CHECKED BY LIN GUO HUI VLPSCOGT350MCQH01
CXA1645P/M. RGB Encoder
 MATRIX CXA1645P/M RGB Encoder Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite
MATRIX CXA1645P/M RGB Encoder Description The CXA1645P/M is an encoder IC that converts analog RGB signals to a composite video signal. This IC has various pulse generators necessary for encoding. Composite
Coastal Amusements, Inc Swarthmore Ave. Lakewood, NJ (732)
 Coastal Amusements, Inc. 1935 Swarthmore Ave. Lakewood, NJ 08701 (732) 905-6662 SPIDER-BOT Redemption Version (version: 2-1-10) HOW TO PLAY 1. Insert coin(s). The spider s back-light will go out after
Coastal Amusements, Inc. 1935 Swarthmore Ave. Lakewood, NJ 08701 (732) 905-6662 SPIDER-BOT Redemption Version (version: 2-1-10) HOW TO PLAY 1. Insert coin(s). The spider s back-light will go out after
Pulse Concentrator User Manual EPC-12
 WARNING Ignoring the instructions in this manual may result in serious injuries or death. Disconnect all power supply inputs before connecting the device. Do not remove the front panel when device is connected
WARNING Ignoring the instructions in this manual may result in serious injuries or death. Disconnect all power supply inputs before connecting the device. Do not remove the front panel when device is connected
NT Output LCD Segment/Common Driver NT7701. Features. General Description. Pin Configuration 1 V1.0
 160 Output LCD Segment/Common Driver Features (Segment mode)! Shift Clock frequency : 14 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 5V ± 10%) 8 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 2.5V - 4.5V)! Adopts a data bus system! 4-bit/8-bit parallel input
160 Output LCD Segment/Common Driver Features (Segment mode)! Shift Clock frequency : 14 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 5V ± 10%) 8 MHz (Max.) (VDD = 2.5V - 4.5V)! Adopts a data bus system! 4-bit/8-bit parallel input
Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI)
 The World Leader in High Performance Signal Processing Solutions Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) Support Email: china.dsp@analog.com ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance
The World Leader in High Performance Signal Processing Solutions Parallel Peripheral Interface (PPI) Support Email: china.dsp@analog.com ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance
0.56" 4 Digital Blue LED Panel Meter (rescalable) User s Guide
 0.56" 4 Digital Blue LED Panel Meter (rescalable) User s Guide 2004-2009 Sure Electronics Inc. ME-SP037B_Ver1.0 0.56" 4 DIGITAL BLUE LED PANEL METER (RESCALABLE) USER S GUIDE Table of Contents Chapter
0.56" 4 Digital Blue LED Panel Meter (rescalable) User s Guide 2004-2009 Sure Electronics Inc. ME-SP037B_Ver1.0 0.56" 4 DIGITAL BLUE LED PANEL METER (RESCALABLE) USER S GUIDE Table of Contents Chapter
NHD MF VIDEO Board V1.1
 NHD 3.5 320240MF VIDEO Board V1.1 TFT Evaluation Video Board NHD Newhaven Display 3.5 3.5 Diagonal 320240 320xRGBx240 pixels MF Model VIDEO Composite VIDEO input V1.1 Version 1.1 Newhaven Display International,
NHD 3.5 320240MF VIDEO Board V1.1 TFT Evaluation Video Board NHD Newhaven Display 3.5 3.5 Diagonal 320240 320xRGBx240 pixels MF Model VIDEO Composite VIDEO input V1.1 Version 1.1 Newhaven Display International,
LCD Module Product Specification
 Website: www.displaytech.com.hk LCD Module Product Specification Product: DT022ATFT 2.2'' TFT Display Module (240RGBx320DOTS) Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of
Website: www.displaytech.com.hk LCD Module Product Specification Product: DT022ATFT 2.2'' TFT Display Module (240RGBx320DOTS) Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of
Digital Video Wall Control Box
 Digital Video Wall Control Box (with RS232 & VGA/HDMI upscale) - ID# 902 Operation Manual Introduction The Multi-Screen Video Wall Control System is ideal for advertising, entertainment and information
Digital Video Wall Control Box (with RS232 & VGA/HDMI upscale) - ID# 902 Operation Manual Introduction The Multi-Screen Video Wall Control System is ideal for advertising, entertainment and information
LM16X21A Dot Matrix LCD Unit
 LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
LCD Data Sheet FEATURES STC (Super Twisted igh Contrast) Yellow Green Transmissive Type Low Power Consumption Thin, Lightweight Design Permits Easy Installation in a Variety of Equipment General Purpose
EPC-12 User Manual.
 EPC-12 User Manual www.entes.com.tr PULSE CONCENTRATOR User Manual EPC-12 WARNING Ignoring the instructions in this manual may result in serious injuries or death. Disconnect all power supply inputs before
EPC-12 User Manual www.entes.com.tr PULSE CONCENTRATOR User Manual EPC-12 WARNING Ignoring the instructions in this manual may result in serious injuries or death. Disconnect all power supply inputs before
Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/ HD66750S
 Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ Preliminary HD66750S (128 x 128-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver with Four-grayscale Functions) Rev 0.1 November
Crystalfontz Thiscontrolerdatasheetwasdownloadedfrom htp:/www.crystalfontz.com/controlers/ Preliminary HD66750S (128 x 128-dot Graphics LCD Controller/Driver with Four-grayscale Functions) Rev 0.1 November
HDMI-UVC/HDMI-Parallel converter [SVO-03 U&P]
![HDMI-UVC/HDMI-Parallel converter [SVO-03 U&P] HDMI-UVC/HDMI-Parallel converter [SVO-03 U&P]](/thumbs/82/85356025.jpg) HDMI-UVC/HDMI-Parallel converter [SVO-03 U&P] Hardware specifications Rev. Net Vision Co., Ltd. SVO-03 U&P hardware specifications Revision history Revision Date Content Charge 1.0 2016/06/08 First edition
HDMI-UVC/HDMI-Parallel converter [SVO-03 U&P] Hardware specifications Rev. Net Vision Co., Ltd. SVO-03 U&P hardware specifications Revision history Revision Date Content Charge 1.0 2016/06/08 First edition
LD-V4300D DUAL STANDARD PLAYER. Industrial LaserDisc TM Player
 LD-V4300D DUAL STANDARD PLAYER Industrial LaserDisc TM Player Designed for Exceptional Versatility and Convenience Pioneer designed the LD-V4300D to make it easier than ever to use LaserDiscs for a broad
LD-V4300D DUAL STANDARD PLAYER Industrial LaserDisc TM Player Designed for Exceptional Versatility and Convenience Pioneer designed the LD-V4300D to make it easier than ever to use LaserDiscs for a broad
AI-1204Z-PCI. Features. 10MSPS, 12-bit Analog Input Board for PCI AI-1204Z-PCI 1. Ver.1.04
 10MSPS, 12-bit Analog Board for PCI AI-1204Z-PCI * Specifications, color and design of the products are subject to change without notice. This product is a PCI bus-compliant interface board that expands
10MSPS, 12-bit Analog Board for PCI AI-1204Z-PCI * Specifications, color and design of the products are subject to change without notice. This product is a PCI bus-compliant interface board that expands
FOM-1090 FOM-1090 FOM FOM-1090 w/ DB-25 Female FOM-1091 w/ DB-25 Male
 Serial Data Communications Synchronous, Asynchronous or Isochronous Signal rates: DC to 20 MHz FOM-1090 w/ DB-25 Female FOM-1091 w/ DB-25 Male Supported Interface Standards TIA-530, TIA-530A TIA-232 TIA-574
Serial Data Communications Synchronous, Asynchronous or Isochronous Signal rates: DC to 20 MHz FOM-1090 w/ DB-25 Female FOM-1091 w/ DB-25 Male Supported Interface Standards TIA-530, TIA-530A TIA-232 TIA-574
Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff III, OSSI With 0-5V & RS232 Output and A Self Grounding Coaxial Staff
 Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff III, OSSI-010-008 With 0-5V & RS232 Output and A Self Grounding Coaxial Staff General Description The OSSI-010-008 Wave Staff III is a water level sensor that combines
Ocean Sensor Systems, Inc. Wave Staff III, OSSI-010-008 With 0-5V & RS232 Output and A Self Grounding Coaxial Staff General Description The OSSI-010-008 Wave Staff III is a water level sensor that combines
Vorne Industries. 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual Industrial Drive Itasca, IL (630) Telefax (630)
 Vorne Industries 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60141849 (60) 875600 elefax (60) 875609 Page 2 2000B Series Buffered Display 2000B Series Buffered Display Release
Vorne Industries 2000B Series Buffered Display Users Manual 1445 Industrial Drive Itasca, IL 60141849 (60) 875600 elefax (60) 875609 Page 2 2000B Series Buffered Display 2000B Series Buffered Display Release
Troubleshooting. 1. Symptom: Status indicator (Red LED) on SSR is constant on. 2. Symptom: Output indicator (Yellow LED) on SSR is flashing.
 Product Data Electrical Data SST (Transmitter) SSR (Receiver) Supply voltage 18 30 V dc Max. Voltage ripple 15 % (within supply range) Current consumption 100 ma (RMS) 75 ma Digital - 100 ma Max. outputs
Product Data Electrical Data SST (Transmitter) SSR (Receiver) Supply voltage 18 30 V dc Max. Voltage ripple 15 % (within supply range) Current consumption 100 ma (RMS) 75 ma Digital - 100 ma Max. outputs
Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL. Models: VS-162AV, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher VS-162AVRCA, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher
 Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL Models: VS-162AV, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher VS-162AVRCA, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher Contents Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Getting Started 1 3 Overview
Kramer Electronics, Ltd. USER MANUAL Models: VS-162AV, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher VS-162AVRCA, 16x16 Audio-Video Matrix Switcher Contents Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Getting Started 1 3 Overview
Manual Version Ver 1.0
 The BG-3 & The BG-7 Multiple Test Pattern Generator with Field Programmable ID Option Manual Version Ver 1.0 BURST ELECTRONICS INC CORRALES, NM 87048 USA (505) 898-1455 VOICE (505) 890-8926 Tech Support
The BG-3 & The BG-7 Multiple Test Pattern Generator with Field Programmable ID Option Manual Version Ver 1.0 BURST ELECTRONICS INC CORRALES, NM 87048 USA (505) 898-1455 VOICE (505) 890-8926 Tech Support
Australia Digital Tone Generator Supervision Tones
 CHAPTER 2 Australia Plan This chapter details the modifications to the Digital Generator (DTG or DTG-2) and Call Progress Analyzer (CPA) cards, and SPC-CPA service circuits to support the supervision tones
CHAPTER 2 Australia Plan This chapter details the modifications to the Digital Generator (DTG or DTG-2) and Call Progress Analyzer (CPA) cards, and SPC-CPA service circuits to support the supervision tones
